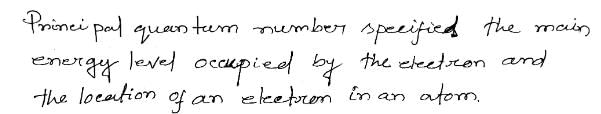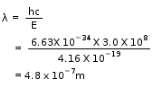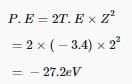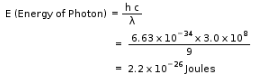All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Structure of Atom for NEET Exam
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.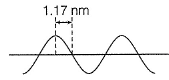 Q. Energy associated with this wave is
Q. Energy associated with this wave is- a)4.24 x 10-19J
- b)2.12 x 10-19J
- c)1.06 x 10-19J
- d)8.49 x 10-19J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 12 and 13) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is pictured here.
Q. Energy associated with this wave is
a)
4.24 x 10-19J
b)
2.12 x 10-19J
c)
1.06 x 10-19J
d)
8.49 x 10-19J
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
A to E makes one complete wave.
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is __________.- a)3
- b)4
- c)2
- d)1
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is __________.
a)
3
b)
4
c)
2
d)
1

|
Amrita Kumar answered |
Number of radial nodes = n-1 – 1
For 3p orbital, n = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1
Number of radial nodes = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1.
For 3p orbital, n = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1
Number of radial nodes = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1.
The nature of positive rays depends on?
- a)The nature of discharge tube.
- b)The nature of residual gas.
- c)The nature of electrode.
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The nature of positive rays depends on?
a)
The nature of discharge tube.
b)
The nature of residual gas.
c)
The nature of electrode.
d)
All of above
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- The nature of positive rays produced in a vacuum discharge tube depends upon the nature of the gas-filled.
- The positive rays consist of positive ions obtained by removing one or more electrons from gas molecules.
The energy of a photon of light has what kind of proportionality to its frequency and its wavelength.- a)directly, inversely
- b)inversely, directly
- c)inversely, inversely
- d)directly, directly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy of a photon of light has what kind of proportionality to its frequency and its wavelength.
a)
directly, inversely
b)
inversely, directly
c)
inversely, inversely
d)
directly, directly
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
As E=h(frequency) E is directly proportional to frequency and as frequency = speed of light / wavelength frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength.
How much energy is needed to ionize a hydrogen atom if electron is present in n=1 orbit?- a)13.6 eV
- b)10.2 eV
- c)3.4eV
- d)1 eV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How much energy is needed to ionize a hydrogen atom if electron is present in n=1 orbit?
a)
13.6 eV
b)
10.2 eV
c)
3.4eV
d)
1 eV
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
For hydrogen Z=1,
and n is given as 1,
Then
E= -13.6 × n power 2/ Z.
E= - 13.6 × 1 power 2/ 1.
E= -13.6e.v.
and n is given as 1,
Then
E= -13.6 × n power 2/ Z.
E= - 13.6 × 1 power 2/ 1.
E= -13.6e.v.
Calculate the wavelength of light that corresponds to the radiation that is given off during the transition of an electron from the n = 5 to n = 2 state of the hydrogen atom.- a)434 nm
- b)275 nm
- c)305 nm
- d)183 nm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the wavelength of light that corresponds to the radiation that is given off during the transition of an electron from the n = 5 to n = 2 state of the hydrogen atom.
a)
434 nm
b)
275 nm
c)
305 nm
d)
183 nm
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
1/wavelength =RH x z2 x (1/22-1/52) =109677 x 1 x (1/4-1/25) =109677 x 21/100 =2303.2m wavelength=1/2303.2m =1/2303.2 x 107nm =434.1nm~434nm
The de – Broglie wavelength of an electron is 600 nm. The velocity of the electron having the mass 9.1 X 10-31 Kg is- a)0.0012 x 10+4 m/s
- b)0.0012 x 10+3 m/s
- c)0.0012 x 10+6 m/s
- d)0.0012 x 10+2 m/s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The de – Broglie wavelength of an electron is 600 nm. The velocity of the electron having the mass 9.1 X 10-31 Kg is
a)
0.0012 x 10+4 m/s
b)
0.0012 x 10+3 m/s
c)
0.0012 x 10+6 m/s
d)
0.0012 x 10+2 m/s
|
|
Arjun Gupta answered |
1nm= 10^-9m.
wavelength= 600nm= 600 ×10-9m
wavelength= h/p.
wavelength= h/mv
v= h/ m wavelength
v=6.625×10^-34/9.1×10^-31×600× 10-9.
v= 6.625 × 10+4/9.1 ×6.
v= 6.625× 10+4/9.1×6.
v= 6.625 ×104/54.6.
v= 0.12 × 104.
v= 0.0012 × 10+6 .
wavelength= 600nm= 600 ×10-9m
wavelength= h/p.
wavelength= h/mv
v= h/ m wavelength
v=6.625×10^-34/9.1×10^-31×600× 10-9.
v= 6.625 × 10+4/9.1 ×6.
v= 6.625× 10+4/9.1×6.
v= 6.625 ×104/54.6.
v= 0.12 × 104.
v= 0.0012 × 10+6 .
The total energy of an electron in the nth orbit of a hydrogen atom is given by the formula
En = -13.6 eV/n2. What does the negative energy for an electron indicate?- a)Energy of electron in an atom is lower than energy of an electron far away from nucleus
- b)The electron has a negative charge.
- c)The electron is far away from nucleus
- d)Electrons have both wave and particle-like properties.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The total energy of an electron in the nth orbit of a hydrogen atom is given by the formula
En = -13.6 eV/n2. What does the negative energy for an electron indicate?
En = -13.6 eV/n2. What does the negative energy for an electron indicate?
a)
Energy of electron in an atom is lower than energy of an electron far away from nucleus
b)
The electron has a negative charge.
c)
The electron is far away from nucleus
d)
Electrons have both wave and particle-like properties.
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The negative sign means that the energy of the electron in the atom is lower than the energy of a free electron at rest. A free electron at rest is an electron that is infinitely far away from the nucleus and is assigned the energy value zero.
Which model describes that there is no change in the energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level and atoms remains stable?- a)Rutherford Model
- b)Bohr’s Model
- c)J.J Thomson Model
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which model describes that there is no change in the energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level and atoms remains stable?
a)
Rutherford Model
b)
Bohr’s Model
c)
J.J Thomson Model
d)
None of the above
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Bohr Model of atom:
- An atom is made up of three particles: Electrons, neutrons and protons.
- The protons and neutrons are located in a small nucleus at the centre of the atom.
- The electrons revolve rapidly around the nucleus at the centre of the atom.
- There is a limit to the number of electrons that each energy level can hold.
- Each energy level is associated with a fixed amount of energy.
- There is no change in the energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level.
Bohr explained the stability through the concept of revolution of electrons in different energy levels.
The change in the energy of an electron occurs when it jumps from lower to higher energy levels. When it gains energy, it excites from lower to higher and vice versa.
Thus energy is not lost and the atom remains stable.
The change in the energy of an electron occurs when it jumps from lower to higher energy levels. When it gains energy, it excites from lower to higher and vice versa.
Thus energy is not lost and the atom remains stable.
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron is 8.7 x 10-11 m. The mass of an electron is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. The velocity of this electron is:- a)0.0837 × 108 m/s
- b)6.9 × 10-5 m/s
- c)8.4 × 103 m/s
- d)1.2 × 10-7 m/s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The de Broglie wavelength of an electron is 8.7 x 10-11 m. The mass of an electron is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. The velocity of this electron is:
a)
0.0837 × 108 m/s
b)
6.9 × 10-5 m/s
c)
8.4 × 103 m/s
d)
1.2 × 10-7 m/s
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Wavelength = h/p = h/ mv.
v= h/ m.wavelength
v= 6.625 × 10-34/9.1×10-31 × 8.7 × 10-11
v= 6.625 × 108/ 9.1× 8.7
v= 0.08367 ×108.
v= h/ m.wavelength
v= 6.625 × 10-34/9.1×10-31 × 8.7 × 10-11
v= 6.625 × 108/ 9.1× 8.7
v= 0.08367 ×108.
The nature of positive rays depends on?- a) The nature of discharge tube.
- b) The nature of residual gas
- c) All of above.
- d) The nature of electrode
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The nature of positive rays depends on?
a)
The nature of discharge tube.
b)
The nature of residual gas
c)
All of above.
d)
The nature of electrode

|
Abhiram Choudhary answered |
The positive charges in these rays, other than negative cathode rays (which are electrons), depend on the gas that is used because they are cations - atoms with mostly one electron missing and thus one positive charge. So, if you accelerate, argon cations and protons over the same electric potential, the particles in the rays will have the same kinetic energy, but the argon ions will be much slower, as they are much heavier than the protons.
Zeeman effect is the splitting of spectral line in presence of:- a)electricity
- b)magnetic effect
- c)molecule
- d)electric field
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Zeeman effect is the splitting of spectral line in presence of:
a)
electricity
b)
magnetic effect
c)
molecule
d)
electric field
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The Zeeman effect is the splitting of the spectral lines of an atom in the presence of a strong magnetic field. The effect is due to the distortion of the electron orbitals because of the magnetic field. The (normal) Zeeman effect can be understood classically, as Lorentz predicted.
Uncertainty in the position of an electron (mass 9.1 x 10-31 kg) moving with a velocity of 300 ms-1, accurate upto 0.001% will be:
- a)1.92 x 10-2 m
- b)3.84 x 10-2 m
- c)19.2 x 10-2 m
- d)5.76 x 10-2 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Uncertainty in the position of an electron (mass 9.1 x 10-31 kg) moving with a velocity of 300 ms-1, accurate upto 0.001% will be:
a)
1.92 x 10-2 m
b)
3.84 x 10-2 m
c)
19.2 x 10-2 m
d)
5.76 x 10-2 m
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Change in position (X),
P= momentum,
P=mv.
X ×P = h/4π.
X× m v = h/4π.
X= h/4πmv.
X=6.625×10-34/4 ×3.14×9.1×10^-31×300.
X=6.625×10-5/342.8.
X=0.0192×10^-5.
X= 19.2× 10-7.
in question it is given to take accurate up to 0.001%.= 1×10-3/100=1 ×10-5.
X= 19.2 ×10-7/10-5.
X=19.2 × 10-2.
P= momentum,
P=mv.
X ×P = h/4π.
X× m v = h/4π.
X= h/4πmv.
X=6.625×10-34/4 ×3.14×9.1×10^-31×300.
X=6.625×10-5/342.8.
X=0.0192×10^-5.
X= 19.2× 10-7.
in question it is given to take accurate up to 0.001%.= 1×10-3/100=1 ×10-5.
X= 19.2 ×10-7/10-5.
X=19.2 × 10-2.
Energy of a mole of radio wave photons with a frequency of 909 kHz is- a)6.02 x 10-28 J
- b)3.62 x 10-4 J
- c)1.00 x 10-4 J
- d)6.02 x 10-31 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy of a mole of radio wave photons with a frequency of 909 kHz is
a)
6.02 x 10-28 J
b)
3.62 x 10-4 J
c)
1.00 x 10-4 J
d)
6.02 x 10-31 J
|
|
Rajeev Nair answered |
E = N0hv
= 6.02 x 1023 x 6.62 x 10-34 Js x 909 x103 s-1
= 3.62 x 10-4 J
= 3.62 x 10-4 J
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is __________.- a)3
- b)4
- c)2
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is __________.
a)
3
b)
4
c)
2
d)
1

|
Swara Saha answered |
Number of radial nodes = n-1 – 1
For 3p orbital, n = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1
Number of radial nodes = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1.
For 3p orbital, n = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1
Number of radial nodes = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1.
In the relationship ∆x. ∆p = 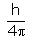 , ∆p is:
, ∆p is:- a)Certainty in momentum
- b)Certainty in position
- c)Uncertainty in momentum
- d)Uncertainty in position
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the relationship ∆x. ∆p = 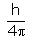 , ∆p is:
, ∆p is:
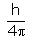 , ∆p is:
, ∆p is:a)
Certainty in momentum
b)
Certainty in position
c)
Uncertainty in momentum
d)
Uncertainty in position
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The uncertainty principle is alternatively expressed in terms of a particle’s momentum and position. The momentum of a particle is equal to the product of its mass times its velocity. Thus, the product of the uncertainties in the momentum and the position of a particle equals h/(4π)
If the value of azimuthal quantum number is 3, the possible values of magnetic quantum numbers would be:- a)0, 1, 2, 3
- b)3, -2, -1, +1, +2, +3
- c)0, -1, -2, -3
- d)3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the value of azimuthal quantum number is 3, the possible values of magnetic quantum numbers would be:
a)
0, 1, 2, 3
b)
3, -2, -1, +1, +2, +3
c)
0, -1, -2, -3
d)
3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The total possible values of m for l range from – through 0 to +.
Which of the following subatomic particles is responsible for the spectrum of radiation emitted by an element or compound?- a)neutron
- b)electron
- c)proton
- d)photon
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following subatomic particles is responsible for the spectrum of radiation emitted by an element or compound?
a)
neutron
b)
electron
c)
proton
d)
photon
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Any radiation is emitted in the quantized form as photons. These photons are actually generated when an electron changes its energy level. This can happen if the atom gets the required work function. For e.g. The emission of X Ray. When the cathode ray hits the nuclei of heavier metals, two cases may occur -
1)Nuclei absorbs the electron from K shell and this process results in radiation of energy in form of X Ray photons.
2)Auger Effect: Sometimes during the collision, an electron from main atom can also be emitted, releasing energy in form of X Ray photons. So, Now it should be more clear that while photons are the product, the real culprit behind the crime scene. So correct option is B These things can be understood easily if you know the basics of Particle Physics.
1)Nuclei absorbs the electron from K shell and this process results in radiation of energy in form of X Ray photons.
2)Auger Effect: Sometimes during the collision, an electron from main atom can also be emitted, releasing energy in form of X Ray photons. So, Now it should be more clear that while photons are the product, the real culprit behind the crime scene. So correct option is B These things can be understood easily if you know the basics of Particle Physics.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11 and 12) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)Photoelectric effect can be expressed in terms of the following graph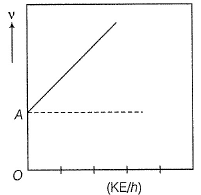
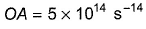 Q. What is work function for this photoelectric emission of electrons?
Q. What is work function for this photoelectric emission of electrons?- a)199.262 kJ mol-1
- b)199.262 J mol-1
- c)3.3 kJ mol-1
- d)3.3 x 10-19 kJ mol-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11 and 12) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given ptions (a),(b),(c),(d)
Photoelectric effect can be expressed in terms of the following graph
Q. What is work function for this photoelectric emission of electrons?
a)
199.262 kJ mol-1
b)
199.262 J mol-1
c)
3.3 kJ mol-1
d)
3.3 x 10-19 kJ mol-1
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Photoelectric effect is represented by
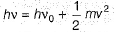
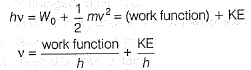

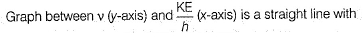
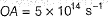
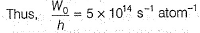
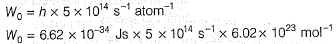
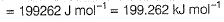
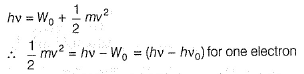
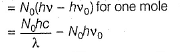
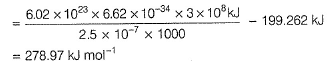
The charge on electron was determined by- a)Crooks
- b)Bohr
- c)Milliken
- d)Schrodinger
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The charge on electron was determined by
a)
Crooks
b)
Bohr
c)
Milliken
d)
Schrodinger
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Millikan
The experiment helped earn Millikan a Nobel prize in 1923 but has been a source of some controversy over the years. J. J. Thomson discovered the electron in 1897 when he measured the charge-to-mass ratio for electrons in a beam. But the value of the charge and whether it was fundamental remained open questions.
Chapter doubts & questions for Structure of Atom - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Structure of Atom - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
NCERT Based Tests for NEET
684 tests
|