All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Redox Reactions for NEET Exam
Which is chlorate (I) ion?
a) 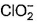
b)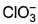
c)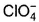
d)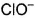
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
- ClO3- : A very reactive inorganic anion.
- The term chlorate can also be used to describe any compound containing the chlorate ion, normally chlorate salts.
- Example: Potassium chlorate, KClO3
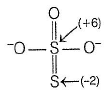
The difference in the oxidation number of the two types of sulphur atoms in Na2S4O6 is .........[HTJEE2011]
Correct answer is '7'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference in the oxidation number of the two types of sulphur atoms in Na2S4O6 is .........
[HTJEE2011]
|
|
Hrishikesh Sengupta answered |
Difference in oxidation number = 6 - (-1) = 7
Which of the following is not an example of redox reaction?- a)BaCl2 + H2SO4 ⎯→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
- b)Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3CO2
- c)2K + F2 ⎯→ 2KF
- d)CuO + H2 ⎯→ Cu + H2O
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an example of redox reaction?
a)
BaCl2 + H2SO4 ⎯→ BaSO4 + 2HCl
b)
Fe2O3 + 3CO ⎯→ 2Fe + 3CO2
c)
2K + F2 ⎯→ 2KF
d)
CuO + H2 ⎯→ Cu + H2O
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
a) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl is not a redox reaction, as there is no change in the oxidation state of any element.
It is an example of double displacement reactions.
It is an example of double displacement reactions.
The oxidation half reaction for following reaction is
Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Cr3+(aq)- a)Fe3+(aq) → Fe2+ (aq)
- b)Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq)
- c)Cr3+(aq) → Cr2O72-(aq)
- d)Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+(aq)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation half reaction for following reaction is
Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Cr3+(aq)
Fe2+(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + Cr3+(aq)
a)
Fe3+(aq) → Fe2+ (aq)
b)
Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq)
c)
Cr3+(aq) → Cr2O72-(aq)
d)
Fe2+ (aq) → Fe3+(aq)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Oxidation half reaction for a reaction is that reaction which gives us the reactant and product formed after the oxidation of the reactant. In this case Fe+2 oxidizes itself to Fe+3 and so the oxidation of Fe+2 is oxidation half reaction. Option d correct.
In the following reaction, 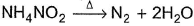 , oxidation number of
, oxidation number of- a)N changes from -2 to +2
- b)N changes from -2 to 0
- c)N in
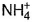 changes from -3 to 0 and that in
changes from -3 to 0 and that in 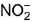 changes from +3 to 0
changes from +3 to 0 - d)N does not change
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reaction, 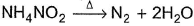 , oxidation number of
, oxidation number of
a)
N changes from -2 to +2
b)
N changes from -2 to 0
c)
N in 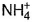 changes from -3 to 0 and that in
changes from -3 to 0 and that in 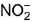 changes from +3 to 0
changes from +3 to 0
d)
N does not change

|
Learners Habitat answered |
In NH4NO2, the oxidation number of N in NH4+ is -3, and of N in NO2- is +3.
Oxidation numbers of P in PO4−3, of S in SO42− and that of Cr in Cr2O72− are respectively,- a) +5, +6 and +6
- b)+3, +6 and +5
- c)+5, +3 and +6
- d)-3, +6 and +6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation numbers of P in PO4−3, of S in SO42− and that of Cr in Cr2O72− are respectively,
a)
+5, +6 and +6
b)
+3, +6 and +5
c)
+5, +3 and +6
d)
-3, +6 and +6
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is option A
(I) xPO43− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −3
⇒x = −3 + 8 = +5
⇒x = +5
Oxidation number of P = +5
(II) xSO42− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −2
⇒x = −2 + 8
⇒x = +6
Oxidation number of S=+6
(III) xCr2O72− ⇒2x + 7 × (−2) = −2
⇒2x =−2+14
⇒2x=12
⇒x= 12/2 = +6
(I) xPO43− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −3
⇒x = −3 + 8 = +5
⇒x = +5
Oxidation number of P = +5
(II) xSO42− ⇒ x + 4 × (−2) = −2
⇒x = −2 + 8
⇒x = +6
Oxidation number of S=+6
(III) xCr2O72− ⇒2x + 7 × (−2) = −2
⇒2x =−2+14
⇒2x=12
⇒x= 12/2 = +6
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
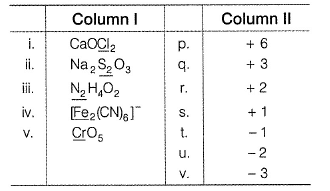
Match the compounds/ions having underlined atoms of different oxidation number (in Column I) with values (in Column II).


- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Match the compounds/ions having underlined atoms of different oxidation number (in Column I) with values (in Column II).


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
(i) CaOCI2 has
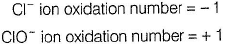
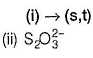
Oxidation number = + 6
Oxidation number = - 2
(ii) → (p,u)
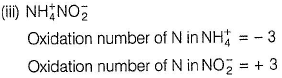
(iii) → (q.v)
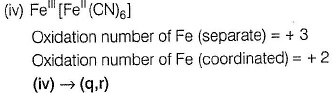
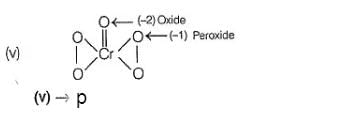
Oxidation number = + 6
Oxidation number = - 2
(ii) → (p,u)
(iii) → (q.v)

Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to oxygen atom in- a)superoxides
- b)when oxygen is bonded to fluorine
- c)when oxygen is bonded to metals
- d)peroxidesperoxides
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to oxygen atom in
a)
superoxides
b)
when oxygen is bonded to fluorine
c)
when oxygen is bonded to metals
d)
peroxidesperoxides
|
|
Arka Desai answered |
The oxidation number is a concept used in chemistry to keep track of the distribution of electrons in a compound or molecule. It is a measure of the charge that an atom would have if all the shared electrons were assigned to the more electronegative atom in a bond.
In the case of oxygen, its most common oxidation number is -2. However, in certain compounds, such as superoxides and peroxides, the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides. Superoxides are a class of compounds that contain the superoxide ion, O2-. In this ion, each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -1/2. This is because the oxygen-oxygen bond in the superoxide ion is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. Therefore, each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1/2 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
In the case of peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. In peroxides, the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1. Each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to fluorine, the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore, it attracts the shared electrons in the bond more strongly than oxygen. As a result, oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the unequal distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to metals, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -2. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as in certain metal peroxides or superoxides, where the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
In summary, the oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides, where the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. In other compounds, such as peroxides, fluorides, and most metal oxides, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -1 or -2.
In the case of oxygen, its most common oxidation number is -2. However, in certain compounds, such as superoxides and peroxides, the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
Oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides. Superoxides are a class of compounds that contain the superoxide ion, O2-. In this ion, each oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -1/2. This is because the oxygen-oxygen bond in the superoxide ion is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. Therefore, each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1/2 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
In the case of peroxides, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. In peroxides, the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1. Each oxygen atom is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to fluorine, the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore, it attracts the shared electrons in the bond more strongly than oxygen. As a result, oxygen is assigned an oxidation number of -1 to account for the unequal distribution of electrons in the bond.
When oxygen is bonded to metals, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -2. However, there are some exceptions to this rule, such as in certain metal peroxides or superoxides, where the oxidation number of oxygen deviates from -2.
In summary, the oxidation number of 1/2 is assigned to the oxygen atom in superoxides, where the oxygen-oxygen bond is a single bond with a bond order of 1/2. In other compounds, such as peroxides, fluorides, and most metal oxides, the oxidation number of oxygen is typically -1 or -2.
In Daniel cell, oxidation takes place at- a)Any of the two electrodes
- b)Depends on the salts and their solutions
- c)Anode
- d)Cathode
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In Daniel cell, oxidation takes place at
a)
Any of the two electrodes
b)
Depends on the salts and their solutions
c)
Anode
d)
Cathode
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The solutions in which the electrodes are immersed are called electrolytes. The chemical reaction that takes place in a galvanic cell is the redox reaction. One electrode acts as anode in which oxidation takes place and the other acts as the cathode in which reduction takes place.
Hydrogen is prepared from H2O by adding- a)Ag, which acts as reducing agent
- b)Ca, which acts as reducing agent
- c)Au, which acts as oxidising agent
- d)AI, which acts as oxidising agent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen is prepared from H2O by adding
a)
Ag, which acts as reducing agent
b)
Ca, which acts as reducing agent
c)
Au, which acts as oxidising agent
d)
AI, which acts as oxidising agent
|
|
Saumya Dey answered |
Preparation of Hydrogen from Water
- Hydrogen gas can be prepared from water by using a reducing agent, which reduces water to hydrogen gas and also gets oxidized in the process.
- Calcium (Ca) is a good reducing agent and can be used to prepare hydrogen gas from water.
- When calcium is added to water, it reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Calcium has a strong affinity for oxygen and readily reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, liberating hydrogen gas.
- This reaction is exothermic and produces a considerable amount of heat, which can be used to heat water or other substances.
- The liberated hydrogen gas can be collected by upward displacement of air or by using a gas syringe or gas jar.
- The purity of hydrogen gas prepared by this method is relatively low, as it may contain impurities like calcium hydroxide, unreacted water, and other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
- Therefore, additional purification steps may be required to obtain pure hydrogen gas.
Advantages of using Calcium as a reducing agent
- Calcium is a readily available and inexpensive reducing agent.
- It reacts readily with water, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is exothermic and produces heat, which can be utilized in other processes.
- Calcium is a relatively safe reducing agent, as it does not react violently with water or other substances.
- The by-products of the reaction, calcium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas, are non-toxic and can be disposed of safely.
- Hydrogen gas can be prepared from water by using a reducing agent, which reduces water to hydrogen gas and also gets oxidized in the process.
- Calcium (Ca) is a good reducing agent and can be used to prepare hydrogen gas from water.
- When calcium is added to water, it reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
- The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2
- Calcium has a strong affinity for oxygen and readily reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, liberating hydrogen gas.
- This reaction is exothermic and produces a considerable amount of heat, which can be used to heat water or other substances.
- The liberated hydrogen gas can be collected by upward displacement of air or by using a gas syringe or gas jar.
- The purity of hydrogen gas prepared by this method is relatively low, as it may contain impurities like calcium hydroxide, unreacted water, and other gases like nitrogen and oxygen.
- Therefore, additional purification steps may be required to obtain pure hydrogen gas.
Advantages of using Calcium as a reducing agent
- Calcium is a readily available and inexpensive reducing agent.
- It reacts readily with water, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas.
- The reaction is exothermic and produces heat, which can be utilized in other processes.
- Calcium is a relatively safe reducing agent, as it does not react violently with water or other substances.
- The by-products of the reaction, calcium hydroxide, and hydrogen gas, are non-toxic and can be disposed of safely.
The reduction potential values of M, N and O are +2.46, -1.13 and -3.13 V respectively. Which of the following order is correct regarding their reducing property?- a)M>N>O
- b)O>M>N
- c)M>O>N
- d)O>N>M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential values of M, N and O are +2.46, -1.13 and -3.13 V respectively. Which of the following order is correct regarding their reducing property?
a)
M>N>O
b)
O>M>N
c)
M>O>N
d)
O>N>M
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Reduction potential means the tendency to reduce itself, i.e SO if we need reducing agent, then we need elements having more oxidising potential or reversing reduction potential order.
The order of reduction potential - O < N < M
So the order of reducing agent = M < N < O
The order of reduction potential - O < N < M
So the order of reducing agent = M < N < O
The complex [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ is formed in the ring-test for nitrate ion 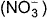 when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of
when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of 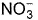 followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).Q. Magnetic moment
followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).Q. Magnetic moment 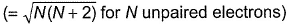 of Fe in the ring is
of Fe in the ring is - a)zero BM
- b)
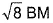
- c)
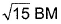
- d)
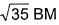
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The complex [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ is formed in the ring-test for nitrate ion 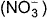 when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of
when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of 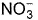 followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).
followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).
Q. Magnetic moment 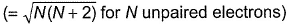 of Fe in the ring is
of Fe in the ring is
a)
zero BM
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Fe2+ is added asFeSO4
Fe+ is formed by charge transfer from NO to Fe2+
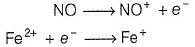
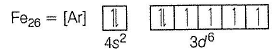
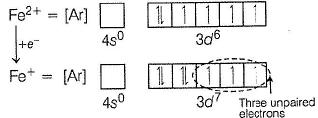
Fe+ has three unpaired electrons (N).
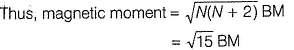
Fe+ is formed by charge transfer from NO to Fe2+
Fe+ has three unpaired electrons (N).
I− reduces IO3- and I2 and itself oxidised to I2 in acidic medium. Thus, final reaction is- a)
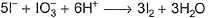
- b)
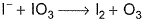
- c)
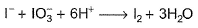
- d)None of the above is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
I− reduces IO3- and I2 and itself oxidised to I2 in acidic medium. Thus, final reaction is
a)
b)
c)
d)
None of the above is correct
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
To balance oxidation number, cross-multiply by change in oxidation number
For the redox reactionMnO4– + C2O42- + H+ → Mn2+ + CO2 + H2O
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are:- a)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 16 5 2
- b)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 16 5
- c)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 5 16
- d)MnO4– C2O42- H+ 5 16 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the redox reaction
MnO4– + C2O42- + H+ → Mn2+ + CO2 + H2O
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are:
The correct coefficients of the reactants for the balanced reaction are:
a)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 16 5 2
b)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 16 5
c)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 2 5 16
d)
MnO4– C2O42- H+ 5 16 2
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
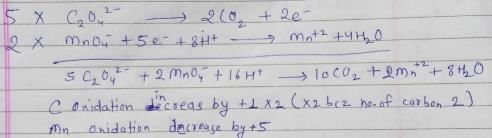
NaHC2O4 is neutralised by NaOH and can also be oxidised by KMnO4 (in acidic medium). Equivalent weight is related to m olecular w eight (M) of NaHC2O4 in these two reactions as- a)M,M
- b)M,M/2
- c)M/2, M/5
- d)M/5, M/2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
NaHC2O4 is neutralised by NaOH and can also be oxidised by KMnO4 (in acidic medium). Equivalent weight is related to m olecular w eight (M) of NaHC2O4 in these two reactions as
a)
M,M
b)
M,M/2
c)
M/2, M/5
d)
M/5, M/2
|
|
Debanshi Datta answered |
Thus, equivalent weight when reacted with NaOH = M
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following species has/have oxidation number of the metal as + 6 ?- a)
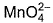
- b)
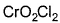
- c)
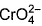
- d)
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 13 and 14) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Which of the following species has/have oxidation number of the metal as + 6 ?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
To balance the oxygen atom in the given reaction in acidic medium
Cr2O72- (aq) → Cr3+(aq) we- a)Add water (H2O) on right side
- b)Add water (H2O) on left side
- c)Add O on right side
- d)Add O on left side
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
To balance the oxygen atom in the given reaction in acidic medium
Cr2O72- (aq) → Cr3+(aq) we
Cr2O72- (aq) → Cr3+(aq) we
a)
Add water (H2O) on right side
b)
Add water (H2O) on left side
c)
Add O on right side
d)
Add O on left side

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Yes because right side is deficient of oxygen.
Assign oxidation number to P in NaH2PO4- a)+6
- b)+1
- c)+4
- d)5.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assign oxidation number to P in NaH2PO4
a)
+6
b)
+1
c)
+4
d)
5.0

|
Raksha Nambiar answered |
Oxidation state of P in NaH2PO4
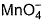
Select the set of compounds with oxidation-reduction duality.- a)Cl2, H3PO4, HCHO, HNO2
- b)Cl2, H3PO3, C6H5CHO, H2O2
- c)Br2, H3PO2, CH3CHO, H3PO4
- d)CrO2Cl2, KMnO4, SO3, CO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the set of compounds with oxidation-reduction duality.
a)
Cl2, H3PO4, HCHO, HNO2
b)
Cl2, H3PO3, C6H5CHO, H2O2
c)
Br2, H3PO2, CH3CHO, H3PO4
d)
CrO2Cl2, KMnO4, SO3, CO2
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Com pounds having oxidising and reducing nature in given reaction are said to have oxidation-reduction duality. Such compounds are said to undergo disproportionation reaction.
(This is called Cannizzaro reaction.)
Note Such compounds have O.N. of the affected atoms intermediate of oxidation part and reduction part
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion(A): Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)Both A and R are false.
- d)A is true but R is false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion(A): Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
Assertion(A): Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
Both A and R are false.
d)
A is true but R is false.
|
|
Dhruba Patel answered |
Assertion(A): Among halogens fluorine is the best oxidant.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
The correct answer is option B: Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Assertion:
Fluorine is the best oxidant among halogens. An oxidant is a substance that accepts electrons from another substance during a chemical reaction. Fluorine has a high tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration, making it a strong oxidant.
Reason:
Fluorine is the most electronegative atom. Electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity value among all the elements, indicating its strong ability to attract electrons. This high electronegativity makes fluorine highly reactive and a strong oxidant.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Both the assertion and reason are true. Fluorine is indeed the best oxidant among halogens due to its high tendency to gain electrons. Additionally, fluorine is the most electronegative atom, which explains its strong oxidizing power. However, the reason provided does not directly explain why fluorine is the best oxidant among halogens. Other factors such as atomic size and electron shielding also play a role in determining the oxidizing power of halogens. Therefore, the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
In conclusion, fluorine's high electronegativity and strong tendency to gain electrons make it the best oxidant among halogens. However, its status as the best oxidant cannot be solely attributed to its electronegativity.
Reason(R): Fluorine is the most electronegative atom.
The correct answer is option B: Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Assertion:
Fluorine is the best oxidant among halogens. An oxidant is a substance that accepts electrons from another substance during a chemical reaction. Fluorine has a high tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration, making it a strong oxidant.
Reason:
Fluorine is the most electronegative atom. Electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Fluorine has the highest electronegativity value among all the elements, indicating its strong ability to attract electrons. This high electronegativity makes fluorine highly reactive and a strong oxidant.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Both the assertion and reason are true. Fluorine is indeed the best oxidant among halogens due to its high tendency to gain electrons. Additionally, fluorine is the most electronegative atom, which explains its strong oxidizing power. However, the reason provided does not directly explain why fluorine is the best oxidant among halogens. Other factors such as atomic size and electron shielding also play a role in determining the oxidizing power of halogens. Therefore, the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
In conclusion, fluorine's high electronegativity and strong tendency to gain electrons make it the best oxidant among halogens. However, its status as the best oxidant cannot be solely attributed to its electronegativity.
The oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is- a)-3
- b)1
- c)4
- d)-2.0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is
a)
-3
b)
1
c)
4
d)
-2.0
|
|
Niharika Nair answered |
Oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Explanation:
- Oxidation number is the number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or loss/gain of electrons.
- Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 because it tends to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration (8 valence electrons).
- For example, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 and the oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -2, which balances out the charge to zero.
- There are some exceptions to this rule, such as in peroxides where oxygen has an oxidation number of -1, and in compounds with more electronegative elements where oxygen may have a positive oxidation number.
- Overall, the oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Explanation:
- Oxidation number is the number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or loss/gain of electrons.
- Oxygen is a highly electronegative element, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- In most compounds, oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 because it tends to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration (8 valence electrons).
- For example, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom has an oxidation number of +1 and the oxygen atom has an oxidation number of -2, which balances out the charge to zero.
- There are some exceptions to this rule, such as in peroxides where oxygen has an oxidation number of -1, and in compounds with more electronegative elements where oxygen may have a positive oxidation number.
- Overall, the oxidation number of oxygen in most compounds is -2.
Equivalent weight of H3PO2 in a reaction is found to be half of its molecular weight. It can be due to its- a)reaction of two H+ ion
- b)oxidation of H3PO3
- c)oxidation of H3PO4
- d)reduction of PH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Equivalent weight of H3PO2 in a reaction is found to be half of its molecular weight. It can be due to its
a)
reaction of two H+ ion
b)
oxidation of H3PO3
c)
oxidation of H3PO4
d)
reduction of PH3

|
Anisha Chauhan answered |
An equivalent weight of H3PO2 when it disproportionates into PH3 and H3PO3 is
For disproportionation reactions, use a trick to find equivalent mass; E = E1 + E2; where E1 and E2 are equivalent masses of oxidation and reduction half-reactions of the same element.Now, find the n-factor(total change in oxidation number per molecule) and then equivalent mass = molar mass/n-factor.
So, when H3PO2 changes into PH3, the oxidation state of phosphorous changes from +1 to -3 so as n-factor is 4. Also when H3PO2 changes into H3PO3, the oxidation state of phosphorous changes from +1 to +5 so as n-factor is again 4.
Now equivalent mass of H3PO2, E =(M/4) + (M/4) = M/2
Hence, the correct option is b.
In this method, the two half equations are balanced separately and then added together to give balanced equation- a)Reluctant method
- b)Oxidizing agent method
- c)Reducing agent method
- d)Half reaction method
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In this method, the two half equations are balanced separately and then added together to give balanced equation
a)
Reluctant method
b)
Oxidizing agent method
c)
Reducing agent method
d)
Half reaction method
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
In the ion-electron method (also called the half-reaction method), the redox equation is separated into two half-equations - one for oxidation and one for reduction. Each of these half-reactions is balanced separately and then combined to give the balanced redox equation.
In which of the following reactions oxidation number of chromium has been affected?- a)
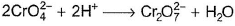
- b)
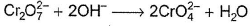
- c)
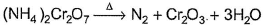
- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following reactions oxidation number of chromium has been affected?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Sankar Bose answered |
Oxidation number of Cr changes from +6 to +3.
The standard electrode potentials, K+/K= -2.93V, Ag+/Ag = 0.80V, the electrode which is negatively charged is- a)Ag+/Ag
- b)K+/K
- c)Any of the two
- d)None of them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard electrode potentials, K+/K= -2.93V, Ag+/Ag = 0.80V, the electrode which is negatively charged is
a)
Ag+/Ag
b)
K+/K
c)
Any of the two
d)
None of them

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Since anode is negatively charged and in anode oxidation takes place, so the element having lower SRP value would act as anode. so answer is K+/K.
Intensity of blue colour increases gradually when _________________- a)copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
- b)silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
- c)zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
- d)copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Intensity of blue colour increases gradually when _________________
a)
copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution
b)
silver rod is dipped in copper nitrate solution
c)
zinc rod is dipped in silver solution
d)
copper rod is dipped in zinc rod solution

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When a copper rod is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a redox reaction occurs between Copper and an aqueous solution of silver nitrate.
- So the intensity of blue colour increases gradually as silver deposits on the rod.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. Sulphate (IV) ion reduces chromate (VI) to green coloured salt. Thus,- a) Cr (III) is formed
- b)Equivalent mass of chromate (VI) = M/3
- c) Equivalent mass of sulphate (IV) =M/2
- d) Oxidation product is sulphate (VI)
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Sulphate (IV) ion reduces chromate (VI) to green coloured salt. Thus,
a)
Cr (III) is formed
b)
Equivalent mass of chromate (VI) = M/3
c)
Equivalent mass of sulphate (IV) =M/2
d)
Oxidation product is sulphate (VI)
|
|
Amrita Choudhary answered |
Thus, (a) is correct.
A cell is prepared by dipping a chromium rod in 1M Cr2(SO4)3 solution and an iron rod in 1M FeSO4 solution. The standard reduction potentials of Chromium and Iron electrodes are -0.75 V and -0.45 V respectively. What will be the standard EMF of the cell?- a)+0.30 V
- b)+0.47 V
- c)– 0.30 V
- d)-0.47 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A cell is prepared by dipping a chromium rod in 1M Cr2(SO4)3 solution and an iron rod in 1M FeSO4 solution. The standard reduction potentials of Chromium and Iron electrodes are -0.75 V and -0.45 V respectively. What will be the standard EMF of the cell?
a)
+0.30 V
b)
+0.47 V
c)
– 0.30 V
d)
-0.47 V

|
Deadpool answered |
Reduction potential of fe is more than that of cr, so fe will reduce and act as cathode and cr will act as anode. now emf of cell is reduction potential of cathode - reduction potential of anode. so EMF= -0.45-(-0.75) = 0.3 V
Reduction is defined in terms ofI. electronation and hydrogenation
II. deelectronation and gain of oxygen
III. increase in oxidation number
IV. decrease in oxidation numberSelect the correct terms- a)I and IV
- b)I and III
- c)II and II
- d)I and II
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Reduction is defined in terms of
I. electronation and hydrogenation
II. deelectronation and gain of oxygen
III. increase in oxidation number
IV. decrease in oxidation number
II. deelectronation and gain of oxygen
III. increase in oxidation number
IV. decrease in oxidation number
Select the correct terms
a)
I and IV
b)
I and III
c)
II and II
d)
I and II

|
Sharmila Sharma answered |
Gain of hydrogen , electron and decrease in oxidation number is reduction
The more positive the value of E0, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent. E0values : Fe3 + / Fe2+ = +0.77; I2(s)/l- = +0.54; cu2+/ Cu = +0.34; Ag+ / Ag = +0.80V- a)Ag+
- b)Fe3+
- c)I2 (s)
- d)Cu2+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The more positive the value of E0, the greater is the tendency of the species to get reduced. Using the standard electrode potential of redox couples given below find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
E0values : Fe3 + / Fe2+ = +0.77; I2(s)/l- = +0.54; cu2+/ Cu = +0.34; Ag+ / Ag = +0.80V
a)
Ag+
b)
Fe3+
c)
I2 (s)
d)
Cu2+

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Oxidation number of H is not always +1 . It can be -1 , 0.
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F. Identify the element(s) that exhibits only negative oxidation state- a)F
- b)I
- c)s
- d)Cs and F
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F. Identify the element(s) that exhibits only negative oxidation state
a)
F
b)
I
c)
s
d)
Cs and F

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
F has negative oxidation state as it is very electro negative.
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is- a)HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
- b)HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
- c)HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
- d)NH4Cl, N2, NO, HN03
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of N-compounds in its decreasing order of oxidation states is
a)
HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
b)
HNO3, NO, NH4Cl, N2
c)
HNO3, NH4Cl, NO, N2
d)
NH4Cl, N2, NO, HN03

|
Infinity Academy answered |
To determine the decreasing order of oxidation states of nitrogen in the given compounds, we need to find the oxidation state of nitrogen in each compound:
- HNO3 (Nitric acid): Oxidation state of nitrogen: +5
- NO (Nitric oxide): Oxidation state of nitrogen: +2
- N2 (Dinitrogen): Oxidation state of nitrogen: 0
- NH4Cl (Ammonium chloride): Oxidation state of nitrogen: -3
Now, let's arrange these compounds in decreasing order of oxidation states:
- HNO3: +5
- NO: +2
- N2: 0
- NH4Cl: -3
So, the correct order in decreasing oxidation state is:
HNO3, NO, N2, NH4Cl
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.Assertion (A) : Redox couple is the combination of oxidised and reduced form of a substance involved in an oxidation or reduction half cell.Reason (R) : In the representation EOFe3+ /Fe2+ and EO Cu2+/Cu, Fe3+/ Fe2+ and Cu2+ / Cu are redox couples.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)Both A and R are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Redox couple is the combination of oxidised and reduced form of a substance involved in an oxidation or reduction half cell.
Reason (R) : In the representation EOFe3+ /Fe2+ and EO Cu2+/Cu, Fe3+/ Fe2+ and Cu2+ / Cu are redox couples.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
Both A and R are false.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
A redox couple is defined as pair of compounds or elements having together the oxidised and reduced forms of it and taking part in an oxidation or reduction half-reaction. So, Fe3+/Fe2+and Cu2+/Cu are redox couples.
Both assertion and reason are true reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
The process in which the strength of an unknown solution is calculated using a known standard solution.- a)Titration
- b)Oxidation
- c)Reduction
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The process in which the strength of an unknown solution is calculated using a known standard solution.
a)
Titration
b)
Oxidation
c)
Reduction
d)
None of these
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
A titration is a technique used to work out the concentration of an unknown solution based on its chemical reaction with a solution of known concentration. The process usually involves adding the known solution (the titrant) to a known quantity of the unknown solution (the analyte) until the reaction is complete.
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.Assertion (A): In the reaction between potassium permanganate and potassium iodide, permanganate ions act as oxidising agent.Reason (R) : Oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7 duringthe reaction.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)Both A and R are false.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): In the reaction between potassium permanganate and potassium iodide, permanganate ions act as oxidising agent.
Reason (R) : Oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7 during
the reaction.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
Both A and R are false.
|
|
Manasa Patel answered |
Assertion (A) Explained
In the reaction between potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and potassium iodide (KI):
- Potassium Permanganate as an Oxidizing Agent:
- Potassium permanganate contains manganese in the +7 oxidation state.
- In acidic conditions, KMnO4 can reduce to Mn^2+ (where manganese has an oxidation state of +2), which indicates that it acts as an oxidizing agent.
- Therefore, Assertion (A) is true.
Reason (R) Explained
- Oxidation State Change:
- The reason states that the oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7.
- This is incorrect; in the reaction, manganese is reduced from +7 to +2, not the other way around.
- Therefore, Reason (R) is false.
Conclusion
- Since Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false, the correct answer is:
- Option (C): A is true but R is false.
This analysis clarifies that while potassium permanganate behaves as an oxidizing agent in the reaction, the stated change in the oxidation state of manganese is inaccurately described in Reason (R).
In the reaction between potassium permanganate (KMnO4) and potassium iodide (KI):
- Potassium Permanganate as an Oxidizing Agent:
- Potassium permanganate contains manganese in the +7 oxidation state.
- In acidic conditions, KMnO4 can reduce to Mn^2+ (where manganese has an oxidation state of +2), which indicates that it acts as an oxidizing agent.
- Therefore, Assertion (A) is true.
Reason (R) Explained
- Oxidation State Change:
- The reason states that the oxidation state of manganese changes from +2 to +7.
- This is incorrect; in the reaction, manganese is reduced from +7 to +2, not the other way around.
- Therefore, Reason (R) is false.
Conclusion
- Since Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false, the correct answer is:
- Option (C): A is true but R is false.
This analysis clarifies that while potassium permanganate behaves as an oxidizing agent in the reaction, the stated change in the oxidation state of manganese is inaccurately described in Reason (R).
Which of the following is true as per metal activity series?- a)Zn>Cu>Ag
- b)Zn<Cu<Ag
- c)Zn>Ag>Cu
- d)Zn<Ag<Cu
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true as per metal activity series?
a)
Zn>Cu>Ag
b)
Zn<Cu<Ag
c)
Zn>Ag>Cu
d)
Zn<Ag<Cu

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Metal activity series or electrochemical series is a series in the decreasing order of metals which are active during a chemical reaction comparatively with each other.
- Here, Zinc’s activity is greater than Copper’s activity and Copper’s activity is greater than that of silver.
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?- a)zinc is deposited on copper
- b)copper is deposited in the beaker
- c)zinc is deposited in the beaker
- d)copper is deposited on zinc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When a zinc rod is kept in a copper nitrate solution what happens?
a)
zinc is deposited on copper
b)
copper is deposited in the beaker
c)
zinc is deposited in the beaker
d)
copper is deposited on zinc

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When zinc is placed in copper nitrate solution the intensity of the blue colour is produced and copper iron is deposited on zinc.
- This is a Redox reaction between zinc and an aqueous solution of copper nitrate occurring in a beaker.
A standard hydrogen electrode has zero electrode potential because- a)Hydrogen is the lightest element
- b)Hydrogen atom has only one electron.
- c)Hydrogen is easiest to oxidize
- d)The electrode potential is assumed to be zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A standard hydrogen electrode has zero electrode potential because
a)
Hydrogen is the lightest element
b)
Hydrogen atom has only one electron.
c)
Hydrogen is easiest to oxidize
d)
The electrode potential is assumed to be zero
|
|
Rashi Sharma answered |
Explanation:
A standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is an electrode that is used as a reference in half-cell reactions to determine the electrode potential of other electrodes. It consists of a platinum electrode immersed in a solution of an acid, typically 1 M HCl, with hydrogen gas bubbling through it.
The electrode potential of a standard hydrogen electrode is considered to be zero because it is used as a reference point to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes. By convention, the electrode potential of the SHE is set to zero, and all other electrode potentials are measured relative to it.
The reasons why the electrode potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is assumed to be zero are as follows:
1. Consistency and ease of measurement: By establishing the electrode potential of the SHE as zero, it provides a consistent reference point for comparing the electrode potentials of other electrodes. This makes it easier to measure and compare the electrode potentials of different reactions.
2. Hydrogen as a neutral element: Hydrogen gas (H2) is composed of two hydrogen atoms, each with one electron. These electrons can easily be lost or gained, making hydrogen a versatile element for redox reactions. Since hydrogen is a neutral element, it is considered to have an electrode potential of zero.
3. Reversibility of the hydrogen electrode: The hydrogen electrode is reversible, meaning that it can be easily converted between an oxidation half-reaction and a reduction half-reaction. This reversibility allows for accurate and reproducible measurements of electrode potentials.
4. Standardization: The choice of the standard hydrogen electrode as the reference electrode is based on convention and standardization. It provides a consistent and universally accepted reference point for measuring and comparing electrode potentials.
Overall, the assumption of a zero electrode potential for the standard hydrogen electrode simplifies the measurement and comparison of electrode potentials in electrochemical reactions. It provides a consistent reference point and allows for the standardization of electrode potential measurements.
A standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) is an electrode that is used as a reference in half-cell reactions to determine the electrode potential of other electrodes. It consists of a platinum electrode immersed in a solution of an acid, typically 1 M HCl, with hydrogen gas bubbling through it.
The electrode potential of a standard hydrogen electrode is considered to be zero because it is used as a reference point to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes. By convention, the electrode potential of the SHE is set to zero, and all other electrode potentials are measured relative to it.
The reasons why the electrode potential of the standard hydrogen electrode is assumed to be zero are as follows:
1. Consistency and ease of measurement: By establishing the electrode potential of the SHE as zero, it provides a consistent reference point for comparing the electrode potentials of other electrodes. This makes it easier to measure and compare the electrode potentials of different reactions.
2. Hydrogen as a neutral element: Hydrogen gas (H2) is composed of two hydrogen atoms, each with one electron. These electrons can easily be lost or gained, making hydrogen a versatile element for redox reactions. Since hydrogen is a neutral element, it is considered to have an electrode potential of zero.
3. Reversibility of the hydrogen electrode: The hydrogen electrode is reversible, meaning that it can be easily converted between an oxidation half-reaction and a reduction half-reaction. This reversibility allows for accurate and reproducible measurements of electrode potentials.
4. Standardization: The choice of the standard hydrogen electrode as the reference electrode is based on convention and standardization. It provides a consistent and universally accepted reference point for measuring and comparing electrode potentials.
Overall, the assumption of a zero electrode potential for the standard hydrogen electrode simplifies the measurement and comparison of electrode potentials in electrochemical reactions. It provides a consistent reference point and allows for the standardization of electrode potential measurements.
In the following reaction,
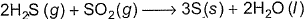
One equivalent of H2S (g)will reduce- a)1 Mole SO2
- b)0.5 Mole SO2
- c)0.25 Mole SO2
- d)2 Mole SO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reaction,
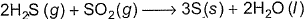
One equivalent of H2S (g)will reduce
One equivalent of H2S (g)will reduce
a)
1 Mole SO2
b)
0.5 Mole SO2
c)
0.25 Mole SO2
d)
2 Mole SO2

|
Rithika Khanna answered |
Change in oxidation number of S of H2S = 2 units
Change in oxidation number of S of SO2 = 4 units
Then one mole H2S = 2 equivalents H2S
One mole SO2 = 4 equivalent SO2
One equivalent H23 one equivalent SO2 = 0.25 mole SO2
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
- a)Better reducing agent is the one that looses more electrons
- b)Better reducing agent is the one that looses less electrons
- c)Both are same in reducing capacity
- d)The reduced metal is a better reducing agent than the reducing metal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal in a compound can be displaced by another metal in the uncombined state. Which metal is a better reducing agent in such a case?
a)
Better reducing agent is the one that looses more electrons
b)
Better reducing agent is the one that looses less electrons
c)
Both are same in reducing capacity
d)
The reduced metal is a better reducing agent than the reducing metal

|
Bhavana Chavan answered |
Concept of Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that loses or "donates" an electron to another substance in a redox chemical reaction. Therefore, a good reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized easily, or in other words, the one that can easily lose electrons.
Characteristics of a Good Reducing Agent:
A reducing agent is a substance that loses or "donates" an electron to another substance in a redox chemical reaction. Therefore, a good reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized easily, or in other words, the one that can easily lose electrons.
Characteristics of a Good Reducing Agent:
- Electron Loss: A better reducing agent is the one that loses more electrons. This is because by losing electrons, the reducing agent gets oxidized and in turn reduces the other substance. This is the basic principle of a redox reaction.
- Reactivity: The reactivity of the metal also determines its capacity as a reducing agent. Metals that are high in the reactivity series are good reducing agents. This is because they can easily lose electrons and get oxidized.
- Stability: Metals that are less stable are better reducing agents because they can easily lose electrons to attain a stable state.
Hence, Option A is the correct answer - a better reducing agent is the one that loses more electrons.
Chapter doubts & questions for Redox Reactions - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Redox Reactions - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
NCERT Based Tests for NEET
684 tests
|