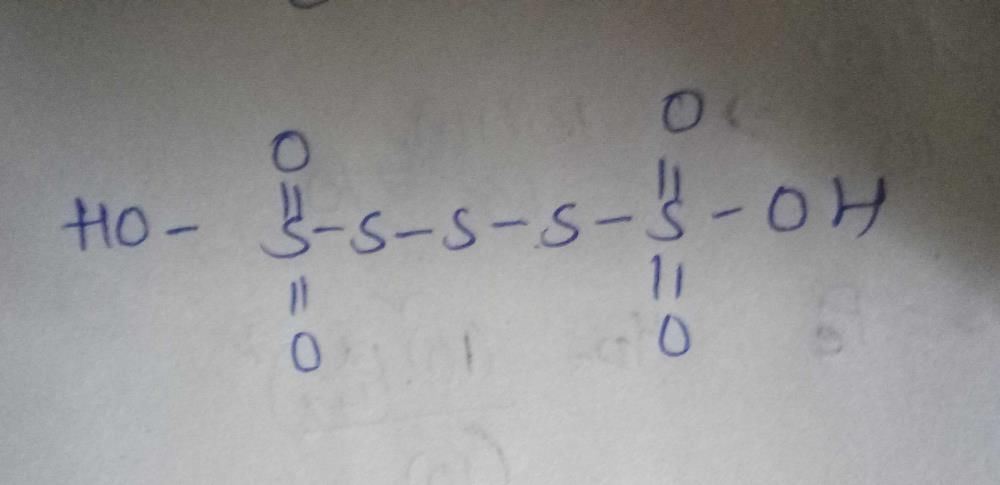All Exams >
Chemistry >
Topicwise Question Bank for IIT JAM/CSIR/GATE Chemistry >
All Questions
All questions of Main Group Elements (s & p blocks) for Chemistry Exam
Hydrolysis of (CH3)2 SiCl2 and CH3SiCl3 leads to:
- a)Cross–linked silicones only.
- b)Cross–linked and linear chain silicones, respectively.
- c)Linear chain silicones only.
- d)Linear chain and cross–linked silicones, respectively.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrolysis of (CH3)2 SiCl2 and CH3SiCl3 leads to:
a)
Cross–linked silicones only.
b)
Cross–linked and linear chain silicones, respectively.
c)
Linear chain silicones only.
d)
Linear chain and cross–linked silicones, respectively.
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Correct Answer :- a
Explanation : The silicon containing residual hydroxyl groups will be cross linked using boric acid and this tri functional acid, B(OH)3 groups, forms Si-O-B linkage between siloxane chains.
The compound having as S–S single bond is: - a)H2S2O3
- b)H2S2O4
- c)H2S2O7
- d)H2S2O8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound having as S–S single bond is:
a)
H2S2O3
b)
H2S2O4
c)
H2S2O7
d)
H2S2O8

|
Pranavi Mishra answered |
Explanation:
The given compound has an SS single bond, which means it contains a peroxo group (-O-O-).
The general formula for peroxo acids is H2O2 + X2Oy, where X and Y can be any element.
Option A (H2S2O3) does not contain a peroxo group, so it cannot be the correct answer.
Option B (H2S2O4) contains a peroxo group (-O-O-) and is the correct answer.
Option C (H2S2O7) contains two peroxo groups (-O-O-) and is known as peroxomonosulfuric acid.
Option D (H2S2O8) contains three peroxo groups (-O-O-) and is known as peroxodisulfuric acid.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B (H2S2O4).
The given compound has an SS single bond, which means it contains a peroxo group (-O-O-).
The general formula for peroxo acids is H2O2 + X2Oy, where X and Y can be any element.
Option A (H2S2O3) does not contain a peroxo group, so it cannot be the correct answer.
Option B (H2S2O4) contains a peroxo group (-O-O-) and is the correct answer.
Option C (H2S2O7) contains two peroxo groups (-O-O-) and is known as peroxomonosulfuric acid.
Option D (H2S2O8) contains three peroxo groups (-O-O-) and is known as peroxodisulfuric acid.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B (H2S2O4).
Do you expect the minimum energy necessary to eject a 3s electron from phosphorus in a photoelectron spectroscopy experiment for the process.
[Ne] 3s23p3 → [Ne] 3s13p3 + e- ,
Be larger than, smaller than, or the same as the 4th io nization energy (IE4) of phosphorus:
a)Largerb) Smallerc)The same d)Cannot be answered from the given informationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Due to better guarding of s electrons by p if we directly remove an s electron without removing the p electrons, it would take more energy had we removed all outer electrons before.
Hence A is correct.
How many moles of P4O10 will react with one mole of water:
- a)2 moles
- b)1/6 mole
- c)1/3 mole
- d)6 moles
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many moles of P4O10 will react with one mole of water:
a)
2 moles
b)
1/6 mole
c)
1/3 mole
d)
6 moles

|
Asf Institute answered |
The coefficients in the balanced chemical equation provide us with information that we can use to build this conversion factor. They tell us that six molecules of H2O are needed to react with one molecule of P4O10 in order to produce four molecules of phosphoric acid:
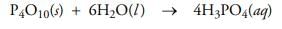
The ease of formation of the adduct, NH3 · BX3 (where X = F, Cl, Br) follows the order:- a)BBr3 < BCl3 < BF3
- b)BCl3 < BF3 < BBr3
- c)BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3
- d)BBr3 < BF3 < BCl3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ease of formation of the adduct, NH3 · BX3 (where X = F, Cl, Br) follows the order:
a)
BBr3 < BCl3 < BF3
b)
BCl3 < BF3 < BBr3
c)
BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3
d)
BBr3 < BF3 < BCl3

|
Bhavana Dasgupta answered |
Formation of Adduct NH3 BX3
The formation of adduct NH3 BX3 (where X = F, Cl, Br) is a common reaction in chemistry. This reaction involves the addition of ammonia (NH3) to a boron trihalide (BX3) to form a complex compound. The ease of formation of this adduct varies depending on the halogen present in the boron trihalide.
Order of Ease of Formation
The order of ease of formation of the adduct NH3 BX3 (where X = F, Cl, Br) is as follows:
BF3 BCl3 BBr3
This means that the adduct formed between ammonia and boron trifluoride (BF3) is the easiest to form, while the adduct formed between ammonia and boron tribromide (BBr3) is the most difficult to form.
Explanation
The ease of formation of the adduct NH3 BX3 can be explained by the following factors:
1. Electronegativity
The electronegativity of the halogen present in the boron trihalide plays a significant role in the ease of formation of the adduct. Fluorine (F) is the most electronegative element, followed by chlorine (Cl) and then bromine (Br). This means that the bond between boron and fluorine is the most polar, while the bond between boron and bromine is the least polar.
2. Size of the Halogen
The size of the halogen present in the boron trihalide also affects the ease of formation of the adduct. The larger the halogen, the more difficult it is for ammonia to approach the boron atom and form a complex. Bromine is larger than chlorine, which is larger than fluorine.
3. Bond Strength
The strength of the bond between boron and the halogen also affects the ease of formation of the adduct. The bond strength decreases as we move from fluorine to bromine.
Based on these factors, we can see that the ease of formation of the adduct NH3 BX3 follows the order BF3 BCl3 BBr3. Fluorine is the most electronegative and has the smallest size, making it the easiest to form a complex with ammonia. Chlorine is less electronegative and larger than fluorine, making it slightly more difficult to form a complex. Bromine has the lowest electronegativity and the largest size, making it the most difficult to form a complex with ammonia.
The formation of adduct NH3 BX3 (where X = F, Cl, Br) is a common reaction in chemistry. This reaction involves the addition of ammonia (NH3) to a boron trihalide (BX3) to form a complex compound. The ease of formation of this adduct varies depending on the halogen present in the boron trihalide.
Order of Ease of Formation
The order of ease of formation of the adduct NH3 BX3 (where X = F, Cl, Br) is as follows:
BF3 BCl3 BBr3
This means that the adduct formed between ammonia and boron trifluoride (BF3) is the easiest to form, while the adduct formed between ammonia and boron tribromide (BBr3) is the most difficult to form.
Explanation
The ease of formation of the adduct NH3 BX3 can be explained by the following factors:
1. Electronegativity
The electronegativity of the halogen present in the boron trihalide plays a significant role in the ease of formation of the adduct. Fluorine (F) is the most electronegative element, followed by chlorine (Cl) and then bromine (Br). This means that the bond between boron and fluorine is the most polar, while the bond between boron and bromine is the least polar.
2. Size of the Halogen
The size of the halogen present in the boron trihalide also affects the ease of formation of the adduct. The larger the halogen, the more difficult it is for ammonia to approach the boron atom and form a complex. Bromine is larger than chlorine, which is larger than fluorine.
3. Bond Strength
The strength of the bond between boron and the halogen also affects the ease of formation of the adduct. The bond strength decreases as we move from fluorine to bromine.
Based on these factors, we can see that the ease of formation of the adduct NH3 BX3 follows the order BF3 BCl3 BBr3. Fluorine is the most electronegative and has the smallest size, making it the easiest to form a complex with ammonia. Chlorine is less electronegative and larger than fluorine, making it slightly more difficult to form a complex. Bromine has the lowest electronegativity and the largest size, making it the most difficult to form a complex with ammonia.
Which one of the following order of the carbonates is correct for their decomposition temperature:- a)BaCO3 > CaCO3 > SrCO3 > MgCO3
- b)BaCO3 > SrCO3 > CaCO3 > MgCO3
- c)MgCO3 > CaCO3 > SrCO3 > BaCO3
- d)MgCO3 > CaCO3 > BaCO3 > SrCO3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following order of the carbonates is correct for their decomposition temperature:
a)
BaCO3 > CaCO3 > SrCO3 > MgCO3
b)
BaCO3 > SrCO3 > CaCO3 > MgCO3
c)
MgCO3 > CaCO3 > SrCO3 > BaCO3
d)
MgCO3 > CaCO3 > BaCO3 > SrCO3

|
Vandana Chopra answered |
Decomposition Temperature of Carbonates
Carbonates are compounds that contain the carbonate ion (CO32-) combined with a metal ion. When heated, carbonates decompose to form metal oxides and carbon dioxide gas. The decomposition temperature of different carbonates depends on the strength of the metal-oxygen bond in the carbonate ion.
The correct order of carbonates in terms of their decomposition temperature is given as:
Option B: BaCO3 SrCO3 CaCO3 MgCO3
This means that Barium Carbonate (BaCO3) has the highest decomposition temperature, followed by Strontium Carbonate (SrCO3), Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3), and Magnesium Carbonate (MgCO3) in decreasing order.
Explanation:
Barium Carbonate (BaCO3) has the highest decomposition temperature because the bond between Barium and Carbonate ions is the strongest due to the large size of Barium ion. This bond requires more energy to break, hence it has a higher decomposition temperature.
Strontium Carbonate (SrCO3) has a slightly lower decomposition temperature because the bond between Strontium and Carbonate ions is weaker than that of Barium and Carbonate ions.
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) has a lower decomposition temperature than Strontium Carbonate because the bond between Calcium and Carbonate ions is weaker than that of Strontium and Carbonate ions.
Magnesium Carbonate (MgCO3) has the lowest decomposition temperature because the bond between Magnesium and Carbonate ions is the weakest due to the small size of Magnesium ion.
Therefore, the correct order of carbonates in terms of their decomposition temperature is BaCO3 SrCO3 CaCO3 MgCO3, as given in option B.
Carbonates are compounds that contain the carbonate ion (CO32-) combined with a metal ion. When heated, carbonates decompose to form metal oxides and carbon dioxide gas. The decomposition temperature of different carbonates depends on the strength of the metal-oxygen bond in the carbonate ion.
The correct order of carbonates in terms of their decomposition temperature is given as:
Option B: BaCO3 SrCO3 CaCO3 MgCO3
This means that Barium Carbonate (BaCO3) has the highest decomposition temperature, followed by Strontium Carbonate (SrCO3), Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3), and Magnesium Carbonate (MgCO3) in decreasing order.
Explanation:
Barium Carbonate (BaCO3) has the highest decomposition temperature because the bond between Barium and Carbonate ions is the strongest due to the large size of Barium ion. This bond requires more energy to break, hence it has a higher decomposition temperature.
Strontium Carbonate (SrCO3) has a slightly lower decomposition temperature because the bond between Strontium and Carbonate ions is weaker than that of Barium and Carbonate ions.
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) has a lower decomposition temperature than Strontium Carbonate because the bond between Calcium and Carbonate ions is weaker than that of Strontium and Carbonate ions.
Magnesium Carbonate (MgCO3) has the lowest decomposition temperature because the bond between Magnesium and Carbonate ions is the weakest due to the small size of Magnesium ion.
Therefore, the correct order of carbonates in terms of their decomposition temperature is BaCO3 SrCO3 CaCO3 MgCO3, as given in option B.
The structure of hyponitrous acid molecule (H2N2O2) is:
- a)Linear (A –B–C–D type)
- b)
- c)
- d)
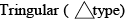
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure of hyponitrous acid molecule (H2N2O2) is:
a)
Linear (A –B–C–D type)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Dronacharya Institute answered |
Correct Answer :- C
Explanation : Trans and cis are the two possible structures of hyponitrous acid. White crystals are obtained from trans-hyponitrous which are explosive when dry and it is a weak acid which decomposes to nitrous oxide when in aqueous solution. Sodium salt can be obtained from cis acid.
Among the following substituted silanes, the one that gives cross–linked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis is:- a)(CH3)4 Si
- b)CH3SiCI3
- c)(CH3)2 SiCI2
- d)(CH3)3SiCI
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following substituted silanes, the one that gives cross–linked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis is:
a)
(CH3)4 Si
b)
CH3SiCI3
c)
(CH3)2 SiCI2
d)
(CH3)3SiCI

|
Shivam Khanna answered |
Substituted silanes give crosslinked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis. The correct option from the given substituted silanes is CH3SiCI3.
Explanation:
Silanes are compounds with the general formula SiHnXm, where X is a halogen or an organic group. Silanes undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water, resulting in the formation of siloxanes. Siloxanes are compounds with the general formula R2SiO, where R is an organic group. When silanes are substituted, they form crosslinked silicone polymers upon hydrolysis.
The given substituted silanes are:
a) (CH3)4Si
b) CH3SiCI3
c) (CH3)2SiCI2
d) (CH3)3SiCI
Out of the given options, CH3SiCI3 will give crosslinked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis. This is because CH3SiCI3 has one halogen atom and two organic groups attached to the silicon atom. The organic groups are capable of crosslinking with other siloxane chains, resulting in the formation of a three-dimensional network of silicone polymers.
The other options do not have the necessary substituents required for crosslinking. (CH3)4Si does not have any halogen or organic group attached to the silicon atom, while (CH3)2SiCI2 and (CH3)3SiCI have only one organic group and one halogen atom attached to the silicon atom, respectively. Therefore, they cannot form crosslinked silicone polymers upon hydrolysis.
In conclusion, CH3SiCI3 is the correct option among the given substituted silanes that will give crosslinked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis due to the presence of two organic groups attached to the silicon atom.
Explanation:
Silanes are compounds with the general formula SiHnXm, where X is a halogen or an organic group. Silanes undergo hydrolysis in the presence of water, resulting in the formation of siloxanes. Siloxanes are compounds with the general formula R2SiO, where R is an organic group. When silanes are substituted, they form crosslinked silicone polymers upon hydrolysis.
The given substituted silanes are:
a) (CH3)4Si
b) CH3SiCI3
c) (CH3)2SiCI2
d) (CH3)3SiCI
Out of the given options, CH3SiCI3 will give crosslinked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis. This is because CH3SiCI3 has one halogen atom and two organic groups attached to the silicon atom. The organic groups are capable of crosslinking with other siloxane chains, resulting in the formation of a three-dimensional network of silicone polymers.
The other options do not have the necessary substituents required for crosslinking. (CH3)4Si does not have any halogen or organic group attached to the silicon atom, while (CH3)2SiCI2 and (CH3)3SiCI have only one organic group and one halogen atom attached to the silicon atom, respectively. Therefore, they cannot form crosslinked silicone polymers upon hydrolysis.
In conclusion, CH3SiCI3 is the correct option among the given substituted silanes that will give crosslinked silicone polymer upon hydrolysis due to the presence of two organic groups attached to the silicon atom.
The role of phosphate in detergent power is to:- a)Control pH level of the detergent water mixture.
- b)Remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions from the water.
- c)Provide whiteness to the fabric.
- d)Prevent liquid detergent from solidifying.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The role of phosphate in detergent power is to:
a)
Control pH level of the detergent water mixture.
b)
Remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions from the water.
c)
Provide whiteness to the fabric.
d)
Prevent liquid detergent from solidifying.

|
Ipsita Patri answered |
Phosphates bind calcium and magnesium ions to prevent 'hard-water' type limescale deposits.
If a mixture of NaCl, conc. H2SO4 and K2Cr2O7 is heated in a dry test tube, a red vapour (P) is formed. This vapour (P) dissolves in aqueous NaOH to form a yellow solution, which upon treatment with AgNO3 forms a red solid (Q). P and Q are, respectively:- a)CrO2Cl2 and Ag2Cr2O7
- b)Na2 [CrOCl5] and Ag2CrO4
- c)Na2 [CrOCl5] and Ag2Cr2O7
- d)CrO2Cl2 and Ag2CrO4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a mixture of NaCl, conc. H2SO4 and K2Cr2O7 is heated in a dry test tube, a red vapour (P) is formed. This vapour (P) dissolves in aqueous NaOH to form a yellow solution, which upon treatment with AgNO3 forms a red solid (Q). P and Q are, respectively:
a)
CrO2Cl2 and Ag2Cr2O7
b)
Na2 [CrOCl5] and Ag2CrO4
c)
Na2 [CrOCl5] and Ag2Cr2O7
d)
CrO2Cl2 and Ag2CrO4

|
Ipsita Chopra answered |
Formation of Red Vapour (P)
- NaCl, conc. H2SO4 and K2Cr2O7 are heated in a dry test tube
- The mixture reacts to form a red vapour (P)
Dissolving Red Vapour (P) in NaOH
- The red vapour (P) is dissolved in aqueous NaOH
- A yellow solution is formed
Treatment of Yellow Solution with AgNO3
- The yellow solution is treated with AgNO3
- A red solid (Q) is formed
Identification of P and Q
- P is identified as CrO2Cl2 because it is formed when K2Cr2O7 is heated with conc. H2SO4 and NaCl
- Q is identified as Ag2CrO4 because it is formed when the yellow solution, which contains CrO2Cl2, is treated with AgNO3
Correct Answer: D
- The red vapour (P) is CrO2Cl2
- The red solid (Q) is Ag2CrO4
- NaCl, conc. H2SO4 and K2Cr2O7 are heated in a dry test tube
- The mixture reacts to form a red vapour (P)
Dissolving Red Vapour (P) in NaOH
- The red vapour (P) is dissolved in aqueous NaOH
- A yellow solution is formed
Treatment of Yellow Solution with AgNO3
- The yellow solution is treated with AgNO3
- A red solid (Q) is formed
Identification of P and Q
- P is identified as CrO2Cl2 because it is formed when K2Cr2O7 is heated with conc. H2SO4 and NaCl
- Q is identified as Ag2CrO4 because it is formed when the yellow solution, which contains CrO2Cl2, is treated with AgNO3
Correct Answer: D
- The red vapour (P) is CrO2Cl2
- The red solid (Q) is Ag2CrO4
Although both NF3 and NCl3 are covalent, NCl3 undergoes hydrolysis whereas NF3 does not because:- a)NF3 is more stable than NCl3
- b)Dipole moment of NF3 is more than NCl3
- c)Electronegativity of F > Cl
- d)Cl expand its octet by using d–orbitals.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Although both NF3 and NCl3 are covalent, NCl3 undergoes hydrolysis whereas NF3 does not because:
a)
NF3 is more stable than NCl3
b)
Dipole moment of NF3 is more than NCl3
c)
Electronegativity of F > Cl
d)
Cl expand its octet by using d–orbitals.

|
Yashvi Roy answered |
Explanation:
NCl3 and NF3 are both covalent molecules, but NCl3 undergoes hydrolysis whereas NF3 does not. The reason for this is that the chlorine atom in NCl3 has an expanded octet, while the nitrogen atom in NF3 does not. This means that chlorine can use its d orbitals to accommodate more electrons than it normally would be able to.
D-orbitals:
D-orbitals are the outermost orbitals in an atom, and they can be used to accommodate additional electrons beyond what is allowed by the octet rule. In NCl3, chlorine uses its d orbitals to accommodate the extra electrons from the water molecule during hydrolysis.
Expanded octet:
An expanded octet is when an atom has more than eight electrons in its outermost energy level. This is possible for atoms with d orbitals that can be used to accommodate additional electrons. Chlorine is one such atom, and it can accommodate up to 10 electrons in its outermost energy level.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reason why NCl3 undergoes hydrolysis while NF3 does not is that chlorine can expand its octet by using its d orbitals to accommodate the extra electrons from the water molecule. This is not possible for nitrogen in NF3, which does not have d orbitals and cannot accommodate additional electrons beyond the octet.
NCl3 and NF3 are both covalent molecules, but NCl3 undergoes hydrolysis whereas NF3 does not. The reason for this is that the chlorine atom in NCl3 has an expanded octet, while the nitrogen atom in NF3 does not. This means that chlorine can use its d orbitals to accommodate more electrons than it normally would be able to.
D-orbitals:
D-orbitals are the outermost orbitals in an atom, and they can be used to accommodate additional electrons beyond what is allowed by the octet rule. In NCl3, chlorine uses its d orbitals to accommodate the extra electrons from the water molecule during hydrolysis.
Expanded octet:
An expanded octet is when an atom has more than eight electrons in its outermost energy level. This is possible for atoms with d orbitals that can be used to accommodate additional electrons. Chlorine is one such atom, and it can accommodate up to 10 electrons in its outermost energy level.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the reason why NCl3 undergoes hydrolysis while NF3 does not is that chlorine can expand its octet by using its d orbitals to accommodate the extra electrons from the water molecule. This is not possible for nitrogen in NF3, which does not have d orbitals and cannot accommodate additional electrons beyond the octet.
What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in di-nitrogen trioxide?- a)+1
- b)+2
- c)+3
- d)+4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the oxidation state of nitrogen in di-nitrogen trioxide?
a)
+1
b)
+2
c)
+3
d)
+4

|
Asf Institute answered |
Di-nitrogen trioxide is formulated as N2O3
The oxidation state of oxygen atom is fixed at -2 since it is the more electronegative atom in this case.
If oxidation state of nitrogen is assumed to be ‘x’, then:
2x + (3x -2) = 0
2x – 6 = 0
x = +3
The oxidation state of nitrogen is +3.
The oxidation state of oxygen atom is fixed at -2 since it is the more electronegative atom in this case.
If oxidation state of nitrogen is assumed to be ‘x’, then:
2x + (3x -2) = 0
2x – 6 = 0
x = +3
The oxidation state of nitrogen is +3.
Heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium tetrahydridoborate gives one liquid product(X), along with other products under ambient conditions.Q. Compound X is:- a)NH4[BH4]
- b)[(NH3)2BH2][BH4]
- c)N3B3H6
- d)N3B3H12
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium tetrahydridoborate gives one liquid product(X), along with other products under ambient conditions.
Q.
Compound X is:
a)
NH4[BH4]
b)
[(NH3)2BH2][BH4]
c)
N3B3H6
d)
N3B3H12
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
NH4Cl + NaBH4 ------------> B3N3H6 + H2 + NaCl
For Et2AlX (X = PPh2–, Ph–, Cl– –and H–), the tendency towards dimeric structure fo llows the order:- a)PPh2– > Cl– > H– > Ph–
- b)Cl– > PPh2– > H– > Ph–
- c)Ph– > H– > Cl– > PPh2–
- d)H– > Ph– > PPh2– > Cl–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For Et2AlX (X = PPh2–, Ph–, Cl– –and H–), the tendency towards dimeric structure fo llows the order:
a)
PPh2– > Cl– > H– > Ph–
b)
Cl– > PPh2– > H– > Ph–
c)
Ph– > H– > Cl– > PPh2–
d)
H– > Ph– > PPh2– > Cl–

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
Explanation:
Et2AlX compounds are organometallic compounds that are commonly used as catalysts in organic reactions. These compounds have a tendency to form dimeric structures, where two molecules of the compound are bonded together. The order of this tendency towards dimerization follows the order of the X group attached to the Et2Al.
The X group can be PPh2, Ph, Cl, or H. Let's look at each of these groups individually:
1. PPh2: This is the triphenylphosphine group, which is a bulky and sterically hindered group. This group reduces the tendency towards dimerization because it takes up more space and makes it difficult for two molecules to come close enough to form a dimer.
2. Cl: The chlorine group is a small and electronegative group. It has a moderate tendency towards dimerization because it can form weak hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules.
3. H: The hydrogen group is the smallest and least polar group. It has a strong tendency towards dimerization because it can form strong hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules.
4. Ph: The phenyl group is a large and non-polar group. It has the strongest tendency towards dimerization because it can form strong pi-pi interactions with neighboring molecules.
Based on these factors, the order of the tendency towards dimerization follows the order of the X group attached to the Et2Al. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', where the order is Ph, H, Cl, PPh2.
Et2AlX compounds are organometallic compounds that are commonly used as catalysts in organic reactions. These compounds have a tendency to form dimeric structures, where two molecules of the compound are bonded together. The order of this tendency towards dimerization follows the order of the X group attached to the Et2Al.
The X group can be PPh2, Ph, Cl, or H. Let's look at each of these groups individually:
1. PPh2: This is the triphenylphosphine group, which is a bulky and sterically hindered group. This group reduces the tendency towards dimerization because it takes up more space and makes it difficult for two molecules to come close enough to form a dimer.
2. Cl: The chlorine group is a small and electronegative group. It has a moderate tendency towards dimerization because it can form weak hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules.
3. H: The hydrogen group is the smallest and least polar group. It has a strong tendency towards dimerization because it can form strong hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules.
4. Ph: The phenyl group is a large and non-polar group. It has the strongest tendency towards dimerization because it can form strong pi-pi interactions with neighboring molecules.
Based on these factors, the order of the tendency towards dimerization follows the order of the X group attached to the Et2Al. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', where the order is Ph, H, Cl, PPh2.
Pyroenes are a class of silicate minerals, which exhibit a polymeric chain structure, as shown below: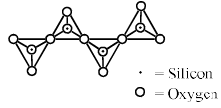 Its simplest repeat unit is
Its simplest repeat unit is - a)[SiO4]4–
- b)[SiO3]2–
- c)[Si2O7]6–
- d)[Si4O11]6–
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyroenes are a class of silicate minerals, which exhibit a polymeric chain structure, as shown below:
Its simplest repeat unit is
a)
[SiO4]4–
b)
[SiO3]2–
c)
[Si2O7]6–
d)
[Si4O11]6–

|
Pooja Shah answered |
It is a chain type silicate which two oxygen is shaired .general formula( sio3 )n2n- .this is a pyeoxine so option b is correct.
The decreasing order of ionic nature of the following compound is:- a)LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF
- b)LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF
- c)CsF > NaBr > KCl > LiI
- d)CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The decreasing order of ionic nature of the following compound is:
a)
LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF
b)
LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF
c)
CsF > NaBr > KCl > LiI
d)
CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI

|
Varun Yadav answered |
The decreasing order of ionic nature of the given compounds is:
a) LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF
b) LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF
c) CsF > NaBr > KCl > LiI
d) CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI
Explanation:
Ionic nature is the measure of the degree of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a compound. The greater the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms, the more ionic the bond will be.
In the given compounds, the cationic and anionic components are:
LiI: Li+ and I-
NaBr: Na+ and Br-
KCl: K+ and Cl-
CsF: Cs+ and F-
The electronegativity values of these atoms are:
Li: 0.98
Na: 0.93
K: 0.82
Cs: 0.79
I: 2.66
Br: 2.96
Cl: 3.16
F: 3.98
Therefore, the greater the difference in electronegativity between the cation and anion, the more ionic the bond will be.
Now, let's analyze the given options:
a) LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF
LiI has the highest ionic character because of the large difference in electronegativity between Li and I. CsF has the lowest ionic character because of the smaller difference in electronegativity between Cs and F. Therefore, the decreasing order of ionic character is LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF.
b) LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF
The trend is similar to option a), but KCl has a slightly lower ionic character than NaBr. Therefore, the decreasing order of ionic character is LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF.
c) CsF > NaBr > KCl > LiI
This option is incorrect as it has the opposite trend of increasing ionic character.
d) CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI
This option is correct as it has the decreasing trend of ionic character, with CsF having the highest and LiI having the lowest ionic character.
Therefore, the correct answer is option d) CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI.
a) LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF
b) LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF
c) CsF > NaBr > KCl > LiI
d) CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI
Explanation:
Ionic nature is the measure of the degree of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions in a compound. The greater the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms, the more ionic the bond will be.
In the given compounds, the cationic and anionic components are:
LiI: Li+ and I-
NaBr: Na+ and Br-
KCl: K+ and Cl-
CsF: Cs+ and F-
The electronegativity values of these atoms are:
Li: 0.98
Na: 0.93
K: 0.82
Cs: 0.79
I: 2.66
Br: 2.96
Cl: 3.16
F: 3.98
Therefore, the greater the difference in electronegativity between the cation and anion, the more ionic the bond will be.
Now, let's analyze the given options:
a) LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF
LiI has the highest ionic character because of the large difference in electronegativity between Li and I. CsF has the lowest ionic character because of the smaller difference in electronegativity between Cs and F. Therefore, the decreasing order of ionic character is LiI > NaBr > KCl > CsF.
b) LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF
The trend is similar to option a), but KCl has a slightly lower ionic character than NaBr. Therefore, the decreasing order of ionic character is LiI > KCl > NaBr > CsF.
c) CsF > NaBr > KCl > LiI
This option is incorrect as it has the opposite trend of increasing ionic character.
d) CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI
This option is correct as it has the decreasing trend of ionic character, with CsF having the highest and LiI having the lowest ionic character.
Therefore, the correct answer is option d) CsF > KCl > NaBr > LiI.
The compound having the highest melting point is:- a)LiCl
- b)LiF
- c)LiI
- d)LiBr
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound having the highest melting point is:
a)
LiCl
b)
LiF
c)
LiI
d)
LiBr

|
Bijoy Kapoor answered |
In general, ionic compounds have high melting points because the electrostatic forces connecting the ions – the ion-ion interaction – are strong. In organic compounds, the presence of polarity, especially hydrogen bonding, usually leads to a higher melting point.
Among the following, the group of molecules that undergoes rapid hydrolysis is:- a)SF6, Al2Cl6, SiMe4
- b)BCl3, SF6, SiCl4
- c)BCl3, SiCl4, PCl5
- d)SF6, Al2Cl6, SiCl4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the group of molecules that undergoes rapid hydrolysis is:
a)
SF6, Al2Cl6, SiMe4
b)
BCl3, SF6, SiCl4
c)
BCl3, SiCl4, PCl5
d)
SF6, Al2Cl6, SiCl4

|
Anshika Chavan answered |
Explanation:
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which water breaks down a compound into two or more products. In this reaction, one part of the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the other part of the molecule, which is often an electrophile.
The rate of hydrolysis depends on the nature of the molecule, as well as the conditions under which the reaction takes place. Some molecules undergo hydrolysis very rapidly, while others are more resistant to this process.
Among the given group of molecules, the group that undergoes rapid hydrolysis is:
BCl3, SiCl4, PCl5
This is because these molecules have polar bonds, which make them susceptible to attack by water molecules. In addition, they have high electron densities, which makes them highly reactive.
On the other hand, SF6, Al2Cl6, and SiMe4 are less likely to undergo hydrolysis because they have nonpolar bonds and low electron densities, which make them less reactive.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which water breaks down a compound into two or more products. In this reaction, one part of the water molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the other part of the molecule, which is often an electrophile.
The rate of hydrolysis depends on the nature of the molecule, as well as the conditions under which the reaction takes place. Some molecules undergo hydrolysis very rapidly, while others are more resistant to this process.
Among the given group of molecules, the group that undergoes rapid hydrolysis is:
BCl3, SiCl4, PCl5
This is because these molecules have polar bonds, which make them susceptible to attack by water molecules. In addition, they have high electron densities, which makes them highly reactive.
On the other hand, SF6, Al2Cl6, and SiMe4 are less likely to undergo hydrolysis because they have nonpolar bonds and low electron densities, which make them less reactive.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Which of the following halogen exists as a solid at room temperature?
- a)Chlorine
- b)Iodine
- c)Fluorine
- d)Bromine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following halogen exists as a solid at room temperature?
a)
Chlorine
b)
Iodine
c)
Fluorine
d)
Bromine
|
|
Vishal answered |
If the answer is B then your eye sight is week, because Chlorine and fluorine are gases at R.T. whereas bromine is liquid and Iodine is Solid at R.T. (room temperature)
Solution of alkali metals in liquid NH3 conducts electricity. It is due to formation of:- a)Na+ + Na– ion in liquid ammonia.
- b)Na+ + e– (NH3)x in liquid ammonia.
- c)Na–, (NH2)– and NH4+ ion in liquid NH3.
- d)The solution conducts like a metallic conductor with solvated electrons carrying the charge.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Solution of alkali metals in liquid NH3 conducts electricity. It is due to formation of:
a)
Na+ + Na– ion in liquid ammonia.
b)
Na+ + e– (NH3)x in liquid ammonia.
c)
Na–, (NH2)– and NH4+ ion in liquid NH3.
d)
The solution conducts like a metallic conductor with solvated electrons carrying the charge.

|
Niharika Kulkarni answered |
Explanation:
Alkali metals such as Na, K, etc. dissolve in liquid ammonia to form a deep blue solution that conducts electricity. This is due to the formation of ammoniated electrons, which are solvated electrons in liquid ammonia. The solvated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution.
Formation of ammoniated electrons:
When an alkali metal is added to liquid ammonia, it reacts with the solvent to form ammoniated cations and solvated electrons. For example, when sodium is added to liquid ammonia, it reacts as follows:
Na + NH3 → Na+ (NH3)x + e- (NH3)x
The reaction produces sodium cations and solvated electrons, which are surrounded by ammonia molecules. The solvated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution.
Conductivity of the solution:
The solution of alkali metals in liquid ammonia conducts electricity like a metallic conductor. The solvated electrons are free to move throughout the solution, carrying the charge. The conductivity of the solution depends on the concentration of solvated electrons, which is affected by the concentration of the alkali metal and the temperature of the solution.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the solution of alkali metals in liquid ammonia conducts electricity due to the formation of solvated electrons. The solvated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution, and their concentration depends on the concentration of the alkali metal and the temperature of the solution.
Alkali metals such as Na, K, etc. dissolve in liquid ammonia to form a deep blue solution that conducts electricity. This is due to the formation of ammoniated electrons, which are solvated electrons in liquid ammonia. The solvated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution.
Formation of ammoniated electrons:
When an alkali metal is added to liquid ammonia, it reacts with the solvent to form ammoniated cations and solvated electrons. For example, when sodium is added to liquid ammonia, it reacts as follows:
Na + NH3 → Na+ (NH3)x + e- (NH3)x
The reaction produces sodium cations and solvated electrons, which are surrounded by ammonia molecules. The solvated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution.
Conductivity of the solution:
The solution of alkali metals in liquid ammonia conducts electricity like a metallic conductor. The solvated electrons are free to move throughout the solution, carrying the charge. The conductivity of the solution depends on the concentration of solvated electrons, which is affected by the concentration of the alkali metal and the temperature of the solution.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the solution of alkali metals in liquid ammonia conducts electricity due to the formation of solvated electrons. The solvated electrons are responsible for the electrical conductivity of the solution, and their concentration depends on the concentration of the alkali metal and the temperature of the solution.
The degree of hydration is expected to be maximum for:- a)Mg2+
- b)Na+
- c)Ba2+
- d)K+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The degree of hydration is expected to be maximum for:
a)
Mg2+
b)
Na+
c)
Ba2+
d)
K+

|
Shilpa Datta answered |
Explanation:
The degree of hydration is defined as the number of water molecules attached to an ion. The degree of hydration increases with the increase in the charge density of the ion because more water molecules are required to neutralize the charge on the ion. The charge density of an ion is directly proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the size of the ion.
Charge and Size of Ions:
The charge and size of ions are as follows:
- Mg2+ has a charge of +2 and a size of 0.72 Å.
- Na+ has a charge of +1 and a size of 1.02 Å.
- Ba2+ has a charge of +2 and a size of 1.61 Å.
- K+ has a charge of +1 and a size of 1.33 Å.
Reasoning:
The charge density of Mg2+ is higher than Na+, Ba2+, and K+. This is because Mg2+ has a smaller size and a higher charge compared to the other ions. As a result, the degree of hydration of Mg2+ is expected to be the highest among the given options.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (Mg2+).
The degree of hydration is defined as the number of water molecules attached to an ion. The degree of hydration increases with the increase in the charge density of the ion because more water molecules are required to neutralize the charge on the ion. The charge density of an ion is directly proportional to the charge and inversely proportional to the size of the ion.
Charge and Size of Ions:
The charge and size of ions are as follows:
- Mg2+ has a charge of +2 and a size of 0.72 Å.
- Na+ has a charge of +1 and a size of 1.02 Å.
- Ba2+ has a charge of +2 and a size of 1.61 Å.
- K+ has a charge of +1 and a size of 1.33 Å.
Reasoning:
The charge density of Mg2+ is higher than Na+, Ba2+, and K+. This is because Mg2+ has a smaller size and a higher charge compared to the other ions. As a result, the degree of hydration of Mg2+ is expected to be the highest among the given options.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (Mg2+).
Oxygen has a positive oxidation state in:- a)O2F2
- b)Na2O2
- c)Cl2O2
- d)H2O2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen has a positive oxidation state in:
a)
O2F2
b)
Na2O2
c)
Cl2O2
d)
H2O2

|
Anshul Mehra answered |
**Oxygen Oxidation States**
Oxidation state is a measure of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a compound. It indicates the number of electrons an atom has gained or lost in order to form the compound. Oxygen can have different oxidation states depending on the compound it is in.
**Oxygen in O2F2**
In O2F2, oxygen has a positive oxidation state. This can be determined by assigning oxidation numbers to each element in the compound and applying the rules for assigning oxidation numbers.
The oxidation number of fluorine is always -1 in compounds, as it is the most electronegative element. Since there are two fluorine atoms in O2F2, the total oxidation number for fluorine is -2.
The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation number of oxygen can be calculated as follows:
2x + (-2) = 0
2x = 2
x = 1
Therefore, oxygen has an oxidation state of +1 in O2F2.
**Explanation of the Answer**
The correct answer is option 'A' because in O2F2, oxygen has a positive oxidation state of +1. This is determined by applying the rules for assigning oxidation numbers and considering the overall charge of the compound.
It is important to note that the other options given (Na2O2, Cl2O2, and H2O2) do not have oxygen with a positive oxidation state.
In Na2O2, the oxidation number of sodium is +1 (as it is an alkali metal) and the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen is -1.
In Cl2O2, the oxidation number of chlorine is 0 (as it is a diatomic molecule) and the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen is -1.
In H2O2, the oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (as it is an alkali metal) and the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen is -1.
Therefore, the only compound in which oxygen has a positive oxidation state is O2F2.
Oxidation state is a measure of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a compound. It indicates the number of electrons an atom has gained or lost in order to form the compound. Oxygen can have different oxidation states depending on the compound it is in.
**Oxygen in O2F2**
In O2F2, oxygen has a positive oxidation state. This can be determined by assigning oxidation numbers to each element in the compound and applying the rules for assigning oxidation numbers.
The oxidation number of fluorine is always -1 in compounds, as it is the most electronegative element. Since there are two fluorine atoms in O2F2, the total oxidation number for fluorine is -2.
The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation number of oxygen can be calculated as follows:
2x + (-2) = 0
2x = 2
x = 1
Therefore, oxygen has an oxidation state of +1 in O2F2.
**Explanation of the Answer**
The correct answer is option 'A' because in O2F2, oxygen has a positive oxidation state of +1. This is determined by applying the rules for assigning oxidation numbers and considering the overall charge of the compound.
It is important to note that the other options given (Na2O2, Cl2O2, and H2O2) do not have oxygen with a positive oxidation state.
In Na2O2, the oxidation number of sodium is +1 (as it is an alkali metal) and the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen is -1.
In Cl2O2, the oxidation number of chlorine is 0 (as it is a diatomic molecule) and the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen is -1.
In H2O2, the oxidation number of hydrogen is +1 (as it is an alkali metal) and the oxidation number of oxygen is -1. The compound is neutral, so the sum of the oxidation numbers must be zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen is -1.
Therefore, the only compound in which oxygen has a positive oxidation state is O2F2.
The conductance at infinite dilution follows the order:- a)Li+ > Na+ > K+
- b)Na+ > Li+ > K+
- c)K+ > Li+ > Na+
- d)K+ > Na+ > Li+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The conductance at infinite dilution follows the order:
a)
Li+ > Na+ > K+
b)
Na+ > Li+ > K+
c)
K+ > Li+ > Na+
d)
K+ > Na+ > Li+

|
Shubham Rajput answered |
As we go down the group conductance at infinite dilution increases.
The Lewis acidity of BF3 is less than BCl3 even though fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine. It is due to:- a)Stronger 2p(B)–2p(F) σ–bonding.
- b)Stronger 2p(B)–2p(F) π–bonding.
- c)Stronger 2p(B)–2p(Cl) σ–bonding.
- d)Stronger 2p(B)–2p(Cl) π–bonding.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Lewis acidity of BF3 is less than BCl3 even though fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine. It is due to:
a)
Stronger 2p(B)–2p(F) σ–bonding.
b)
Stronger 2p(B)–2p(F) π–bonding.
c)
Stronger 2p(B)–2p(Cl) σ–bonding.
d)
Stronger 2p(B)–2p(Cl) π–bonding.

|
Tejas Goyal answered |
Explanation:
The Lewis acidity of a compound refers to its ability to accept an electron pair. In the case of BF3 and BCl3, both compounds are Lewis acids because they have an incomplete octet of electrons in their central boron atom. However, the Lewis acidity of BF3 is lower than BCl3, despite fluorine being more electronegative than chlorine. This can be explained by considering the bonding between the boron atom and the fluorine or chlorine atoms.
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity:
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine, indicating that it has a higher affinity for electrons. This leads to a polar covalent bond between boron and fluorine in BF3 and boron and chlorine in BCl3.
Strength of Bonding:
The strength of the bonding between the boron and the fluorine or chlorine atoms can be evaluated by considering the overlapping of their atomic orbitals. The 2p orbitals of boron and the 2p orbitals of fluorine or chlorine participate in the formation of sigma bonds in BF3 and BCl3.
Explanation of Option B:
The correct answer, option B, states that the stronger 2p(B)2p(F) bonding in BF3 compared to BCl3 is the reason for the lower Lewis acidity of BF3.
Reasoning:
The 2p orbitals of boron and fluorine overlap to form sigma bonds in BF3. Due to the higher electronegativity of fluorine, these bonding orbitals are more strongly attracted towards fluorine, resulting in a stronger bond. This stronger bonding in BF3 makes it less willing to accept an electron pair, reducing its Lewis acidity.
On the other hand, in BCl3, the bonding between boron and chlorine is weaker due to the lower electronegativity of chlorine. This weaker bonding makes BCl3 more willing to accept an electron pair, leading to a higher Lewis acidity compared to BF3.
In summary, despite fluorine being more electronegative than chlorine, the stronger bonding between boron and fluorine in BF3 reduces its Lewis acidity compared to BCl3.
The Lewis acidity of a compound refers to its ability to accept an electron pair. In the case of BF3 and BCl3, both compounds are Lewis acids because they have an incomplete octet of electrons in their central boron atom. However, the Lewis acidity of BF3 is lower than BCl3, despite fluorine being more electronegative than chlorine. This can be explained by considering the bonding between the boron atom and the fluorine or chlorine atoms.
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity:
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine, indicating that it has a higher affinity for electrons. This leads to a polar covalent bond between boron and fluorine in BF3 and boron and chlorine in BCl3.
Strength of Bonding:
The strength of the bonding between the boron and the fluorine or chlorine atoms can be evaluated by considering the overlapping of their atomic orbitals. The 2p orbitals of boron and the 2p orbitals of fluorine or chlorine participate in the formation of sigma bonds in BF3 and BCl3.
Explanation of Option B:
The correct answer, option B, states that the stronger 2p(B)2p(F) bonding in BF3 compared to BCl3 is the reason for the lower Lewis acidity of BF3.
Reasoning:
The 2p orbitals of boron and fluorine overlap to form sigma bonds in BF3. Due to the higher electronegativity of fluorine, these bonding orbitals are more strongly attracted towards fluorine, resulting in a stronger bond. This stronger bonding in BF3 makes it less willing to accept an electron pair, reducing its Lewis acidity.
On the other hand, in BCl3, the bonding between boron and chlorine is weaker due to the lower electronegativity of chlorine. This weaker bonding makes BCl3 more willing to accept an electron pair, leading to a higher Lewis acidity compared to BF3.
In summary, despite fluorine being more electronegative than chlorine, the stronger bonding between boron and fluorine in BF3 reduces its Lewis acidity compared to BCl3.
Ammonolysis of S2Cl2 in an inert solvent gives:- a)S2N2
- b)S2N2Cl
- c)S2N2H4
- d)S4N4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ammonolysis of S2Cl2 in an inert solvent gives:
a)
S2N2
b)
S2N2Cl
c)
S2N2H4
d)
S4N4

|
Harshitha Sharma answered |
Ammonolysis of S2Cl2 in an inert solvent gives S4N4.
Explanation:
Ammonolysis is a reaction in which ammonia (NH3) is used to replace a functional group in a compound. In this case, S2Cl2 (disulfur dichloride) reacts with ammonia (NH3) in an inert solvent to form S4N4 (tetrasulfur tetranitride).
The reaction can be represented as follows:
S2Cl2 + 4NH3 → S4N4 + 4HCl
Here is a detailed explanation of the reaction:
1. Disulfur dichloride (S2Cl2) is a yellowish liquid that is used as a reagent in various chemical reactions. It is a covalent compound formed by the combination of two sulfur atoms and two chlorine atoms.
2. Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is a versatile compound that can act as both a base and a nucleophile in chemical reactions.
3. In an inert solvent, such as a non-reactive organic solvent like benzene or toluene, S2Cl2 reacts with NH3. The inert solvent provides a medium for the reaction to occur without interfering or reacting with the reactants.
4. During the reaction, each sulfur atom in S2Cl2 is replaced by two ammonia molecules. The chlorine atoms are displaced as chloride ions (Cl-) and combine with hydrogen ions (H+) from the ammonium ion (NH4+) formed in the reaction.
5. The product of the reaction is S4N4, which is a yellow solid. It is a covalent compound composed of four sulfur atoms and four nitrogen atoms. The nitrogen atoms are derived from the ammonia molecules used in the reaction.
Overall, the ammonolysis of S2Cl2 in an inert solvent results in the formation of S4N4, which is a solid compound with unique chemical properties.
Explanation:
Ammonolysis is a reaction in which ammonia (NH3) is used to replace a functional group in a compound. In this case, S2Cl2 (disulfur dichloride) reacts with ammonia (NH3) in an inert solvent to form S4N4 (tetrasulfur tetranitride).
The reaction can be represented as follows:
S2Cl2 + 4NH3 → S4N4 + 4HCl
Here is a detailed explanation of the reaction:
1. Disulfur dichloride (S2Cl2) is a yellowish liquid that is used as a reagent in various chemical reactions. It is a covalent compound formed by the combination of two sulfur atoms and two chlorine atoms.
2. Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It is a versatile compound that can act as both a base and a nucleophile in chemical reactions.
3. In an inert solvent, such as a non-reactive organic solvent like benzene or toluene, S2Cl2 reacts with NH3. The inert solvent provides a medium for the reaction to occur without interfering or reacting with the reactants.
4. During the reaction, each sulfur atom in S2Cl2 is replaced by two ammonia molecules. The chlorine atoms are displaced as chloride ions (Cl-) and combine with hydrogen ions (H+) from the ammonium ion (NH4+) formed in the reaction.
5. The product of the reaction is S4N4, which is a yellow solid. It is a covalent compound composed of four sulfur atoms and four nitrogen atoms. The nitrogen atoms are derived from the ammonia molecules used in the reaction.
Overall, the ammonolysis of S2Cl2 in an inert solvent results in the formation of S4N4, which is a solid compound with unique chemical properties.
Among the following, the incorrect statement is:- a)At low pressure, real gases show ideal behaviour.
- b)At high temperature, real gases show ideal behaviour.
- c)At very large volume, real gases show ideal behaviour
- d)At Boyle’s temperature, real gases show ideal behaviour.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following, the incorrect statement is:
a)
At low pressure, real gases show ideal behaviour.
b)
At high temperature, real gases show ideal behaviour.
c)
At very large volume, real gases show ideal behaviour
d)
At Boyle’s temperature, real gases show ideal behaviour.
|
|
Ananya Kumari answered |
The following sentences is astat mentioned
and being of there about ,
at very large volume, real gases show ideal bheviour ans
and being of there about ,
at very large volume, real gases show ideal bheviour ans
Among the following donors, the one that forms most stable adduct with the Lewis acid B(CH3)3 is:- a)4–Methylpyridine
- b)2,6–Dimethylpyridine
- c)4–Nitropyridine
- d)2,6–Di–tert–butylpyridine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following donors, the one that forms most stable adduct with the Lewis acid B(CH3)3 is:
a)
4–Methylpyridine
b)
2,6–Dimethylpyridine
c)
4–Nitropyridine
d)
2,6–Di–tert–butylpyridine

|
Vipin Singh answered |
The more the election density on nitrogen more stable adduct will form with Lewis acid.but in case of b and d part crowding increases so stability decrease. so a part will be the answer.
Hope ,this will help you.
Hope ,this will help you.
In borazine (B3N3H6) molecule, the number of isomers which are possible of its disubstituted borazine molecule of the formula [B3N3H4X2] without changing its ring structure is:- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Four
- d)Six
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In borazine (B3N3H6) molecule, the number of isomers which are possible of its disubstituted borazine molecule of the formula [B3N3H4X2] without changing its ring structure is:
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Four
d)
Six

|
Sparsh Menon answered |
if you put a=b=pi/4, then c=0 and tan a = 1.
Hence, (b) or (c) can be the correct answers.
Now, let us suppose that a = pi/8, then b = 3pi/8. Then c = - pi/4.
Then ‘tan b + tan c’ will not fit. Hence, (c) is the correct answer.
The atomicity and the total number of bonds in the elemental white phosphorous molecule are respectively:- a)4 and 6
- b)6 and 4
- c)4 and 4
- d)6 and
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The atomicity and the total number of bonds in the elemental white phosphorous molecule are respectively:
a)
4 and 6
b)
6 and 4
c)
4 and 4
d)
6 and

|
Sahana Sharma answered |
Atomicity and Bonds in White Phosphorous Molecule
Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule. The white phosphorus molecule (P4) is a simple covalent molecule consisting of four phosphorus atoms. Therefore, the atomicity of the white phosphorus molecule is 4.
Bonds refer to the connections between atoms in a molecule. In the white phosphorus molecule, each phosphorus atom is covalently bonded to three other phosphorus atoms. This means that the total number of bonds in the white phosphorus molecule is 6 (3 bonds per atom x 4 atoms).
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, which states that the atomicity and the total number of bonds in the elemental white phosphorus molecule are 4 and 6, respectively.
Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule. The white phosphorus molecule (P4) is a simple covalent molecule consisting of four phosphorus atoms. Therefore, the atomicity of the white phosphorus molecule is 4.
Bonds refer to the connections between atoms in a molecule. In the white phosphorus molecule, each phosphorus atom is covalently bonded to three other phosphorus atoms. This means that the total number of bonds in the white phosphorus molecule is 6 (3 bonds per atom x 4 atoms).
Therefore, the correct answer is option A, which states that the atomicity and the total number of bonds in the elemental white phosphorus molecule are 4 and 6, respectively.
Aqua regia is a powerful oxidizing agent because it contains:- a)Free O2 and Cl2O
- b)Free O2 and N2
- c)Free Cl2 and ClNO
- d)Free N2 and Cl2O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Aqua regia is a powerful oxidizing agent because it contains:
a)
Free O2 and Cl2O
b)
Free O2 and N2
c)
Free Cl2 and ClNO
d)
Free N2 and Cl2O

|
Anagha Chauhan answered |
Aqua regia is a highly corrosive mixture of concentrated nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizing agent, which means it is capable of oxidizing other substances. The power of this oxidizing agent is due to the presence of free chlorine and nitrosyl chloride in the mixture. Let's break down the answer into headings and HTML bullet points for better understanding:
Components of Aqua Regia:
- Aqua regia is a mixture of concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- The concentration of both acids varies, but typically it is a 3:1 mixture of HCl and HNO3.
Oxidizing Properties:
- Aqua regia is a powerful oxidizing agent because it contains free chlorine (Cl) and nitrosyl chloride (NOCl) in the mixture.
- Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent, while hydrochloric acid is a strong reducing agent.
- When mixed together, they react to form chlorine and nitrosyl chloride, which are even stronger oxidizing agents than the individual acids.
Reaction Mechanism:
- When aqua regia is added to a substance, it reacts with the substance to form chlorine gas (Cl2) and nitrosyl chloride gas (NOCl).
- The chlorine gas oxidizes the substance by removing electrons, while the nitrosyl chloride oxidizes the substance by adding oxygen atoms.
Applications:
- Aqua regia is commonly used in the extraction and purification of gold and platinum.
- It is also used in the analysis of metals and minerals.
- However, due to its highly corrosive nature, it must be handled with extreme caution and only by trained professionals.
In conclusion, aqua regia is a powerful oxidizing agent due to the presence of free chlorine and nitrosyl chloride in the mixture. Its oxidizing properties make it useful in a variety of applications, but it must be handled with care due to its corrosive nature.
Components of Aqua Regia:
- Aqua regia is a mixture of concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- The concentration of both acids varies, but typically it is a 3:1 mixture of HCl and HNO3.
Oxidizing Properties:
- Aqua regia is a powerful oxidizing agent because it contains free chlorine (Cl) and nitrosyl chloride (NOCl) in the mixture.
- Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent, while hydrochloric acid is a strong reducing agent.
- When mixed together, they react to form chlorine and nitrosyl chloride, which are even stronger oxidizing agents than the individual acids.
Reaction Mechanism:
- When aqua regia is added to a substance, it reacts with the substance to form chlorine gas (Cl2) and nitrosyl chloride gas (NOCl).
- The chlorine gas oxidizes the substance by removing electrons, while the nitrosyl chloride oxidizes the substance by adding oxygen atoms.
Applications:
- Aqua regia is commonly used in the extraction and purification of gold and platinum.
- It is also used in the analysis of metals and minerals.
- However, due to its highly corrosive nature, it must be handled with extreme caution and only by trained professionals.
In conclusion, aqua regia is a powerful oxidizing agent due to the presence of free chlorine and nitrosyl chloride in the mixture. Its oxidizing properties make it useful in a variety of applications, but it must be handled with care due to its corrosive nature.
Which of the following interhalogen compounds does not exist:- a)ClF3
- b)FCl3
- c)IF5
- d)BrF3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following interhalogen compounds does not exist:
a)
ClF3
b)
FCl3
c)
IF5
d)
BrF3

|
Jaya Sen answered |
Explanation:
Interhalogen compounds are formed between two different halogens. These are of different types such as IF, BrF, ClF, BrCl, etc. They can be easily prepared by the direct combination of halogens under appropriate conditions. Some examples of interhalogen compounds are:
a) ClF3
b) FCl3
c) IF5
d) BrF3
Out of these, FCl3 is the only compound that does not exist. This can be explained as follows:
Reasons for non-existence of FCl3:
1. Violation of the Octet Rule: FCl3 violates the octet rule as the central atom (Cl) has only 6 electrons in its valence shell.
2. High Electron Density: Fluorine is a highly electronegative element, so it attracts electrons towards itself. Due to this, the electron density around the central atom (Cl) becomes very high. As a result, it is difficult to add more electrons to the central atom.
3. Lack of Empty d-orbitals: Chlorine does not have any empty d-orbitals, which are required to accommodate the lone pairs of electrons from the fluorine atoms. Therefore, FCl3 cannot be formed.
Conclusion:
FCl3 does not exist due to the violation of the octet rule, high electron density, and lack of empty d-orbitals.
Interhalogen compounds are formed between two different halogens. These are of different types such as IF, BrF, ClF, BrCl, etc. They can be easily prepared by the direct combination of halogens under appropriate conditions. Some examples of interhalogen compounds are:
a) ClF3
b) FCl3
c) IF5
d) BrF3
Out of these, FCl3 is the only compound that does not exist. This can be explained as follows:
Reasons for non-existence of FCl3:
1. Violation of the Octet Rule: FCl3 violates the octet rule as the central atom (Cl) has only 6 electrons in its valence shell.
2. High Electron Density: Fluorine is a highly electronegative element, so it attracts electrons towards itself. Due to this, the electron density around the central atom (Cl) becomes very high. As a result, it is difficult to add more electrons to the central atom.
3. Lack of Empty d-orbitals: Chlorine does not have any empty d-orbitals, which are required to accommodate the lone pairs of electrons from the fluorine atoms. Therefore, FCl3 cannot be formed.
Conclusion:
FCl3 does not exist due to the violation of the octet rule, high electron density, and lack of empty d-orbitals.
BaSO4 is insoluble in a water because:- a)Hydration energy is equal to lattice energy.
- b)Hydration energy is more than lattice energy.
- c)Lattice energy is more than hydrogen energy.
- d)BaSO4 does not form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
BaSO4 is insoluble in a water because:
a)
Hydration energy is equal to lattice energy.
b)
Hydration energy is more than lattice energy.
c)
Lattice energy is more than hydrogen energy.
d)
BaSO4 does not form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.

|
Swara Reddy answered |
**Explanation:**
**Insolubility of BaSO4 in water is due to the fact that the lattice energy of the compound is greater than the hydration energy.**
**Lattice Energy:**
- Lattice energy is the energy released when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions.
- It is a measure of the strength of the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions in the crystal lattice.
- The higher the lattice energy, the stronger the forces holding the ions together, and the more difficult it is for the compound to dissolve in a solvent.
- In the case of BaSO4, the lattice energy is high due to the strong electrostatic forces between the Ba2+ and SO42- ions in the crystal lattice.
**Hydration Energy:**
- Hydration energy is the energy released when 1 mole of gaseous ions is hydrated (surrounded by water molecules) to form 1 mole of aqueous ions.
- It is a measure of the strength of the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules.
- The higher the hydration energy, the stronger the forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules, and the more likely the compound is to dissolve in water.
- In the case of BaSO4, the hydration energy is lower than the lattice energy, meaning that the forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules are not strong enough to overcome the strong forces holding the ions in the crystal lattice.
**Overall Explanation:**
- When BaSO4 is added to water, the strong electrostatic forces between the Ba2+ and SO42- ions in the crystal lattice prevent the compound from breaking apart.
- The water molecules are unable to effectively solvate the ions and separate them from the crystal lattice.
- As a result, BaSO4 remains insoluble in water because the lattice energy is greater than the hydration energy.
- It is important to note that BaSO4 does not form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, but this is not the primary reason for its insolubility in water.
- The main factor is the difference in energy between the forces holding the ions in the crystal lattice and the forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules.
**Insolubility of BaSO4 in water is due to the fact that the lattice energy of the compound is greater than the hydration energy.**
**Lattice Energy:**
- Lattice energy is the energy released when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions.
- It is a measure of the strength of the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions in the crystal lattice.
- The higher the lattice energy, the stronger the forces holding the ions together, and the more difficult it is for the compound to dissolve in a solvent.
- In the case of BaSO4, the lattice energy is high due to the strong electrostatic forces between the Ba2+ and SO42- ions in the crystal lattice.
**Hydration Energy:**
- Hydration energy is the energy released when 1 mole of gaseous ions is hydrated (surrounded by water molecules) to form 1 mole of aqueous ions.
- It is a measure of the strength of the electrostatic forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules.
- The higher the hydration energy, the stronger the forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules, and the more likely the compound is to dissolve in water.
- In the case of BaSO4, the hydration energy is lower than the lattice energy, meaning that the forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules are not strong enough to overcome the strong forces holding the ions in the crystal lattice.
**Overall Explanation:**
- When BaSO4 is added to water, the strong electrostatic forces between the Ba2+ and SO42- ions in the crystal lattice prevent the compound from breaking apart.
- The water molecules are unable to effectively solvate the ions and separate them from the crystal lattice.
- As a result, BaSO4 remains insoluble in water because the lattice energy is greater than the hydration energy.
- It is important to note that BaSO4 does not form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, but this is not the primary reason for its insolubility in water.
- The main factor is the difference in energy between the forces holding the ions in the crystal lattice and the forces of attraction between the ions and water molecules.
Based on Wade’s rules of electron counting, structure of carborane, CB8H14, is expected to be:- a)Closo
- b)Nido
- c)Arachno
- d)Galacto
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on Wade’s rules of electron counting, structure of carborane, CB8H14, is expected to be:
a)
Closo
b)
Nido
c)
Arachno
d)
Galacto

|
Srishti Khanna answered |
Structure of Carborane, CB8H14, based on Wade's rules of electron counting
Wade's rules of electron counting are used to predict the structure of cluster compounds such as carboranes. Carboranes are a class of compounds that consist of carbon, boron, and hydrogen atoms. The structure of carborane, CB8H14, can be predicted using Wade's rules of electron counting.
Wade's Rules of Electron Counting
- Rule 1: Count the total number of valence electrons contributed by each atom in the cluster.
- Rule 2: Assume that all atoms in the cluster are bonded to each other by two-electron, covalent bonds.
- Rule 3: Start with the minimum number of skeletal electrons required to connect all of the atoms in the cluster with two-electron bonds.
- Rule 4: Add additional pairs of electrons to the skeleton until all valence electrons have been used.
- Rule 5: The structure with the lowest number of skeletal atoms is the most stable.
Prediction of the Structure of Carborane, CB8H14
- Rule 1: Carbon has 4 valence electrons, boron has 3 valence electrons, and hydrogen has 1 valence electron. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in carborane is:
4(C) + 3(B) + 14(H) = 32
- Rule 2: Assume that all atoms in the cluster are bonded to each other by two-electron, covalent bonds.
- Rule 3: Start with the minimum number of skeletal electrons required to connect all of the atoms in the cluster with two-electron bonds.
There are two possible skeletal structures for carborane, as shown below:
- Rule 4: Add additional pairs of electrons to the skeleton until all valence electrons have been used.
There are two possible structures that can be obtained by adding additional pairs of electrons to each skeletal structure:
- Rule 5: The structure with the lowest number of skeletal atoms is the most stable.
The second structure has a lower number of skeletal atoms and is therefore the most stable. This structure is known as the arachno-structure and is shown below:
Therefore, based on Wade's rules of electron counting, the structure of carborane, CB8H14, is expected to be arachno.
Wade's rules of electron counting are used to predict the structure of cluster compounds such as carboranes. Carboranes are a class of compounds that consist of carbon, boron, and hydrogen atoms. The structure of carborane, CB8H14, can be predicted using Wade's rules of electron counting.
Wade's Rules of Electron Counting
- Rule 1: Count the total number of valence electrons contributed by each atom in the cluster.
- Rule 2: Assume that all atoms in the cluster are bonded to each other by two-electron, covalent bonds.
- Rule 3: Start with the minimum number of skeletal electrons required to connect all of the atoms in the cluster with two-electron bonds.
- Rule 4: Add additional pairs of electrons to the skeleton until all valence electrons have been used.
- Rule 5: The structure with the lowest number of skeletal atoms is the most stable.
Prediction of the Structure of Carborane, CB8H14
- Rule 1: Carbon has 4 valence electrons, boron has 3 valence electrons, and hydrogen has 1 valence electron. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in carborane is:
4(C) + 3(B) + 14(H) = 32
- Rule 2: Assume that all atoms in the cluster are bonded to each other by two-electron, covalent bonds.
- Rule 3: Start with the minimum number of skeletal electrons required to connect all of the atoms in the cluster with two-electron bonds.
There are two possible skeletal structures for carborane, as shown below:
- Rule 4: Add additional pairs of electrons to the skeleton until all valence electrons have been used.
There are two possible structures that can be obtained by adding additional pairs of electrons to each skeletal structure:
- Rule 5: The structure with the lowest number of skeletal atoms is the most stable.
The second structure has a lower number of skeletal atoms and is therefore the most stable. This structure is known as the arachno-structure and is shown below:
Therefore, based on Wade's rules of electron counting, the structure of carborane, CB8H14, is expected to be arachno.
The correct order of acidic character is:- a)Al2O3 > MgO > SiO2 > P4O10
- b)P4O10 > Al2O3 > MgO > SiO2
- c)P4O10 > SiO2 > Al2O3 > MgO
- d)SiO2 > P4O10 > Al2O3 > MgO
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of acidic character is:
a)
Al2O3 > MgO > SiO2 > P4O10
b)
P4O10 > Al2O3 > MgO > SiO2
c)
P4O10 > SiO2 > Al2O3 > MgO
d)
SiO2 > P4O10 > Al2O3 > MgO

|
Shivam Khanna answered |
Acidic character of oxides:
1. Definition:
Acidic character refers to the ability of an oxide to donate a proton (H+) in the presence of water.
2. Factors affecting acidic character:
The acidic character of an oxide depends on the electronegativity of the central atom and the oxidation state of the central atom.
3. Order of acidic character:
The correct order of acidic character is based on the electronegativity of the central atom and the oxidation state of the central atom. The correct order is:
P4O10 > SiO2 > Al2O3 > MgO
Explanation of the order of acidic character:
1. P4O10:
Phosphorus has a high electronegativity and an oxidation state of +5, which makes P4O10 a highly acidic oxide.
2. SiO2:
Silicon has a moderate electronegativity and an oxidation state of +4, which makes SiO2 a moderately acidic oxide.
3. Al2O3:
Aluminum has a low electronegativity and an oxidation state of +3, which makes Al2O3 a weakly acidic oxide.
4. MgO:
Magnesium has a very low electronegativity and an oxidation state of +2, which makes MgO a non-acidic oxide.
Therefore, the correct order of acidic character is P4O10 > SiO2 > Al2O3 > MgO.
1. Definition:
Acidic character refers to the ability of an oxide to donate a proton (H+) in the presence of water.
2. Factors affecting acidic character:
The acidic character of an oxide depends on the electronegativity of the central atom and the oxidation state of the central atom.
3. Order of acidic character:
The correct order of acidic character is based on the electronegativity of the central atom and the oxidation state of the central atom. The correct order is:
P4O10 > SiO2 > Al2O3 > MgO
Explanation of the order of acidic character:
1. P4O10:
Phosphorus has a high electronegativity and an oxidation state of +5, which makes P4O10 a highly acidic oxide.
2. SiO2:
Silicon has a moderate electronegativity and an oxidation state of +4, which makes SiO2 a moderately acidic oxide.
3. Al2O3:
Aluminum has a low electronegativity and an oxidation state of +3, which makes Al2O3 a weakly acidic oxide.
4. MgO:
Magnesium has a very low electronegativity and an oxidation state of +2, which makes MgO a non-acidic oxide.
Therefore, the correct order of acidic character is P4O10 > SiO2 > Al2O3 > MgO.
The reaction of so lid XeF2 with AsF5 in 1:1 ratio affords:- a)XeF4 and AsF3
- b)XeF6 and AsF3
- c)[XeF]+[AsF6]–
- d)[Xe2F3]+[AsF6]–
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction of so lid XeF2 with AsF5 in 1:1 ratio affords:
a)
XeF4 and AsF3
b)
XeF6 and AsF3
c)
[XeF]+[AsF6]–
d)
[Xe2F3]+[AsF6]–

|
Aryan Gupta answered |
Formation of [XeF][AsF6]
When solid XeF2 reacts with AsF5 in a 1:1 ratio, the following reaction takes place:
XeF2 + AsF5 → [XeF][AsF6]
Here, the product formed is [XeF][AsF6] which is a complex compound.
Explanation:
- XeF2 is a binary compound of xenon and fluorine, whereas AsF5 is a binary compound of arsenic and fluorine.
- When they react in a 1:1 ratio, one mole of XeF2 reacts with one mole of AsF5 to form the product.
- The product formed is [XeF][AsF6], which is a complex compound.
- In this compound, XeF+ ion acts as a Lewis acid and AsF6- ion acts as a Lewis base.
- The xenon atom in XeF+ ion has a vacant 5d orbital, which can accept a pair of electrons from AsF6- ion to form a coordinate covalent bond.
- Thus, the compound [XeF][AsF6] is formed, which is a stable complex compound.
Conclusion:
The reaction of solid XeF2 with AsF5 in a 1:1 ratio leads to the formation of a complex compound [XeF][AsF6].
When solid XeF2 reacts with AsF5 in a 1:1 ratio, the following reaction takes place:
XeF2 + AsF5 → [XeF][AsF6]
Here, the product formed is [XeF][AsF6] which is a complex compound.
Explanation:
- XeF2 is a binary compound of xenon and fluorine, whereas AsF5 is a binary compound of arsenic and fluorine.
- When they react in a 1:1 ratio, one mole of XeF2 reacts with one mole of AsF5 to form the product.
- The product formed is [XeF][AsF6], which is a complex compound.
- In this compound, XeF+ ion acts as a Lewis acid and AsF6- ion acts as a Lewis base.
- The xenon atom in XeF+ ion has a vacant 5d orbital, which can accept a pair of electrons from AsF6- ion to form a coordinate covalent bond.
- Thus, the compound [XeF][AsF6] is formed, which is a stable complex compound.
Conclusion:
The reaction of solid XeF2 with AsF5 in a 1:1 ratio leads to the formation of a complex compound [XeF][AsF6].
Which one of the following contain (3c–2e) bonds:(I) Mg(CH3)2
(II) BeCl2
(III) BeH2
(IV) Be(NO3)2- a)I, II and III
- b)I and III
- c)I, III, and IV
- d)II and III
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following contain (3c–2e) bonds:
(I) Mg(CH3)2
(II) BeCl2
(III) BeH2
(IV) Be(NO3)2
(II) BeCl2
(III) BeH2
(IV) Be(NO3)2
a)
I, II and III
b)
I and III
c)
I, III, and IV
d)
II and III

|
Aditi Basak answered |
The correct option is (b)I and III.
Explanation:
(3c2e) bonds are formed by sharing of 3 electrons between 2 atoms. They are also called as banana bonds because of their shape.
Mg(CH3)2:
In this compound, magnesium is bonded to two methyl groups (CH3). The Mg-C bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Mg and C atoms. There are no (3c2e) bonds present in this compound.
BeCl2:
In this compound, beryllium is bonded to two chlorine atoms. The Be-Cl bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Be and Cl atoms. There are no (3c2e) bonds present in this compound.
BeH2:
In this compound, beryllium is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The Be-H bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Be and H atoms. The two H atoms share their electrons with the Be atom to form (3c2e) bonds. Hence, this compound contains (3c2e) bonds.
Be(NO3)2:
In this compound, beryllium is bonded to two nitrate ions (NO3-). The Be-O bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Be and O atoms. There are no (3c2e) bonds present in this compound.
Therefore, the compounds that contain (3c2e) bonds are only I and III, i.e. Mg(CH3)2 and BeH2. The correct option is (b)I and III.
Explanation:
(3c2e) bonds are formed by sharing of 3 electrons between 2 atoms. They are also called as banana bonds because of their shape.
Mg(CH3)2:
In this compound, magnesium is bonded to two methyl groups (CH3). The Mg-C bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Mg and C atoms. There are no (3c2e) bonds present in this compound.
BeCl2:
In this compound, beryllium is bonded to two chlorine atoms. The Be-Cl bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Be and Cl atoms. There are no (3c2e) bonds present in this compound.
BeH2:
In this compound, beryllium is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The Be-H bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Be and H atoms. The two H atoms share their electrons with the Be atom to form (3c2e) bonds. Hence, this compound contains (3c2e) bonds.
Be(NO3)2:
In this compound, beryllium is bonded to two nitrate ions (NO3-). The Be-O bond is a polar covalent bond formed by sharing electrons between Be and O atoms. There are no (3c2e) bonds present in this compound.
Therefore, the compounds that contain (3c2e) bonds are only I and III, i.e. Mg(CH3)2 and BeH2. The correct option is (b)I and III.
What is the correct order of enthalpy of dissociation of halogens?- a)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
- b)Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
- c)Cl2 > F2 > Br2 > I2
- d)F2 > Br2 > Cl2 > I2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct order of enthalpy of dissociation of halogens?
a)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
b)
Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
c)
Cl2 > F2 > Br2 > I2
d)
F2 > Br2 > Cl2 > I2

|
Sampathi Sagar answered |
It's very simple haha
I 2 is single
f2 is single
cl2and br2 are minlgle that's it.
I 2 is single
f2 is single
cl2and br2 are minlgle that's it.
What shape is the HNO3 molecule in its gaseous state?- a)Bent
- b)Linear
- c)Planar
- d)See Saw
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What shape is the HNO3 molecule in its gaseous state?
a)
Bent
b)
Linear
c)
Planar
d)
See Saw
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
In the gas state, the nitric acid molecule has a triangular planar shape with a steric number of 3 no lone pairs of electron. There are two major resonance forms of nitric acid.
Which of the following will be strongest acid in pure liquid HF:- a)H2O
- b)SbF5
- c)CH3COOH
- d)NaF
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will be strongest acid in pure liquid HF:
a)
H2O
b)
SbF5
c)
CH3COOH
d)
NaF
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Correct Answer :- b
Explanation : Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest superacid based on the measured value of its Hammett acidity function (H0), which has been determined for different ratios of HF:SbF5. While the H0 of pure HF is −15, addition of just 1 mol % of SbF5 lowers it to around −20.
What is the nature of silicon–oxygen bonds in silica(SiO2): - a)Polar covalent
- b)Ionic
- c)Non–polar covalent
- d)Coordinate covalent
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the nature of silicon–oxygen bonds in silica(SiO2):
a)
Polar covalent
b)
Ionic
c)
Non–polar covalent
d)
Coordinate covalent
|
|
Neha Choudhury answered |
SiO2 is the chemical compound silicon dioxide. It is formed when silicon is exposed to oxygen. It has a covalent bond and is a superior electric insulator, posessing high chemical stability. Quartz is the second most common mineral in the Earth's continental crust.
The characteristics of the blue solution of solution of sodium in liquid ammonia is/are:- a)Diamagnetic
- b)Paramagnetic
- c)Reducing in nature
- d)Conducts electricit y.
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The characteristics of the blue solution of solution of sodium in liquid ammonia is/are:
a)
Diamagnetic
b)
Paramagnetic
c)
Reducing in nature
d)
Conducts electricit y.

|
Anirban Khanna answered |
Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia giving deep blue solutions which are conducting in nature. The blue colour of the solution is due to ammoniated electrons which absorb energy in the visible region of light.
Egyptian blue CaCuSi4O10 is an example of:- a)Sheet silicate
- b)Cyclic silicate
- c)Pyrosilicate
- d)Chain silicate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Egyptian blue CaCuSi4O10 is an example of:
a)
Sheet silicate
b)
Cyclic silicate
c)
Pyrosilicate
d)
Chain silicate
|
|
Zoya Sharma answered |
Examples of such minerals include quartz, zeolites, and feldspars. Three-dimensional structure of zeoliteIn the mineral zeolite, silica and oxygen atoms are bonded layers of sheets.
The correct order of the ionic radii is:- a)In3+ > Sn4+ > Sr2+ > Rb+
- b)Sn4+ > In3+ > Sr2+ > Rb+
- c)Rb+ > In3+ > Sr2+ > Sn4+
- d)Rb+ > Sr2+ > In3+ > Sn4+
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of the ionic radii is:
a)
In3+ > Sn4+ > Sr2+ > Rb+
b)
Sn4+ > In3+ > Sr2+ > Rb+
c)
Rb+ > In3+ > Sr2+ > Sn4+
d)
Rb+ > Sr2+ > In3+ > Sn4+

|
Priya Saha answered |
Explanation:
Ionic radius is the distance between the nucleus of an ion and its outermost electron. The ionic radii depend on the size of the ion, its charge, and the number of electrons it has.
Order of ionic radii:
The correct order of the ionic radii is Rb > Sr2+ > In3+ > Sn4+. This can be explained as follows:
Rb:
Rb has one valence electron in its outermost shell, which is far from the nucleus. Therefore, it has a large ionic radius.
Sr2+:
Sr2+ has lost two electrons from its outermost shell, and the remaining electrons are attracted more strongly by the nucleus. Therefore, it has a smaller ionic radius than Rb.
In3+:
In3+ has lost three electrons from its outermost shell and has a greater nuclear charge than Sr2+. Therefore, it has a smaller ionic radius than Sr2+.
Sn4+:
Sn4+ has lost four electrons from its outermost shell and has an even greater nuclear charge than In3+. Therefore, it has the smallest ionic radius among the four ions.
Order of the given options:
Among the given options, the correct order of the ionic radii is Rb > Sr2+ > In3+ > Sn4+. Option D, Rb Sr2+ In3+ Sn4+, is the correct answer.
Ionic radius is the distance between the nucleus of an ion and its outermost electron. The ionic radii depend on the size of the ion, its charge, and the number of electrons it has.
Order of ionic radii:
The correct order of the ionic radii is Rb > Sr2+ > In3+ > Sn4+. This can be explained as follows:
Rb:
Rb has one valence electron in its outermost shell, which is far from the nucleus. Therefore, it has a large ionic radius.
Sr2+:
Sr2+ has lost two electrons from its outermost shell, and the remaining electrons are attracted more strongly by the nucleus. Therefore, it has a smaller ionic radius than Rb.
In3+:
In3+ has lost three electrons from its outermost shell and has a greater nuclear charge than Sr2+. Therefore, it has a smaller ionic radius than Sr2+.
Sn4+:
Sn4+ has lost four electrons from its outermost shell and has an even greater nuclear charge than In3+. Therefore, it has the smallest ionic radius among the four ions.
Order of the given options:
Among the given options, the correct order of the ionic radii is Rb > Sr2+ > In3+ > Sn4+. Option D, Rb Sr2+ In3+ Sn4+, is the correct answer.
Alkali metals have the biggest atomic radii.- a)true
- b)false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Alkali metals have the biggest atomic radii.
a)
true
b)
false

|
Niti Mukherjee answered |
Atomic Radii of Alkali Metals
The statement "Alkali metals have the biggest atomic radii" is true. The atomic radius refers to the size of an atom, which is determined by the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell. The atomic radius generally increases as you move down a group on the periodic table.
Explanation:
1. Alkali Metals
- Alkali metals are a group of elements located in Group 1 of the periodic table.
- This group includes elements such as lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
- These elements are highly reactive and typically have one valence electron in their outermost electron shell.
2. Atomic Radii
- Atomic radius is defined as the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell of an atom.
- It is often measured as half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a crystal lattice.
- Atomic radius generally increases as you move down a group on the periodic table due to the addition of a new electron shell with each successive element.
3. Trends in Atomic Radii
- The atomic radius generally increases from top to bottom within a group.
- This is because each successive element in a group has an additional electron shell, leading to an increase in the size of the atom.
- As you move down Group 1 (alkali metals), the atomic radius increases due to the addition of a new electron shell with each successive element.
- Therefore, alkali metals have the largest atomic radii among the elements in their respective periods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the statement that alkali metals have the biggest atomic radii is true. As you move down Group 1 of the periodic table, the atomic radius of alkali metals increases due to the addition of a new electron shell with each successive element. This trend is observed throughout the periodic table, where atomic radii generally increase as you move down a group.
The statement "Alkali metals have the biggest atomic radii" is true. The atomic radius refers to the size of an atom, which is determined by the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell. The atomic radius generally increases as you move down a group on the periodic table.
Explanation:
1. Alkali Metals
- Alkali metals are a group of elements located in Group 1 of the periodic table.
- This group includes elements such as lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
- These elements are highly reactive and typically have one valence electron in their outermost electron shell.
2. Atomic Radii
- Atomic radius is defined as the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell of an atom.
- It is often measured as half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a crystal lattice.
- Atomic radius generally increases as you move down a group on the periodic table due to the addition of a new electron shell with each successive element.
3. Trends in Atomic Radii
- The atomic radius generally increases from top to bottom within a group.
- This is because each successive element in a group has an additional electron shell, leading to an increase in the size of the atom.
- As you move down Group 1 (alkali metals), the atomic radius increases due to the addition of a new electron shell with each successive element.
- Therefore, alkali metals have the largest atomic radii among the elements in their respective periods.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the statement that alkali metals have the biggest atomic radii is true. As you move down Group 1 of the periodic table, the atomic radius of alkali metals increases due to the addition of a new electron shell with each successive element. This trend is observed throughout the periodic table, where atomic radii generally increase as you move down a group.
What catalyst is used for oxidation of ammonia to produce nitric acid?- a)Palladium hydride
- b)Sodium amalgam
- c)Platinum-Rhodium gauze
- d)Vanadium (V) oxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What catalyst is used for oxidation of ammonia to produce nitric acid?
a)
Palladium hydride
b)
Sodium amalgam
c)
Platinum-Rhodium gauze
d)
Vanadium (V) oxide
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
Ammonia is oxidized to nitrogen (II) oxide in the presence of Pt/Rh gauze catalyst at a temperature of 500 K and a pressure of 9 bars. The nitrous oxide is then converted to nitrogen dioxide which is further reacted with water to produce nitric acid. The NO formed is recycled.
Alkali metals dissolving in Ammonia liquid give the blue solution, this is due to the formation of ammoniated ____
- a)ions
- b)metal cations only
- c)electrons only
- d)metal cations and electrons
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Alkali metals dissolving in Ammonia liquid give the blue solution, this is due to the formation of ammoniated ____
a)
ions
b)
metal cations only
c)
electrons only
d)
metal cations and electrons
|
|
Vivek Khatri answered |
Alkali metals dissolve in liquid ammonia giving deep blue solutions which are conducting in nature. The blue colour of the solution is due to ammoniated electrons which absorb energy in the visible region of light.
Among the molecules, BiF3, BiCl3 BiBr3 and BiI3, the one which is most coloured is:- a)BiF3
- b)BiBr3
- c)BiCl3
- d)BiI3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the molecules, BiF3, BiCl3 BiBr3 and BiI3, the one which is most coloured is:
a)
BiF3
b)
BiBr3
c)
BiCl3
d)
BiI3

|
Swati Swarnkar answered |
Valance electrons are loosely attached in iodine hence easily jumps to higher level.. When returning to its ground state it emits light..
Among the three allotropes of an element, one is a good electrical conductor, the second one is known to be one of the hardest materials and the third one has a molecule form with an icosahedral structure. The element is:- a)Boron
- b)Carbon
- c)Silicon
- d)Sulfur
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the three allotropes of an element, one is a good electrical conductor, the second one is known to be one of the hardest materials and the third one has a molecule form with an icosahedral structure. The element is:
a)
Boron
b)
Carbon
c)
Silicon
d)
Sulfur

|
Mamta Jani answered |
A
Chapter doubts & questions for Main Group Elements (s & p blocks) - Topicwise Question Bank for IIT JAM/CSIR/GATE Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Main Group Elements (s & p blocks) - Topicwise Question Bank for IIT JAM/CSIR/GATE Chemistry in English & Hindi are available as part of Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup