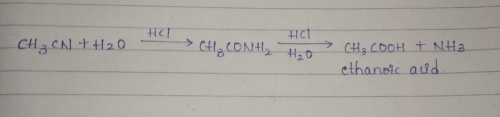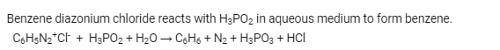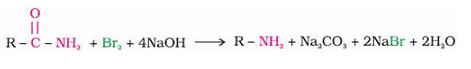All Exams >
ACT >
Chemistry for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Amines for ACT Exam
Which of the following has highest boiling point?- a)(C2H5)2NH
- b)C2H5N(CH3)2
- c)C2H5NH(CH3)2
- d)n-C4H9NH2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has highest boiling point?
a)
(C2H5)2NH
b)
C2H5N(CH3)2
c)
C2H5NH(CH3)2
d)
n-C4H9NH2
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Because C4H9NH2 is primary amine and can form hydrogen bonding more than secondary amine (C2H5)2NH and tertiary amine C2H5N(CH3)2 . More hydrogen bonding leads to strong bonding between the molecules, hence increases the boiling point.
Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation reaction is shown by __________.- a) ArNH2
- b)ArCONH2
- c)ArNO2
- d)ArCH2NH2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation reaction is shown by __________.
a)
ArNH2
b)
ArCONH2
c)
ArNO2
d)
ArCH2NH2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The Correct answer is option B
Hoffman bromamide degradation reaction is shown by ArCONH2.
Where the aryl amide is converted to aryl amine in the presence of Br2 and NaOH
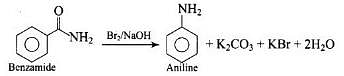
Hoffman bromamide degradation reaction is shown by ArCONH2.
Where the aryl amide is converted to aryl amine in the presence of Br2 and NaOH

Nitro compounds are reduced to amines. The catalyst that is preferred is:- a)Sn + HCl
- b)Fe + HCl
- c)Ethanol
- d)Mg + HCl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitro compounds are reduced to amines. The catalyst that is preferred is:
a)
Sn + HCl
b)
Fe + HCl
c)
Ethanol
d)
Mg + HCl
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Fe + HCl is preferred due to the following reasons:
- Scrap iron i.e Fe is cheap and commercially easily available
- FeCl2 formed will get hydrolysed and release HCl, so, HCl which is required in the reaction will be produced by itself
- Hence only small amount of HCl is required to initiate the reaction.
- Scrap iron i.e Fe is cheap and commercially easily available
- FeCl2 formed will get hydrolysed and release HCl, so, HCl which is required in the reaction will be produced by itself
- Hence only small amount of HCl is required to initiate the reaction.
Which of the following amine liberates nitrogen gas on reaction with HNO2 ?- a)(CH3)2NH
- b)(CH3)3 N
- c)C6H5 NH2
- d)CH3NH2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amine liberates nitrogen gas on reaction with HNO2 ?
a)
(CH3)2NH
b)
(CH3)3 N
c)
C6H5 NH2
d)
CH3NH2
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Only primary amines liberate nitrogen gas on reaction with HNO2.
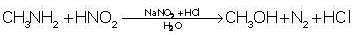
Only primary amines liberate nitrogen gas on reaction with HNO2.
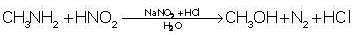
In amines ,the hybridisation state of N is:- a)sp
- b)sp2d
- c)sp2
- d)sp3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In amines ,the hybridisation state of N is:
a)
sp
b)
sp2d
c)
sp2
d)
sp3
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Hybridisation of N in amine is sp3 with nitrogen having a one pair and 3 bond pair. Remember that amine is RR’R”N where R, R’ and R” may be alkyl or hydrogen.
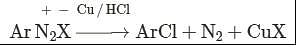
- a)Sandmeyers reaction
- b)Gattermanns reaction
- c)Dehydrogenation reaction
- d)Esterification reaction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
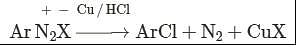
a)
Sandmeyers reaction
b)
Gattermanns reaction
c)
Dehydrogenation reaction
d)
Esterification reaction
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
 This reaction is called Gattermann reaction. In this reaction, Cl, Br and CN can be introduced into the benzene ring by simply treating diazonium salts with HCl, HBr, KCN. Respectively in presnce of copper powder instead of using Cu(I) salts.
This reaction is called Gattermann reaction. In this reaction, Cl, Br and CN can be introduced into the benzene ring by simply treating diazonium salts with HCl, HBr, KCN. Respectively in presnce of copper powder instead of using Cu(I) salts.Which reaction can be used for the direct conversion of amides into 10 amine ?- a)Reduction with LiAlH4
- b)Perkin’s reaction
- c)Claissen reaction
- d)Hoffmann ammonolysis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which reaction can be used for the direct conversion of amides into 10 amine ?
a)
Reduction with LiAlH4
b)
Perkin’s reaction
c)
Claissen reaction
d)
Hoffmann ammonolysis
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The correct answer is option A
Reduction with LiAlH4

Reduction with LiAlH4

Reduction of alkanenitriles with sodium and alcohol or LiAlH4 is called:- a)Wolf-Kishner reduction
- b)Rosenmund reduction
- c)Mendius reaction
- d)Catalytic reduction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Reduction of alkanenitriles with sodium and alcohol or LiAlH4 is called:
a)
Wolf-Kishner reduction
b)
Rosenmund reduction
c)
Mendius reaction
d)
Catalytic reduction
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The reaction is a Mendius reaction as because in this reaction the organic nitrile is reduced by nascent hydrogen(from sodium in ethanol) to a primary amine. (RCN+2H2=RCH2NH2).
where as LiAlH4 is a strong reducing agent and can be used as an abstract source of H neucophile.
where as LiAlH4 is a strong reducing agent and can be used as an abstract source of H neucophile.
Pyridine is less basic than triethylamine because:- a)Pyridine has aromatic character
- b)Nitrogen in pyridine is sp2 hybridized.
- c)Pyridine has a cyclic system.
- d)Lone pair of nitrogen in pyridine is delocalized.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyridine is less basic than triethylamine because:
a)
Pyridine has aromatic character
b)
Nitrogen in pyridine is sp2 hybridized.
c)
Pyridine has a cyclic system.
d)
Lone pair of nitrogen in pyridine is delocalized.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Basicity of amines is due to availability of an unshared pair (lone pair) of electrons on nitrogen. This lone pair of electrons is available for the formation of a new bond with a proton or Lewis acid. Pyridine is less basic than triethylamine because lone pair of nitrogen in pyridine is delocalised.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.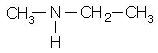
- a)N-Methylethanamine
- b)Methylethanamine
- c)Ethylmethanamine
- d)N-Ethylmethanamine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.
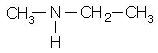
a)
N-Methylethanamine
b)
Methylethanamine
c)
Ethylmethanamine
d)
N-Ethylmethanamine
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option A
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
N-Methylethanamine
N-Methylethanamine
When Primary amide is treated with an aqueous solution of KOH and bromine, it gives a primary amine. The name of the reaction is:- a)Gabriel-phthalamine reaction
- b)Reimer-Tiemann reaction
- c)Ammonolysis
- d)Hoffmann Bromamide reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When Primary amide is treated with an aqueous solution of KOH and bromine, it gives a primary amine. The name of the reaction is:
a)
Gabriel-phthalamine reaction
b)
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
c)
Ammonolysis
d)
Hoffmann Bromamide reaction
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
Hoffmann Bromamide reaction is Treatment of alkylamide with KOH and Bromine gas which converts it into alkylamine with one less carbon atom, this reaction is generally helpful in converting Carboxylic acids to amines with one less carbon atom . For reaction you may refer to internet but i can give you a hint .
Acetamide + KOH + Bromine gas —-> Alkylamine+ KBr + K2CO3 + H20 ( not sure about the products)
When hypophosphorous acid is treated with diazonium salts, it is reduced to:- a)Arenes
- b)Methane
- c)Ethyl alcohol
- d)Amines
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When hypophosphorous acid is treated with diazonium salts, it is reduced to:
a)
Arenes
b)
Methane
c)
Ethyl alcohol
d)
Amines
|
|
Lavisha Yadav answered |
Answer is arenes because they are more stable product than the other products obtained.
The following reaction takes place in the presence of 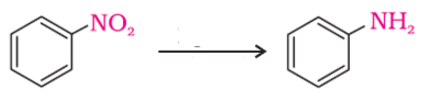
- a)NaOH/Pd
- b)H2/Pd
- c)HCl/Pd
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following reaction takes place in the presence of
a)
NaOH/Pd
b)
H2/Pd
c)
HCl/Pd
d)
None of these
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
−NO2 group is reduced to –NH2 using H2/Pd.
Which of the following amine will form stable diazonium salt at 273-283 K ?- a)C6H5NH2
- b)C6H5N(CH3)2
- c)C2H5NH2
- d)C6H5CH2NH2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amine will form stable diazonium salt at 273-283 K ?
a)
C6H5NH2
b)
C6H5N(CH3)2
c)
C2H5NH2
d)
C6H5CH2NH2
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Aromatic Primary amine will form the most stable diazonium salt because it releases water when it reacts with nitronium ions. If aliphatic primary amine reacts with nitrosonium ion it Also releases water but in this case water reacts with alkyl diazonium salt and it forms alcohol while benzene diazonium salt does not react with water at this temperature.
Aromatic Primary amine will form the most stable diazonium salt because it releases water when it reacts with nitronium ions. If aliphatic primary amine reacts with nitrosonium ion it Also releases water but in this case water reacts with alkyl diazonium salt and it forms alcohol while benzene diazonium salt does not react with water at this temperature.
The stability of benzene diazonium salts is because of- a)Inductive effect
- b)Mesomeric effect
- c)Hyperconjugation
- d)Resonance
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The stability of benzene diazonium salts is because of
a)
Inductive effect
b)
Mesomeric effect
c)
Hyperconjugation
d)
Resonance
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
None of the errors that are pointed are correct.
Their stability is because of resonance. D is the correct answer.
Replacement of diazo group by other groups is helpful in preparing those substituted aromatic compounds which cannot be prepared by
- a)Direct elimination
- b)Addition reaction
- c)Direct substitution
- d)Replacement reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Replacement of diazo group by other groups is helpful in preparing those substituted aromatic compounds which cannot be prepared by
a)
Direct elimination
b)
Addition reaction
c)
Direct substitution
d)
Replacement reaction
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
Replacement of diazo group by other groups is helpful in preparing those substituted aromatic compounds which cannot be prepared by direct substitution. ... The cyano group usually cannot be introduced by nucleophilic substitution of haloarenes, but such compounds can be easily prepared from diazonium salts.
Benzene diazonium chloride on reaction with phenol in weakly basic medium gives:- a)p-Hydroxyazobenzene
- b)Benzene
- c)Diphenyl ether
- d)Chlorobenzene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Benzene diazonium chloride on reaction with phenol in weakly basic medium gives:
a)
p-Hydroxyazobenzene
b)
Benzene
c)
Diphenyl ether
d)
Chlorobenzene
|
|
Arka Das answered |
**Benzene diazonium chloride**
Benzene diazonium chloride (C6H5N2Cl) is an organic compound that is commonly used in diazotization reactions. It is formed by the reaction of aniline (C6H5NH2) with nitrous acid (HNO2) in the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl).
**Reaction with Phenol**
When benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol (C6H5OH) in a weakly basic medium, it undergoes a substitution reaction known as the Sandmeyer reaction. This reaction involves the replacement of the diazonium group (-N2Cl) with the phenolic group (-OH) to form a new compound.
**Formation of p-Hydroxyazobenzene**
The reaction between benzene diazonium chloride and phenol results in the formation of p-hydroxyazobenzene (C12H10N2O), which is the correct answer (option A).
The reaction proceeds as follows:
1. The weakly basic medium provides the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur. It helps in the deprotonation of phenol to form the phenoxide ion (C6H5O-).
2. The diazonium group of benzene diazonium chloride is highly reactive and undergoes nucleophilic substitution. The nitrogen atom of the diazonium group attacks the phenoxide ion, leading to the formation of a new carbon-nitrogen bond.
3. The chlorine atom attached to the nitrogen atom is replaced by the phenoxide group, resulting in the formation of p-hydroxyazobenzene.
The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
C6H5N2Cl + C6H5O- → C12H10N2O + Cl-
**Explanation of Other Options**
Option B: Benzenedoes not participate in the reaction. It remains unchanged.
Option C: Diphenyl ether is not formed in this reaction. It involves the formation of a carbon-oxygen bond between two phenyl groups, which is not observed in the given reaction.
Option D: Chlorobenzene is not formed in this reaction. The chlorine atom from the diazonium chloride is replaced by the phenoxide group, not by another chlorine atom.
Thus, the correct answer is option A: p-Hydroxyazobenzene.
Benzene diazonium chloride (C6H5N2Cl) is an organic compound that is commonly used in diazotization reactions. It is formed by the reaction of aniline (C6H5NH2) with nitrous acid (HNO2) in the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl).
**Reaction with Phenol**
When benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol (C6H5OH) in a weakly basic medium, it undergoes a substitution reaction known as the Sandmeyer reaction. This reaction involves the replacement of the diazonium group (-N2Cl) with the phenolic group (-OH) to form a new compound.
**Formation of p-Hydroxyazobenzene**
The reaction between benzene diazonium chloride and phenol results in the formation of p-hydroxyazobenzene (C12H10N2O), which is the correct answer (option A).
The reaction proceeds as follows:
1. The weakly basic medium provides the necessary conditions for the reaction to occur. It helps in the deprotonation of phenol to form the phenoxide ion (C6H5O-).
2. The diazonium group of benzene diazonium chloride is highly reactive and undergoes nucleophilic substitution. The nitrogen atom of the diazonium group attacks the phenoxide ion, leading to the formation of a new carbon-nitrogen bond.
3. The chlorine atom attached to the nitrogen atom is replaced by the phenoxide group, resulting in the formation of p-hydroxyazobenzene.
The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
C6H5N2Cl + C6H5O- → C12H10N2O + Cl-
**Explanation of Other Options**
Option B: Benzenedoes not participate in the reaction. It remains unchanged.
Option C: Diphenyl ether is not formed in this reaction. It involves the formation of a carbon-oxygen bond between two phenyl groups, which is not observed in the given reaction.
Option D: Chlorobenzene is not formed in this reaction. The chlorine atom from the diazonium chloride is replaced by the phenoxide group, not by another chlorine atom.
Thus, the correct answer is option A: p-Hydroxyazobenzene.
The main product formed by treating an alkyl or benzyl halide with excess ammonia- a)Mixed
- b)Tertiary
- c)Secondary
- d)Primary
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main product formed by treating an alkyl or benzyl halide with excess ammonia
a)
Mixed
b)
Tertiary
c)
Secondary
d)
Primary
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The N in ammonia functions as the nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic C of the alkyl halide displacing the bromide and creating the new C-N bond.
Step 2: An acid/base reaction. The base (excess ammonia) deprotonates the positive N (ammonium) center creating the alkylation product, the primary amine.
. IUPAC name of NH2CH2CH2CH2COOH is :- a)1-Aminobutanoic acid
- b)4-Aminobutanoic acid
- c)4-Nitrobutanoic acid
- d)4-Aminopropanoic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
. IUPAC name of NH2CH2CH2CH2COOH is :
a)
1-Aminobutanoic acid
b)
4-Aminobutanoic acid
c)
4-Nitrobutanoic acid
d)
4-Aminopropanoic acid
|
|
Vikas Choudhury answered |
4 3 2 1
NH2CH2CH2 CH2 COOH is 4-Aminobutanoic acid , here carboxy group gets preferred over amino group as a main chain.
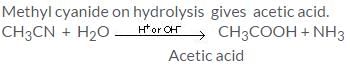
To convert methyl cyanide to ethylamine we use:- a)Br2
- b)HNO3
- c)KOH
- d)LiAlH4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To convert methyl cyanide to ethylamine we use:
a)
Br2
b)
HNO3
c)
KOH
d)
LiAlH4
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
LiAlH4 reduces all oxiginated functional groups to alcohol and all nitrogenated functional groups to amine thus cyanide is a nitrogenated functional group and to convert cyanide to amine LiAlH4 can be used.
. Identify the most basic compound from the following.- a)C6H5NH2
- b)(C6H5)2NH
- c)CH3NH2
- d)(CH3)2NH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
. Identify the most basic compound from the following.
a)
C6H5NH2
b)
(C6H5)2NH
c)
CH3NH2
d)
(CH3)2NH
|
|
Jyoti Aiims Aspirant answered |
In a and b lone pair are in resonance
+I group of d is more than c which increase electron density on nitrogen
+I group of d is more than c which increase electron density on nitrogen
The molecular formula of ethyl acetate is- a)C4H8O
- b)C4H8O2
- c)C5H10O2
- d)C5H8O2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecular formula of ethyl acetate is
a)
C4H8O
b)
C4H8O2
c)
C5H10O2
d)
C5H8O2

|
Tejas Singh answered |
Its molecular formula is C4H8O2
When ethanol is treated with benzene diazoniumchloride it forms:- a)Arenes
- b)Ethyl alcohol
- c)Amines
- d)Methane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When ethanol is treated with benzene diazoniumchloride it forms:
a)
Arenes
b)
Ethyl alcohol
c)
Amines
d)
Methane
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option A
When C2H5OH (ethanol) is treated with C6H5N2Cl it forms benzene.
Some mild reducing agents like C2H5OH themselves get oxidized to ethanol after reducing C6H5N2Cl to benzene.
When C2H5OH (ethanol) is treated with C6H5N2Cl it forms benzene.
Some mild reducing agents like C2H5OH themselves get oxidized to ethanol after reducing C6H5N2Cl to benzene.
. Acrylonitrile is the common name of:- a)CH3CH2CH2CN
- b)CH3CH2CN
- c)CH2=CHCN
- d)CH3CN
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
. Acrylonitrile is the common name of:
a)
CH3CH2CH2CN
b)
CH3CH2CN
c)
CH2=CHCN
d)
CH3CN
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHCN. It is a colorless volatile liquid, although commercial samples can be yellow due to impurities. In terms of its molecular structure, it consists of a vinyl group linked to a nitrile. It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics such as polyacrylonitrile. It is reactive and toxic at low doses. Acrylonitrile was first synthesized by the French chemist Charles Moureu (1863–1929) in 1893.
We can obtain ethylamine by Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide used in this reaction is:- a)Methanamide
- b)Acetamide
- c)Propanamide
- d)Butanamide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
We can obtain ethylamine by Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide used in this reaction is:
a)
Methanamide
b)
Acetamide
c)
Propanamide
d)
Butanamide

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
The correct answer is option C
CH3CH2CONH2 (A)⟶ CH3 − CH2 − NH2 (B)⟶ CH3 − CH2 − OH
In the above sequence A & B respectively are Br2/KOH and HNO2
The first step is Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction in which an amide (propanamide) is converted to an amine (ethylamine) containing one carbon atom less. The reagent A is bromine in presence of KOH. In the second step, aliphatic primary amine (ethyl amine) reacts with nitrous acid (reagent B) to form aliphatic primary alcohol (ethyl alcohol).
CH3CH2CONH2 (A)⟶ CH3 − CH2 − NH2 (B)⟶ CH3 − CH2 − OH
In the above sequence A & B respectively are Br2/KOH and HNO2
The first step is Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction in which an amide (propanamide) is converted to an amine (ethylamine) containing one carbon atom less. The reagent A is bromine in presence of KOH. In the second step, aliphatic primary amine (ethyl amine) reacts with nitrous acid (reagent B) to form aliphatic primary alcohol (ethyl alcohol).
Ambident group among the following are:- a)Cyanides and Isocyanides
- b)Acetone and aldehydes
- c)Ethers and esters
- d)Acetal and ketal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ambident group among the following are:
a)
Cyanides and Isocyanides
b)
Acetone and aldehydes
c)
Ethers and esters
d)
Acetal and ketal
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Ambident groups are those which can attack from both sides. So option a is correct because cyanides is C-N and carbon forms bonds here. Isocyanides are N-C in which nitrogen contains lone pairs which initiates reaction and attaches from nitrogen side.
C6H5-NH-C6H5 is :- a)Dibenzenamine
- b)Diphenyl amine
- c)1,2 Diphenyl amine
- d)Toluidine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
C6H5-NH-C6H5 is :
a)
Dibenzenamine
b)
Diphenyl amine
c)
1,2 Diphenyl amine
d)
Toluidine
|
|
Vikas Choudhury answered |
In the structure two phenyl groups are attached to the amino group, hence the name Diphenyl amine.
When diazonium salt solution is treated with water at a temperature of 283 K it forms?- a)Ester
- b)Phenol
- c)Amines
- d)Alcohol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When diazonium salt solution is treated with water at a temperature of 283 K it forms?
a)
Ester
b)
Phenol
c)
Amines
d)
Alcohol

|
Vatturi Anjani answered |
Yes as when the temperature of the diazonium salt is allowed to rise upto 283K then the salt is reduced to phenol releasing N2 and hydrochloric acid as the by-products.
. When diazonium salt solution is treated with KI, it forms:- a)Bromobenzene
- b)Iodobenzene
- c)Phenol
- d)Acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
. When diazonium salt solution is treated with KI, it forms:
a)
Bromobenzene
b)
Iodobenzene
c)
Phenol
d)
Acid

|
Kshitij Pandey answered |
This reaction is unique this is only reaction in which idobenzene formed by diaazonium salt , to make idobenzene first we make diaazonium salt by aniline then we treated diaazonium salt with ki
C6H5N2Cl(diaazonium salt)+KI=C6H5I
C6H5N2Cl(diaazonium salt)+KI=C6H5I
Which of the following amine gives diazonium salt on reaction with HNO2?- a)(CH3)2NH
- b)CH3NH2
- c)C6H5NH2
- d)(CH3)3N
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following amine gives diazonium salt on reaction with HNO2?
a)
(CH3)2NH
b)
CH3NH2
c)
C6H5NH2
d)
(CH3)3N
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
C6H5NH2 reacts with HNO2 to forms diazonium salts, the reaction are as follows,
C6H5NH2 + HNO2 ------> C6H5OH + H2O + N2
C6H5NH2 + HNO2 ------> C6H5OH + H2O + N2
Which one of the following is a tertiary amine?- a)Ethylamine
- b)Triethylamine
- c)Aniline
- d)Diethylamine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a tertiary amine?
a)
Ethylamine
b)
Triethylamine
c)
Aniline
d)
Diethylamine
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.

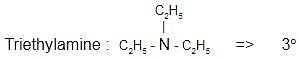
Aniline :


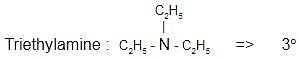
Aniline :

Benzonitrile is the IUPAC name of the compound:- a)C6H5NH2
- b)C6H5-CH2NH2
- c)C6H5CN
- d)C6H5-CH2CN
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Benzonitrile is the IUPAC name of the compound:
a)
C6H5NH2
b)
C6H5-CH2NH2
c)
C6H5CN
d)
C6H5-CH2CN

|
Aayush Agarwal answered |
The correct answer is C you can refer ncert of class 11 part 2
Alkyl cyanides are isomeric with:- a)Diazonium salts
- b)Nitroalkanes
- c)Ethers
- d)Isocyanides
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Alkyl cyanides are isomeric with:
a)
Diazonium salts
b)
Nitroalkanes
c)
Ethers
d)
Isocyanides
|
|
Vikas Choudhury answered |
Cyanides and isocyanides are isomeric compounds.
p-amino azo benzene is obtained by treating diazoniumchloride with:- a)Phenol
- b)Aniline
- c)Alcohol
- d)Benzoic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
p-amino azo benzene is obtained by treating diazoniumchloride with:
a)
Phenol
b)
Aniline
c)
Alcohol
d)
Benzoic acid
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
p-amino azo benzene is obtained by treating diazonium chloride with aniline. The reactions are specifically acid catalyzed and involve pre‐equilibrium formation of amine and diazonium salt followed by rate‐limiting attack of the diazonium ion at a C‐atom (C‐coupling) to give the corresponding amino azo compounds.
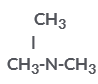 is a tertiary amine with IUPAC name:
is a tertiary amine with IUPAC name:- a)N,N-Dimethyl-methanamine
- b)N-methyl-ethanamine
- c)N-Phenyl-methanamine
- d)N-Methylmethanamine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
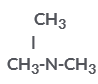 is a tertiary amine with IUPAC name:
is a tertiary amine with IUPAC name:a)
N,N-Dimethyl-methanamine
b)
N-methyl-ethanamine
c)
N-Phenyl-methanamine
d)
N-Methylmethanamine
|
|
Varsha Mangla answered |
C'oz 2 methyl group (CH3) are attached to the N group and as per the rule for the amine, the naming can only be done as N,N-Dimethyl methanamine.
Which one of the following is used to increase blood pressure- a)Ephedrine
- b)Novocain
- c)Benadryl
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is used to increase blood pressure
a)
Ephedrine
b)
Novocain
c)
Benadryl
d)
None of these
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Correct answer is d) none of these:
1. Fludrocortisone is a medication that seems to help most types of low blood pressure. It works by promoting sodium retention by the kidney, thereby causing fluid retention and some swelling, which is necessary to improve blood pressure.
2. Midodrine activates receptors on the smallest arteries and veins to produce an increase in blood pressure. It is used to help increase standing blood pressure in people with postural hypotension related to nervous system dysfunction.
By treating diazonium salts with cuprous cyanide or KCN and copper powder it forms:- a)Citric acid
- b)Benzoic acid
- c)Aryl nitrile
- d)Oxalic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
By treating diazonium salts with cuprous cyanide or KCN and copper powder it forms:
a)
Citric acid
b)
Benzoic acid
c)
Aryl nitrile
d)
Oxalic acid
|
|
Rishika Patel answered |
Formation of Aryl Nitrile from Diazonium Salts
Diazonium salts are compounds containing a positively charged nitrogen atom that is linked to an aromatic ring. These salts are often used in organic synthesis as a source of the aryl group. When treated with cuprous cyanide or KCN and copper powder, diazonium salts undergo a reaction known as Sandmeyer reaction, which forms aryl nitriles.
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism involves several steps:
1. Formation of Copper(I) Salt
First, cuprous cyanide or KCN is added to the diazonium salt solution to form a copper(I) salt. The copper(I) salt plays a crucial role in the reaction by catalyzing the formation of the aryl nitrile.
2. Formation of Aryl Copper(I) Intermediate
Next, copper powder is added to the reaction mixture, which reduces the copper(I) salt to copper metal. The copper metal then reacts with the diazonium salt to form an aryl copper(I) intermediate.
3. Formation of Aryl Cyanide
The aryl copper(I) intermediate then reacts with the cyanide ion from the cuprous cyanide or KCN to form the aryl cyanide. The reaction releases copper metal, which can then react with more diazonium salt to form more aryl copper(I) intermediate.
Overall Reaction
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
ArN2+X- + CuCN/KCN → [CuX] + N2 + ArCu + HX
ArCu + CN- → ArCN + Cu
Where Ar represents the aryl group, X represents the anion of the diazonium salt, and HX represents the acid formed in the reaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treatment of diazonium salts with cuprous cyanide or KCN and copper powder forms aryl nitriles through the Sandmeyer reaction. This reaction is an important method for the synthesis of aryl nitriles, which have a variety of applications in organic synthesis and industry.
Diazonium salts are compounds containing a positively charged nitrogen atom that is linked to an aromatic ring. These salts are often used in organic synthesis as a source of the aryl group. When treated with cuprous cyanide or KCN and copper powder, diazonium salts undergo a reaction known as Sandmeyer reaction, which forms aryl nitriles.
Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism involves several steps:
1. Formation of Copper(I) Salt
First, cuprous cyanide or KCN is added to the diazonium salt solution to form a copper(I) salt. The copper(I) salt plays a crucial role in the reaction by catalyzing the formation of the aryl nitrile.
2. Formation of Aryl Copper(I) Intermediate
Next, copper powder is added to the reaction mixture, which reduces the copper(I) salt to copper metal. The copper metal then reacts with the diazonium salt to form an aryl copper(I) intermediate.
3. Formation of Aryl Cyanide
The aryl copper(I) intermediate then reacts with the cyanide ion from the cuprous cyanide or KCN to form the aryl cyanide. The reaction releases copper metal, which can then react with more diazonium salt to form more aryl copper(I) intermediate.
Overall Reaction
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
ArN2+X- + CuCN/KCN → [CuX] + N2 + ArCu + HX
ArCu + CN- → ArCN + Cu
Where Ar represents the aryl group, X represents the anion of the diazonium salt, and HX represents the acid formed in the reaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treatment of diazonium salts with cuprous cyanide or KCN and copper powder forms aryl nitriles through the Sandmeyer reaction. This reaction is an important method for the synthesis of aryl nitriles, which have a variety of applications in organic synthesis and industry.
Chapter doubts & questions for Amines - Chemistry for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Amines - Chemistry for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for ACT
110 videos|124 docs|114 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup

 A
A  B
B