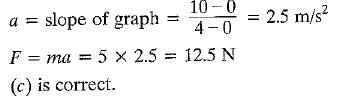All Exams >
Class 9 >
Science Class 9 >
All Questions
All questions of Force and Laws of Motion for Class 9 Exam
Impulse is the other name of- a)inertia
- b)momentum
- c)force
- d)change in momentum
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Impulse is the other name of
a)
inertia
b)
momentum
c)
force
d)
change in momentum
|
|
Dhiraj Sarma answered |
Since momentum depends on impulse
I.e if momentum increase impulse increase vice versa
I.e if momentum increase impulse increase vice versa
The S.I. unit of force is- a)Newton-metre
- b)Newton
- c)Newton per second
- d)Newton per square metre
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The S.I. unit of force is
a)
Newton-metre
b)
Newton
c)
Newton per second
d)
Newton per square metre

|
Prachi Rathore answered |
Yes the si unit of force is newton.
If no external force acts on a moving object:
- a)It will not be affected at all.
- b)It should remain in motion But, it will stop due to Friction
- c)It will stop moving.
- d)It will remain at rest forever.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If no external force acts on a moving object:
a)
It will not be affected at all.
b)
It should remain in motion But, it will stop due to Friction
c)
It will stop moving.
d)
It will remain at rest forever.

|
Jaitavi answered |
No external force is being applied on that moving object. If no force is applied then it will continue doing it's work. Just like in the question they have asked, it was moving in a straight line, so no external force is applied that's why it is moving in the same sped in a straight line.
Change in momentum when a car weighing 700kg changes its speed from 100m/s to 200 m/s is:- a)14000 kg.m/s
- b)10500000 kg.m/s
- c)21000000 kg.m/s
- d)70000 kg.m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Change in momentum when a car weighing 700kg changes its speed from 100m/s to 200 m/s is:
a)
14000 kg.m/s
b)
10500000 kg.m/s
c)
21000000 kg.m/s
d)
70000 kg.m/s
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Change in momentum = mv - mu
When m = 7000kg, v= 200m/s, u = 100 m/s
Now, 700 * 200 - 700 x 100 = 140000 - 70000 = 70000 kg. m/s
When m = 7000kg, v= 200m/s, u = 100 m/s
Now, 700 * 200 - 700 x 100 = 140000 - 70000 = 70000 kg. m/s
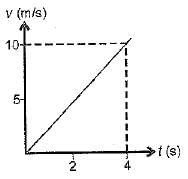
Find the time taken by a body of mass 16 kg to come to rest from a uniform velocity of magnitude 10 m/s, when a force of 4N is applied continously
- a)20 s
- b)30 s
- c)40 s
- d)50 s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the time taken by a body of mass 16 kg to come to rest from a uniform velocity of magnitude 10 m/s, when a force of 4N is applied continously
a)
20 s
b)
30 s
c)
40 s
d)
50 s
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
To find the time taken for the body to come to rest, we can use the formula derived from Newton's second law:
F=ma
where:
- F is the force applied,
- m is the mass of the body,
- a is the acceleration.
First, we calculate the acceleration:
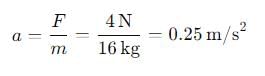
The body is initially moving with a velocity of 10 m/s and will come to rest, so the final velocity v=0v = 0v=0.
Using the equation of motion:
v=u+at
where:
- v is the final velocity (0 m/s),
- u is the initial velocity (10 m/s),
- a is the acceleration (-0.25 m/s²) (negative because the force is acting opposite to the direction of motion),
- t is the time taken.
Substitute the values:
0=10+(−0.25)t
0.25t=10
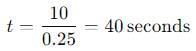
So, the time taken by the body to come to rest is 40 seconds.
Answer: 3 (40 s)
If the force acting on the body is zero. Its momentum is:- a)Zero
- b)Constant
- c)Infinite
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the force acting on the body is zero. Its momentum is:
a)
Zero
b)
Constant
c)
Infinite
d)
None of the above

|
Vrinda Maheshwari answered |
yes it will be constant because force acting on both sides equally it will be zero that's why ans is constant... hope it is helpful for you!
A player is catching a ball. Consider the action force to be the impact of the ball against the player’s glove. What is the reaction force?- a)Force that the glove exerts on the ball.
- b)The players grip on the ball.
- c)Friction of the ground.
- d)The muscular effort in the player’s arm.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A player is catching a ball. Consider the action force to be the impact of the ball against the player’s glove. What is the reaction force?
a)
Force that the glove exerts on the ball.
b)
The players grip on the ball.
c)
Friction of the ground.
d)
The muscular effort in the player’s arm.
|
|
Arjun Sharma answered |
Reaction force: Force that the glove exerts on the ball is the reaction force opposite to the impact of ball on player’s hand.
A person standing on a weighing scale sees a reading on the scale as 148 pounds. This person is acted on by- a)No forces at all.
- b)Two forces of equal magnitude acting in opposite directions.
- c)Only one force of 148 pounds, as shown by the reading on the scale.
- d)Only one force, of 296 pounds (= 2 × 148 pounds)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person standing on a weighing scale sees a reading on the scale as 148 pounds. This person is acted on by
a)
No forces at all.
b)
Two forces of equal magnitude acting in opposite directions.
c)
Only one force of 148 pounds, as shown by the reading on the scale.
d)
Only one force, of 296 pounds (= 2 × 148 pounds)

|
Rohini Seth answered |
- Gravitational force is acting in the downward direction. As we know every action has a reaction.
- So, there is an equal and opposite force acting in opposite direction also.
Which one is correct if a bullet is fired from a rifle?- a)There is no motion of bullet and rifle.
- b)Rifle moves in backward direction and bullet moves in forward direction.
- c)Bullet and rifle both move in backward direction.
- d)Bullet moves in backward direction and rifle moves in forward direction.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is correct if a bullet is fired from a rifle?
a)
There is no motion of bullet and rifle.
b)
Rifle moves in backward direction and bullet moves in forward direction.
c)
Bullet and rifle both move in backward direction.
d)
Bullet moves in backward direction and rifle moves in forward direction.

|
Aryan Will Be Back answered |
Here came the application of Newton's third law of motion.. A gun recoils when a shot is fired from it.. initially both the gun and the bullet are at rest so the total momentum of the system is constant ....
when a shot is fired the bullet moves forward pushing the gun backward this phenomenon is known as recoiling of gun...
Due to recoiling of gun a backward jerk is experience on the shoulder of the shooter..
when a shot is fired the bullet moves forward pushing the gun backward this phenomenon is known as recoiling of gun...
Due to recoiling of gun a backward jerk is experience on the shoulder of the shooter..
In high jump competition the athlete is made to fall on a cushioned bed to:- a)To decrease his momentum fast.
- b)Make him stop quickly.
- c)Increase the time to stop.
- d)Make him sleep comfortably.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In high jump competition the athlete is made to fall on a cushioned bed to:
a)
To decrease his momentum fast.
b)
Make him stop quickly.
c)
Increase the time to stop.
d)
Make him sleep comfortably.
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
In a high jump athletic event, the athletes are made to fall either on a cushioned bed or sand bed. This is to increase the time that the athletes fall to stop after making the jump. This decreases the rate of change of momentum and hence the force. As a result, the athlete does not get injured.
Momentum is a:- a)Vector quantity
- b)Scalar quantity
- c)Fundamental quantity
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Momentum is a:
a)
Vector quantity
b)
Scalar quantity
c)
Fundamental quantity
d)
None of the above
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Momentum is a vector quantity. For a particle with mass, the momentum equals mass times velocity, and velocity is a vector quantity while mass is a scalar quantity. A scalar multiplied by a vector is a vector. A moving body would be a particle with a mass.
A cyclist of mass 30 kg exerts a force of 250 N to move his cycle. The acceleration is 4 ms−2. The force of friction between the road and tyres will be- a)120 N
- b)130 N
- c)150N
- d)115 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A cyclist of mass 30 kg exerts a force of 250 N to move his cycle. The acceleration is 4 ms−2. The force of friction between the road and tyres will be
a)
120 N
b)
130 N
c)
150N
d)
115 N
|
|
Ankita jain answered |
Force - force of friction = mass × acceleration
250 - f = 30 × 4
f = 250 - 120
= 130N
250 - f = 30 × 4
f = 250 - 120
= 130N
The SI unit of momentum is :- a)Newton
- b)Newton-second
- c)Dyne
- d)Dyne-second
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The SI unit of momentum is :
a)
Newton
b)
Newton-second
c)
Dyne
d)
Dyne-second
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
If we consider the situation when force is equivalent to the rate of change of momentum. I.e Force = (change in momentum)(time interval)
then, change in momentum = Force * (time interval).
Therefore, the unit for momentum can be Newton - second (Ns)
then, change in momentum = Force * (time interval).
Therefore, the unit for momentum can be Newton - second (Ns)
When a fireman directs a powerful stream of water from a hose-pipe, the hose-pipe tends to go backward. This is due to:- a)Law of Inertia.
- b)Newton’s 3rd law.
- c)Law of conservation of charges.
- d)Law of conservation of energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a fireman directs a powerful stream of water from a hose-pipe, the hose-pipe tends to go backward. This is due to:
a)
Law of Inertia.
b)
Newton’s 3rd law.
c)
Law of conservation of charges.
d)
Law of conservation of energy
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- According to the circumstances mentioned in the question, a powerful stream of water on a fire from a hose-pipe tend to go backward.
- This phenomenon is the practical life example of Newton's third law, " Every action has an equal and opposite reaction."
A body will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line, unless acted by some external force. The statement represents :- a)Newton's second law of motion
- b)Newton's first law of motion
- c)Newton's third law of motion
- d)Law of conservation of momentum
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line, unless acted by some external force. The statement represents :
a)
Newton's second law of motion
b)
Newton's first law of motion
c)
Newton's third law of motion
d)
Law of conservation of momentum
|
|
Sankar Basak answered |
Newton's First Law of Motion
Newton's first law of motion is also known as the law of inertia. It states that a body will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by some external force. This means that if an object is at rest, it will stay at rest, and if it is moving at a constant speed in a straight line, it will continue to do so unless something else interferes.
Explanation
The first law of motion is based on the concept of inertia, which is the tendency of an object to resist a change in its state of motion. In other words, an object will continue to do what it is doing unless something else makes it change. This can be seen in everyday life when you try to push a stationary object, such as a heavy box. It will not move unless you apply a force to it.
Similarly, if an object is already in motion, it will keep moving in a straight line at a constant speed unless some external force acts upon it. For example, if you slide a hockey puck across the ice, it will keep moving until it hits something or is acted upon by another force, such as friction.
Conclusion
Newton's first law of motion is a fundamental concept in physics. It explains how objects behave when no external forces are acting upon them. By understanding this law, scientists and engineers can design better machines and devices, and also predict how objects will behave in various situations.
Newton's first law of motion is also known as the law of inertia. It states that a body will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by some external force. This means that if an object is at rest, it will stay at rest, and if it is moving at a constant speed in a straight line, it will continue to do so unless something else interferes.
Explanation
The first law of motion is based on the concept of inertia, which is the tendency of an object to resist a change in its state of motion. In other words, an object will continue to do what it is doing unless something else makes it change. This can be seen in everyday life when you try to push a stationary object, such as a heavy box. It will not move unless you apply a force to it.
Similarly, if an object is already in motion, it will keep moving in a straight line at a constant speed unless some external force acts upon it. For example, if you slide a hockey puck across the ice, it will keep moving until it hits something or is acted upon by another force, such as friction.
Conclusion
Newton's first law of motion is a fundamental concept in physics. It explains how objects behave when no external forces are acting upon them. By understanding this law, scientists and engineers can design better machines and devices, and also predict how objects will behave in various situations.
When a running motorbike accelerates suddenly, the pillion rider has a tendency to fall backward. This is an example of:- a)Newton's first law of motion
- b)Newton's second law of motion
- c)Newton's third law of motion
- d)Newton's law of gravitation of motion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a running motorbike accelerates suddenly, the pillion rider has a tendency to fall backward. This is an example of:
a)
Newton's first law of motion
b)
Newton's second law of motion
c)
Newton's third law of motion
d)
Newton's law of gravitation of motion
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Law of Inertia or First law of motion.
As the body tends to be in its original state when the horse suddenly stops, The lower part of the rider stops with it but the upper part remains in motion. So, the rider falls forward.
As the body tends to be in its original state when the horse suddenly stops, The lower part of the rider stops with it but the upper part remains in motion. So, the rider falls forward.
Force is defined as- a)change in momentum
- b)rate of change of momentum
- c)the quantity that opposes inertia
- d)the quantity that keeps the velocity constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Force is defined as
a)
change in momentum
b)
rate of change of momentum
c)
the quantity that opposes inertia
d)
the quantity that keeps the velocity constant
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
"The rate of change of momentum is called force”. “ When a net force acts on a body, it produces acceleration in thr body and will be equal to rate of change of momentum”. Hence , we found that Rate of change of momentum is equal to Force applied on the object .
Which of the following is an equation of motion of a body?
- a)p = mv
- b)F = ma
- c)v = u + at
- d)Ft = mv - mu
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an equation of motion of a body?
a)
p = mv
b)
F = ma
c)
v = u + at
d)
Ft = mv - mu
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
v = u +at is the only equation of motion present here in the options. Hence, C is the correct answer
A man throws a ball weighing 200 g vertically upwards with a speed of 10m/s. Its momentum at the highest point of its flight will be:- a)2 kg. m/s
- b)2000 kg.m/s
- c)Insufficient data to find the momentum.
- d)zero.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man throws a ball weighing 200 g vertically upwards with a speed of 10m/s. Its momentum at the highest point of its flight will be:
a)
2 kg. m/s
b)
2000 kg.m/s
c)
Insufficient data to find the momentum.
d)
zero.
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Mass of the ball, m = 0.5 kg
Initial velocity, u = 10 m/s
Initial momentum = mu = 0.5 x 10 = 5 kg m/s
At the highest point, velocity of ball is zero.
So, momentum of the ball 0.5 x 0 = 0.
A child on a cart with wheels throws a sandbag forward. As a result:- a)He moves to the left.
- b)He moves backward.
- c)He moves forward.
- d)He moves to the right.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A child on a cart with wheels throws a sandbag forward. As a result:
a)
He moves to the left.
b)
He moves backward.
c)
He moves forward.
d)
He moves to the right.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The child moves in the backward direction as a consequence of action-reaction law. Sandbag exerts an equal and opposite force in the backward direction.
According to second law of Newton, force is the cause and the outcome is- a)acceleration
- b)velocity
- c)momentum
- d)time
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to second law of Newton, force is the cause and the outcome is
a)
acceleration
b)
velocity
c)
momentum
d)
time
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
According to Newton’s second law of motion, also known as the Law of Force and Acceleration, a force upon an object's causes it to accelerate according to the formula:
Net force = mass x acceleration.
Net force = mass x acceleration.
So, the acceleration of the object is directly proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass.
Two balls A and B, of masses m and 2m are in motion with velocities 2v and v respectively. Compare the force needed to stop them in the same time- a)2 : 1
- b)1 : 2
- c)1 : 1
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two balls A and B, of masses m and 2m are in motion with velocities 2v and v respectively. Compare the force needed to stop them in the same time
a)
2 : 1
b)
1 : 2
c)
1 : 1
d)
None of the above
|
|
Vikram Khanna answered |
Since the change takes place in the same time: ratio of force needed to stop the balls is equal to the ratio of their momentum.
FA / FB = (m)(2v) / (2m)(v) = 1 : 1
In a football and stone of same size, the inertia of
- a)Football is greater.
- b)Stone is greater.
- c)Both the objects is equal.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a football and stone of same size, the inertia of
a)
Football is greater.
b)
Stone is greater.
c)
Both the objects is equal.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Inertia of stone is greater than the inertia of football because mass of stone is higher than the mass of football even both are of same size.
The inertia of an object tends to cause the object - a)to increase its speed
- b)to decrease its speed
- c)to resist any change in the state of rest or of motion
- d)to decelerate due to friction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The inertia of an object tends to cause the object
a)
to increase its speed
b)
to decrease its speed
c)
to resist any change in the state of rest or of motion
d)
to decelerate due to friction
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
Inertia of an object is the tendency of the object to resist change in motion. The inertia is directly dependent on the mass of the body.
Inertia resist any change in its state of motion and is of three types:
Inertia resist any change in its state of motion and is of three types:
- Inertia of rest
- Inertia of motion
- Inertia of direction
Which is incorrect statement about action and reaction forces:a)They act on different objects.b)They are equal.c)They are opposite.d)They act on the same object. Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Neeharika Shah answered |
Action and Reaction Forces
Action and reaction forces are two forces that are always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. These forces always act on different objects. Let's understand this concept in detail.
Action Force
An action force is a force that occurs when one object exerts force on another object. This force can be a push, pull, or any other force that one object exerts on another. For example, when you push a table, you are applying an action force on the table.
Reaction Force
A reaction force is a force that occurs when an object exerts force back on the object that applied the action force. This force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the action force. For example, when you push a table, the table exerts a reaction force back on you.
Key Points
- Action and reaction forces always act on different objects.
- They are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
- They are always present in pairs.
- They occur simultaneously.
Incorrect Statement
The incorrect statement is option 'D', which says that action and reaction forces act on the same object. This statement is incorrect because action and reaction forces always act on different objects. When one object exerts force on another object, the second object exerts a reaction force back on the first object. For example, when you jump off a diving board, you exert a force on the board, and the board exerts a reaction force back on you. These forces always act on different objects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. They always act on different objects and occur simultaneously. It is essential to understand this concept because it is a fundamental principle of physics that explains how objects move and interact with each other.
Action and reaction forces are two forces that are always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. These forces always act on different objects. Let's understand this concept in detail.
Action Force
An action force is a force that occurs when one object exerts force on another object. This force can be a push, pull, or any other force that one object exerts on another. For example, when you push a table, you are applying an action force on the table.
Reaction Force
A reaction force is a force that occurs when an object exerts force back on the object that applied the action force. This force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the action force. For example, when you push a table, the table exerts a reaction force back on you.
Key Points
- Action and reaction forces always act on different objects.
- They are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
- They are always present in pairs.
- They occur simultaneously.
Incorrect Statement
The incorrect statement is option 'D', which says that action and reaction forces act on the same object. This statement is incorrect because action and reaction forces always act on different objects. When one object exerts force on another object, the second object exerts a reaction force back on the first object. For example, when you jump off a diving board, you exert a force on the board, and the board exerts a reaction force back on you. These forces always act on different objects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, action and reaction forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. They always act on different objects and occur simultaneously. It is essential to understand this concept because it is a fundamental principle of physics that explains how objects move and interact with each other.
If a body is allowed to freely fall from a height, its speed increases continuously. It is because:
- a)Air does not exert frictional force
- b)Magnetic force of earth increases its speed
- c)Gravitational force of earth increases its speed
- d)Pressure of air forces it downward
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If a body is allowed to freely fall from a height, its speed increases continuously. It is because:
a)
Air does not exert frictional force
b)
Magnetic force of earth increases its speed
c)
Gravitational force of earth increases its speed
d)
Pressure of air forces it downward
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The gravitational force for a falling object is along the direction of motion. Hence, its speed increases continuously till it touches the ground.
The people in a bus are pushed backwards when the bus starts suddenly because of:- a)Inertia due to direction
- b)External force
- c)Inertia due to motion
- d)Inertia due to rest
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The people in a bus are pushed backwards when the bus starts suddenly because of:
a)
Inertia due to direction
b)
External force
c)
Inertia due to motion
d)
Inertia due to rest
|
|
Arjun Sharma answered |
This is due to inertia of rest of upper part of the passengers body when the bus or train suddenly starts moving, The lower part of the passenger’s body starts moving along with the bus or train while the upper part of the body has a tendency to remain in the state of rest due to inertia of rest, and hence falls backwards.
The acceleration of an object is- a)inversely proportional to its mass
- b)directly proportional to the applied force
- c)resisted by inertia
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The acceleration of an object is
a)
inversely proportional to its mass
b)
directly proportional to the applied force
c)
resisted by inertia
d)
all of the above
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Newton's second law of motion can be formally stated as follows:- The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
While dusting a carpet we beat it with a stick because:- a)Force applied on the carpet.
- b)No inertia is involved.
- c)Inertia of motion removes the dust.
- d)Inertia of rest keeps the dust in its position.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
While dusting a carpet we beat it with a stick because:
a)
Force applied on the carpet.
b)
No inertia is involved.
c)
Inertia of motion removes the dust.
d)
Inertia of rest keeps the dust in its position.

|
Sneha answered |
Because the dust particle is in rest position hence if we beat the carpet the inertia of rest will break and tey fall down .
Which one of the following statements is not correct for an object moving along a straight path in an accelerated motion?- a)Its speed keeps changing
- b)Its velocity always changes
- c)It always goes away from earth
- d)A force is always acting on it
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is not correct for an object moving along a straight path in an accelerated motion?
a)
Its speed keeps changing
b)
Its velocity always changes
c)
It always goes away from earth
d)
A force is always acting on it
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- The question states an accelerated motion of an object along a straight line, this implies a non zero force is acting on the object, which is increasing its velocity and speed.
- However the direction of force is not given so it can’t be determined that it is moving away from the earth, Hence the correct answer is C.
Force remaining constant, if the mass of body increases, its acceleration is likely to :
- a)Increase
- b)Remain same
- c)Decrease
- d)Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Force remaining constant, if the mass of body increases, its acceleration is likely to :
a)
Increase
b)
Remain same
c)
Decrease
d)
Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
When the mass of a body increases while keeping the force constant, the acceleration of the body is likely to decrease. This is because acceleration is inversely proportional to mass when force is constant, as described by Newton's second law of motion (F = ma).
- Explanation:
- Increase: Incorrect, as mass and acceleration are inversely proportional when force is constant.
- Remain same: Incorrect, as acceleration changes with mass.
- Decrease: Correct. With increased mass, acceleration decreases.
- Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases: Incorrect; acceleration consistently decreases with increased mass.
- Explanation:
- Increase: Incorrect, as mass and acceleration are inversely proportional when force is constant.
- Remain same: Incorrect, as acceleration changes with mass.
- Decrease: Correct. With increased mass, acceleration decreases.
- Sometimes increases and sometimes decreases: Incorrect; acceleration consistently decreases with increased mass.
While catching a stone thrown by your friend you pul! the hands back to- a)avoid getting hurt
- b)increase the time to slow down
- c)decrease the time to slow down
- d)avoid the breaking of the stone
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
While catching a stone thrown by your friend you pul! the hands back to
a)
avoid getting hurt
b)
increase the time to slow down
c)
decrease the time to slow down
d)
avoid the breaking of the stone
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
- While catching a fast moving cricket ball, a fielder in the ground gradually pulls his hand backward with the moving ball, in doing so, the fielder increases the time during which the high velocity of the moving ball decrease to zero.
- This, the acceleration of the ball is decreased and therefore, the impact of catching the fast moving ball is also reduced.
A force F acts on a stationary body for the time t. The distance covered by the body 'S' will be proportional to:- a)t
- b)1/t
- c)t2
- d)1/t2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A force F acts on a stationary body for the time t. The distance covered by the body 'S' will be proportional to:
a)
t
b)
1/t
c)
t2
d)
1/t2
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
S=ut+1/2at^2 Since the mass is constant, and i guess you dont mean above to be dealt in relativistic speed, and a constant force is applied then we will have constant acceleration. So distance covered will be only dependent on elapsed time t.So s ∝ t^2
The impact which a body can produce due to the combined effect of mass and velocity is called:- a)Momentum
- b)Force
- c)Moment of force
- d)Pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The impact which a body can produce due to the combined effect of mass and velocity is called:
a)
Momentum
b)
Force
c)
Moment of force
d)
Pressure

|
Kavya Nambiar answered |
Momentum is a word you're probably very familiar with. Often, you'll hear that something is gaining or gathering momentum. It might be an actual moving object or it might be used more metaphorically like with a sports team. But have you ever taken a moment to think what, exactly, momentum means?
Momentum is the quantity of motion of a moving body. In a basic sense, the more momentum a moving object has, the harder it is to stop. This is why you see the term used metaphorically like in the example of the sports team. It means the team is on a roll (generally, a winning streak) and is becoming a stronger team for it. The other teams will have a harder time stopping the team gaining momentum.
Quantitative expression of force is given by:- a)Newton’s second law of motion.
- b)Newton’s third law of motion.
- c)Newton’s first law of motion.
- d)Newton’s law of gravitation.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Quantitative expression of force is given by:
a)
Newton’s second law of motion.
b)
Newton’s third law of motion.
c)
Newton’s first law of motion.
d)
Newton’s law of gravitation.
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Force can be calculated from Newton’s second law of motion which gives that force is the product of mass and acceleration.
A body P has mass 2 m and velocity 5 v. Another body Q has mass 8 m and velocity 1.25 v. The ratio
of momentum of P and Q is :- a)2 : 1
- b)1 : 1
- c)1 : 2
- d)3 : 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body P has mass 2 m and velocity 5 v. Another body Q has mass 8 m and velocity 1.25 v. The ratio
of momentum of P and Q is :
of momentum of P and Q is :
a)
2 : 1
b)
1 : 1
c)
1 : 2
d)
3 : 2
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Momentum = mass x velocity
Therefore in first case momentum = 2m x 5v = 10mv
Therefore in second case momentum = 8m x 1.25v = 10mv
Thus in both the cases momentum is the same, so, Ratio is 1:1
A force F produces an acceleration 'a' in a body. The same force produces and acceleration 4a in another
body. The mass of other body is :
- a)Four times the mass of first body
- b)Four times less the mass of other body
- c)Mass does not play role
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A force F produces an acceleration 'a' in a body. The same force produces and acceleration 4a in another
body. The mass of other body is :
body. The mass of other body is :
a)
Four times the mass of first body
b)
Four times less the mass of other body
c)
Mass does not play role
d)
None of the above

|
EduRev Class 9 answered |
According to the Newton’s Second Law of Motion, the change in momentum of a body per unit time is directly proportional to the unbalanced force acting on the body and the change in momentum takes place in the direction of the unbalanced force of the body. It can be represented as F = ma. From the equation we can see that mass is inversely proportional to acceleration so if the acceleration of the body increases by 4 times, the mass of the body will reduce by 4 times.
A resistive force of 16 N acts on a ball of mass 40 g continuously. If the initial velocity of the ball is 24 ms-1 ,the time taken by it to come to rest is:- a)0.04 s
- b)0.08 s
- c)0.06 s
- d)0.02 s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A resistive force of 16 N acts on a ball of mass 40 g continuously. If the initial velocity of the ball is 24 ms-1 ,the time taken by it to come to rest is:
a)
0.04 s
b)
0.08 s
c)
0.06 s
d)
0.02 s

|
Subham Gupta answered |
Mass of ball: m= 40 g = 0.040kg
resistive force: F = -16 N
thus resistive acceleration, a = F/m (because force, F= ma)
thus a = -400m/s^2
initial velocity, u = 24m/s
final velocity, v = 0m/s
Thus according to first equation of motion, v = u+at (t=timetaken)
t= 0.06s
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Force and Newton's Law of Motion" are available for CBSE Class 9 Science and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 9 Science Q. An external influence which changes or tends to change the state of rest or uniform motion of body or its
dimensions is called :- a)Momentum
- b)Force
- c)Moment of force
- d)Pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Force and Newton's Law of Motion" are available for CBSE Class 9 Science and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 9 Science
Q. An external influence which changes or tends to change the state of rest or uniform motion of body or its
dimensions is called :
dimensions is called :
a)
Momentum
b)
Force
c)
Moment of force
d)
Pressure

|
Learners Habitat answered |
Force is a phenomenon which is responsible for the change in state or shape or size of a body either from rest to motion or motion to rest.
Action and reaction forces are always:- a)Unequal and in opposite direction
- b)Unequal and in same direction.
- c)Equal and in same direction.
- d)Equal and in opposite direction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Action and reaction forces are always:
a)
Unequal and in opposite direction
b)
Unequal and in same direction.
c)
Equal and in same direction.
d)
Equal and in opposite direction

|
Vikas Rahar answered |
It is Newton's third law of motion that every action has an equal and opposite reaction
So, every action and reaction forces are equal and in opposite direction
So, every action and reaction forces are equal and in opposite direction
Newton’s third law of motion explains the two forces namely ‘action’ and ‘reaction’ coming into action when the two bodies are in contact with each other. These two forces:
- a) Always act on the same body
- b)Have same magnitude and direction
- c)Acts on either body at normal to each other
- d)Always act on the different bodies in opposite directions
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Newton’s third law of motion explains the two forces namely ‘action’ and ‘reaction’ coming into action when the two bodies are in contact with each other. These two forces:

a)
Always act on the same body
b)
Have same magnitude and direction
c)
Acts on either body at normal to each other
d)
Always act on the different bodies in opposite directions

|
Netbhet Solutions answered |
Always act on the different bodies in opposite directions.
When we vigorously a shake branch of a tree, some leaves get detached. It is due to the:- a)inertia of rest
- b)inertia of motion
- c)some leaves are loosely held by the branch
- d)none of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When we vigorously a shake branch of a tree, some leaves get detached. It is due to the:
a)
inertia of rest
b)
inertia of motion
c)
some leaves are loosely held by the branch
d)
none of the above.
|
|
Disha Yadav answered |
Answer:
The correct answer to the question is option 'a) inertia of rest'. When we vigorously shake a branch of a tree, some leaves get detached from the branch. This phenomenon can be explained by the concept of inertia of rest.
Inertia of Rest:
Inertia is the property of an object to resist any change in its state of rest or motion. The inertia of rest specifically refers to an object's resistance to being set in motion when it is at rest. According to Newton's first law of motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force.
Explanation:
When we vigorously shake a branch of a tree, we apply an external force to the branch. This force causes the branch to move and oscillate. However, the leaves attached to the branch initially tend to remain at rest due to their inertia of rest. As a result, they resist the change in their state of rest and do not move along with the branch immediately.
Loosely Held Leaves:
Another factor contributing to the detachment of leaves is that some of them are loosely held by the branch. The attachment between leaves and branches can vary depending on various factors such as age, health, and natural growth. If a leaf is loosely attached to the branch, the force applied by shaking can exceed the holding force, causing the leaf to detach and fall off.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when we vigorously shake a branch of a tree, the detachment of some leaves is primarily due to the inertia of rest exhibited by the leaves and the fact that some leaves are loosely held by the branch. The leaves resist the change in their state of rest initially, but if the force applied is strong enough or if their attachment is weak, they can detach from the branch and fall off.
The correct answer to the question is option 'a) inertia of rest'. When we vigorously shake a branch of a tree, some leaves get detached from the branch. This phenomenon can be explained by the concept of inertia of rest.
Inertia of Rest:
Inertia is the property of an object to resist any change in its state of rest or motion. The inertia of rest specifically refers to an object's resistance to being set in motion when it is at rest. According to Newton's first law of motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an external force.
Explanation:
When we vigorously shake a branch of a tree, we apply an external force to the branch. This force causes the branch to move and oscillate. However, the leaves attached to the branch initially tend to remain at rest due to their inertia of rest. As a result, they resist the change in their state of rest and do not move along with the branch immediately.
Loosely Held Leaves:
Another factor contributing to the detachment of leaves is that some of them are loosely held by the branch. The attachment between leaves and branches can vary depending on various factors such as age, health, and natural growth. If a leaf is loosely attached to the branch, the force applied by shaking can exceed the holding force, causing the leaf to detach and fall off.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when we vigorously shake a branch of a tree, the detachment of some leaves is primarily due to the inertia of rest exhibited by the leaves and the fact that some leaves are loosely held by the branch. The leaves resist the change in their state of rest initially, but if the force applied is strong enough or if their attachment is weak, they can detach from the branch and fall off.
What is the momentum of a body of mass 2m and velocity v/2?- a)mv/4
- b)mv
- c)2mv
- d)mv/2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the momentum of a body of mass 2m and velocity v/2?
a)
mv/4
b)
mv
c)
2mv
d)
mv/2
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Mass of the object = m
Velocity = v
Momentum = Mass x Velocity
Momentum = mv
The acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to:- a)Force.
- b)Momentum.
- c)Mass.
- d)Velocity.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to:
a)
Force.
b)
Momentum.
c)
Mass.
d)
Velocity.
|
|
Sarita Reddy answered |
For the same force, an object with twice the mass will have half the acceleration. If it had three times the mass, the same force will produce one-third the acceleration. Four times the mass gives one-fourth of the acceleration, and so on.
This type of relationship between quantities (double one, get half the other) is called an inverse proportion or inverse variation. In other words, then:
The acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
Newton's Second Law
"If the net force on an object is not zero, the object will accelerate. The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force. The magnitude of the acceleration is directly proportional to the net force applied, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object."
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which is the incorrect statement?
A spaceship continues moving in space with uniform speed because:
- A:
no force of friction due to air acts on it
- B:
its mass is zero in space
- C:
no force of gravitation acts on it
- D:
no force of friction due to earth acts on it
The answer is B.
Which is the incorrect statement?
A spaceship continues moving in space with uniform speed because:
no force of friction due to air acts on it
its mass is zero in space
no force of gravitation acts on it
no force of friction due to earth acts on it

|
Jasneet Kaur answered |
A spaceship continues moving in space with uniform speed because no force of gravitation acts on it but not it's mass is zero in space and everything in the space appear to be floating that is why the astronauts also appear to float in space but their mass is not zero actually.
A bullet of mass 10g travelling horizontally with a velocity of 150ms−1 strikes a stationary wooden block and come to rest in 0.03s. Calculate the distance of penetration of the bullet into the block. Also, Calculate the magnitude of the force exerted by the wooden block on the bullet.- a)120 N
- b)50 N
- c)- 50 N
- d)- 120 N
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bullet of mass 10g travelling horizontally with a velocity of 150ms−1 strikes a stationary wooden block and come to rest in 0.03s. Calculate the distance of penetration of the bullet into the block. Also, Calculate the magnitude of the force exerted by the wooden block on the bullet.
a)
120 N
b)
50 N
c)
- 50 N
d)
- 120 N

|
Let's Tute answered |
- Initial velocity of the bullet, u = 150 m/s
- Final velocity of the bullet, v = 0
- Mass of the bullet, m = 10 g = 0.01 kg
- Time taken by the bullet to come to rest, t = 0.03 s
- Let the distance of penetration be s
Using the first equation of motion:
v = u + at
Substituting the known values:
0 = 150 + a(0.03)
⇒ a = -5000 m/s² (Negative sign indicates retardation)
v = u + at
Substituting the known values:
0 = 150 + a(0.03)
⇒ a = -5000 m/s² (Negative sign indicates retardation)
Now using the second equation of motion:
v² = u² + 2as
Substituting the known values:
0 = 150² + 2 × (-5000) × s
⇒ s = 2.25 m (Distance of penetration)
v² = u² + 2as
Substituting the known values:
0 = 150² + 2 × (-5000) × s
⇒ s = 2.25 m (Distance of penetration)
Magnitude of the force exerted by the wooden block:
Using |F| = m|a|
|F| = 0.01 × 5000 = 50 N
Using |F| = m|a|
|F| = 0.01 × 5000 = 50 N
So, the force exerted by the wooden block is 50 N.
The magnitude of a physical quantity is 8.5 Ns. The physical quantity is :- a)force
- b)momentum
- c)pressure
- d)moment of force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnitude of a physical quantity is 8.5 Ns. The physical quantity is :
a)
force
b)
momentum
c)
pressure
d)
moment of force

|
Srijita answered |
The newton second (also newton-second, symbol N s or N·s) is the derived SI unit of impulse. It is dimensionally equivalent to the momentum unit kilogram metre per second (kg·m/s). One newton second corresponds to a one-newton force applied for one second. Derivation- p=mv =kg×m/s =kgm/s×s/s =kgm/s^2×s =N×s
Chapter doubts & questions for Force and Laws of Motion - Science Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Force and Laws of Motion - Science Class 9 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Class 9
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup