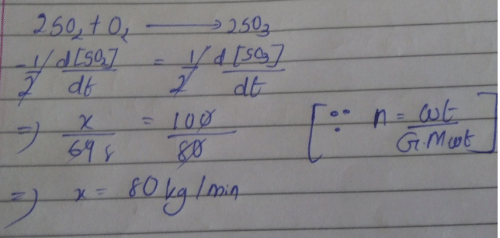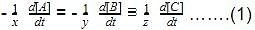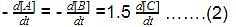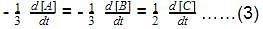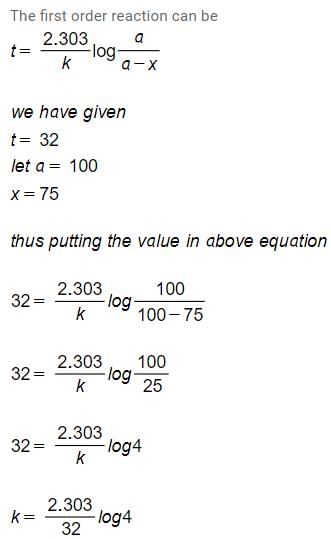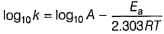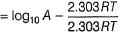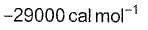All Exams >
ACT >
Science for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Kinetics for ACT Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:For the reaction,
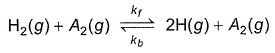
kf = 2.2 x 104 L mol-1s-1 and Kc = 1.00 x 10-4 at 3000 K. Thus, kb is
- A:
2.2 x 108 L2mol-2s-1
- B:
0.45 x 10-8L-2mol2s-1
- C:
2.2 L mol-1s-1
- D:
0.45L-1mol s-1
The answer is a.
For the reaction,
kf = 2.2 x 104 L mol-1s-1 and Kc = 1.00 x 10-4 at 3000 K. Thus, kb is
2.2 x 108 L2mol-2s-1
0.45 x 10-8L-2mol2s-1
2.2 L mol-1s-1
0.45L-1mol s-1

|
Dewansh Tripathi answered |
Given;kf=2.2×10^4Lmol^-1s^-1;KC=1×10^-4at 3000k . we, know that,KC=kf/kb and put the value and solve.
In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (Aand B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as - a)Rate = k[A] [B]
- b)Rate = k[A]2[B]
- c)Rate = k[A][B]2
- d)Rate = k[A]2[B]2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (Aand B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as
a)
Rate = k[A] [B]
b)
Rate = k[A]2[B]
c)
Rate = k[A][B]2
d)
Rate = k[A]2[B]2

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
The correct answer is option B
When conc. of B is doubled, the rate is doubled.
So, Order w.r.t. [B] is 1.
The rate increases by a factor of 8 when conc. of [A] and [B] are doubled.
So, Order w.r.t. [A] is 2.
Overall Rate is
Rate=k[A]2[B]
When conc. of B is doubled, the rate is doubled.
So, Order w.r.t. [B] is 1.
The rate increases by a factor of 8 when conc. of [A] and [B] are doubled.
So, Order w.r.t. [A] is 2.
Overall Rate is
Rate=k[A]2[B]
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
- a)k[NO2]
- b)k[NO2]0
- c)k[NO2]3
- d)k[NO2]2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 14 and 15) This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
The decomposition of NO2 at 400 K proceeds at a of rate of 5.4 x 10 -5 mol L-1 s-1 when [NO2] = 0.01 mol-1
2 NO2(g) → 2NO(g ) + O2(g).
Q. What is the rate law when observed rate is 1.35 x 10-5 mol L-1 s-1 at [NO2] = 0.005 mol L-1?
a)
k[NO2]
b)
k[NO2]0
c)
k[NO2]3
d)
k[NO2]2
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Given unit of rate = mol L-1 s-1
General formula for unit of rate = mol n-1 Ln-1 s -1
On equating,
1-n = 1 ⇒ n = 0
n-1 = -1 ⇒ n = 0
General formula for unit of rate = mol n-1 Ln-1 s -1
On equating,
1-n = 1 ⇒ n = 0
n-1 = -1 ⇒ n = 0
Hence, it is a zero order reaction.
The term 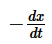 in the rate expression refers to the:
in the rate expression refers to the:- a)Increase in concentration of the reactants
- b)Average rate of the reaction
- c)Instantaneous rate of the reaction
- d)Concentration of the reactants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term 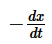 in the rate expression refers to the:
in the rate expression refers to the:
a)
Increase in concentration of the reactants
b)
Average rate of the reaction
c)
Instantaneous rate of the reaction
d)
Concentration of the reactants
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
The term —dx/dt in the rate expression refers to theinstantaneous rate of the reaction.
Which of the following represents the expression for the 3/4th life of a first order reaction?
- a)
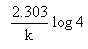
- b)
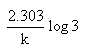
- c)
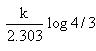
- d)
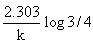
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the expression for the 3/4th life of a first order reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The correct answer is option A
As we know, for a first order reaction,

As we know, for a first order reaction,

If Ef and Eb are the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions and the reaction is known to be exothermic, then:- a)Ef = Eb
- b)Ef < EbData insufficient to predict
- c)f < EbData insufficient to predict
- d)Ef > Eb
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If Ef and Eb are the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions and the reaction is known to be exothermic, then:
a)
Ef = Eb
b)
Ef < EbData insufficient to predict
c)
f < EbData insufficient to predict
d)
Ef > Eb
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
For exothermic reaction, ΔH<0
Eb = Ef + ∣ΔH∣ or
Ef < Eb
Eb = Ef + ∣ΔH∣ or
Ef < Eb
The reactions with low activation energy are- a)Slow
- b)Non-spontaneous
- c)Fast
- d)Always spontaneous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reactions with low activation energy are
a)
Slow
b)
Non-spontaneous
c)
Fast
d)
Always spontaneous
|
|
Vivek Godara answered |
Low activation energy mean energy reguire for reaction to occur is low so product making is fast
The unit of rate constant for a first order reaction is- a)Mol/L
- b)Mol2 / L2 / S2
- c)S-1
- d)Mol/L/S
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The unit of rate constant for a first order reaction is
a)
Mol/L
b)
Mol2 / L2 / S2
c)
S-1
d)
Mol/L/S
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The correct answer is Option C.
Let R be the rate of reaction.
For first order reaction,
R=K[A]1
⇒K=R[A]-1
Whereas, K and [A] are rate constant and initial concentration of reactant respectively.
Therefore,
Unit of rate constant =(mol L-1)1-nsec-1
For first order reaction, n=1
Unit of rate constant = sec-1
Hence the unit of rate constant for first order reaction is sec-1.
For first order reaction,
R=K[A]1
⇒K=R[A]-1
Whereas, K and [A] are rate constant and initial concentration of reactant respectively.
Therefore,
Unit of rate constant =(mol L-1)1-nsec-1
For first order reaction, n=1
Unit of rate constant = sec-1
Hence the unit of rate constant for first order reaction is sec-1.
Study of rate of chemical reaction is known as- a)Chemical thermodynamics
- b)Chemical kinetics
- c)Chemical equilibrium
- d)Chemical change
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study of rate of chemical reaction is known as
a)
Chemical thermodynamics
b)
Chemical kinetics
c)
Chemical equilibrium
d)
Chemical change

|
Sarthak Khanna answered |
Chemical Kinetics deals with rate of a Chemical reactions.
A Certain Zeroth Order reaction has k = 0.025 Ms-1 for the disappearance of A. What will be the concentration of A after 15s, if the intial concentration is 0.50 M?- a)0.50 M
- b)0.375 M
- c)0.125 M
- d)0.060 M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A Certain Zeroth Order reaction has k = 0.025 Ms-1 for the disappearance of A. What will be the concentration of A after 15s, if the intial concentration is 0.50 M?
a)
0.50 M
b)
0.375 M
c)
0.125 M
d)
0.060 M

|
Sinjini Tiwari answered |
x (product) formed after 15 s = 0.025 Ms-1 x 15s= 0.375 M Then, reactant left = 0.500 - 0.375= 0.125 M
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O- a)O2
- b)NO
- c)H2O
- d)Equal
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
a)
O2
b)
NO
c)
H2O
d)
Equal
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
By stoichiometry of the reaction

similarly,
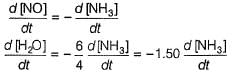
A foreign substance that increase the speed of a chemical reaction is called- a)promotor
- b)catalyst
- c)moderator
- d)inhibitor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A foreign substance that increase the speed of a chemical reaction is called
a)
promotor
b)
catalyst
c)
moderator
d)
inhibitor
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Catalyst: Substances which alter the rate of a chemical reaction and themselves remain chemically and quantitatively unchanged after the reaction are known as catalysts and the phenomenon is known as catalysis.
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of- a)Rate of reaction
- b)Mechanism of reaction
- c)Factors which affects the rate of reaction
- d)All of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of
a)
Rate of reaction
b)
Mechanism of reaction
c)
Factors which affects the rate of reaction
d)
All of the mentioned
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Reaction kinetics deals with the study of rate of reaction, their mechanism and the factors which affects the rate of reaction. It specifies all the general characteristics of a chemical reaction.
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given byrate = k[A]n [B]mIf concentration of A is doubled and that of 8 is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be - a)
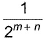
- b)(m + n)
- c)(n - m)
- d)2(n-m)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and 8 is given by
rate = k[A]n [B]m
If concentration of A is doubled and that of 8 is halved, the new rate as compared to the earlier rate would be
a)
b)
(m + n)
c)
(n - m)
d)
2(n-m)
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by- a)Arrhenius equation
- b)Kirchoff’s Equation
- c)Clauius Claperyron equation
- d)Gibb’s Helmholtz equation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by
a)
Arrhenius equation
b)
Kirchoff’s Equation
c)
Clauius Claperyron equation
d)
Gibb’s Helmholtz equation
|
|
T.ttttt answered |
Increasing the temperature increasesreaction rates because of the disproportionately large increase in the number of high energy collisions. It is only these collisions (possessing at least the activation energy for the reaction) which result in a reaction.
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by __________0C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.- a)2
- b)10
- c)100
- d)50
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by __________0C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.
a)
2
b)
10
c)
100
d)
50
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Explanation: Half-life period of a first order reaction is directly proportional to the rate constant. So, it increases with increase in temperature.
The rate is independent of the concentration of the reactants in- a)First order
- b)Second order
- c)Third order
- d)Zero order
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate is independent of the concentration of the reactants in
a)
First order
b)
Second order
c)
Third order
d)
Zero order
|
|
Naiham Difoesa answered |
Bcz rate is proportional to the zeroth power of the concentration of reactant.
The rate of a chemical reaction doubles for every 10°C rise of temperature. If the temperature is raised by 50°C, the rate of the reaction increases by about [AIEEE 2011]a)64 timesb)32 timesc)24 timesd)10 timesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Rate at 50 degree C/(Rate at T1 degree C)
= (2)^(ΔT/T1)
= (2)^(50/10)
= 2^5
= 32
Hence, the rate of the reaction increases by 32 times.
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants. Thus, rate law is equal to
Thus, rate law is equal to- a)k[A][B]
- b)k[A][B]2
- c) k[A]
- d) k[B]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The initial rates of reaction for the equation, 2A + B → Products.
Products were determined under various initial concentrations of reactants.
Thus, rate law is equal to
a)
k[A][B]
b)
k[A][B]2
c)
k[A]
d)
k[B]
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Let order w.r.t. A = a, order w.r.t. B = b
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correctQ. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O- a)O2
- b)NO
- c)H2O
- d)Equal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-13) This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
Q. In the following reaction, which has maximum rate w.r.t. rate of disappearance of NH3?
4NH3 + 502 → 4NO + 6H2O
a)
O2
b)
NO
c)
H2O
d)
Equal
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
By stoichiometry of the reaction
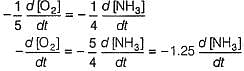
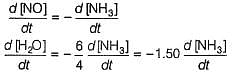
Inversion of sucrose (C12H22O11) is a first order reaction and is studied by measuring angle of rotation at different interval of time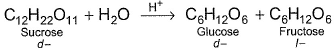 r0 = angle of rotation at the start, rt = angle of rotation at time t
r0 = angle of rotation at the start, rt = angle of rotation at time t
r∞ = angle of rotation at the complete reactionThere is 50% inversion, when- a)r0 = 2rt - r∞
- b)r0 = rt - r∞
- c)r0 = rt - 2r∞
- d)r0 = rt + r∞
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Inversion of sucrose (C12H22O11) is a first order reaction and is studied by measuring angle of rotation at different interval of time
r0 = angle of rotation at the start, rt = angle of rotation at time t
r∞ = angle of rotation at the complete reaction
r∞ = angle of rotation at the complete reaction
There is 50% inversion, when
a)
r0 = 2rt - r∞
b)
r0 = rt - r∞
c)
r0 = rt - 2r∞
d)
r0 = rt + r∞

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
r0 = rotation at the start, rt = rotation at time t
r∞ = rotation at the end then (r∞ - r0) = a and (r∞ - rt) = (a - x)
r∞ = rotation at the end then (r∞ - r0) = a and (r∞ - rt) = (a - x)
When 50% inversion has taken place
∴ 2 (a - x) = a
2(r∞ - rt) = r∞ - r0
2r∞ - 2rt = r∞ - r0
∴ r0 = (2rt - r∞)
For the first order reaction,A → ProductQ. The concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in 40 min. The rate of the reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M is[AIEEE 2012]- a)1.73 x 10-6 Mmin-1
- b)3.47 x 10-4 M min-1
- c)3.47 x 10-5 M min-1
- d)1.73 x 10-6 M min-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the first order reaction,
A → Product
Q. The concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in 40 min. The rate of the reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M is
[AIEEE 2012]
a)
1.73 x 10-6 Mmin-1
b)
3.47 x 10-4 M min-1
c)
3.47 x 10-5 M min-1
d)
1.73 x 10-6 M min-1

|
Sanjana Bajaj answered |
A first-order reaction is a type of chemical reaction where the rate of reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant. The rate equation for a first-order reaction can be written as follows:
rate = k[A]
Where:
- rate is the rate of reaction
- k is the rate constant
- [A] is the concentration of reactant A
This means that as the concentration of reactant A decreases, the rate of reaction also decreases. The half-life of a first-order reaction is constant, meaning that it takes the same amount of time for the concentration of reactant A to decrease by half, regardless of the initial concentration.
rate = k[A]
Where:
- rate is the rate of reaction
- k is the rate constant
- [A] is the concentration of reactant A
This means that as the concentration of reactant A decreases, the rate of reaction also decreases. The half-life of a first-order reaction is constant, meaning that it takes the same amount of time for the concentration of reactant A to decrease by half, regardless of the initial concentration.
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by- a)Gibb’s Helmholtz equation
- b)Clausius Claperon equation
- c)Arrhenius equation
- d)Kirchoff’s equation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by
a)
Gibb’s Helmholtz equation
b)
Clausius Claperon equation
c)
Arrhenius equation
d)
Kirchoff’s equation
|
|
Manoj Chauhan answered |
Arrhenius equation describes the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a chemical reaction. It is given by:
k = Ae^(-Ea/RT)
where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Explanation:
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance. When the temperature is increased, the molecules move faster and collide more frequently. This increases the chance of successful collisions between reactant molecules, leading to an increase in the reaction rate.
Arrhenius equation explains this relationship between temperature and reaction rate by stating that the rate constant (k) of a reaction increases exponentially with increasing temperature. The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur, and it determines the rate at which the reaction proceeds.
The pre-exponential factor (A) takes into account the frequency of collisions between reactant molecules. It is a constant that depends on the nature of the reaction and the reactants involved.
The Arrhenius equation is widely used to describe the temperature dependence of chemical reactions in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Conclusion:
In summary, the Arrhenius equation is used to describe the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a chemical reaction. It explains that the rate constant increases exponentially with increasing temperature, due to an increase in the frequency and energy of collisions between reactant molecules.
k = Ae^(-Ea/RT)
where k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Explanation:
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance. When the temperature is increased, the molecules move faster and collide more frequently. This increases the chance of successful collisions between reactant molecules, leading to an increase in the reaction rate.
Arrhenius equation explains this relationship between temperature and reaction rate by stating that the rate constant (k) of a reaction increases exponentially with increasing temperature. The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy required for a reaction to occur, and it determines the rate at which the reaction proceeds.
The pre-exponential factor (A) takes into account the frequency of collisions between reactant molecules. It is a constant that depends on the nature of the reaction and the reactants involved.
The Arrhenius equation is widely used to describe the temperature dependence of chemical reactions in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Conclusion:
In summary, the Arrhenius equation is used to describe the effect of temperature on the rate constant of a chemical reaction. It explains that the rate constant increases exponentially with increasing temperature, due to an increase in the frequency and energy of collisions between reactant molecules.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)In the following reaction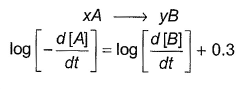 Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?- a)2
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16-18) This section contains 3 questions. When worked out will result in one integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
In the following reaction
Q. Where negative sign indicates rate of disappearance of the reactant. What is the value of x/y ?
a)
2
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6
|
|
Praveen Reddy answered |
The minimum amount of energy required by the reacting molecules at the time of collisions in order to produce effective collisions is called- a)Threshold energy
- b)Potential energy
- c)Internal energy
- d)Activation energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum amount of energy required by the reacting molecules at the time of collisions in order to produce effective collisions is called
a)
Threshold energy
b)
Potential energy
c)
Internal energy
d)
Activation energy

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
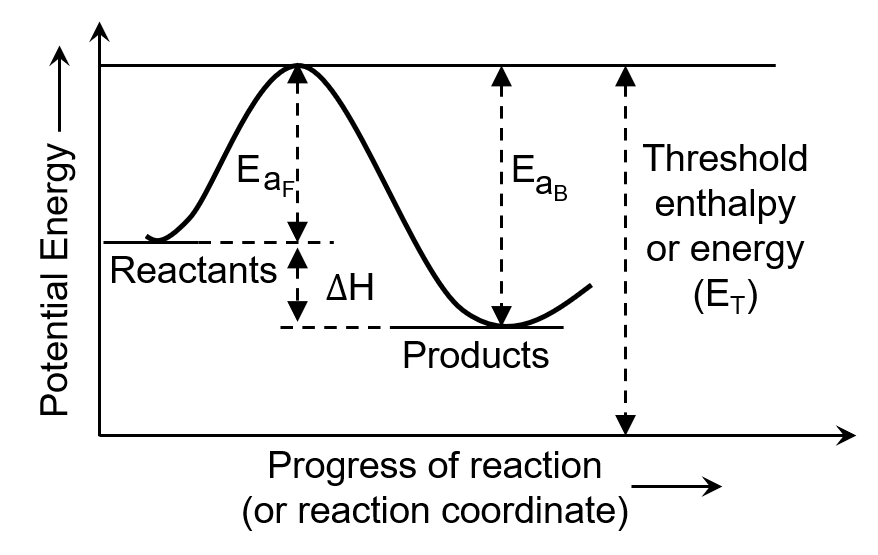
The minimum energy that the colliding molecules must possess for the chemical reaction to occur is known as threshold energy.
The extra energy required by a reactant to participate in a reaction is called activation energy.
Which among the following is an example of photochemistry used in our daily life?- a)In inversion of cane sugar
- b)In photography
- c)In decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is an example of photochemistry used in our daily life?
a)
In inversion of cane sugar
b)
In photography
c)
In decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
d)
All of these

|
Nilesh Goyal answered |
Photography is an example of photochemistry used in our daily life.
The activation energies of two reactions are given as Ea1= 40 J and Ea2= 80 J, then the relation between their rate constants can be written as:- a)k1 > k2
- b)k1 < k2
- c)k1 = k2
- d)k1 + k2 = 0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The activation energies of two reactions are given as Ea1= 40 J and Ea2= 80 J, then the relation between their rate constants can be written as:
a)
k1 > k2
b)
k1 < k2
c)
k1 = k2
d)
k1 + k2 = 0
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
As the value of activation energy, Ea increases, the value of rate constant, k decreases.
So, k1 > k2 since E1 < E2
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?- a)1.26 × 1015 s
- b)2.52 × 1014 s
- c)2.52 × 1028 s
- d) infinite
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?
a)
1.26 × 1015 s
b)
2.52 × 1014 s
c)
2.52 × 1028 s
d)
infinite
|
|
Neha Chauhan answered |
The time taken for half the reaction to complete, i.e., the time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to half of its original value is called half-life period of the reaction. But it is impossible to perform 100% of the reaction. Whole of the substance never reacts because in every half-life, 50% of the substance reacts. Hence, time taken for 100% completion of a reaction is infinite.
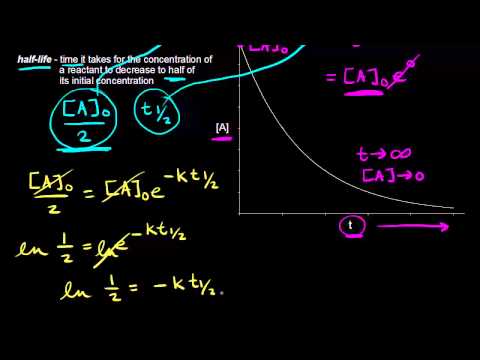
The half life period of first order reaction is 15 min. Its rate constant will be equal to- a)0.0462 min-1
- b)0.462 min-1
- c)0.00462 min-1
- d)0.562 min-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The half life period of first order reaction is 15 min. Its rate constant will be equal to
a)
0.0462 min-1
b)
0.462 min-1
c)
0.00462 min-1
d)
0.562 min-1
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The half life of a reaction is 15 min
So,
Here we go..
Formula to be used :
K =0.693/t = 0.693/15
__= 0.462/10 = 0.0462 min^-1
So,
Here we go..
Formula to be used :
K =0.693/t = 0.693/15
__= 0.462/10 = 0.0462 min^-1
Rate of ionic reactions are generally- a)Very slow
- b)Very fast
- c)Slow
- d)Moderate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of ionic reactions are generally
a)
Very slow
b)
Very fast
c)
Slow
d)
Moderate

|
Siya Arora answered |
Ionic compounds in solution react faster than molecular compounds. This is because ionic compounds break apart to form free ions. Therefore, there are no bonds to break so the reaction is fast.
If a reaction proceeds with a uniform rate throughout, the reaction is- a)Third order
- b)Second order
- c)First order
- d)Zero order
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a reaction proceeds with a uniform rate throughout, the reaction is
a)
Third order
b)
Second order
c)
First order
d)
Zero order
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
A reaction with uniform rate means dC/dt is a constant, where C is the concentration of the reactant being consumed.
For an n-th order reaction,
dC/dt = kC^n
As dC/dt is independent of C
dC/dt = k C^0
Thus, n = 0, and the reaction is a zero order reaction.
Chapter doubts & questions for Kinetics - Science for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Kinetics - Science for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Science for ACT
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev