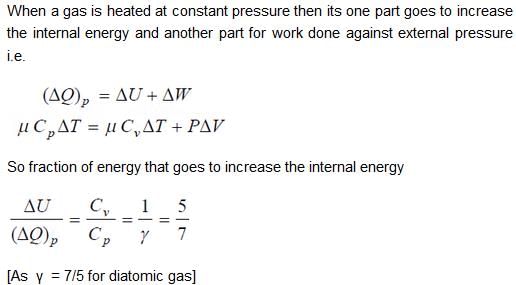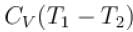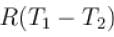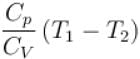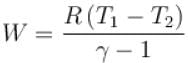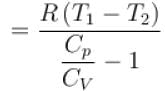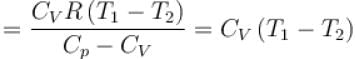All Exams >
ACT >
Physics for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of First law of thermodynamics for ACT Exam
Internal energy of a perfect gas depends on.
Select one:
- a)temperature, specific heat and enthalpy
- b)temperature only
- c)temperature, specific heat and entropy
- d)emperature, specific heat and pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Internal energy of a perfect gas depends on.
Select one:
Select one:
a)
temperature, specific heat and enthalpy
b)
temperature only
c)
temperature, specific heat and entropy
d)
emperature, specific heat and pressure
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
For an ideal gas, internal energy depends only on temperature. Thus, there is no change in the internal energy of an ideal gas in an isothermal process.
The processes or systems that do not involve heat is called.
Select one:- a)Equilibrium processes
- b)Isothermal processes
- c)Adiabatic processes
- d)Thermal processes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The processes or systems that do not involve heat is called.
Select one:
Select one:
a)
Equilibrium processes
b)
Isothermal processes
c)
Adiabatic processes
d)
Thermal processes
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
In adiabatic processes, dQ = 0 heat remains fixed in the process, hence adiabatic processes do not involve heat.
The correct answer is: Adiabatic processes
The correct answer is: Adiabatic processes
In a given process of an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. The for the gas
Select one:- a)the volume will increase
- b)the temperature will decrease
- c)the pressure will remain constant
- d)the temperature will increase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a given process of an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. The for the gas
Select one:
Select one:
a)
the volume will increase
b)
the temperature will decrease
c)
the pressure will remain constant
d)
the temperature will increase
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
From first law of thermodynamics,
dQ = dU + dW
dQ = dU if dW = 0
Since, dQ < 0
Therefore,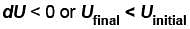 or temperature will decrease
or temperature will decrease
The correct answer is: the temperature will decrease
dQ = dU + dW
dQ = dU if dW = 0
Since, dQ < 0
Therefore,
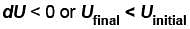 or temperature will decrease
or temperature will decreaseThe correct answer is: the temperature will decrease
One gram of water on evaporation at atmospheric pressure forms 1671cm3 of steam. Heat of vaporization at this pressure is 540 cal/g. Calculate the increase in the internal energy. (Atmospheric pressure = 1×105N/m2)Select one:- a)250cal
- b)100cal
- c)500cal
- d)1500cal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One gram of water on evaporation at atmospheric pressure forms 1671cm3 of steam. Heat of vaporization at this pressure is 540 cal/g. Calculate the increase in the internal energy. (Atmospheric pressure = 1×105N/m2)
Select one:
a)
250cal
b)
100cal
c)
500cal
d)
1500cal
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
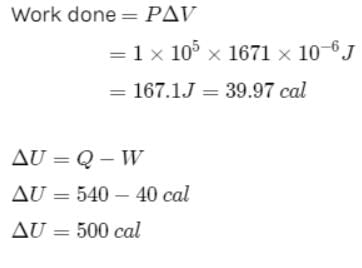
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume V1 to V2 in three different ways, the work done by the gas is W1 if the process is purely isothermal, W2 if purely isobaric and W3 if purely adiabatic, then- a)W2 > W3 > W1
- b)W2 > W1 > W3
- c)W1 > W3 > W2
- d)W1 > W2 > W3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume V1 to V2 in three different ways, the work done by the gas is W1 if the process is purely isothermal, W2 if purely isobaric and W3 if purely adiabatic, then
a)
W2 > W3 > W1
b)
W2 > W1 > W3
c)
W1 > W3 > W2
d)
W1 > W2 > W3
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The corresponding p-V graph (also called indicator diagram) in three different process will be as shown :
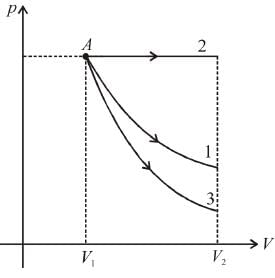
Area under the graph gives the work done by the gas.
(Area)2 > (Area)1 > (Area)3
∴ W2 > W1 > W3
The correct answer is:
W2 > W1 > W3

Area under the graph gives the work done by the gas.
(Area)2 > (Area)1 > (Area)3
∴ W2 > W1 > W3
The correct answer is:
W2 > W1 > W3
One mole of a perfect gas is compressed adiabatically. The initial pressure and volume of the gas are 105N/m and 6L respectively. The final volume of the gas is 2L, molar specific heat of the gas at constant volume is 3R/2. The total work done is
Select one:- a)-600 J
- b)540 J
- c)450 J
- d)-972 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of a perfect gas is compressed adiabatically. The initial pressure and volume of the gas are 105N/m and 6L respectively. The final volume of the gas is 2L, molar specific heat of the gas at constant volume is 3R/2. The total work done is
Select one:
Select one:
a)
-600 J
b)
540 J
c)
450 J
d)
-972 J
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
In adiabatic process 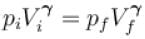
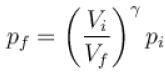
Further,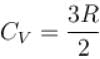
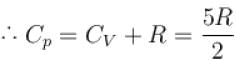
or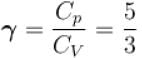
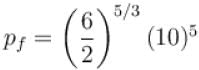
= 6.24 × 105 N/m2
New york done in adiabatic process is given by
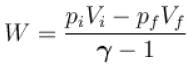
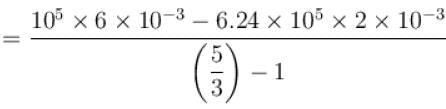
= –972 J
The correct answer is: -972 J
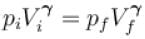
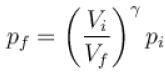
Further,
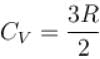
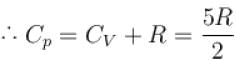
or
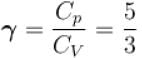
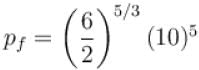
= 6.24 × 105 N/m2
New york done in adiabatic process is given by
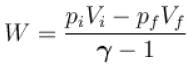
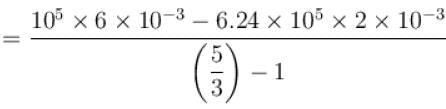
= –972 J
The correct answer is: -972 J
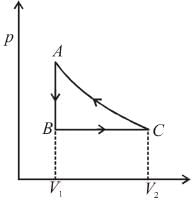
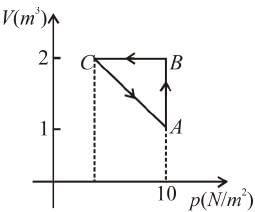
An ideal gas expands isothermally from a volume V1 to V2 and then compressed to original volumes V1 adiabatically. Initial pressure is p1 and final pressure is p3. The total work done is W. Then,
Select one:- a)p3= p1 , W = 0
- b)p3> p1, W < 0
- c)p3 < p1, W < 0
- d)p3 > p1, W > 0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas expands isothermally from a volume V1 to V2 and then compressed to original volumes V1 adiabatically. Initial pressure is p1 and final pressure is p3. The total work done is W. Then,
Select one:
Select one:
a)
p3= p1 , W = 0
b)
p3> p1, W < 0
c)
p3 < p1, W < 0
d)
p3 > p1, W > 0
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
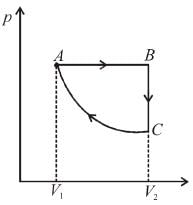
Slope of adiabatic process at a given state (p, V, T) is more than the slope of isothermal process. The corresponding p-V graph for the two process is as shown in figure.
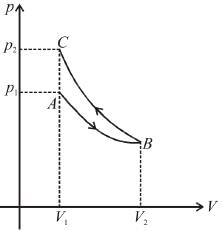
In the graph, AB is isothermal and BC is adiabatic.
WAB is positive (as volume is increasing)
and WBC is negative (as volume is decreasing)
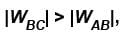 as area under p–V graph gives the work done.
as area under p–V graph gives the work done.
Hence,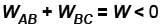
From the graph itself, it is clear that p3 > p1
The correct answer is: p3 > p1 , W < 0

In the graph, AB is isothermal and BC is adiabatic.
WAB is positive (as volume is increasing)
and WBC is negative (as volume is decreasing)
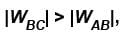 as area under p–V graph gives the work done.
as area under p–V graph gives the work done.Hence,
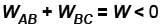
From the graph itself, it is clear that p3 > p1
The correct answer is: p3 > p1 , W < 0
Heat capacity of a substance is infinite. It means... more :Select one:a)infinite heat is given outb)infinite heat is taken inc)no change in temperature where heat is taken in or given outd)all of theseCorrect answer is option 'c'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shivansh Shukla answered |
Bcz, heat capacity means heat required to raise temperature by 1C, and if heat capacity is infinite then, this means we have to give infinite temperature to raise temperature by 1C.
Which indicates that there is no change in temperature if we give any amount of heat.
Which indicates that there is no change in temperature if we give any amount of heat.
Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken through a cycle ABCA as shown in the p-T diagram. During the process AB, Pressure and temperature of the gas vary such that pT = constant. If T1 = 300K then the work done on the gas in the process AB is
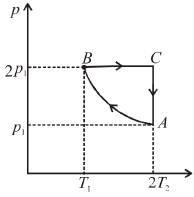
Select one:- a)–1200 R
- b)–600 R
- c)–900 R
- d)2400 R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is taken through a cycle ABCA as shown in the p-T diagram. During the process AB, Pressure and temperature of the gas vary such that pT = constant. If T1 = 300K then the work done on the gas in the process AB is

Select one:

Select one:
a)
–1200 R
b)
–600 R
c)
–900 R
d)
2400 R
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Number of moles, n = 2, T1= 300 K, T2 = 2T1 = 600 K
During process A → B
pT = constant
or p2V = constant = k [∴ pV = nRT]
p2V = k
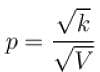
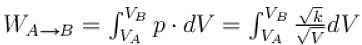

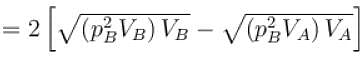
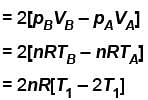
= 2 × 2 × R × [300 – 600] = -1200 R
The correct answer is: –1200 R
During process A → B
pT = constant
or p2V = constant = k [∴ pV = nRT]
p2V = k
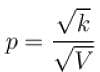
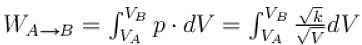

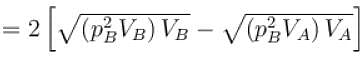
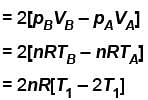
= 2 × 2 × R × [300 – 600] = -1200 R
The correct answer is: –1200 R
If a system A is in thermal equilibrium separately with B and C, then B and C are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This is the statement for.
Select one:- a)Third law of thermodynamics
- b)First law of thermodynamics
- c)Second law of thermodynamics
- d)Zeroth law of thermodynamics
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a system A is in thermal equilibrium separately with B and C, then B and C are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This is the statement for.
Select one:
Select one:
a)
Third law of thermodynamics
b)
First law of thermodynamics
c)
Second law of thermodynamics
d)
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The above statement is nothing but zeroth law of thermodynamics.
The correct answer is: Zeroth law of thermodynamics
The correct answer is: Zeroth law of thermodynamics
Steam at 100°C is passed into 1.1 kg of water ... morecontained in a calorimeter of water equivalent 0.02 kg at 15°C till the temperature of the calorimeter and its contents rises to 80°C. The mass of the steam condensed (in kg) isSelect one:a)0.065b)0.130c)0.260d)0.135Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Heat lost by steam =Heat gained by
(water +calorimeter)
(water +calorimeter)
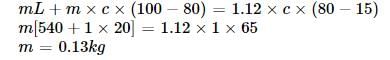
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B is
Select one:- a)42 K
- b)50 K
- c)30 K
- d)18 K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two cylinders A and B fitted with pistons contain equal amounts of an ideal diatomic gas at 300 K. The pistons of A is free to move, while that of B is kept fixed. The same amount of heat is given to the gas in each cylinder. If the rise in temperature of the gas in A is 30 K, then the rise in temperature of the gas in B is
Select one:
Select one:
a)
42 K
b)
50 K
c)
30 K
d)
18 K
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
A is free to move, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant pressure
∴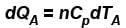 ...(i)
...(i)
B is held fixed, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant volume.
∴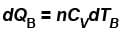 ...(ii)
...(ii)
But dQA = dQB (given)
∴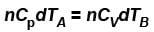
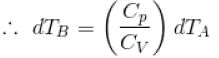
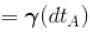 [
[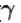 = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= (1.4) (30 K)
dTB = 42 K
The correct answer is: 42 K
∴
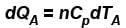 ...(i)
...(i)B is held fixed, therefore, heat will be supplied at constant volume.
∴
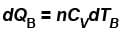 ...(ii)
...(ii)But dQA = dQB (given)
∴
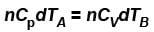
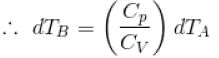
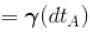 [
[ = 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)
= 1.4 (diatomic)] (dTA = 30 K)= (1.4) (30 K)
dTB = 42 K
The correct answer is: 42 K
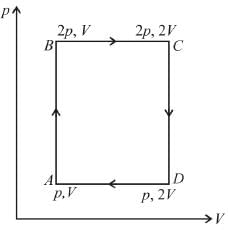
An ideal monoatomic gas is taken round that cycle ABCDA as shown in the p-V diagram (see figure). The work done during the cycle is
- a)2pV
- b)0
- c)pV
- d)pv/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal monoatomic gas is taken round that cycle ABCDA as shown in the p-V diagram (see figure). The work done during the cycle is


a)
2pV
b)
0
c)
pV
d)
pv/2
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Work done in a cyclic process = area under the graph in p-V diagram
Area = AB × BC = (2p – p) × (2V – V) = pV
∴ So, work done = pV
The correct answer is: pV
Area = AB × BC = (2p – p) × (2V – V) = pV
∴ So, work done = pV
The correct answer is: pV
Which of the following is not a property of the system?
Select one:- a)Temperature
- b)Specific heat
- c)Pressure
- d)Heat
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a property of the system?
Select one:
Select one:
a)
Temperature
b)
Specific heat
c)
Pressure
d)
Heat
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Heat is thermal energy transferred from a hotter body to a cooler body that arein contact. Hence, it is not a property of the system.
The correct answer is: Heat
The correct answer is: Heat
In a cyclic process.
Select one:
- a)Work done by the system is equal the quantity of heat given to the system
- b)The internal energy of the system increases
- c)Work done is zero
- d)Work done does not depend on the quantity of heat given to the system
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a cyclic process.
Select one:
Select one:
a)
Work done by the system is equal the quantity of heat given to the system
b)
The internal energy of the system increases
c)
Work done is zero
d)
Work done does not depend on the quantity of heat given to the system

|
Pie Academy answered |
Correct Answer :- a
Explanation : In a cyclic process, the system starts and returns to the same thermodynamic state.
Thus, change in internal energy in a cyclic process ΔU=0
From !st law of thermodynamics, ΔQ = ΔU + ΔW
⟹ ΔQ = 0 + ΔW
ΔQ = ΔW
An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature ΔT pressure remaining constant. The quantity 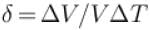 varies with temperature as
varies with temperature as
Select one:- a)
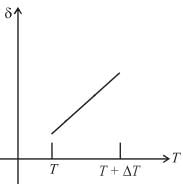
- b)
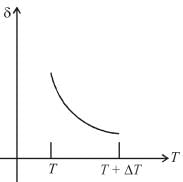
- c)
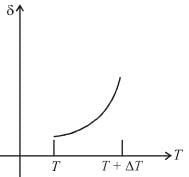
- d)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume V. Its volume is increased by ΔV due to an increase in temperature ΔT pressure remaining constant. The quantity 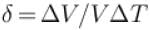 varies with temperature as
varies with temperature as
Select one:
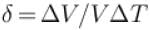 varies with temperature as
varies with temperature asSelect one:
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
For an ideal gas : pV = nRT
For p = constant
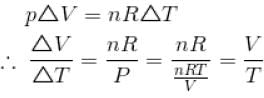

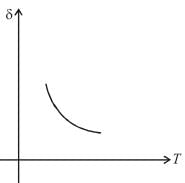
Therefore,δ is inversely proportional to temperature T i.e., when T increases, δ decreases and vice-versa.
Hence,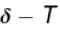 graph will be rectangular hyperbola as shown in the above figure.
graph will be rectangular hyperbola as shown in the above figure.
The correct answer is: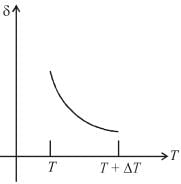

For p = constant
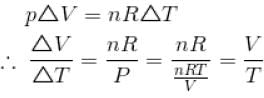

Therefore,δ is inversely proportional to temperature T i.e., when T increases, δ decreases and vice-versa.
Hence,
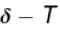 graph will be rectangular hyperbola as shown in the above figure.
graph will be rectangular hyperbola as shown in the above figure.The correct answer is:

In case of isothermal expansion, which of the following are not forbidden?
Select one or more:- a)W = 0
- b)W < Wmax
- c)W = Wmax
- d)W > Wmax
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of isothermal expansion, which of the following are not forbidden?
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
W = 0
b)
W < Wmax
c)
W = Wmax
d)
W > Wmax

|
Rohan Desai answered |
Let psurrdV work done by an ideal gas in the three types of expansion.
psurr is a pressure surrounding
Since
The maximum work is done when the gas pressure
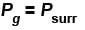
For reversible expansion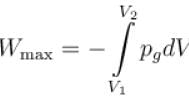
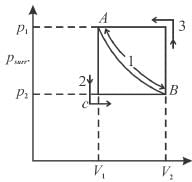
Path 2 corresponds to a permitted or irreversible expansion, in this case, work done

In a forbidden expansion i.e. one against an external pressure greater than the gas pressure, the work done by the gas would have to be grater than the maximum work, such an expansion is never observed.
∴ In case of isothermal expansion
Permitted process :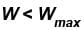
Reversible process :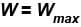
Forbidden process :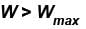
The correct answers are:
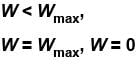
psurr is a pressure surrounding
Since

The maximum work is done when the gas pressure
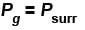
For reversible expansion
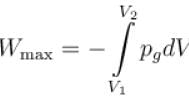

Path 2 corresponds to a permitted or irreversible expansion, in this case, work done

In a forbidden expansion i.e. one against an external pressure greater than the gas pressure, the work done by the gas would have to be grater than the maximum work, such an expansion is never observed.
∴ In case of isothermal expansion
Permitted process :
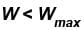
Reversible process :
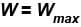
Forbidden process :
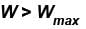
The correct answers are:
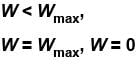
An ideal gas having initial pressure P, volume V and temperature T is allowed to expand adiabatically until its volume becomes 5.66V and its temperature falls to How many degree of freedom do gas molecule have?
Select one:- a)10
- b)7
- c)5
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas having initial pressure P, volume V and temperature T is allowed to expand adiabatically until its volume becomes 5.66V and its temperature falls to How many degree of freedom do gas molecule have?
Select one:
Select one:
a)
10
b)
7
c)
5
d)
3
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
In adiabatic process 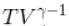 = constant
= constant
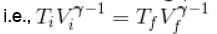
Here,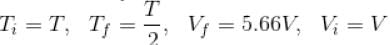
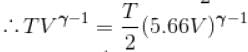
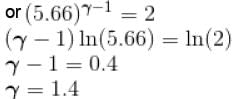
We know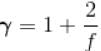
Here f = degree of freedom
So, putting the value of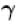
f = 5
The correct answer is: 5
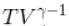 = constant
= constant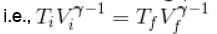
Here,
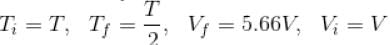
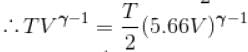
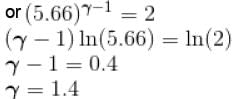
We know
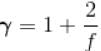
Here f = degree of freedom
So, putting the value of
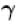
f = 5
The correct answer is: 5
A monoatomic ideal gas, initially at temperature T1, is enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is allowed to expand adiabatically to a temperature T2 by releasing the piston suddenly. If L1 and L2 are the lengths of the gas column before and after expansion respectively, then T1 /T2 is given by
Select one:- a)
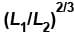
- b)
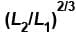
- c)L2 /L1
- d)(L1 /L2)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A monoatomic ideal gas, initially at temperature T1, is enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston. The gas is allowed to expand adiabatically to a temperature T2 by releasing the piston suddenly. If L1 and L2 are the lengths of the gas column before and after expansion respectively, then T1 /T2 is given by
Select one:
Select one:
a)
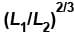
b)
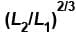
c)
L
2
/L1d)
(L1 /L2)
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
During adiabatic expansion, we known
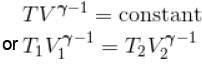
For a monoatomic gas,
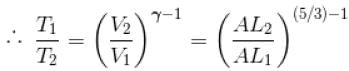 (A = Area of cross-section of piston)
(A = Area of cross-section of piston)
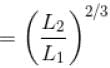
The correct answer is: (L2 /L
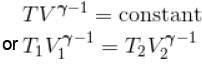
For a monoatomic gas,

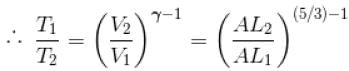 (A = Area of cross-section of piston)
(A = Area of cross-section of piston)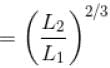
The correct answer is: (L2 /L
1
)2/3A thermos bottle containing coffee is vigorously shaken and thereby the temperature of coffee rises. Regard the coffee as the system.
Select one or more:- a)W = –ve
- b)Q = 0
- c)ΔU = +ve
- d)W = +ve
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A thermos bottle containing coffee is vigorously shaken and thereby the temperature of coffee rises. Regard the coffee as the system.
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
W = –ve
b)
Q = 0
c)
ΔU = +ve
d)
W = +ve

|
Rohan Desai answered |
The heat has not been transferred to coffee which is thermally insulated by shaking, work has been done on coffee (system) against the viscous forces in it.
According to first law,
ΔU = Q – W
Here Q = 0
And W is negative as work is done on the system so that
ΔU = 0 – (–W)
i.e. ΔU is positive. The internal energy of system (coffee) increases.
Q = 0, W = -ve, ΔU = +ve
The correct answers are: Q = 0, W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
According to first law,
ΔU = Q – W
Here Q = 0
And W is negative as work is done on the system so that
ΔU = 0 – (–W)
i.e. ΔU is positive. The internal energy of system (coffee) increases.
Q = 0, W = -ve, ΔU = +ve
The correct answers are: Q = 0, W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
Consider that 214 J of work done on a system, and 293 J of heat are extracted from the system. Then
Select one or more:- a)Q = –293 J
- b)Q = 293 J
- c)ΔU = 79 J
- d)ΔU = –79 J
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider that 214 J of work done on a system, and 293 J of heat are extracted from the system. Then
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
Q = –293 J
b)
Q = 293 J
c)
ΔU = 79 J
d)
ΔU = –79 J

|
Akshat Saini answered |
Since work is done on the system, therefore, algebraic sign of work done will be positive and magnitude of work done is 214J.
Since heat is extracted from the system,
∴ Q = –293 J
Now ΔU = Q + W
= –293 J + 214 J
ΔU = –79 J
The correct answers are: Q = –293 J, ΔU = –79 J
Since heat is extracted from the system,
∴ Q = –293 J
Now ΔU = Q + W
= –293 J + 214 J
ΔU = –79 J
The correct answers are: Q = –293 J, ΔU = –79 J
A sample of gas expands from volume V1 to V2. The amount of work done by the gas in greatest when the expansion is.
Select one:- a)equal in all case
- b)adiabatic
- c)isothermal
- d)isobaric
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A sample of gas expands from volume V1 to V2. The amount of work done by the gas in greatest when the expansion is.
Select one:
Select one:
a)
equal in all case
b)
adiabatic
c)
isothermal
d)
isobaric
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
pV curves for 3 processes are show is below. Note that the area under isobaric curve is maximum
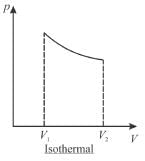
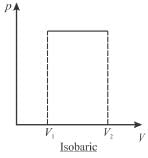
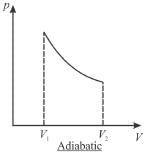
The correct answer is: isobaric



The correct answer is: isobaric
A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at temperature T. Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is- a)15 RT
- b)9 RT
- c)4 RT
- d)11 RT
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at temperature T. Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is
a)
15 RT
b)
9 RT
c)
4 RT
d)
11 RT
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Internal energy of n moles of an ideal gas at temperature T is given by
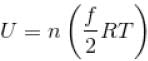
where, f = degrees of freedom
= 5 for O3 and 3 for Ar [∴ O2 is diatomic, Ar is monoatomic]
Hence,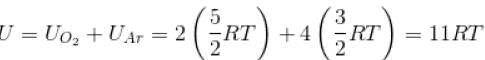
The correct answer is: 11 RT
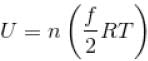
where, f = degrees of freedom
= 5 for O3 and 3 for Ar [∴ O2 is diatomic, Ar is monoatomic]
Hence,
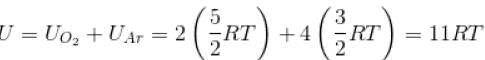
The correct answer is: 11 RT
70 cal of heat are required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at constant pressure from 30ºC to 35°C. The amount of heat required (in calorie) to raise the temperature of the same gas through the same range (30°C to 35°C) at constant volume is- a)50
- b)90
- c)70
- d)30
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
70 cal of heat are required to raise the temperature of 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at constant pressure from 30ºC to 35°C. The amount of heat required (in calorie) to raise the temperature of the same gas through the same range (30°C to 35°C) at constant volume is
a)
50
b)
90
c)
70
d)
30
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
We know that heat required to raise the temperature at constant pressure is Cp.
So,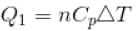
Similarly, at constant volume CV

or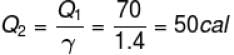
The correct answer is: 50
So,
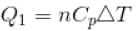
Similarly, at constant volume CV

or
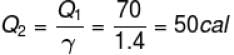
The correct answer is: 50
The piston containing an ideal gas is originally is the state x (see figure). The gas is taken through a thermal cycle 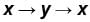 as shown.
as shown.
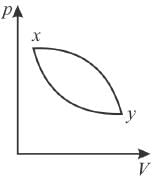
The work done by the gas is positive, if the direction of the thermal cycle is
Select one:- a)neither clockwise nor counter clockwise
- b)clockwise
- c)counter-clockwise
- d)clockwise from x → y and counter clockwise from i to x
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The piston containing an ideal gas is originally is the state x (see figure). The gas is taken through a thermal cycle 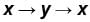 as shown.
as shown.

The work done by the gas is positive, if the direction of the thermal cycle is
Select one:
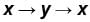 as shown.
as shown.
The work done by the gas is positive, if the direction of the thermal cycle is
Select one:
a)
neither clockwise nor counter clockwise
b)
clockwise
c)
counter-clockwise
d)
clockwise from x → y and counter clockwise from i to x
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Since work done = Area between p-V curve and volume axis
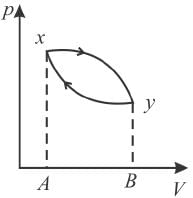
Hence, work in positive direction is clockwise
Wxy = Area xyBA
W
and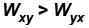
The correct answer is: clockwise

Hence, work in positive direction is clockwise
Wxy = Area xyBA
W
yx
= Area yBAxand
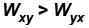
The correct answer is: clockwise
One gram of water on evaporation at atmospheric pressure forms 1671cm3 of steam. Heat of vaporization at this pressure is 540 cal/g. The increase in internal energy is
Select one:- a)1000 cal
- b)1500 cal
- c)500 cal
- d)250 cal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One gram of water on evaporation at atmospheric pressure forms 1671cm3 of steam. Heat of vaporization at this pressure is 540 cal/g. The increase in internal energy is
Select one:
Select one:
a)
1000 cal
b)
1500 cal
c)
500 cal
d)
250 cal
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
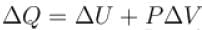
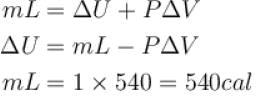
or
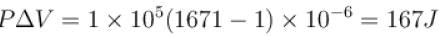
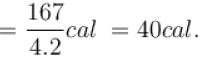
∴
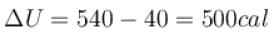
The correct answer is: 500 cal
A system changes from the state (p1, V1 ) to the state (p2, V2 ) as shown in the figure. The work done by the system is.
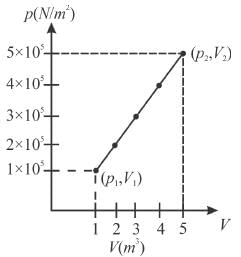
Select one:- a)6 × 105J
- b)7.5 × 105 ergs
- c)7.5 × 105J
- d)12 × 105J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A system changes from the state (p1, V1 ) to the state (p2, V2 ) as shown in the figure. The work done by the system is.

Select one:

Select one:
a)
6 × 105J
b)
7.5 × 105 ergs
c)
7.5 × 105J
d)
12 × 105J

|
Pie Academy answered |
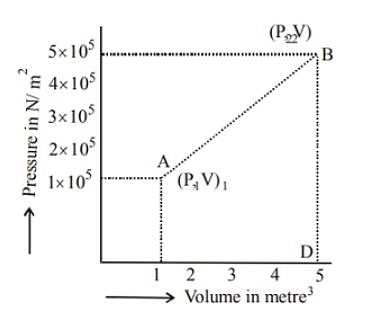
Work done = Area of graph ABD;
From above we get,
Area = 1/2 × 4 (1 × 105 + 5 × 105) = 2 × 6 × 105 = 12 × 105J
A cyclic process ABCA shown in the V-T diagram is performed with a constant mass of an ideal gas. Show the same process on a P-V diagram
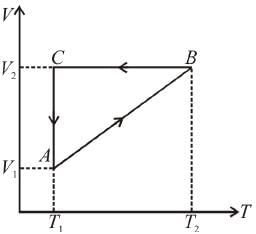
Select one:- a)

- b)
- c)
- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cyclic process ABCA shown in the V-T diagram is performed with a constant mass of an ideal gas. Show the same process on a P-V diagram

Select one:

Select one:
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Process A → B
From the graph,
From ideal gas equation, pV = nRT
⇒ p = constant
⇒ A → B, is isobaric process
So, in process A → B, when volume increases, pressure remains constant.
So, pV graph will be straight line parallel to V–axis as p = constant
Process B → C
From the graph, V = constant
From ideal gas equation, pV = nRT
⇒ pV = nRT
 [V is constant]
[V is constant]
But from the graph T is decreasing, so p also decrease.
But V remain constant.
pV graph will be straight line parallel to p-axis as V = constant
Process C → A
From the graph,
T = constant
From ideal gas equation, pV = nRT
⇒pV = nRT [T is constant]
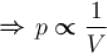
But from the graph, V decreases, so p should increase.
so, pV graph will be rectangular hyperbola as
The correct answer is:
From the graph,
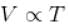
From ideal gas equation, pV = nRT
⇒ p = constant
⇒ A → B, is isobaric process
So, in process A → B, when volume increases, pressure remains constant.
So, pV graph will be straight line parallel to V–axis as p = constant
Process B → C
From the graph, V = constant
From ideal gas equation, pV = nRT
⇒ pV = nRT
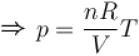 [V is constant]
[V is constant]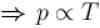
But from the graph T is decreasing, so p also decrease.
But V remain constant.
pV graph will be straight line parallel to p-axis as V = constant
Process C → A
From the graph,
T = constant
From ideal gas equation, pV = nRT
⇒pV = nRT [T is constant]
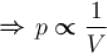
But from the graph, V decreases, so p should increase.
so, pV graph will be rectangular hyperbola as

The correct answer is:

If W is the work done by a system against its surrounding, what will –W stand for ?
Select one:- a)Work done on the system by its surroundings
- b)Work done by the system on its surroundings
- c)Work done is zero
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If W is the work done by a system against its surrounding, what will –W stand for ?
Select one:
Select one:
a)
Work done on the system by its surroundings
b)
Work done by the system on its surroundings
c)
Work done is zero
d)
None of the above
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
If W is work done by the system then –W would be the work done on the system by its surroundings.
The correct answer is: Work done on the system by its surroundings
The correct answer is: Work done on the system by its surroundings
A resistor immersed in running water carries an electric current. Consider the resistor as the system.
Select one or more:- a)W = –ve, ΔU = –ve
- b)W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
- c)Q = 0
- d)W = +ve, ΔU = +ve
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A resistor immersed in running water carries an electric current. Consider the resistor as the system.
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
W = –ve, ΔU = –ve
b)
W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
c)
Q = 0
d)
W = +ve, ΔU = +ve

|
Rohan Desai answered |
There is no flow of heat into the resistor and work is done on the resistor (system).
According to first law as applied to the system, we write,
ΔU = Q – W
For resistor Q = 0
W = –ve. Thus
ΔU = 0 – (–W) = W
∴ Q = 0; W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
The correct answers are: Q = 0, W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
According to first law as applied to the system, we write,
ΔU = Q – W
For resistor Q = 0
W = –ve. Thus
ΔU = 0 – (–W) = W
∴ Q = 0; W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
The correct answers are: Q = 0, W = –ve, ΔU = +ve
An ideal gas is taken through the cycle A → B → C → A a shown in the figure. If the net heat supplied to the gas in the cycle is 5J, the work done by the gas in the process C → A is
- a)–15 J
- b)–20 J
- c)–10 J
- d)–5 J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas is taken through the cycle A → B → C → A a shown in the figure. If the net heat supplied to the gas in the cycle is 5J, the work done by the gas in the process C → A is


a)
–15 J
b)
–20 J
c)
–10 J
d)
–5 J
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
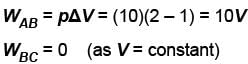
From first law of thermodynamics
Q = W + ΔU
ΔU = 0 (process ABCA is cyclic)
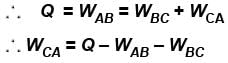
= 5 – 10 – 0 = –5 J
The correct answer is: –5 J
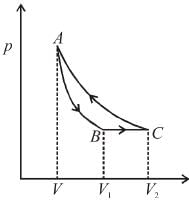
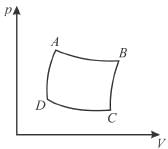
The pressure-volume graph of an ideal gas cycle consisting of isothermal and adiabatic process is shown in the figure. The adiabatic process is described by
Select one:- a)AD and BC
- b)AB and CD
- c)AB and BC
- d)BC and CD
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure-volume graph of an ideal gas cycle consisting of isothermal and adiabatic process is shown in the figure. The adiabatic process is described by

Select one:

Select one:
a)
AD and BC
b)
AB and CD
c)
AB and BC
d)
BC and CD
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
BC and DA represent the adiabatic expansion and the compression since we know that the adiabatic curves are more steeper than isothermal curves.
The correct answer is: AD and BC
The correct answer is: AD and BC
First law of the thermodynamics is conservation of.
Select one:- a)momentum
- b)energy
- c)both (a) and (b)
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
First law of the thermodynamics is conservation of.
Select one:
Select one:
a)
momentum
b)
energy
c)
both (a) and (b)
d)
none
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
dθ = dU + dW
The correct answer is: energy
The correct answer is: energy
Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contains the same ideal gas at the same temperature and the same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume 2V. The changes in the pressure in A and B are found to be Δp and 1.5 Δp respectively. Then
Select one:- a)
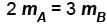
- b)
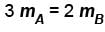
- c)
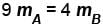
- d)

Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contains the same ideal gas at the same temperature and the same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume 2V. The changes in the pressure in A and B are found to be Δp and 1.5 Δp respectively. Then
Select one:
Select one:
a)
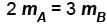
b)
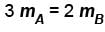
c)
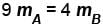
d)

|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Process is isothermal. Therefore, T = constant. 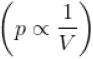 volume is increasing, therefore, pressure will decrease.
volume is increasing, therefore, pressure will decrease.
In chamber A, as Pressure decrease,
So,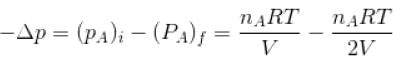
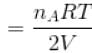 ...(i)
...(i)
Similarly, in chamber B→
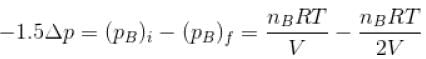
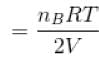 ...(ii)
...(ii)
From equation (1) and (2)
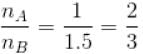
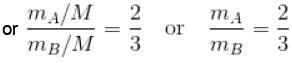
or 2mA = 2mA
The correct answer is: 3 mA = 2 mB
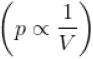 volume is increasing, therefore, pressure will decrease.
volume is increasing, therefore, pressure will decrease.In chamber A, as Pressure decrease,
So,
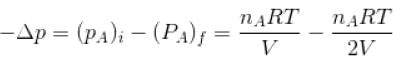
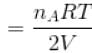 ...(i)
...(i)Similarly, in chamber B→
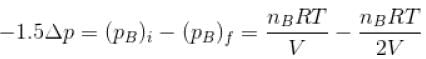
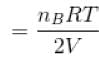 ...(ii)
...(ii)From equation (1) and (2)
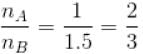
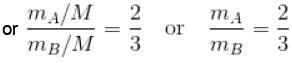
or 2mA = 2mA
The correct answer is: 3 mA = 2 mB
In the pV diagram below, which is the correct statement?
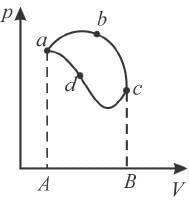
Select one:- a)Any point on the line abc represents a higher temperature then any point on adc
- b)The area abcda represents the work done by the system for the process
- c)The path abc and adc represents isotherm
- d)Heat is lost to the surroundings during the process is represented by path adc
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the pV diagram below, which is the correct statement?

Select one:

Select one:
a)
Any point on the line abc represents a higher temperature then any point on adc
b)
The area abcda represents the work done by the system for the process
c)
The path abc and adc represents isotherm
d)
Heat is lost to the surroundings during the process is represented by path adc

|
Pie Academy answered |
In a cyclic process as shown above, the area enclosed by the curve gives the work done by the system.
The correct answer is: The area abcda represents the work done by the system for the process
The correct answer is: The area abcda represents the work done by the system for the process
An ideal gas has specific heat at constant pressure 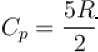 The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The final pressure and temperature of the gas are
Select one:
- a)2.6 × 16 N/m2, 500 K
- b)3.6 × 106 N/m2 , 675 K
- c)1.2 × 106 N/m2 , 375 K
- d)7.2 × 106 N/m2, 300 K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas has specific heat at constant pressure 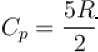 The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The final pressure and temperature of the gas are
Select one:
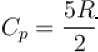 The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.
The gas is kept in a closed vessel of volume 0.00833m , at a temperature of 300K and a pressure of 1.6 × 106N/m2. An amount of 2.49 × 104J of heat energy is supplied to the gas.The final pressure and temperature of the gas are
Select one:
a)
2.6 × 16 N/m2, 500 K
b)
3.6 × 106 N/m2 , 675 K
c)
1.2 × 106 N/m2 , 375 K
d)
7.2 × 106 N/m2, 300 K
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Vessel is closed. Therefore, ΔW = 0
From first law of thermodynamics and ideal gas equation.
Q = ΔU + W
and pV = nRT
∴ W = 0
⇒ Q = ΔU
Also, Δ = nCVΔT
or,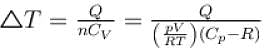
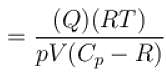
Substituting the values, we have
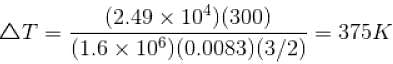
ΔT = 375K
Tf = ΔT + T = 675K
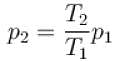
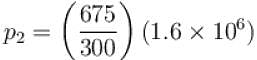
= 3.6 × 106N/m2
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
From first law of thermodynamics and ideal gas equation.
Q = ΔU + W
and pV = nRT
∴ W = 0
⇒ Q = ΔU
Also, Δ = nCVΔT
or,
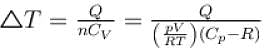
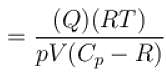
Substituting the values, we have
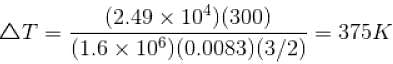
ΔT = 375K
Tf = ΔT + T = 675K
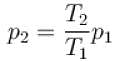
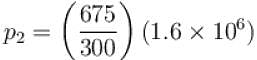
= 3.6 × 106N/m2
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
A water fall is 168m high. Assuming that half the kinetic energy of the falling water gets converted into heat, the rise in temperature of water is approximately (take g = 10m/s2)
Select one:- a)0.4ºC
- b)0.2ºC
- c)0.1ºC
- d)0.3ºC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A water fall is 168m high. Assuming that half the kinetic energy of the falling water gets converted into heat, the rise in temperature of water is approximately (take g = 10m/s2)
Select one:
Select one:
a)
0.4ºC
b)
0.2ºC
c)
0.1ºC
d)
0.3ºC
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
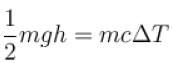
⇒
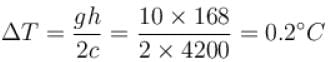
The correct answer is: 0.2ºC
Which type of ideal gas will have largest value of CP – CV?
Select one or more:- a)Monatomic
- b)Diatomic
- c)Polyatomic
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of ideal gas will have largest value of CP – CV?
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
Monatomic
b)
Diatomic
c)
Polyatomic
d)
None of the above
|
|
Waanya Singh answered |
The type of ideal gas that will have the largest value of CP is a monatomic gas.
In thermodynamics, CP refers to the molar heat capacity at constant pressure. For a monatomic gas, the heat capacity at constant pressure (CP) is given by:
CP = (5/2)R
Where R is the gas constant. The factor of (5/2) arises from the fact that a monatomic gas has three degrees of freedom for translation, and two degrees of freedom for rotation (since it does not have any rotational energy associated with vibration). Therefore, a monatomic gas has a higher CP value compared to diatomic or polyatomic gases, which have additional degrees of freedom associated with molecular vibrations.
Thus, a monatomic gas will have the largest value of CP among ideal gases.
In thermodynamics, CP refers to the molar heat capacity at constant pressure. For a monatomic gas, the heat capacity at constant pressure (CP) is given by:
CP = (5/2)R
Where R is the gas constant. The factor of (5/2) arises from the fact that a monatomic gas has three degrees of freedom for translation, and two degrees of freedom for rotation (since it does not have any rotational energy associated with vibration). Therefore, a monatomic gas has a higher CP value compared to diatomic or polyatomic gases, which have additional degrees of freedom associated with molecular vibrations.
Thus, a monatomic gas will have the largest value of CP among ideal gases.
1 mole of ideal monoatomic gas at 27ºC expands under adiabatic conditions at a pressure of 1.5 atm from a volume of 4dm3 to 16dm3.
Select one or more:- a)

- b)
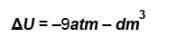
- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
1 mole of ideal monoatomic gas at 27ºC expands under adiabatic conditions at a pressure of 1.5 atm from a volume of 4dm3 to 16dm3.
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)

b)
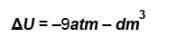
c)

d)


|
Pie Academy answered |
Since processes is adiabatic q = 0.
As the gas expands against constant external processes

= –1.5(16–4) = –18atm-dm3
ΔU = Q + W = 0 + (–18) = –18atm-dm3
The correct answers are: W = –18atm – dm3 , ΔU = –18atm – dm3
As the gas expands against constant external processes

= –1.5(16–4) = –18atm-dm3
ΔU = Q + W = 0 + (–18) = –18atm-dm3
The correct answers are: W = –18atm – dm3 , ΔU = –18atm – dm3
A body of mass 25kg is dragged on a rough horizontal road for one hour with a speed of 20km/hr.
If the coefficient of friction is 0.5 and half of the heat produced is absorbed by the body, the rise in its temperature is (specific heat of body = 0.1cal/g ºC, g = 10m/s2)
Select one:- a)59.5ºC
- b)84.5ºC
- c)39ºC
- d)119ºC
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass 25kg is dragged on a rough horizontal road for one hour with a speed of 20km/hr.
If the coefficient of friction is 0.5 and half of the heat produced is absorbed by the body, the rise in its temperature is (specific heat of body = 0.1cal/g ºC, g = 10m/s2)
Select one:
If the coefficient of friction is 0.5 and half of the heat produced is absorbed by the body, the rise in its temperature is (specific heat of body = 0.1cal/g ºC, g = 10m/s2)
Select one:
a)
59.5ºC
b)
84.5ºC
c)
39ºC
d)
119ºC
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Distance traveled in one hour,
S = 20km
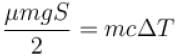
Now,⇒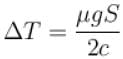
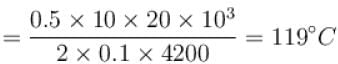
The correct answer is: 119ºC
S = 20km
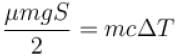
Now,⇒
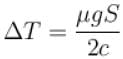
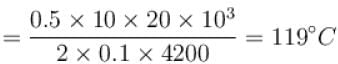
The correct answer is: 119ºC
Which among the following statements are correct?
Select one or more:- a)Energy is an extensive property
- b)Energy is a point function
- c)Heat capacity is an extensive property
- d)Specific energy is an extensive property
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following statements are correct?
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
Energy is an extensive property
b)
Energy is a point function
c)
Heat capacity is an extensive property
d)
Specific energy is an extensive property

|
Stuti Patel answered |
Energy changes with mass of the body, therefore, it is an extensive property.
Specific energy is the energy of the system per unit mass of the system, therefore, it will become intensive property. Heat capacity is product of specific heat and mass of the body. It depends on mass of the system,
∴ heat capacity is an extensive property. Internal energy of the system is independent of the path followed by system. It has fixed value along the path
∴ energy is the point function
The correct answers are: Energy is an extensive property, Energy is a point function, Heat capacity is an extensive property
Specific energy is the energy of the system per unit mass of the system, therefore, it will become intensive property. Heat capacity is product of specific heat and mass of the body. It depends on mass of the system,
∴ heat capacity is an extensive property. Internal energy of the system is independent of the path followed by system. It has fixed value along the path
∴ energy is the point function
The correct answers are: Energy is an extensive property, Energy is a point function, Heat capacity is an extensive property
Which of the following are path function?
Select one or more:- a)Work
- b)None
- c)Heat Energy
- d)Internal energy
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are path function?
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
Work
b)
None
c)
Heat Energy
d)
Internal energy

|
Rohan Desai answered |
Heat transfer as well as work transfer between the system and surrounding depends upon the path by which the process is occurred. Therefore heat energy and work energy are path function. The change in internal energy ΔE remains constant, no matter which path is followed by a system to undergo a change of a certain state. Thus, internal energy is a point function or state function.
The correct answers are: Heat Energy, Work
The correct answers are: Heat Energy, Work
p-V plots for two gas during adiabatic process are shown in the figure. Plots 1 and 2 should correspond respectively to

Select one:- a)O2 and He
- b)O2 and H2
- c)O2 and N2
- d)He and Ar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
p-V plots for two gas during adiabatic process are shown in the figure. Plots 1 and 2 should correspond respectively to

Select one:

Select one:
a)
O2 and He
b)
O2 and H2
c)
O2 and N2
d)
He and Ar

|
Pie Academy answered |
For adiabatic processes, PVγ=constant
When Pressure decrease, Volume has to increase to maintain the above relation.
Even as Volume increases, the increase is volume would be higher when the exponent γ has a lower value than when the value of γ is higher.
So, when γ is higher, for monoatomic it is 1.6, the value of V is smaller compared to the value of V for which γ is lower, diatomic it is 1.4
Hence, Plot 1 corresponds to lower γ-diatomic - O2
Plot 2 corresponds to higher γ-monoatomic - He
When Pressure decrease, Volume has to increase to maintain the above relation.
Even as Volume increases, the increase is volume would be higher when the exponent γ has a lower value than when the value of γ is higher.
So, when γ is higher, for monoatomic it is 1.6, the value of V is smaller compared to the value of V for which γ is lower, diatomic it is 1.4
Hence, Plot 1 corresponds to lower γ-diatomic - O2
Plot 2 corresponds to higher γ-monoatomic - He
In an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas,
Select one or more:- a)ΔH = 0
- b)ΔQ = 0
- c)ΔW = 0
- d)ΔU = 0
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas,
Select one or more:
Select one or more:
a)
ΔH = 0
b)
ΔQ = 0
c)
ΔW = 0
d)
ΔU = 0

|
Jay Nambiar answered |
For one mole of an ideal gas
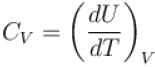
⇒ dU = CVdT
For isothermal process, T is constant
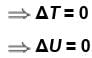
Also ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV)
pV = RT

= ΔU + RΔT
ΔH = 0.
The correct answers are: ΔU = 0, ΔH = 0
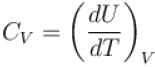
⇒ dU = CVdT
For isothermal process, T is constant
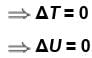
Also ΔH = ΔU + Δ(pV)
pV = RT

= ΔU + RΔT
ΔH = 0.
The correct answers are: ΔU = 0, ΔH = 0
Chapter doubts & questions for First law of thermodynamics - Physics for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of First law of thermodynamics - Physics for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for ACT
169 videos|131 docs|69 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup