All Exams >
ACT >
Biology for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Cell: The Unit of Life for ACT Exam
Which cell organelle is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- a)Mitochondria
- b)Endoplasmic reticulum
- c)Nucleus
- d)Ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which cell organelle is present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Endoplasmic reticulum
c)
Nucleus
d)
Ribosomes
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the two different types of cells.
- Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria while prokaryotic cells do not but the ribosome is the only organelle that can be seen in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes perform the same functions that is protein synthesis, however, eukaryotic ribosomes are much larger than prokaryotic ones.
Which of the following is a prokaryote?- a)Bacteria
- b)Amoeba
- c)Chlamydomonas
- d)Spirogyra
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a prokaryote?
a)
Bacteria
b)
Amoeba
c)
Chlamydomonas
d)
Spirogyra
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Prokaryotic cells are cells that do not have a true nucleus or most other cell organelles. Organisms that have prokaryotic cells are unicellular and called prokaryotes. Bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes.

The largest subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes is- a)40S
- b)60S
- c)30S
- d)50S
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The largest subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes is
a)
40S
b)
60S
c)
30S
d)
50S
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
50S, roughly equivalent to the 60S ribosomal subunit in eukaryotic cells, is the larger subunit of the 70S ribosome of prokaryotes. The 50S subunit is primarily composed of proteins but also contains single-stranded RNA known as ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
Glycocalyx is associated with ___________
- a)Nucleosome
- b)Nucleus
- c)Plasma membrane
- d)Nucleolus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glycocalyx is associated with ___________
a)
Nucleosome
b)
Nucleus
c)
Plasma membrane
d)
Nucleolus
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The glycocalyx is a thick outer covering of the plasma membrane. It is composed of strands of sugars and proteins bound together. The result is a thick, sticky layer that helps cells stay put in environments with lots of physical stress.
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:- a)Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion
- b)Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
- c)Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
- d)Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
a)
Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for assertion
b)
Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
c)
Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
d)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
|
|
Prasenjit Chavan answered |
Explanation:
• Prokaryotic cells, which are found in bacteria and archaea, lack the membrane-bound organelles that are present in eukaryotic cells. These organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
• The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement, which is a characteristic of eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasmic streaming is driven by motor proteins that move along actin filaments and microtubules.
• The absence of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotic cells is related to their small size and simpler structure. They are able to carry out all their necessary functions within the cytoplasm without the need for specialized compartments.
• The lack of cytoplasmic streaming in prokaryotic cells is also related to their small size, as diffusion is sufficient for most of their metabolic processes.
Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
The correct answer is option 'A'. Both the assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
• Prokaryotic cells, which are found in bacteria and archaea, lack the membrane-bound organelles that are present in eukaryotic cells. These organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
• The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement, which is a characteristic of eukaryotic cells. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasmic streaming is driven by motor proteins that move along actin filaments and microtubules.
• The absence of membrane-bound organelles in prokaryotic cells is related to their small size and simpler structure. They are able to carry out all their necessary functions within the cytoplasm without the need for specialized compartments.
• The lack of cytoplasmic streaming in prokaryotic cells is also related to their small size, as diffusion is sufficient for most of their metabolic processes.
Assertion (A): Prokaryotic cells have no membrane-bound organelles.
Reason (R): The cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells does not show a streaming movement.
The correct answer is option 'A'. Both the assertion and reason are correct, and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
Which is common in plant and animal cells- a)Mitochondria
- b)Plastids
- c)Centrioles
- d)Central vacuoles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is common in plant and animal cells
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Plastids
c)
Centrioles
d)
Central vacuoles

|
Ashwini Khanna answered |
Mitochondria are present in both plant as well as animal cells. Plastids and central vacuoles are present in plant cells and centrioles are present in only animal cells.
The process of movement of few ions or molecules across the membrane against a concentration gradient from lower to higher concentration, it is called
a) Diffusionb)Passive transportc)Active transportd) OsmosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Passive transport, also known as passive diffusion, is a process by which an ion or molecule passes through a cell wall via a concentration gradient, or from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It’s like moving from the train to the platform of a subway station, or stepping out of a crowded room. Basically, passive transport gives an ion or molecule “room to breathe.”
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Organisms which lack mitosis division and use binary fission method for cell division are known as
- A:
prokaryotes
- B:
eukaryotes
- C:
yeast
- D:
fungi
The answer is a.
Organisms which lack mitosis division and use binary fission method for cell division are known as
prokaryotes
eukaryotes
yeast
fungi
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
- As in prokaryotes, centrioles are absent.
- Centrioles play an important part in mitosis during spindle fibre formation. so mitosis is not seen in them, thus they use binary fission.
Cell organelles with single membrane is- a)Lysosomes
- b)Chloroplast
- c)Plastids
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell organelles with single membrane is
a)
Lysosomes
b)
Chloroplast
c)
Plastids
d)
Mitochondria

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Lysosomes are single membrane structures containing enzymes for digestion of all types of macromolecules.
Who was the first to explain that cells divide?
- a)Schwann
- b)Robert Brown
- c)Rudolf Virchow
- d)Anton von LeeuwenHoek
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who was the first to explain that cells divide?
a)
Schwann
b)
Robert Brown
c)
Rudolf Virchow
d)
Anton von LeeuwenHoek

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Rudolf Virchow(1855) first explained that cells divided and new cells are formed .
Nuclear membrane is absent in- a)Nostoc
- b)Penicillium
- c)Volvox
- d)Agaricus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Nuclear membrane is absent in
a)
Nostoc
b)
Penicillium
c)
Volvox
d)
Agaricus
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Nostoc, genus of blue-green algae with cells arranged in beadlike chains that are grouped together in a gelatinous mass. Ranging from microscopic to walnut-sized, masses of Nostoc may be found on soil and floating in quiet water. Reproduction is by fragmentation. A special thick-walled cell (akinete) has the ability to withstand desiccation for long periods of time. After 70 years of dry storage, the akinete of one species germinates into a filament when moistened. Like most blue-green algae, Nostoc contains two pigments, blue phycocyanin and red phycoerythrin, as well as chlorophyll, and has the ability to fix nitrogen in specialized cells called heterocysts. A terrestrial species has been used as a supplementary food source in Asia.
Smallest free living organism are- a)PPLOs
- b)Bacteria
- c)Viroids
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Smallest free living organism are
a)
PPLOs
b)
Bacteria
c)
Viroids
d)
Virus
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Pelagibacter ubique is one of the smallest known free-living bacterium with a length of 0.37-0.89 μm and an average cell diameter of 0.12-0.20 μm. They also have the smallest free-living bacterium genome; 1.8Mbp, 1354 protein genes, 35 RNA genes.
The prokaryotic cells are characterised by- a)Presence of a distinct chromosome
- b)Absence of chromatin material
- c)Absence of a nuclear membrane
- d)Presence of a distinct nuclear membrane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The prokaryotic cells are characterised by
a)
Presence of a distinct chromosome
b)
Absence of chromatin material
c)
Absence of a nuclear membrane
d)
Presence of a distinct nuclear membrane
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Prokaryotes lack an organized nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. The cell wall of a prokaryote acts as an extra layer of protection, helps maintain cell shape, and prevents dehydration.prokaryotic cells are those that do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. In fact "pro-karyotic" is Greek for "before nucleus". Besides bacteria, the cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) are a major group of prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic cells in having:
- a)
True nucleus
- b)Mitochondria in mesosome form
- c)Only smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- d)70S ribosomes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Eukaryotic cells are different from prokaryotic cells in having:
a)
True nucleus
b)
Mitochondria in mesosome form
c)
Only smooth endoplasmic reticulum
d)
70S ribosomes
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Correct option is A)
- Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus whereas prokaryotic cells have a primitive nucleus.
- The true nucleus of eukaryotes is a double membrane-covered protoplasmic body that contains hereditary information.
- A true nucleus is made up of five parts- nuclear envelope, nucleoplasm, nuclear matrix, chromatin, and nucleolus.
- The primitive nucleus of a prokaryote is also called as nucleoid as it lacks these parts. It is comprised of only the genetic material. So, option A is correct.
Protoplasm found inside the nucleus is known as- a)Amyloplast
- b)Nucleoplasm
- c)cytoplasm
- d)Elaioplast
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Protoplasm found inside the nucleus is known as
a)
Amyloplast
b)
Nucleoplasm
c)
cytoplasm
d)
Elaioplast
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Protoplasm is the living content of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a general term for the cytoplasm. Protoplasm is composed of a mixture of small molecules such as ions, amino acids, monosaccharides and water, and macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and polysaccharides.Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains 'nucleoplasm' (nucleus sap) or karyoplasm. The nucleoplasm is one of the types of protoplasm, and it is enveloped by the nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope. The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleoli.
The rod shaped bacteria is called as- a)Bacillus
- b)Vibrio
- c)Spiral
- d)Spherical
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The rod shaped bacteria is called as
a)
Bacillus
b)
Vibrio
c)
Spiral
d)
Spherical

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The shapes of bacteria are bacillus (rod like), coccus (spherical), vibrio (comma shaped) and spirillum (spiral).
The structure of plasma membrane fluid mosaic model is proposed by- a)Gram
- b)Singer and Nicolson
- c)Schwann and Schleiden
- d)Robert brown
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure of plasma membrane fluid mosaic model is proposed by
a)
Gram
b)
Singer and Nicolson
c)
Schwann and Schleiden
d)
Robert brown
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
An improved model of the structure of cell membrane was proposed by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson (1972) widely accepted as fluid mosaic model.CORRECT OPTION IS B.
Lysosomes are produced by- a)Leucoplast
- b)Golgi bodies
- c)Mitochondria
- d)Endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lysosomes are produced by
a)
Leucoplast
b)
Golgi bodies
c)
Mitochondria
d)
Endoplasmic reticulum

|
Rohan Unni answered |
These are membrane bound vesicular structures formed by the process of packaging in the Golgi apparatus.
Who first saw and described a live cell?- a)T. Schwann
- b)R. Virchow
- c)A.V. Leeuwenhoek
- d)M. Schleiden
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who first saw and described a live cell?
a)
T. Schwann
b)
R. Virchow
c)
A.V. Leeuwenhoek
d)
M. Schleiden

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek first saw and described a live cell.
Animal cell do not possess- a)Centriole
- b)Plamsodesmata
- c)Ribosomes
- d)Plasmalemma
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Animal cell do not possess
a)
Centriole
b)
Plamsodesmata
c)
Ribosomes
d)
Plasmalemma

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Animal cell do not possess plasmodesmata but it contain ribosomes, centriole andplamalemma. Plasmodesmata is the connection between two plant cells.
Which one is present nearest to plasmamembrane?- a)Secondary wall
- b)Tonoplast
- c)Middle lamella
- d)Primary wall
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is present nearest to plasmamembrane?
a)
Secondary wall
b)
Tonoplast
c)
Middle lamella
d)
Primary wall

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
The cell wall of a young plant cell, the primary wallis capable of growth, which gradually diminishes as the cell matures and the secondary wall is formed on the inner (towards membrane) side of the cell.
How much percent of vacuoles occupy the volume of the cell in plant cells?- a)80%
- b)90%
- c)50%
- d)70%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How much percent of vacuoles occupy the volume of the cell in plant cells?
a)
80%
b)
90%
c)
50%
d)
70%

|
Arya Nair answered |
In plant cells the vacuoles can occupy up to 90 per cent of the volume of the cell.
Cytoskeleton is made of- a)Phosphoglycerides
- b)Micro tubules
- c)Proteinaceousfilaments
- d)Hemicellulose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cytoskeleton is made of
a)
Phosphoglycerides
b)
Micro tubules
c)
Proteinaceousfilaments
d)
Hemicellulose
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Proteinaceous filaments
The cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells is crisscrossed by a network of protein fibres that support the shape of the cell and anchor organelles to fixed locations. It is a dynamic system with three types of fibres-actin filaments, microtubule and intermediate filaments.
Elaioplasts belongs to- a)Chloroplast
- b)Leucoplast
- c)Amyloplast
- d)Chromoplast
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Elaioplasts belongs to
a)
Chloroplast
b)
Leucoplast
c)
Amyloplast
d)
Chromoplast

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids of varied shapes and sizes with stored nutrients. Leucoplast includes: a) Amyloplasts storing carbohydrates. b) Elaioplastsstoring oils and fats and c) Aleuroplasts storing proteins.
Lipid molecules of plasma membrane occur- a)Parallel
- b)In series
- c)Scattered
- d)Alternately
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lipid molecules of plasma membrane occur
a)
Parallel
b)
In series
c)
Scattered
d)
Alternately

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
The lipid molecules of plasma membrane occurs parallel to each other in plasma membrane of the cell.
The organelle involved in respiration is- a)Mitochondria
- b)Endoplasmic reticulum
- c)Chloroplast
- d)Golgi complex
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The organelle involved in respiration is
a)
Mitochondria
b)
Endoplasmic reticulum
c)
Chloroplast
d)
Golgi complex

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Mitochondria are the sites of aerobic respiration. They producecellular energy in the form of ATP
In prokaryotes, the reserved food material is stored in- a)Cytoplasm
- b)Vacuole
- c)Centrosome
- d)Endoplasmic reticulum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In prokaryotes, the reserved food material is stored in
a)
Cytoplasm
b)
Vacuole
c)
Centrosome
d)
Endoplasmic reticulum

|
Rajat Roy answered |
Reserve material in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies.
Chlorophyll is located inside- a)Stroma
- b)Plasma lemma
- c)Chromatophores
- d)Thylakoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll is located inside
a)
Stroma
b)
Plasma lemma
c)
Chromatophores
d)
Thylakoids

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
The chloroplast consists of a number of organised flattened membranous sacs called the thylakoids,Chlorophyll pigments are present in the thylakoids.
The photograph or diagram of metaphasicchromosome arranged in homologous pair according to their length and thickness, position of centromere is called- a)Karyogram
- b)Chromogram
- c)Idiogram
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The photograph or diagram of metaphasicchromosome arranged in homologous pair according to their length and thickness, position of centromere is called
a)
Karyogram
b)
Chromogram
c)
Idiogram
d)
None of these
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Ideogram is a photograph or diagram of metaphases chromosomes of an organism arranged in homologous pair according to their length, thickness and position of centromere, length of arm, shape and other characteristics. The sex chromosomes are usually placed at the end.
The ability of a living somatic nucleated cell to form the complete organism is called- a)Cellular totipotancy
- b)Morphogenesis
- c)Cell differentiation
- d)Regeneration
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ability of a living somatic nucleated cell to form the complete organism is called
a)
Cellular totipotancy
b)
Morphogenesis
c)
Cell differentiation
d)
Regeneration
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Totipotency is defined in Wikipedia as the ability of a single cell to divide and produce all the differentiated cells in an organism, including extraembryonic tissues. Totipotent cells formed during sexual and asexual reproduction include spores and zygotes.
The staining procedure is developed by- a)Schleiden
- b)Gram
- c)A.V.Leeuwenhoek
- d)Schwann
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The staining procedure is developed by
a)
Schleiden
b)
Gram
c)
A.V.Leeuwenhoek
d)
Schwann

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
The staining procedure developed by Gram viz., those that take up the gram stain are gram positiveand the others that do not are called gram negative bacteria.
The stacks of closely packed thylakoids is called- a)Lumen
- b)Matrix
- c)Stroma
- d)Granum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The stacks of closely packed thylakoids is called
a)
Lumen
b)
Matrix
c)
Stroma
d)
Granum

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
The stacks or closely packed thylakoids is called granum. Chlorophyll is present inside the thylakoidsto perform photosynthesis in plant cells.
Glycocalyx is associated with- a)Nucleosome
- b)Nucleus
- c)Plasma membrane
- d)Nucleolus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glycocalyx is associated with
a)
Nucleosome
b)
Nucleus
c)
Plasma membrane
d)
Nucleolus

|
Advait Chakraborty answered |
Glycocalyx is associated with Plasma membrane. It is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering the membrane. It is also known as peculiar matrix.
Each centriole is surrounded by dense amorphous protoplasmic masses called- a)Cytoplasmic particles
- b)Meta-molecule
- c)Cell granules
- d)Massules
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Each centriole is surrounded by dense amorphous protoplasmic masses called
a)
Cytoplasmic particles
b)
Meta-molecule
c)
Cell granules
d)
Massules

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
All animal cell have two small organelles called centrioles. Each centriole is surrounded by dense amorphous protoplasmic masses called Massules.
The plasma membrane consists mainly of- a)Proteins embedded in a polymer of glucose molecules
- b)Proteins embedded in a phospholipids layer
- c)Proteins embedded in a glucose molecules
- d)Proteins embedded in a carbohydrate bilayer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The plasma membrane consists mainly of
a)
Proteins embedded in a polymer of glucose molecules
b)
Proteins embedded in a phospholipids layer
c)
Proteins embedded in a glucose molecules
d)
Proteins embedded in a carbohydrate bilayer

|
Charvi Shah answered |
The plasma membrane is composed of lipids that are arranged in a bilayer. Also, the lipids are arranged within the membrane with the polar head towards the outer sides and the hydrophobic tails towards the inner part. The membrane proteins can be classified as integral or peripheral. Peripheral proteins lie on the surface
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).Assertion: Eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells.Reason: Eukaryotes are genetically more complex than prokaryotes.For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells.
Reason: Eukaryotes are genetically more complex than prokaryotes.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Gaurav Basu answered |
Explanation:
• Eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells. This statement is true because eukaryotic cells are typically multicellular and have more complex structures than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotes also have more genes and regulatory elements than prokaryotes.
• Eukaryotes are genetically more complex than prokaryotes. This statement is also true because eukaryotes have more complex genetic regulation mechanisms, such as alternative splicing, RNA editing, and epigenetic modifications. These mechanisms allow eukaryotes to produce more proteins from a single gene and regulate gene expression more precisely than prokaryotes.
• Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A). The reason (R) provided in the statement correctly explains why eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells. The increased genetic complexity of eukaryotes requires a larger genome size to accommodate more genes and regulatory elements.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
• Eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells. This statement is true because eukaryotic cells are typically multicellular and have more complex structures than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotes also have more genes and regulatory elements than prokaryotes.
• Eukaryotes are genetically more complex than prokaryotes. This statement is also true because eukaryotes have more complex genetic regulation mechanisms, such as alternative splicing, RNA editing, and epigenetic modifications. These mechanisms allow eukaryotes to produce more proteins from a single gene and regulate gene expression more precisely than prokaryotes.
• Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A). The reason (R) provided in the statement correctly explains why eukaryotic cells have more DNA than prokaryotic cells. The increased genetic complexity of eukaryotes requires a larger genome size to accommodate more genes and regulatory elements.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).Assertion: Ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in the prokaryotic cells only.Reason: These are present in the cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria & on rough ER.For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in the prokaryotic cells only.
Reason: These are present in the cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria & on rough ER.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The Assertion (A) that ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in prokaryotic cells only is false.
- Ribosomes are non-membrane bound organelles found in eukaryotic as well as prokaryotic cells.
The Reason (R) that ribosomes are present in the cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and on rough ER is true.
- Within the cell, ribosomes are found not only in the cytoplasm but also within the two organelles – chloroplasts (in plants) and mitochondria and on rough ER.
Therefore, Assertion (A) is false, and Reason (R) is true.
Select the incorrect matching- a)Cristae --- Mitochondria
- b)Chromosome—RNA
- c)Thylakoid – chloroplast
- d)Digestive enzyme – Lysosome
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect matching
a)
Cristae --- Mitochondria
b)
Chromosome—RNA
c)
Thylakoid – chloroplast
d)
Digestive enzyme – Lysosome

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
Mitochondria contain cristae, finger like projection of inner layer, thylakoid is present in chloroplast and lysosome is a digestive enzyme but RNA is absent in Chromosome.
The eukaryotic ribosomes are of- a)50S
- b)30S
- c)80S
- d)70S
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The eukaryotic ribosomes are of
a)
50S
b)
30S
c)
80S
d)
70S

|
Sushant Goyal answered |
The eukaryotic ribosomes are 80S while the prokaryotic ribosomes are 70S. Here ‘S’ stands for the sedimentation coefficient; it indirectly is a measure of density and size.
Which of the following is the correct sequence/route of the secretory product?- a)ER → Vesicles → Cis region of GB → Trans region of GB → Vesicle → Plasma membrane
- b)RER → GB → Lysosome → Nuclear membrane → Plasma membrane
- c)ER → Vesicles → Trans region of GB → Cis region of GB → Vesicles → Plasma membrane
- d)Lysosome → ER → GB → Vesicles → Cell membrane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct sequence/route of the secretory product?
a)
ER → Vesicles → Cis region of GB → Trans region of GB → Vesicle → Plasma membrane
b)
RER → GB → Lysosome → Nuclear membrane → Plasma membrane
c)
ER → Vesicles → Trans region of GB → Cis region of GB → Vesicles → Plasma membrane
d)
Lysosome → ER → GB → Vesicles → Cell membrane
|
|
Nishanth Chawla answered |
Correct Sequence of Secretory Product Pathway
The correct sequence of the secretory pathway is outlined in option 'A':
ER → Vesicles → Cis region of Golgi Body → Trans region of Golgi Body → Vesicle → Plasma membrane
Explanation of the Pathway
1. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- The secretory proteins are synthesized in the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER), where ribosomes are attached.
- The RER plays a crucial role in the initial post-translational modifications and folding of proteins.
2. Vesicles
- Once proteins are synthesized and properly folded, they are packaged into transport vesicles.
- These vesicles bud off from the ER and are directed toward the Golgi apparatus.
3. Golgi Apparatus: Cis Region
- The vesicles fuse with the Cis region of the Golgi body, where they undergo further modifications.
- Here, proteins may undergo glycosylation and other enzymatic processes.
4. Golgi Apparatus: Trans Region
- Proteins are then moved through the Golgi apparatus to the Trans region, where they are sorted and packaged for delivery to their final destinations.
5. Final Vesicle Formation
- After processing, proteins are enclosed in new vesicles that bud off from the Trans region of the Golgi.
6. Plasma Membrane
- These vesicles are transported to the plasma membrane, where they fuse with it to release their contents outside the cell or integrate with the membrane.
Conclusion
- The pathway outlined in option 'A' accurately represents the route taken by secretory products from synthesis to secretion, emphasizing the critical roles of the ER and Golgi apparatus in this process.
The correct sequence of the secretory pathway is outlined in option 'A':
ER → Vesicles → Cis region of Golgi Body → Trans region of Golgi Body → Vesicle → Plasma membrane
Explanation of the Pathway
1. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- The secretory proteins are synthesized in the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER), where ribosomes are attached.
- The RER plays a crucial role in the initial post-translational modifications and folding of proteins.
2. Vesicles
- Once proteins are synthesized and properly folded, they are packaged into transport vesicles.
- These vesicles bud off from the ER and are directed toward the Golgi apparatus.
3. Golgi Apparatus: Cis Region
- The vesicles fuse with the Cis region of the Golgi body, where they undergo further modifications.
- Here, proteins may undergo glycosylation and other enzymatic processes.
4. Golgi Apparatus: Trans Region
- Proteins are then moved through the Golgi apparatus to the Trans region, where they are sorted and packaged for delivery to their final destinations.
5. Final Vesicle Formation
- After processing, proteins are enclosed in new vesicles that bud off from the Trans region of the Golgi.
6. Plasma Membrane
- These vesicles are transported to the plasma membrane, where they fuse with it to release their contents outside the cell or integrate with the membrane.
Conclusion
- The pathway outlined in option 'A' accurately represents the route taken by secretory products from synthesis to secretion, emphasizing the critical roles of the ER and Golgi apparatus in this process.
Cytoskeleton is made of- a)Cellulose microfibrils
- b)Protienaceous filaments
- c)Callose deposit
- d)Calcium carbonate granules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cytoskeleton is made of
a)
Cellulose microfibrils
b)
Protienaceous filaments
c)
Callose deposit
d)
Calcium carbonate granules

|
Saptarshi Menon answered |
The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments,and intermediate filaments. These structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell’s parts. They also provide a basis for movement and cell division.
Longest cell in human body are- a)Muscle cell
- b)Nerve cells
- c)Blood cells
- d)Mast cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Longest cell in human body are
a)
Muscle cell
b)
Nerve cells
c)
Blood cells
d)
Mast cells

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
Nerve cell or neuron is the longest cell in human body. They are responsible for transferof information from one part of the body to the other in form of nerve impulses.
The fluid filled vacuoles or vesicles which are separated from cytoplasm by a selectively permeable membrane called- a)Symplast
- b)Aquaplast
- c)Hydroplast
- d)Tonoplast
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The fluid filled vacuoles or vesicles which are separated from cytoplasm by a selectively permeable membrane called
a)
Symplast
b)
Aquaplast
c)
Hydroplast
d)
Tonoplast

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
Tonoplasts are the fluid filled vacuoles or vesicles which are separatedfrom cytoplasm by a selectively permeable membrane. It help in maintaining turgidity of the cell.
Golgi apparatus are the site for formation of- a)Glycolipids and glycoproteins
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Lipids
- d)Enzymes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Golgi apparatus are the site for formation of
a)
Glycolipids and glycoproteins
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Lipids
d)
Enzymes

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Golgi apparatus is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
The inner membrane of mitochondria thrown into folds to form finger like structure is called- a)Matrix
- b)Inter membrane space
- c)Amyloplast
- d)Cristae
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The inner membrane of mitochondria thrown into folds to form finger like structure is called
a)
Matrix
b)
Inter membrane space
c)
Amyloplast
d)
Cristae

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Mitochondria are double membranous structure. The inner membrane of mitochondria thrown into folds to form finger-like structureis called cristae.
Arrangement ofciliary microtubules is- a)9 + 3
- b)9 + 2
- c)9 + 4
- d)9 + 9
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrangement ofciliary microtubules is
a)
9 + 3
b)
9 + 2
c)
9 + 4
d)
9 + 9

|
Krish Khanna answered |
Cilia present in prokaryotic organisms consist of microtubules. These microtubules are arranged in 9+2 order in which 2 forms the center and 9 are arranged at periphery.
How does the composition of the glycocalyx vary among different bacteria?- a) It remains consistent in its thickness across all bacterial species.
- b) It is absent in some bacteria but present in others.
- c) It can be a loose sheath known as the slime layer in certain bacteria.
- d) It is always thick and tough, termed as the capsule in all bacteria.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How does the composition of the glycocalyx vary among different bacteria?
a)
It remains consistent in its thickness across all bacterial species.
b)
It is absent in some bacteria but present in others.
c)
It can be a loose sheath known as the slime layer in certain bacteria.
d)
It is always thick and tough, termed as the capsule in all bacteria.
|
|
Ananya Chakraborty answered |
Introduction to the Glycocalyx
The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-rich layer found on the surface of many bacteria, playing a crucial role in their interaction with the environment. Its composition varies significantly among different bacterial species.
Variability in Composition
- The glycocalyx can be either a capsule or a slime layer.
- Capsules are organized and tightly bound structures, providing protection from phagocytosis and desiccation.
- Slime layers are more loosely associated with the cell surface, offering less protection but facilitating adherence to surfaces and biofilm formation.
Presence in Bacteria
- Not all bacteria possess a glycocalyx:
- Some bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, may have a capsule, while others may not have any glycocalyx at all.
- The presence of a glycocalyx can be an important factor in pathogenicity.
Functionality
- The glycocalyx serves multiple functions:
- Adhesion: Helps bacteria attach to surfaces and each other, forming biofilms.
- Protection: Shields bacteria from environmental threats, including immune responses.
- Nutrient Capture: Assists in the absorption of nutrients from the environment.
Conclusion
In summary, the glycocalyx can vary widely among bacterial species, existing as either a capsule or a slime layer, or may even be absent. Its composition and structure play significant roles in survival, pathogenicity, and ecological interactions. Thus, option 'C' is correct as it accurately reflects the diversity of the glycocalyx among bacteria.
The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-rich layer found on the surface of many bacteria, playing a crucial role in their interaction with the environment. Its composition varies significantly among different bacterial species.
Variability in Composition
- The glycocalyx can be either a capsule or a slime layer.
- Capsules are organized and tightly bound structures, providing protection from phagocytosis and desiccation.
- Slime layers are more loosely associated with the cell surface, offering less protection but facilitating adherence to surfaces and biofilm formation.
Presence in Bacteria
- Not all bacteria possess a glycocalyx:
- Some bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, may have a capsule, while others may not have any glycocalyx at all.
- The presence of a glycocalyx can be an important factor in pathogenicity.
Functionality
- The glycocalyx serves multiple functions:
- Adhesion: Helps bacteria attach to surfaces and each other, forming biofilms.
- Protection: Shields bacteria from environmental threats, including immune responses.
- Nutrient Capture: Assists in the absorption of nutrients from the environment.
Conclusion
In summary, the glycocalyx can vary widely among bacterial species, existing as either a capsule or a slime layer, or may even be absent. Its composition and structure play significant roles in survival, pathogenicity, and ecological interactions. Thus, option 'C' is correct as it accurately reflects the diversity of the glycocalyx among bacteria.
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles.
Reason: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane bound organelles.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
- a)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- b)Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
- c)Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
- d)Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Each question consists of two statements, namely, Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles.
Reason: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane bound organelles.
For selecting the correct answer, use the following code:
a)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true and Reason (R) is a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b)
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are the true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c)
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
d)
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
|
|
Aryan Chaudhary answered |
Explanation:
• Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, etc.
• Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, lack membrane-bound organelles. They have a simple structure with no specialized compartments.
• Hence, both the assertion and reason are true.
• However, the reason provided does not correctly explain why eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles and prokaryotic cells do not. It only provides a contrasting characteristic between the two types of cells.
• Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer as both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
• Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, etc.
• Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, lack membrane-bound organelles. They have a simple structure with no specialized compartments.
• Hence, both the assertion and reason are true.
• However, the reason provided does not correctly explain why eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles and prokaryotic cells do not. It only provides a contrasting characteristic between the two types of cells.
• Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer as both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their size:- a)virus < PPLO < typical bacteria < typical eukaryotic cell
- b)PPLO < virus < typical bacteria < typical eukaryotic cell
- c)virus < PPLO < typical eukaryotic cell < typical bacteria
- d)virus > PPLO > typical bacteria > typical eukaryotic cell
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their size:
a)
virus < PPLO < typical bacteria < typical eukaryotic cell
b)
PPLO < virus < typical bacteria < typical eukaryotic cell
c)
virus < PPLO < typical eukaryotic cell < typical bacteria
d)
virus > PPLO > typical bacteria > typical eukaryotic cell

|
Top Rankers answered |
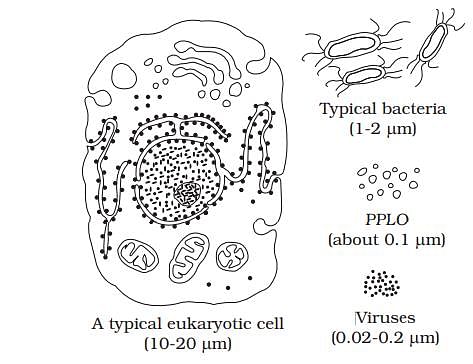
The correct order from smallest to largest is virus, PPLO (Mycoplasma), typical bacteria, and typical eukaryotic cell. Viruses are the smallest, usually only visible with an electron microscope. PPLOs are slightly larger than the largest viruses but smaller than typical bacteria. Typical bacteria are larger than viruses and PPLOs and are visible under light microscopes. Eukaryotic cells are the largest, significantly bigger than viruses, PPLOs, and typical bacteria, making Option A the correct choice.
Proteins synthesized by ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum are modified in- a)Stroma
- b)Cisternae
- c)Tubules
- d)Vesicles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins synthesized by ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum are modified in
a)
Stroma
b)
Cisternae
c)
Tubules
d)
Vesicles

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
The number of proteins synthesised by ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum are modified in the cisternae of the golgiapparatus .
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell: The Unit of Life - Biology for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell: The Unit of Life - Biology for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for ACT
208 videos|226 docs|136 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










