All Exams >
JAMB >
Chemistry for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Halogens for JAMB Exam
HClO is known as- a)chloric acid
- b)Chlorine
- c)bacteria killer
- d)water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
HClO is known as
a)
chloric acid
b)
Chlorine
c)
bacteria killer
d)
water
|
|
Nada Sharin answered |
Hypohalous acid is also known as CHLORIC (I) ACID
Find the sum of bond pairs and non-bonding electron pairs in ICI molecule.
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the sum of bond pairs and non-bonding electron pairs in ICI molecule.

|
Tarun Chakraborty answered |
3 lone pairs and 1 bond pair.
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
In the MOT of F2 molecule, number of electrons occupying antibonding orbitals are
|
|
Nandita Ahuja answered |
Fluorine atom have 2+7 electrons so an F2 molecule contain 18 electrons.
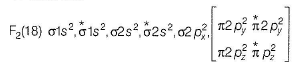
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
Hence, 8 electrons occupy the antibonding orbitals.
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?- a)SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
- c)Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
- d)Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is incorrect ?
a)
SRP values of halogens F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
Bond dissociation enthalpy of Br2 > F2 > Cl2 > I2
c)
Boiling points of I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
d)
Reducing power of I- > Br- > Cl- > F-
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct order of bond dissociation enthalpy is
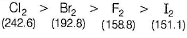
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Regarding the properties of hydrogen halides, which is wrong order?- a)Melting point order HI> HF > HBr > HCI
- b)Boiling point order HF > HI > HBr > HC
- c)Acidic nature HI > HBr > HCI > HF
- d)Percentage of ionic character HF > HI > HBr > HCI
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Regarding the properties of hydrogen halides, which is wrong order?
a)
Melting point order HI> HF > HBr > HCI
b)
Boiling point order HF > HI > HBr > HC
c)
Acidic nature HI > HBr > HCI > HF
d)
Percentage of ionic character HF > HI > HBr > HCI
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct order of % of ionic character is
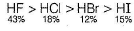
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are- a)NaCI
- b)NaOCI
- c)NaCIO3
- d)HCI
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
When chlorine reacts with hot, cone. NaOH, the products formed are
a)
NaCI
b)
NaOCI
c)
NaCIO3
d)
HCI

|
Anupama Nair answered |
When Cl2 reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH, then....6NaOH+3Cl2→5NaCl +NaClO3+3H2O...When Cl2 reacts with cold and dilute NaOH then ...2NaOH+Cl2→NaCl+NaOCl+H2O
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
The total number of positive oxidation states shown by fluorine is
|
|
Puja Gupta answered |
Fluorine is an element that belongs to the halogen group in the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 9, and its electron configuration is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^5. Fluorine is highly electronegative, meaning it has a strong tendency to attract electrons towards itself when it forms chemical bonds. This property is due to its relatively small atomic size and high effective nuclear charge.
Fluorine has a total of 7 valence electrons, which are electrons in its outermost energy level (2s^2 2p^5). In order to achieve a stable electron configuration, fluorine tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. By gaining one electron, fluorine achieves a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, neon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6).
Fluorine's strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain electrons result in it having only one common oxidation state, which is -1. In this oxidation state, fluorine gains one electron to achieve a stable configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. This oxidation state is commonly observed in compounds where fluorine acts as an anion, such as in the compound sodium fluoride (NaF). In NaF, fluorine gains an electron from sodium to form the F- ion.
It is important to note that although fluorine is highly electronegative and tends to gain electrons, it does not have the capability to lose electrons easily and form positive oxidation states. This is because fluorine's valence shell is almost full, and losing electrons would require a significant amount of energy.
In conclusion, fluorine has only one common oxidation state, which is -1. This is due to its strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Fluorine has a total of 7 valence electrons, which are electrons in its outermost energy level (2s^2 2p^5). In order to achieve a stable electron configuration, fluorine tends to gain one electron to complete its octet. By gaining one electron, fluorine achieves a stable electron configuration similar to the nearest noble gas, neon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6).
Fluorine's strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain electrons result in it having only one common oxidation state, which is -1. In this oxidation state, fluorine gains one electron to achieve a stable configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6. This oxidation state is commonly observed in compounds where fluorine acts as an anion, such as in the compound sodium fluoride (NaF). In NaF, fluorine gains an electron from sodium to form the F- ion.
It is important to note that although fluorine is highly electronegative and tends to gain electrons, it does not have the capability to lose electrons easily and form positive oxidation states. This is because fluorine's valence shell is almost full, and losing electrons would require a significant amount of energy.
In conclusion, fluorine has only one common oxidation state, which is -1. This is due to its strong electronegativity and its tendency to gain one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Mixture which contains equal amount of sodium chloride (NaCl) and sodium chlorate (NaClO3) gives off- a)bleach
- b)aerosols
- c)solvents
- d)refrigerants
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mixture which contains equal amount of sodium chloride (NaCl) and sodium chlorate (NaClO3) gives off
a)
bleach
b)
aerosols
c)
solvents
d)
refrigerants
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option A
On decomposition of NaClO3 , it gives NaCl and O in nascent form. it might get decomposed. As we know nascent [O] shows bleaching action due to its oxidizing properties.
Which of the following shows disproportionation reaction?
a)CaF2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2HFb)Cl2 + 2OH- → Cl + OCI- + H2Oc)Br- + 3OCI- → BrO-3 + 3CI-d)HOI + 2HCL → H+ + ICI-2 + H2OCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Sinjini Tiwari answered |
Cl2 + 2OH- → Cl + OCI- + H2O is not a disproportionation reaction.
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.Q. Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below. 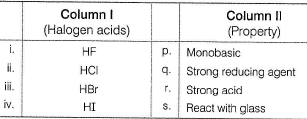
- a)
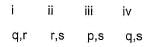
- b)

- c)

- d)
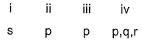
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
a)
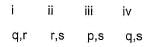
b)

c)

d)
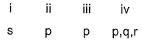

|
Ishita Deshpande answered |
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q.Paramagnetic oxide among the following is/are- a)CIO2
- b)Cl2O
- c)NO2
- d)NO
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Paramagnetic oxide among the following is/are
a)
CIO2
b)
Cl2O
c)
NO2
d)
NO

|
Rashi Bose answered |
Paramagnetic oxide has unpaired electrons or odd number of electrons.
Which is incorrect statement?- a)The stability of oxides formed by l > Br > Cl
- b)Fluorine forms only one oxoacid while other halogens form different oxoacids
- c)I2O5 is very good oxidising agent and used in the estimation of CO
- d)CIO2 is used as a bleaching agent for paper pulp and textiles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is incorrect statement?
a)
The stability of oxides formed by l > Br > Cl
b)
Fluorine forms only one oxoacid while other halogens form different oxoacids
c)
I2O5 is very good oxidising agent and used in the estimation of CO
d)
CIO2 is used as a bleaching agent for paper pulp and textiles

|
Gauri Sharma answered |
As we move down the group, stability of oxides decreases because the size increases.
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-24) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The total number of lone pairs in Cl2O molecule are ............
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 21-24) This section contains 4 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The total number of lone pairs in Cl2O molecule are ............

|
Mrinalini Chopra answered |
Two lone pairs on oxygen and three lone pairs on each chlorine.
The reaction 3ClO-(aq) → 2Cl- (aq) + ClO3-(aq) is an example of- a)oxidation reaction
- b)reduction reaction
- c)disproportionation reaction
- d)decomposition reaction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction 3ClO-(aq) → 2Cl- (aq) + ClO3-(aq) is an example of
a)
oxidation reaction
b)
reduction reaction
c)
disproportionation reaction
d)
decomposition reaction

|
Mrinalini Chopra answered |
The reaction in which a species is simultaneously reduced and oxidised to form two different products is known as disproportionation reaction.
A salt A when heated with K2Cr2O7 and cone. H2SO4 liberates a gas which is absorbed in NaOH solution. The NaOH solution turns yellow. When this solution is acidified with acetic acid and lead acetate solution is added, a yellow precipitate B is formed. When A is mixed with MnO2 and heated with cone. H2SO4 , a gas C is evolved which turns a starch-iodide paper blue.Q. When the salt A is heated with cone. H2SO4, colourless gas is evolved which gives dense fumes when exposed with ammonia. The gas is- a)chlorine
- b)HCI
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)SO2 and HCI
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A salt A when heated with K2Cr2O7 and cone. H2SO4 liberates a gas which is absorbed in NaOH solution. The NaOH solution turns yellow. When this solution is acidified with acetic acid and lead acetate solution is added, a yellow precipitate B is formed. When A is mixed with MnO2 and heated with cone. H2SO4 , a gas C is evolved which turns a starch-iodide paper blue.
Q.
When the salt A is heated with cone. H2SO4, colourless gas is evolved which gives dense fumes when exposed with ammonia. The gas is
a)
chlorine
b)
HCI
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
SO2 and HCI

|
Prashanth Banerjee answered |
Chloride salt produce colourless HCI vapours with conc. H2SO4 and these become dense due to NH4Cl on exposure to ammonia.
Correct order of bond angles are in - a)H2O > OF2 > Cl2O > CIO2
- b)CIO2 > Cl2O > H2O > OF2
- c)OF2 > H2O > Cl2O > ClO2
- d)OF2 > OCI2 > H2O > CIO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct order of bond angles are in
a)
H2O > OF2 > Cl2O > CIO2
b)
CIO2 > Cl2O > H2O > OF2
c)
OF2 > H2O > Cl2O > ClO2
d)
OF2 > OCI2 > H2O > CIO2

|
Ishita Deshpande answered |
In CIO2, due to larger size of chlorine atom, repulsion between non-bonding electrons on the chlorine atoms overcome the lone pair-lone pair repulsion. Hence, the order of bond angle
CIO2 > Cl2O > H2O > OF2
CIO2 > Cl2O > H2O > OF2
Identify the interhalogen compound with zero dipole moment,- a)ICl3
- b)BrF5
- c) IF7
- d) IF5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the interhalogen compound with zero dipole moment,
a)
ICl3
b)
BrF5
c)
IF7
d)
IF5

|
Mrinalini Chopra answered |
Due to pentagonal bipyramidal geometry, IF7 has zero dipole momen
In XA5, the central atom has (both X and A are halogens)- a)5 bond pairs and no lone pairs
- b)5 bond pairs and one lone pair
- c)6 bond pairs and no lone pairs
- d)4 bond pairs and one lone pair
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In XA5, the central atom has (both X and A are halogens)
a)
5 bond pairs and no lone pairs
b)
5 bond pairs and one lone pair
c)
6 bond pairs and no lone pairs
d)
4 bond pairs and one lone pair

|
Maitri Sharma answered |
It has square pyramidal shape and it has 5 bond pairs and one lone pair.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. The fluoride ores are- a)carnalite
- b)cryolite
- c)fluorspar
- d)chile saltpetre
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
The fluoride ores are
a)
carnalite
b)
cryolite
c)
fluorspar
d)
chile saltpetre

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
The cryolite (Na3AIF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) are two ores of fluoride.
Solid iodine is an example of- a)covalent solid
- b)ionic solid
- c)molecular solid
- d)metallic solid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Solid iodine is an example of
a)
covalent solid
b)
ionic solid
c)
molecular solid
d)
metallic solid

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
Solid iodine is a molecular solid.
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from- a)zero to +1 and zero to -5
- b)zero to -1 and zero to +5
- c)zero to -1 and zero to +5
- d)zero to +1 and zero to -3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When Cl2 gas reacts with hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, the oxidation number of chlorine changes from
a)
zero to +1 and zero to -5
b)
zero to -1 and zero to +5
c)
zero to -1 and zero to +5
d)
zero to +1 and zero to -3

|
Shail Chakraborty answered |
When chlorine gas reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH solution, it disproportionates into Chloride (Cl-) and Chlorate (ClO3-) ions.
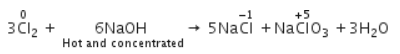
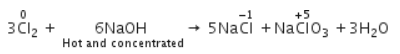
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : All halogens are coloured.Statement II : Halogens absorbs part of the light in the visible region.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : All halogens are coloured.
Statement II : Halogens absorbs part of the light in the visible region.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
Halogen molecule absorbs light in the visible region as a result of which their electrons are excited to higher energy level while the remaining light is transmitted.
The colour of halogens is actually the colour of this transmitted light, i.e. halogens have complementary colours.
The colour of halogens is actually the colour of this transmitted light, i.e. halogens have complementary colours.
Which of the following arrangements gives the correct order of increasing oxidation number of iodine?- a)I2 < HI < ICI < HIO4
- b)HI < ICI < I2 < HIO4
- c)ICI < HI < HIO4< I2
- d)HI < I2< ICI < HIO4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following arrangements gives the correct order of increasing oxidation number of iodine?
a)
I2 < HI < ICI < HIO4
b)
HI < ICI < I2 < HIO4
c)
ICI < HI < HIO4< I2
d)
HI < I2< ICI < HIO4

|
Preethi Kaur answered |
Correct answer: Option D
To determine the correct order of increasing oxidation number of iodine in the given arrangements, we need to understand the concept of oxidation numbers and how they change in different compounds.
Oxidation number is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds in a compound were 100% ionic. It is a useful tool for keeping track of electron transfers during chemical reactions.
In the given arrangements, we have the following compounds:
a) I2, HI, ICI, HIO4
b) HI, ICI, I2, HIO4
c) ICI, HI, HIO4, I2
d) HI, I2, ICI, HIO4
Explanation:
In order to determine the oxidation number of iodine in each compound, we need to consider the following rules:
1. The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge.
3. In compounds, the oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, and the oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2.
4. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero, and it is equal to the charge of the compound in an ion.
Now, let's analyze each compound in the given arrangements and determine the oxidation number of iodine:
a) I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
HIO4: Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2, and since the total oxidation number of the compound is zero, iodine in HIO4 has an oxidation number of +7.
b) HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
HIO4: Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2, and since the total oxidation number of the compound is zero, iodine in HIO4 has an oxidation number of +7.
c) ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
HIO4: Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2, and since the total oxidation number of the compound is zero, iodine in HIO4 has an oxidation number of +7.
I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
d) HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
To determine the correct order of increasing oxidation number of iodine in the given arrangements, we need to understand the concept of oxidation numbers and how they change in different compounds.
Oxidation number is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds in a compound were 100% ionic. It is a useful tool for keeping track of electron transfers during chemical reactions.
In the given arrangements, we have the following compounds:
a) I2, HI, ICI, HIO4
b) HI, ICI, I2, HIO4
c) ICI, HI, HIO4, I2
d) HI, I2, ICI, HIO4
Explanation:
In order to determine the oxidation number of iodine in each compound, we need to consider the following rules:
1. The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to its charge.
3. In compounds, the oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, and the oxidation number of oxygen is usually -2.
4. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is zero, and it is equal to the charge of the compound in an ion.
Now, let's analyze each compound in the given arrangements and determine the oxidation number of iodine:
a) I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
HIO4: Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2, and since the total oxidation number of the compound is zero, iodine in HIO4 has an oxidation number of +7.
b) HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
HIO4: Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2, and since the total oxidation number of the compound is zero, iodine in HIO4 has an oxidation number of +7.
c) ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
HIO4: Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2, and since the total oxidation number of the compound is zero, iodine in HIO4 has an oxidation number of +7.
I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
d) HI: Hydrogen usually has an oxidation number of +1.
I2: The oxidation number of a free element is always zero.
ICI: Since the total oxidation number of a compound is zero, and hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, we can deduce that iodine in ICI has an oxidation number of +1.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following property decreases down the group in the halogens?- a)Electropositive nature
- b)Density
- c)Boiling point
- d)Ionisation enthalp
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following property decreases down the group in the halogens?
a)
Electropositive nature
b)
Density
c)
Boiling point
d)
Ionisation enthalp

|
Amar Jain answered |
Due to increase in atomic size, ionisation enthalpy decreases down the group.
One gas bleaches the colour of flowers by reduction and another gas by oxidation. The gases respectively are- a)SO2 and CI2
- b)CO2 and CI2
- c)NO and CI2
- d)H2S and Br2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One gas bleaches the colour of flowers by reduction and another gas by oxidation. The gases respectively are
a)
SO2 and CI2
b)
CO2 and CI2
c)
NO and CI2
d)
H2S and Br2

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
Cl2 bleaches by oxidation while SO2 does it by reduction.
When carnallite is dissolved in water the number of ions formed are
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
When carnallite is dissolved in water the number of ions formed are

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
Carnallite is a double salt. It will dissociate into simple substances or ions completely when dissolved in water.
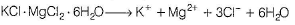
Hence, 5 ions are produced.
Hence, 5 ions are produced.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following is not a pseudo halideion?- a)CNO-
- b)CN-
- c)SCN-
- d)S2-
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which of the following is not a pseudo halideion?
a)
CNO-
b)
CN-
c)
SCN-
d)
S2-
|
|
Rutuja Ahuja answered |
Explanation:
Pseudo halides are ions that have similar chemical properties to halide ions (such as chloride, bromide, and iodide) but are not actually halides. They typically have a negative charge and contain a central atom bonded to one or more electronegative atoms.
In the given options, CNO-, CN-, and SCN- are all examples of pseudo halide ions because they exhibit similar chemical properties to halides. However, S2- is not a pseudo halide ion.
The reason S2- is not a pseudo halide ion is because it does not have similar chemical properties to halide ions. Unlike halides, which are typically good nucleophiles and are often used in substitution reactions, S2- is a strong reducing agent and is not commonly involved in substitution reactions.
S2- is a reducing agent because it can easily gain two electrons to form S2-, which has a filled valence shell. This makes it a good reducing agent in redox reactions. In contrast, halides are not strong reducing agents because they have a filled valence shell and do not readily gain electrons.
Additionally, S2- does not have the same size or electronegativity as halide ions. Halides (such as Cl-, Br-, and I-) have larger atomic radii and lower electronegativities than sulfur (S). This difference in size and electronegativity affects their chemical properties and reactivity.
In summary, S2- is not a pseudo halide ion because it does not exhibit the same chemical properties as halide ions and has different size and electronegativity characteristics.
Pseudo halides are ions that have similar chemical properties to halide ions (such as chloride, bromide, and iodide) but are not actually halides. They typically have a negative charge and contain a central atom bonded to one or more electronegative atoms.
In the given options, CNO-, CN-, and SCN- are all examples of pseudo halide ions because they exhibit similar chemical properties to halides. However, S2- is not a pseudo halide ion.
The reason S2- is not a pseudo halide ion is because it does not have similar chemical properties to halide ions. Unlike halides, which are typically good nucleophiles and are often used in substitution reactions, S2- is a strong reducing agent and is not commonly involved in substitution reactions.
S2- is a reducing agent because it can easily gain two electrons to form S2-, which has a filled valence shell. This makes it a good reducing agent in redox reactions. In contrast, halides are not strong reducing agents because they have a filled valence shell and do not readily gain electrons.
Additionally, S2- does not have the same size or electronegativity as halide ions. Halides (such as Cl-, Br-, and I-) have larger atomic radii and lower electronegativities than sulfur (S). This difference in size and electronegativity affects their chemical properties and reactivity.
In summary, S2- is not a pseudo halide ion because it does not exhibit the same chemical properties as halide ions and has different size and electronegativity characteristics.
The stability of interhalogen compounds follows the order- a)IF3 > BrF3 > CIF3
- b)BrF3 > IF3 > CIF3
- c)CIF3 > BrF3 > IF3
- d)CIF3 > IF3 > BrF3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The stability of interhalogen compounds follows the order
a)
IF3 > BrF3 > CIF3
b)
BrF3 > IF3 > CIF3
c)
CIF3 > BrF3 > IF3
d)
CIF3 > IF3 > BrF3

|
Pragati Choudhury answered |
Electropositive character of halogens is in order I > Br > Cl . Central atom is bigger in size, more electropositive nature form stable interhalogen compound.
The correct order of acidic strength is- a)Cl2O7 > SO2 > P4O10
- b)SO2 > Cl2O7 > P4O10
- c)P4O10 > SO2 > Cl2O7
- d)N2O5 > P4O10 > SO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of acidic strength is
a)
Cl2O7 > SO2 > P4O10
b)
SO2 > Cl2O7 > P4O10
c)
P4O10 > SO2 > Cl2O7
d)
N2O5 > P4O10 > SO2

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
The correct order of acidic strength is Cl2O7 > SO2 > P4O10
In perchloric acid (HCIO4), the number of σ and π-bonds- a)5σ and 4π-bonds
- b)6σ and 3π-bonds
- c)5σ and 3π-bonds
- d)5σ and 2π-bonds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In perchloric acid (HCIO4), the number of σ and π-bonds
a)
5σ and 4π-bonds
b)
6σ and 3π-bonds
c)
5σ and 3π-bonds
d)
5σ and 2π-bonds
|
|
Maya Reddy answered |
Perchloric Acid (HCIO4)
Perchloric acid (HCIO4) is a strong acid with the chemical formula HClO4. It is a colorless, odorless, and highly corrosive liquid.
Number of O and Cl bonds
- In perchloric acid (HCIO4), there are 5 oxygen (O) atoms bonded to the central chlorine (Cl) atom.
- These oxygen atoms are connected to the central chlorine atom through single bonds, resulting in a total of 5 single bonds (O-Cl).
- There are also 3 oxygen atoms in perchloric acid that are not directly bonded to the central chlorine atom. These oxygen atoms are connected to each other through single bonds, resulting in a total of 3 single bonds (O-O).
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, which states that there are 5 O-Cl bonds and 3 O-O bonds in perchloric acid (HCIO4).
In chlorination of water, reactive oxygen atoms are produced by- a)Cl2 + H2O
- b)H2CO3
- c)HClO
- d)H2ClO2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In chlorination of water, reactive oxygen atoms are produced by
a)
Cl2 + H2O
b)
H2CO3
c)
HClO
d)
H2ClO2

|
Preethi Kaur answered |
Reactive oxygen atoms are produced during the chlorination of water. This process involves the addition of chlorine gas (Cl2) to water (H2O) to disinfect it and kill harmful bacteria and microorganisms. The reaction is as follows:
Cl2 + H2O -> HCl + HClO
In this reaction, chlorine gas reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hypochlorous acid (HClO). It is the hypochlorous acid that produces reactive oxygen atoms.
Explanation:
1. Chlorine gas (Cl2):
Chlorine gas is introduced into water to kill bacteria and microorganisms. It is a powerful disinfectant and reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid.
2. Water (H2O):
Water is the medium in which the chlorination process takes place. It is the reactant that reacts with chlorine gas to form hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid.
3. Hydrochloric acid (HCl):
Hydrochloric acid is formed during the reaction between chlorine gas and water. It is a strong acid and has disinfectant properties. However, it does not produce reactive oxygen atoms.
4. Hypochlorous acid (HClO):
Hypochlorous acid is the primary product of the chlorination reaction. It is a weak acid and has powerful disinfectant properties. It is also responsible for producing reactive oxygen atoms.
5. Reactive oxygen atoms:
Hypochlorous acid (HClO) can undergo a process called disassociation, where it breaks down into reactive oxygen atoms. These reactive oxygen atoms are highly reactive and can attack and destroy organic matter, including bacteria and microorganisms.
In conclusion, during the chlorination of water, reactive oxygen atoms are produced by the disassociation of hypochlorous acid (HClO), which is formed when chlorine gas reacts with water. These reactive oxygen atoms play a crucial role in disinfecting water and killing harmful bacteria and microorganisms.
Cl2 + H2O -> HCl + HClO
In this reaction, chlorine gas reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hypochlorous acid (HClO). It is the hypochlorous acid that produces reactive oxygen atoms.
Explanation:
1. Chlorine gas (Cl2):
Chlorine gas is introduced into water to kill bacteria and microorganisms. It is a powerful disinfectant and reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid.
2. Water (H2O):
Water is the medium in which the chlorination process takes place. It is the reactant that reacts with chlorine gas to form hydrochloric acid and hypochlorous acid.
3. Hydrochloric acid (HCl):
Hydrochloric acid is formed during the reaction between chlorine gas and water. It is a strong acid and has disinfectant properties. However, it does not produce reactive oxygen atoms.
4. Hypochlorous acid (HClO):
Hypochlorous acid is the primary product of the chlorination reaction. It is a weak acid and has powerful disinfectant properties. It is also responsible for producing reactive oxygen atoms.
5. Reactive oxygen atoms:
Hypochlorous acid (HClO) can undergo a process called disassociation, where it breaks down into reactive oxygen atoms. These reactive oxygen atoms are highly reactive and can attack and destroy organic matter, including bacteria and microorganisms.
In conclusion, during the chlorination of water, reactive oxygen atoms are produced by the disassociation of hypochlorous acid (HClO), which is formed when chlorine gas reacts with water. These reactive oxygen atoms play a crucial role in disinfecting water and killing harmful bacteria and microorganisms.
Which of the following reactions is/are not feasible?- a)I2 + 2NaBr → Br2 + 2NaI
- b)I2 + 2NaCl → Cl2 + 2NaI
- c)Br2 + 2NaCl → Cl2 + 2NaBr
- d)Cl2 + 2NaBr → Br2 + 2NaCl
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions is/are not feasible?
a)
I2 + 2NaBr → Br2 + 2NaI
b)
I2 + 2NaCl → Cl2 + 2NaI
c)
Br2 + 2NaCl → Cl2 + 2NaBr
d)
Cl2 + 2NaBr → Br2 + 2NaCl

|
Sai Chakraborty answered |
Iodine cannot displace Cl- and Br- from their salt and bromine cannot displace Cl-from their salt.
Which of the following represents the decreasing order of van der Waals’ forces in halogens ?- a)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
- c)Br2 > Cl2 > F2 > I2
- d)Cl2 > F2 > I2 > Br2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following represents the decreasing order of van der Waals’ forces in halogens ?
a)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
c)
Br2 > Cl2 > F2 > I2
d)
Cl2 > F2 > I2 > Br2
|
|
Nishtha Dasgupta answered |
The question is incomplete as it does not provide the options for the van der Waals forces. Please provide the options so I can assist you further.
The source of iodine is- a)in free state
- b)in seaweeds
- c)as caliche
- d)As Agl
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The source of iodine is
a)
in free state
b)
in seaweeds
c)
as caliche
d)
As Agl

|
Ishita Deshpande answered |
Certain deep seaweeds contain 0.5% of iodine in their ashes. Caliche or crude chile saltpetre contain about 0.2% of NaIO3.
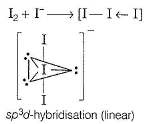
Direction (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. The num ber of lone pair of electrons present on the central iodine in I-3 ion is
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q, Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
The num ber of lone pair of electrons present on the central iodine in I-3 ion is

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
Three lone pairs are present on the central iodine in triiodide ion.
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).Passage
Group 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.
Q. Valence shell configuration that belongs to most reactive non-metal is
a) (n-1)s2p6ns1
b) ns2np5
c) ns2np6
d) (n-1)s2p6ns2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a) (n-1)s2p6ns1
b) ns2np5
c) ns2np6
d) (n-1)s2p6ns2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
All the halogens are highly reactive. They react with metals and non-metals to form halides due to readily acceptance of an electron
The number of water insoluble salts amongAgF, AgCI, AgBr, Agl BeF2, CaF2,KF, PbCI2, HgCI2- a)

- b)

- c)
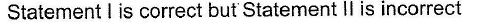
- d)
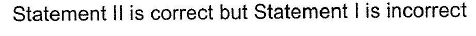
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of water insoluble salts among
AgF, AgCI, AgBr, Agl BeF2, CaF2,KF, PbCI2, HgCI2
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Pritam Malik answered |
AgCI, AgBr, Agl CaF2, PbCI2, HgCI2, are water insoluble.
Which option is incorrect among the following for the given property?- a)Dipole moment (HF > HCI > HBr > HI)
- b)Bond length (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
- c)Acidic strength (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
- d)Thermal stability (HF < HCI < HBr < HI)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which option is incorrect among the following for the given property?
a)
Dipole moment (HF > HCI > HBr > HI)
b)
Bond length (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
c)
Acidic strength (HI > HBr > HCI > HF)
d)
Thermal stability (HF < HCI < HBr < HI)

|
Kavya Das answered |
Thermal stability decreases as the strength of H-X bond decreases which in turn decreases as the size of the halogen increases, i.e. HF > HCI > HBr > HI
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).PassageA salt A when heated with K2Cr2O7 and cone. H2SO4 liberates a gas which is absorbed in NaOH solution. The NaOH solution turns yellow. When this solution is acidified with acetic acid and lead acetate solution is added, a yellow precipitate B is formed. When A is mixed with MnO2 and heated with cone. H2SO4 , a gas C is evolved which turns a starch-iodide paper blue.Q. What is the colour of the gas which is evolved when salt A is heated with MnO2 and H2SO4?- a)Violet
- b)Brown
- c)Greenish yellow
- d)Colourless
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
A salt A when heated with K2Cr2O7 and cone. H2SO4 liberates a gas which is absorbed in NaOH solution. The NaOH solution turns yellow. When this solution is acidified with acetic acid and lead acetate solution is added, a yellow precipitate B is formed. When A is mixed with MnO2 and heated with cone. H2SO4 , a gas C is evolved which turns a starch-iodide paper blue.
Q.
What is the colour of the gas which is evolved when salt A is heated with MnO2 and H2SO4?
a)
Violet
b)
Brown
c)
Greenish yellow
d)
Colourless

|
Niti Saha answered |
Greenish yellow gas is chlorine.
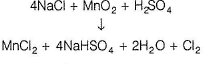
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : On dehydration with P2O5 at 263 K, HCIO4 gives Cl2O7.Statement II : This method is used in the preparation of Cl2O7- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : On dehydration with P2O5 at 263 K, HCIO4 gives Cl2O7.
Statement II : This method is used in the preparation of Cl2O7
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Niti Saha answered |
On dehydration with P2O5 at - 10°C, HCIO4 gives Cl2O7 which is the anhydride of perchloric acid.
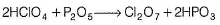
This reaction has been used for the preparation of Cl2O7.
This reaction has been used for the preparation of Cl2O7.
In the known interhalogen compounds, the maximum number of atoms are
- a)4
- b)5
- c)8
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the known interhalogen compounds, the maximum number of atoms are
a)
4
b)
5
c)
8
d)
7

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
In IF7, iodine is the least electronegative halogen, so its higher oxidation number (+7) is more stable than those of the lighter member of the group. So clearly there are a total of 8 atoms
In CIF3, if both lone pairs occupy axial positions then find the number of lone pair-bond pair repulsions.
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
In CIF3, if both lone pairs occupy axial positions then find the number of lone pair-bond pair repulsions.

|
Malavika Shah answered |
In this geometry, each lone pair is 90° with the bond pairs. Hence, lone pair-bond pair repulsions are six.
Match the following molecules or ions to their shapes. Which pairing is correct? - a)[I3]- : bent
- b)BrF5 : trigonal bipyramidal
- c)CIF3 : trigonal planar
- d)[BrF4]- : square planar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following molecules or ions to their shapes. Which pairing is correct?
a)
[I3]- : bent
b)
BrF5 : trigonal bipyramidal
c)
CIF3 : trigonal planar
d)
[BrF4]- : square planar

|
Tarun Chakraborty answered |
[I3]- = Linear ; BrF5 = Square pyramidal; ClF3 = 'T' shaped
The correct order of in creasing order of radiiions 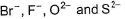 is as follow
is as follow- a)
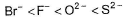
- b)
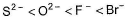
- c)
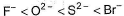
- d)
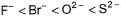
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of in creasing order of radiiions 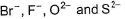 is as follow
is as follow
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Atomic and ionic radii increase down the group due to increasing number of quantum shells.
Pseudo halogens among the following are- a)(CN)2
- b)(OCN)2
- c) BrF3
- d)(SeCN)2
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pseudo halogens among the following are
a)
(CN)2
b)
(OCN)2
c)
BrF3
d)
(SeCN)2

|
Tarun Chakraborty answered |
(CN)2, (OCN)2 and (SeCN)2 are pseudo halogens.
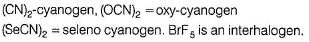
PassageGroup 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.Q. In which of the following chlorine has different oxidation states?- a) CrO2CI2
- b)CaOCI2
- c)Cl2O7
- d)Ca(OCI)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage
Group 17 elements are known as halogens ( sea salt forming). Their general configuration is ns2np5 where, n = 2 to 7. Fluorine is the first member of the group differs in several ways from the rest of the group. Halogens are highly reactive elements having strong affinity for hydrogen. All the halogens form both ionic and covalent compounds .Fluorine is always monovalent and shows -1 oxidation state in its compounds .The other halogens exhibit 1, 3, 5, 7 valencies in their compounds and show - 1 to + 7 oxidation states.
Q.
In which of the following chlorine has different oxidation states?
a)
CrO2CI2
b)
CaOCI2
c)
Cl2O7
d)
Ca(OCI)2

|
Gauri Kaur answered |
In calcium oxychloride (CaOCI)CI) has different oxidation states, Hence, chlorine has +1 and -1 oxidation states.
Chapter doubts & questions for Halogens - Chemistry for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Halogens - Chemistry for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for JAMB
213 videos|209 docs|162 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











