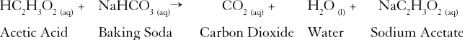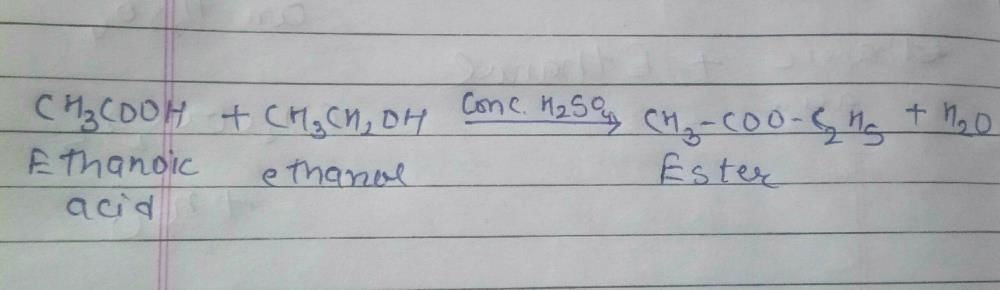All Exams >
Class 10 >
Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Carbon and its compounds for Class 10 Exam
The major constituent of biogas is- a)Propane
- b)Acetylene
- c)Methane
- d)Benzene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The major constituent of biogas is
a)
Propane
b)
Acetylene
c)
Methane
d)
Benzene
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Biogas comprises primarily methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulphide (H2S), moisture and siloxanes.
In methane, the valency of carbon is:- a)four
- b)two
- c)one
- d)three
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In methane, the valency of carbon is:
a)
four
b)
two
c)
one
d)
three

|
Vp Classes answered |
Methane has its molecular formula CH4.
It is formed by one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
Hydrogen has its valency 1 and carbon being tetravalent needs four valence electrons to acquire noble gas configuration, where it shares its 4 electrons with four hydrogen atoms.
Therefore, the valency of carbon atom in Methane (CH4) is 4.
It is formed by one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
Hydrogen has its valency 1 and carbon being tetravalent needs four valence electrons to acquire noble gas configuration, where it shares its 4 electrons with four hydrogen atoms.
Therefore, the valency of carbon atom in Methane (CH4) is 4.
The property of carbon of self combination is called:- a)Covalency
- b)Catenation
- c)Tetravalency
- d)Isomerism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The property of carbon of self combination is called:
a)
Covalency
b)
Catenation
c)
Tetravalency
d)
Isomerism
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
The property of self combination of carbon atoms to form long chains is called catenation.
Which of the following is a non-polar molecule?- a)O2
- b)HF
- c)NH3
- d)H2O
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a non-polar molecule?
a)
O2
b)
HF
c)
NH3
d)
H2O
|
|
Pooja sengupta answered |
When 2 molecules of different electronegativity are bonded together covalently the bonding electron cloud is more attracted towards atom with higher electronegativity. ... So, the bond between 2 Oxygen atom is non-polar . Since, it is the only bonding in oxygen molecule Oxygen molecule is non-polar
The major constituent of natural gas is- a)Butane
- b)Methane
- c)Propane
- d)Ethane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The major constituent of natural gas is
a)
Butane
b)
Methane
c)
Propane
d)
Ethane
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane, but also contains ethane, propane and heavier hydrocarbons. It also contains small amounts of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulphide and trace amounts of water.
Which of the following will give a pleasant smell of ester when heated with ethanol and a small quantity of sulphuric acid?- a)CH3COOH
- b)CH2CH2OH
- c)CH3OH
- d)CH3CHO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will give a pleasant smell of ester when heated with ethanol and a small quantity of sulphuric acid?
a)
CH3COOH
b)
CH2CH2OH
c)
CH3OH
d)
CH3CHO
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Acetic acid gives a pleasant smell on rejection with ethanol due to the formation of ethyl acetate as :-
CH3COOH +C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 +H2O
CH3COOH +C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 +H2O
MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) or Practice Quiz with solutions of Chapter - "Carbon and its Compounds" of Class 10 Science, the questions are available for practiceQ. Which of the following will not decolourise bromine water?- a)C4H8
- b)C3H4
- c)C3H8
- d)C4H6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) or Practice Quiz with solutions of Chapter - "Carbon and its Compounds" of Class 10 Science, the questions are available for practice
Q. Which of the following will not decolourise bromine water?
a)
C4H8
b)
C3H4
c)
C3H8
d)
C4H6
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
C3H8 is alkane and all other are alkene or alkyne. To decolourise the bromine water is the property of unsaturated compound not of saturated compound.
What type of isomerism is shown by 1-bromo propane and 2-bromo propane?- a)Position isomerism
- b)Chain isomerism
- c)Metamerism
- d)Functional isomerism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of isomerism is shown by 1-bromo propane and 2-bromo propane?
a)
Position isomerism
b)
Chain isomerism
c)
Metamerism
d)
Functional isomerism
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
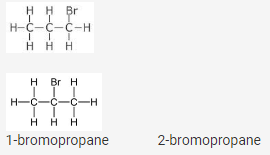
They are positional isomers of molecular formula C3H7Br
Position Isomerism : When two or more compounds with the same molecular formula differ in the position of substituent atom or functional group on the carbon atom, they are called position isomers and this phenomenon is termed as position isomerism.
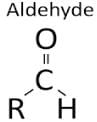
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is
- a)Ethanal
- b)Ethanol
- c)Methanol
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is
a)
Ethanal
b)
Ethanol
c)
Methanol
d)
Acetone
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The IUPAC name of CH3CHO is Ethanal.
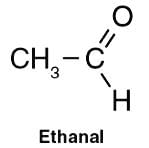
The IUPAC name for CH3CHO is Ethanal, also known as Acetaldehyde. It has 2 carbons, so the term “Eth” is used as prefix and it belongs to the aldehyde group, so the term “al” is used as suffix.

The IUPAC name for CH3CHO is Ethanal, also known as Acetaldehyde. It has 2 carbons, so the term “Eth” is used as prefix and it belongs to the aldehyde group, so the term “al” is used as suffix.
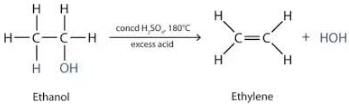
In conversion from ethanol to ethene, concentrated sulphuric acid is used as:
- a)Precipitating agent
- b)Oxidizing agent
- c)Dehydrating agent
- d)Reducing agent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In conversion from ethanol to ethene, concentrated sulphuric acid is used as:
a)
Precipitating agent
b)
Oxidizing agent
c)
Dehydrating agent
d)
Reducing agent
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Sulphuric acid is used as a dehydrating agent because sulphuric acid has a great affinity for water. It readily removes elements of water from other compounds i.e, it acts as a dehydrating agent, it being a hygroscopic substance absorbs water from other substances without dissolving in it, so it is considered a good drying agent.

An allotrope of carbon which conducts electricity is:- a)Diamond
- b)Fullerenes
- c)Graphite
- d)Both Diamond and Fullerenes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An allotrope of carbon which conducts electricity is:
a)
Diamond
b)
Fullerenes
c)
Graphite
d)
Both Diamond and Fullerenes
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Graphite can conduct electricity because in graphite every carbon atom is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms and has 1 free electron. This free electrons help in conducting electricity.
Shared electron pair in covalent compound AB will be drawn:- a)On the top of A
- b)On the left side of A
- c)On the right side of B
- d)Between A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Shared electron pair in covalent compound AB will be drawn:
a)
On the top of A
b)
On the left side of A
c)
On the right side of B
d)
Between A and B
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Because the shared pair of electrons always stays in between two elements.
Most of covalent compounds are found in- a)solid state
- b)gaseous state
- c)liquid state
- d)both in liquid and gaseous state
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of covalent compounds are found in
a)
solid state
b)
gaseous state
c)
liquid state
d)
both in liquid and gaseous state
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Compounds having lesser number of carbon atoms are gases like CH4, C4H10 and some are liquids. Compounds having greater number of carbon atoms are solids.
The functional group in methanol and methanal respectively are :- a)–OH, –CHO
- b)–CHO, –OH
- c)–OH, –COOH
- d)–CHO, –COOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The functional group in methanol and methanal respectively are :
a)
–OH, –CHO
b)
–CHO, –OH
c)
–OH, –COOH
d)
–CHO, –COOH
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Methane + ol = Methanol
Methane + al = Methanal
Methane + al = Methanal
The characteristic reaction of alkanes is- a)Addition
- b)Substitution
- c)Polymerization
- d)Isomerization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The characteristic reaction of alkanes is
a)
Addition
b)
Substitution
c)
Polymerization
d)
Isomerization
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
They being saturated and cannot undergo addition reaction.
Graphite is a soft lubricant extremely difficult to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour is that graphite.- a)Has carbon atoms arranged in large plates of rings of strongly bound carbon atoms with weak interplate bonds
- b)Is a non-crystalline substance
- c)Is an allotropic form of carbon
- d)Has only single bonds between carbon atoms
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Graphite is a soft lubricant extremely difficult to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour is that graphite.
a)
Has carbon atoms arranged in large plates of rings of strongly bound carbon atoms with weak interplate bonds
b)
Is a non-crystalline substance
c)
Is an allotropic form of carbon
d)
Has only single bonds between carbon atoms
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Graphite has a hexagonal sheet structure in which every carbon atom is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms and the adjacent layers are arranged together by weak van der waal forces of attraction.
The gap between the adjacent layers makes it soft and slippery.
The gap between the adjacent layers makes it soft and slippery.
A covalent bond is formed by- a)Complete transfer of electrons
- b)One sided sharing of electron
- c)Mutual sharing of electron
- d)All of the three above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A covalent bond is formed by
a)
Complete transfer of electrons
b)
One sided sharing of electron
c)
Mutual sharing of electron
d)
All of the three above
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
A covalent bond is formed by mutual sharing of electrons between the 2 atoms.

The reaction 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2 suggests that ethanol is
- a)Acidic in nature
- b)Basic in nature
- c)Amphoteric
- d)Neutral
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2 suggests that ethanol is
a)
Acidic in nature
b)
Basic in nature
c)
Amphoteric
d)
Neutral
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Ethanol is neutral in nature as it shows no effect on litmus paper.But here it is acting as an acid as,Na is highly reactive.
Open-chain saturated hydrocarbons are called- a)Paraffins
- b)Alkenes
- c)Alkynes
- d)Alkyl groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Open-chain saturated hydrocarbons are called
a)
Paraffins
b)
Alkenes
c)
Alkynes
d)
Alkyl groups
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
Paraffins are also called Alkanes and have the general formula, CnH2n+2 , where n is the no. of carbon atoms in a given molecule. They are open - chain saturated hydrocarbons.
The cooking gas used in our homes is mainly an:- a)Alkane
- b)Haloalkane
- c)Carboxylic acid
- d)Alkene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cooking gas used in our homes is mainly an:
a)
Alkane
b)
Haloalkane
c)
Carboxylic acid
d)
Alkene
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carbon–carbon bonds are single. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. The alkanes range in complexity from the simplest case of methane (CH4), where n = 1 (sometimes called the parent molecule), to arbitrarily large and complex molecules, like pentacontane (C50H102) or 6-ethyl-2-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)octane, an isomer of tetradecane (C14H30)
Which family of organic compounds does not contain any multiple bonds?- a)Aldehydes
- b)Alkenes
- c)Ketones
- d)Alkyl Halides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which family of organic compounds does not contain any multiple bonds?
a)
Aldehydes
b)
Alkenes
c)
Ketones
d)
Alkyl Halides
|
|
Anjana Khatri answered |
Alkanes have only single bonds
An alkyl halide is another name for a halogen-substituted alkane. The carbon atom, which is bonded to the halogen atom, has sp3 hybridized bonding orbitals and exhibits a tetrahedral shape.
Which of the following salts when dissolved in water produce hard water?- a)Calcium sulphate
- b)Magnesium bicarbonate
- c)Calcium chloride
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following salts when dissolved in water produce hard water?
a)
Calcium sulphate
b)
Magnesium bicarbonate
c)
Calcium chloride
d)
All of these
|
|
Maheshwari Jii answered |
Ca and mg compounds provide hardness thats why all the compounds is answer
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has- a)6 covalent bonds
- b)7 covalent bonds
- c)8 covalent bonds
- d)9 covalent bonds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
a)
6 covalent bonds
b)
7 covalent bonds
c)
8 covalent bonds
d)
9 covalent bonds
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
It has 7 covalent bonds as .1 bond is between two carbon atoms and rest of the six are with hydrogen atoms.
Which of the following is not a saturated hydrocarbon?- a)Cyclohexane
- b)Benzene
- c)Butane
- d)Isobutane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a saturated hydrocarbon?
a)
Cyclohexane
b)
Benzene
c)
Butane
d)
Isobutane
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Benzene is C6H6 an aromatic compound in the form of a closed ring. It contains alternate double and single bond.
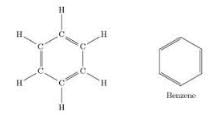

Butane has molecular formula:- a)C4H6
- b)C3H6
- c)C4H10
- d)C3H4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Butane has molecular formula:
a)
C4H6
b)
C3H6
c)
C4H10
d)
C3H4
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Butane is a saturated hydrocarbon. But + ane = Butane.

The general formula of cyclic alkanes is- a)CnH2n+2
- b)CnH2n-2
- c)CnH2n-1
- d)CnH2n
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The general formula of cyclic alkanes is
a)
CnH2n+2
b)
CnH2n-2
c)
CnH2n-1
d)
CnH2n
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
CnH2n.
The general formula for rings is CnH2n. For cyclic alkanes, carbon must still have four bonds, hence each carbon is attached to two others and two hydrogens are groups may be attached to each carbon (structure on the right).
Alkanes have a general formula:- a)CnH2n+2
- b)CnH2n-2
- c)CnH2n
- d)CnH2n+1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Alkanes have a general formula:
a)
CnH2n+2
b)
CnH2n-2
c)
CnH2n
d)
CnH2n+1
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons having C-C single bond and general formula CnH2n+2.
Which of the following substance is added to denature ethanol?- a)Methanol
- b)Benzene
- c)Copper nitrate
- d)Poison
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following substance is added to denature ethanol?
a)
Methanol
b)
Benzene
c)
Copper nitrate
d)
Poison
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Ethanol + methanol leads in formation of denatured alcohol. Methanol is added to make industrial alcohol unfit for drinking.
The bond which is formed by sharing of an electron pair between two atoms is known as:- a)Ionic bond
- b)Covalent bond
- c)Dative bond
- d)Metallic bond
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The bond which is formed by sharing of an electron pair between two atoms is known as:
a)
Ionic bond
b)
Covalent bond
c)
Dative bond
d)
Metallic bond
|
|
Rajiv Gupta answered |
A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding.
Ethanol on complete oxidation gives- a)CO2 and water
- b)Acetaldehyde
- c)Acetic acid
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethanol on complete oxidation gives
a)
CO2 and water
b)
Acetaldehyde
c)
Acetic acid
d)
Acetone
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Ethanol is firstly oxidized to acetaldehyde and the acetaldehyde is then oxidized to acetic acid. This reaction is considered as a green catalytic process for the only reduction product is water.
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that:- a)Fuel is burning completely.
- b)Fuel is wet.
- c)Food is not cooked completely.
- d)Fuel is not burning completely.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that:
a)
Fuel is burning completely.
b)
Fuel is wet.
c)
Food is not cooked completely.
d)
Fuel is not burning completely.

|
Shivangi Jasrotia answered |
Fuel is not burning completely because there is a lack of oxygen. Hence, incombustion is taking place over here.
Ethanol on complete oxidation gives- a)Acetic acid
- b)Acetaldehyde
- c)CO2 and water
- d)Acetone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethanol on complete oxidation gives
a)
Acetic acid
b)
Acetaldehyde
c)
CO2 and water
d)
Acetone
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
The correct option is A.
Ethanol is oxidised to produce ethanal by removing two hydrogen atoms. Ethanal is then oxidised to produce ethanoic acid, by adding an oxygen atom.
Ethanol is oxidised to produce ethanal by removing two hydrogen atoms. Ethanal is then oxidised to produce ethanoic acid, by adding an oxygen atom.
n-butane and isobutane are- a)Alkenes
- b)Alkynes
- c)Isomers
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
n-butane and isobutane are
a)
Alkenes
b)
Alkynes
c)
Isomers
d)
None of these

|
Kshitij Pandey answered |
It is isomer because in n butane number of carbon is 4 and in isobutane also 4 and it is chain isomerism because it is generated by chain of carbon
An example of soap is- a)CH3COONa
- b)CH3ONa
- c)C17H35COONa
- d)C17H35COOC2H5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of soap is
a)
CH3COONa
b)
CH3ONa
c)
C17H35COONa
d)
C17H35COOC2H5
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
C17H35COOC2H5 + NaOH → C17H35COONa + C2H5OH
The molecular formula of benzene is:- a)C6H6
- b)C6H10
- c)C6H12
- d)C6H8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecular formula of benzene is:
a)
C6H6
b)
C6H10
c)
C6H12
d)
C6H8
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
The chemical formula of benzene is C6H6, so it has six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms.
The functional group present in ethanol is- a)alcoholic group
- b)Ester group
- c)Carboxyl group
- d)Aldehydic group
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The functional group present in ethanol is
a)
alcoholic group
b)
Ester group
c)
Carboxyl group
d)
Aldehydic group
|
|
Madhu Sulaniya answered |
C2H5 -OH. hence the functional group present in Ethanol is alcoholic group.
How many structural isomers are possible for pentane-- a)3.0
- b)4.0
- c)2.0
- d)1.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many structural isomers are possible for pentane-
a)
3.0
b)
4.0
c)
2.0
d)
1.0
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Pentane (C5H12) has three structural isomers.
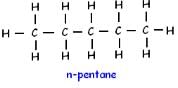
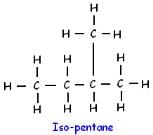



Which of the following will give a pleasant smell of ester when heated with ethyl alcohol and a small quantity of sulphuric acid?- a)CH3OH
- b)CH3CHO
- c)CH3COCH3
- d)CH3COOH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will give a pleasant smell of ester when heated with ethyl alcohol and a small quantity of sulphuric acid?
a)
CH3OH
b)
CH3CHO
c)
CH3COCH3
d)
CH3COOH
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
Carboxylic acids react with alcohols in presence of acid (catalyst) to produce sweet smelling compounds called esters.
The acid present in vinegar is- a)CH3COOH
- b)HCOOH
- c)CH3CH2COOH
- d)CH3CH2CH2COOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The acid present in vinegar is
a)
CH3COOH
b)
HCOOH
c)
CH3CH2COOH
d)
CH3CH2CH2COOH
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid. Vinegar typically contains 5–8% acetic acid by volume.
Unsaturated carbon compounds on combustion give:- a)Yellow sooty flame
- b)Clean Blue flame
- c)Green flame
- d)Intense white flame
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Unsaturated carbon compounds on combustion give:
a)
Yellow sooty flame
b)
Clean Blue flame
c)
Green flame
d)
Intense white flame
|
|
Arun Yadav answered |
Unsaturated hydrocarbons like ethyne, also known as acetylene, burn to produce a yellow, sooty flame due to incomplete combustion in air.
The flame is sooty because the percentage of carbon is comparatively higher than that of alkanes and so does not get completely oxidized in air.
The oxidising agent used to convert alcohols into carboxylic acid is:- a)Conc. sulphuric acid
- b)Phosphorus trichloride
- c)Alkaline Potassium permanganate
- d)Sodium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidising agent used to convert alcohols into carboxylic acid is:
a)
Conc. sulphuric acid
b)
Phosphorus trichloride
c)
Alkaline Potassium permanganate
d)
Sodium
|
|
Praveenkumar Angadi answered |
Pottassium permanganate is a very strong oxidant able to react with many functional groups, such as secondary alcohols, 1,2-diols , aldehydes, alkenes, oxides, sulphides and thiols. Under controlled conditions potassium permanganate oxidizes primary alcohols into alcoholic acids very efficiently. I think you understand this.
Methane is a major constituent of- a)Coal gas
- b)Water gas
- c)Petroleum
- d)Biogas
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Methane is a major constituent of
a)
Coal gas
b)
Water gas
c)
Petroleum
d)
Biogas
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
Biogas comprises primarily methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) and may have small amounts of hydrogen sulphide (H2S), moisture and siloxanes.
Which of the following substances cannot be used to distinguish ethanol from ethanoic acid?- a)Na metal
- b)NaHCO3
- c)Hot alkaline KMnO4 solution
- d)Hot acidified K2Cr2O7 solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following substances cannot be used to distinguish ethanol from ethanoic acid?
a)
Na metal
b)
NaHCO3
c)
Hot alkaline KMnO4 solution
d)
Hot acidified K2Cr2O7 solution
|
|
Anjali Rao answered |
Option ( a) Na metal is the correct answer because other options ( b) ,( c) and ( d) are used to distinguish ethanol from ethanoic acid.
Which class of organic compounds give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution ?- a)Esters
- b)Alcohols
- c)Carboxylic acids
- d)Aldehydes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which class of organic compounds give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution ?
a)
Esters
b)
Alcohols
c)
Carboxylic acids
d)
Aldehydes
|
|
Gauri Desai answered |
Organic compounds are compounds that contain carbon atoms bonded to other atoms such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and others. They are widely found in nature and have a variety of properties and uses. One common characteristic of organic compounds is their ability to react with other substances, including inorganic compounds.
Effervescence is the process of rapid escape of gas from a liquid or solid. When a substance reacts with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), it releases carbon dioxide gas (CO2), resulting in effervescence. The gas bubbles formed during effervescence are visible as a frothy or fizzy reaction.
Among the given options, carboxylic acids are the class of organic compounds that give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution. Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a hydrocarbon chain. They are weak acids and can easily donate a hydrogen ion (H+) to form a carboxylate ion (RCOO-).
When a carboxylic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate, the following reaction occurs:
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + H2O + CO2
The carboxylic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form a salt (RCOONa), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. It is the release of carbon dioxide gas that causes effervescence. The carbon dioxide gas bubbles escape rapidly from the solution, resulting in the frothy reaction.
Other classes of organic compounds such as esters, alcohols, and aldehydes do not undergo the same reaction with sodium bicarbonate. Esters are organic compounds formed from the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a hydrocarbon chain. Aldehydes are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to at least one hydrogen atom.
These classes of organic compounds do not have the same acidic properties as carboxylic acids and therefore do not react with sodium bicarbonate to release carbon dioxide gas. Hence, they do not give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution.
In conclusion, carboxylic acids are the class of organic compounds that give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution. This is due to their ability to donate a hydrogen ion and react with sodium bicarbonate to release carbon dioxide gas.
Effervescence is the process of rapid escape of gas from a liquid or solid. When a substance reacts with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), it releases carbon dioxide gas (CO2), resulting in effervescence. The gas bubbles formed during effervescence are visible as a frothy or fizzy reaction.
Among the given options, carboxylic acids are the class of organic compounds that give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution. Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a hydrocarbon chain. They are weak acids and can easily donate a hydrogen ion (H+) to form a carboxylate ion (RCOO-).
When a carboxylic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate, the following reaction occurs:
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + H2O + CO2
The carboxylic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form a salt (RCOONa), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. It is the release of carbon dioxide gas that causes effervescence. The carbon dioxide gas bubbles escape rapidly from the solution, resulting in the frothy reaction.
Other classes of organic compounds such as esters, alcohols, and aldehydes do not undergo the same reaction with sodium bicarbonate. Esters are organic compounds formed from the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Alcohols are organic compounds that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a hydrocarbon chain. Aldehydes are organic compounds that contain a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to at least one hydrogen atom.
These classes of organic compounds do not have the same acidic properties as carboxylic acids and therefore do not react with sodium bicarbonate to release carbon dioxide gas. Hence, they do not give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution.
In conclusion, carboxylic acids are the class of organic compounds that give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution. This is due to their ability to donate a hydrogen ion and react with sodium bicarbonate to release carbon dioxide gas.
Ethanol on oxidation gives- a)Ethane
- b)Formalin
- c)Ethanoic acid
- d)Methane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethanol on oxidation gives
a)
Ethane
b)
Formalin
c)
Ethanoic acid
d)
Methane

|
Anisha Basak answered |
Ethanol is oxidised to produce ethanal by removing two hydrogen atoms. Ethanal is then oxidised to produce ethanoic acid, by adding an oxygen atom. The O:H ratio changes from 1:6 (ethanol) to 1:4 (ethanal) to 1:2 (ethanoic acid).
Chapter doubts & questions for Carbon and its compounds - Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Carbon and its compounds - Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Related Class 10 Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup