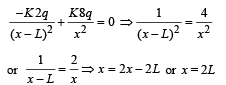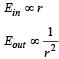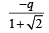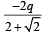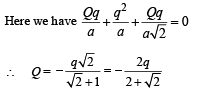All Exams >
JEE >
35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE >
All Questions
All questions of Electrostatics for JEE Exam
A parallel plate capacitor of area A, plate separation d and capacitance C is filled with three different dielectric materials having dielectric constants k1, k2 and k3 as shown. If a single dielectric material is to be used to have the same capacitance C in this capacitor, then its dielectric constant k is given by
- a)
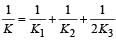
- b)
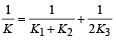
- c)
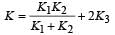
- d)K = K1 + K2 + 2K3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor of area A, plate separation d and capacitance C is filled with three different dielectric materials having dielectric constants k1, k2 and k3 as shown. If a single dielectric material is to be used to have the same capacitance C in this capacitor, then its dielectric constant k is given by

a)
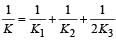
b)
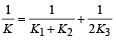
c)
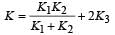
d)
K = K1 + K2 + 2K3

|
Bs Academy answered |
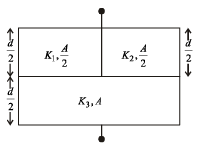
Let C1 = Capacity of capacitor with K1
C2 = Capacity of capacitor with K2
C3 = Capacity of capacitor with K3
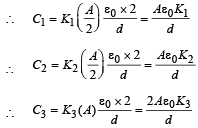
C2 = Capacity of capacitor with K2
C3 = Capacity of capacitor with K3
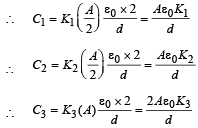
C1 and C2 are in parallel
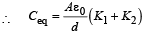
Ceq and C3 are in series
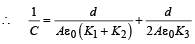
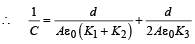
But 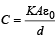 for single equivalent capacitor
for single equivalent capacitor
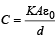 for single equivalent capacitor
for single equivalent capacitor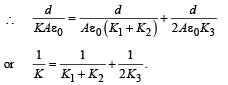
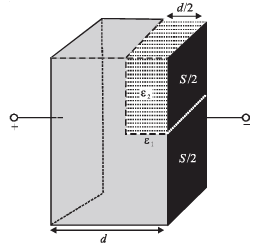
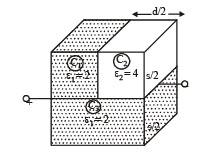
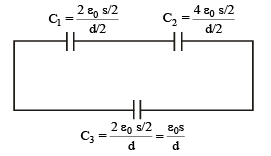
A parallel plate capacitor having plates of area S and plate separation d, has capacitance C1 in air. When two dielectrics of different relative primitivities (ε1 = 2 and ε2 = 4) are introduced between the two plates as shown in the figure, the capacitance becomes C2. The ratio 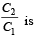
- a)6/5
- b)5/3
- c)7/5
- d)7/3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor having plates of area S and plate separation d, has capacitance C1 in air. When two dielectrics of different relative primitivities (ε1 = 2 and ε2 = 4) are introduced between the two plates as shown in the figure, the capacitance becomes C2. The ratio 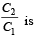

a)
6/5
b)
5/3
c)
7/5
d)
7/3
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
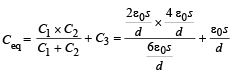
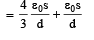
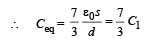
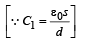
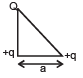
Two identical thin rings, each of radius R metres, are coaxially placed a distance R metres apart. If Q1 coulomb, and Q2 coulomb, are respectively the charges uniformly spread on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q from the centre of one ring to that of the other is- a)zero
- b)
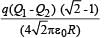
- c)
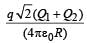
- d)
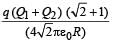
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical thin rings, each of radius R metres, are coaxially placed a distance R metres apart. If Q1 coulomb, and Q2 coulomb, are respectively the charges uniformly spread on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q from the centre of one ring to that of the other is
a)
zero
b)
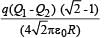
c)
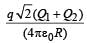
d)
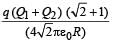
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
The work done in moving a charge from A to B
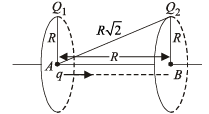
W = (T.P.E.)A – (T.P.E.)B where T.P.E. = Total Potential Energy
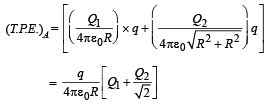
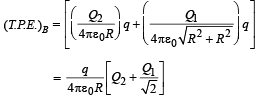
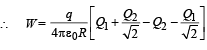
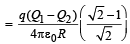
A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K between its plates that covers 1/3 of the area of its plates, as shown in the figure. The total capacitance of the capacitor is C while that of the portion with dielectric in between is C1. When the capacitor is charged, the plate area covered by the dielectric gets charge Q1 and the rest of the area gets charge Q2. The electric field in the dielectric is E, and that in the other portion is E2. Choose the correct option/ options, ignoring edge effects.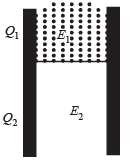
- a)
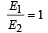
- b)
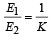
- c)
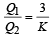
- d)
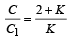
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K between its plates that covers 1/3 of the area of its plates, as shown in the figure. The total capacitance of the capacitor is C while that of the portion with dielectric in between is C1. When the capacitor is charged, the plate area covered by the dielectric gets charge Q1 and the rest of the area gets charge Q2. The electric field in the dielectric is E, and that in the other portion is E2. Choose the correct option/ options, ignoring edge effects.

a)
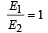
b)
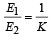
c)
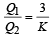
d)
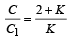
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
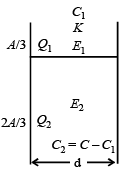
This is a combination of two capacitors in parallel.
Therefore C = C1 + C2 ∴ C2 = C – C1
Therefore C = C1 + C2 ∴ C2 = C – C1
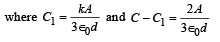
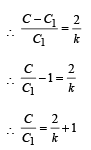
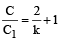
∴ (d) is a correct option.
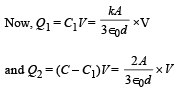
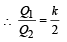 ∴ (c) is incorrect
∴ (c) is incorrectAlso V = E × d
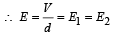 ∴ (a) is a correct option
∴ (a) is a correct optionSix point charges are kept at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side L and centre O, as shown in the figure. Given that 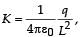 which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?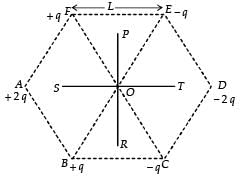
- a)The electric field at O is 6K along OD
- b)The potential at O is zero
- c)The potential at all points on the line PR is same
- d)The potential at all points on the line ST is same
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Six point charges are kept at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side L and centre O, as shown in the figure. Given that 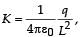 which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
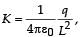 which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
a)
The electric field at O is 6K along OD
b)
The potential at O is zero
c)
The potential at all points on the line PR is same
d)
The potential at all points on the line ST is same
|
|
Pavan Kalyan Dinesh answered |
A
A 2 μF capacitor is charged as shown in the figure. The percentage of its stored energy dissipated after the switch S is turned to position 2 is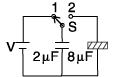
- a)0%
- b)20%
- c)75%
- d)80%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A 2 μF capacitor is charged as shown in the figure. The percentage of its stored energy dissipated after the switch S is turned to position 2 is
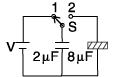
a)
0%
b)
20%
c)
75%
d)
80%

|
Cstoppers Instructors answered |
When S and 1 are connected
The 2μF capacitor gets charged. The potential difference across its plates will be V.
The potential energy stored in 2 μF capacitor
The potential energy stored in 2 μF capacitor
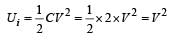
When S and 2 are connected The 8mF capacitor also gets charged. During this charging process current flows in the wire and some amount of energy is dissipated as heat. The energy loss is
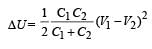
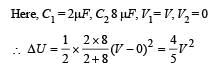
The percentage of the energy dissipated 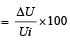
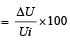
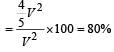
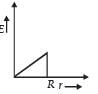
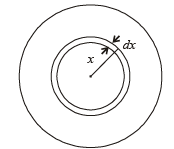
Let there be a spherically symmetric charge distribution with charge density varying as 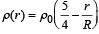 upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R , where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the origin is given by
upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R , where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the origin is given by- a)
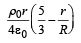
- b)
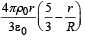
- c)
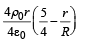
- d)
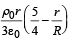
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Let there be a spherically symmetric charge distribution with charge density varying as 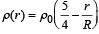 upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R , where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the origin is given by
upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R , where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the origin is given by
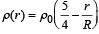 upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R , where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the origin is given by
upto r = R, and ρ(r) = 0 for r > R , where r is the distance from the origin. The electric field at a distance r(r < R) from the origin is given bya)
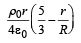
b)
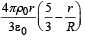
c)
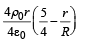
d)
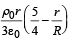
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Let us con sider a spher ical shell of r adius x and thickness dx.
Charge on this shell
Charge on this shell
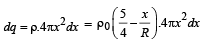
∴ Total charge in the spherical region from centre to r (r < R ) is
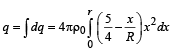
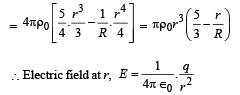
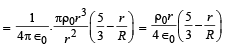
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and the charging battery is then disconnected. If the plates of the capacitor are moved farther apart by means of insulating handles :- a)the charge on the capacitor increases.
- b)the voltage across the plates increases.
- c)the capacitance increases.
- d)the electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor increases
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and the charging battery is then disconnected. If the plates of the capacitor are moved farther apart by means of insulating handles :
a)
the charge on the capacitor increases.
b)
the voltage across the plates increases.
c)
the capacitance increases.
d)
the electrostatic energy stored in the capacitor increases
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Charge on plate is q
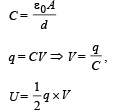
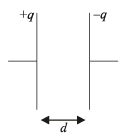
Charge on plate is q
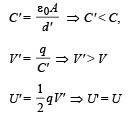
Consider an evacuated cylindrical chamber of height h having rigid conducting plates at the ends and an insulating curved surface as shown in the figure. A number of spherical balls made of a light weight and soft material and coated with a conducting material are placed on the bottom plate. The balls have a radius r <<h. Now a high voltage source (HV) is connected across the conducting plates such that the bottom plate is at +V0 and the top plate at –V0. Due to their conducting surface, the balls will get charged, will become equipotential with the plate and are repelled by it. The balls will eventually collide with the top plate, where the coefficient of restitution can be taken to be zero due to the soft nature of the material of the balls. The electric field in the chamber can be considered to be that of a parallel plate capacitor.
Assume that there are no collisions between the balls and the interaction between them is negligible. (Ignore gravity)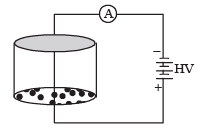 Q. The aver age current in the steady state registered by the ammeter in the circuit will be
Q. The aver age current in the steady state registered by the ammeter in the circuit will be- a)zero
- b)proportional to the potential V0
- c)proportional to V01/2
- d)proportional t o V02
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider an evacuated cylindrical chamber of height h having rigid conducting plates at the ends and an insulating curved surface as shown in the figure. A number of spherical balls made of a light weight and soft material and coated with a conducting material are placed on the bottom plate. The balls have a radius r <<h. Now a high voltage source (HV) is connected across the conducting plates such that the bottom plate is at +V0 and the top plate at –V0. Due to their conducting surface, the balls will get charged, will become equipotential with the plate and are repelled by it. The balls will eventually collide with the top plate, where the coefficient of restitution can be taken to be zero due to the soft nature of the material of the balls. The electric field in the chamber can be considered to be that of a parallel plate capacitor.
Assume that there are no collisions between the balls and the interaction between them is negligible. (Ignore gravity)
Assume that there are no collisions between the balls and the interaction between them is negligible. (Ignore gravity)

Q. The aver age current in the steady state registered by the ammeter in the circuit will be
a)
zero
b)
proportional to the potential V0
c)
proportional to V01/2
d)
proportional t o V02

|
Veda Institute answered |
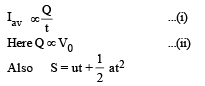
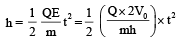
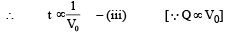
From (i), (ii) and (iii)
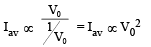
The region between two concentric spheres of radii 'a' and 'b', respectively (see figure), have volume charge density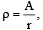 where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant, is :
where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant, is :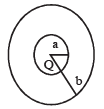
- a)
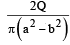
- b)
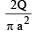
- c)
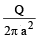
- d)
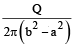
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The region between two concentric spheres of radii 'a' and 'b', respectively (see figure), have volume charge density
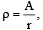 where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant, is :
where A is a constant and r is the distance from the centre. At the centre of the spheres is a point charge Q. The value of A such that the electric field in the region between the spheres will be constant, is :
a)
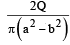
b)
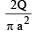
c)
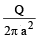
d)
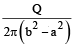
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Applying Gauss's law
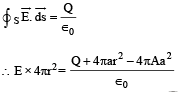
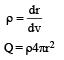
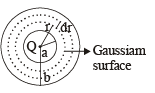
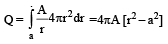
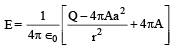
For E to be independent of 'r'
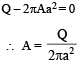
A charge +q is fixed at each of the points x = x0, x = 3x0, x = 5x0,..... x = ∞ on the x axis, and a charge –q is fixed at each of the points x = 2x0, x = 4x0, x = 6x0,.... x = ∞. Here x0 is a positive constant. Take the electric potential at a point due to a charge Q at a distance r from it to be Q/(4πε0r).
Then, the potential at the origin due to the above system of charges is- a)0
- b)
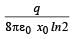
- c)∞
- d)
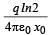
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A charge +q is fixed at each of the points x = x0, x = 3x0, x = 5x0,..... x = ∞ on the x axis, and a charge –q is fixed at each of the points x = 2x0, x = 4x0, x = 6x0,.... x = ∞. Here x0 is a positive constant. Take the electric potential at a point due to a charge Q at a distance r from it to be Q/(4πε0r).
Then, the potential at the origin due to the above system of charges is
Then, the potential at the origin due to the above system of charges is
a)
0
b)
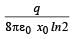
c)
∞
d)
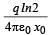
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
The potential will become (q/4π€o(1-1/2+1/3-1/4+1/5-1/6.
....)= q ln2/4π€o.
(The above series reaching upto (1/infinity ) converges to ln(1+x) where x is 1.. thus ln2.)
....)= q ln2/4π€o.
(The above series reaching upto (1/infinity ) converges to ln(1+x) where x is 1.. thus ln2.)
A spherical portion has been removed from a solid sphere having a charge distributed uniformly in its volume as shown in the figure. The electric field inside the emptied space is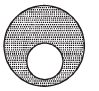
- a)zero everywhere
- b)non-zero and uniform
- c)non-uniform
- d)zero only at its center
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A spherical portion has been removed from a solid sphere having a charge distributed uniformly in its volume as shown in the figure. The electric field inside the emptied space is

a)
zero everywhere
b)
non-zero and uniform
c)
non-uniform
d)
zero only at its center
|
|
Akash Kumar answered |

A dielectric slab of thickness d is inserted in a parallel plate capacitor whose negative plate is at x = 0 and positive plate is at x = 3d. The slab is equidistant from the plates. The capacitor is given some charge. As one goes from 0 to 3d,- a)the magnitude of the electric field remains the same.
- b)the direction of the electric field remains the same.
- c)the electric potential increases continuously.
- d)the electric poten tial increases at first, then decreases and again increases.
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A dielectric slab of thickness d is inserted in a parallel plate capacitor whose negative plate is at x = 0 and positive plate is at x = 3d. The slab is equidistant from the plates. The capacitor is given some charge. As one goes from 0 to 3d,
a)
the magnitude of the electric field remains the same.
b)
the direction of the electric field remains the same.
c)
the electric potential increases continuously.
d)
the electric poten tial increases at first, then decreases and again increases.
|
|
Silent Nisarg answered |
Oh this is difficult question
Let E1 (r), E2(r) and E3(r) be the respective electric field at a distance r from a point charge Q, an infinitely long wire with constant linear charge density λ, and an infinite plane with uniform surface charge density σ. If E1(r0) = E2(r0) = E3(r0) at a given distance r0, then- a)

- b)
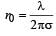
- c)E1 (r0 / 2) = 2E2 (r0 /2)
- d)E2 (r0 /2) = 4 E3 (r0 /2)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Let E1 (r), E2(r) and E3(r) be the respective electric field at a distance r from a point charge Q, an infinitely long wire with constant linear charge density λ, and an infinite plane with uniform surface charge density σ. If E1(r0) = E2(r0) = E3(r0) at a given distance r0, then
a)

b)
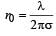
c)
E1 (r0 / 2) = 2E2 (r0 /2)
d)
E2 (r0 /2) = 4 E3 (r0 /2)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
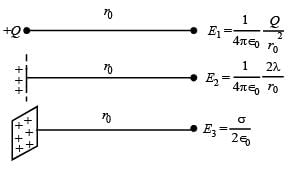
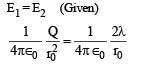
∴ Q = 2λr0 ...(1)
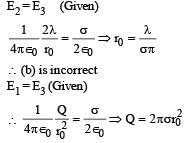
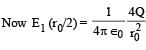
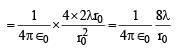
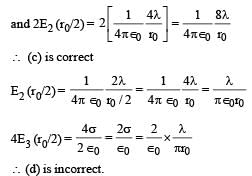
Consider a uniform spherical charge distribution of radius R1 centred at the origin O. In this distribution, a spherical cavity of radius R2, centred at P with distance OP = a = R1 – R2 (see figure) is made. If the electric field inside the cavity at position 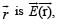 then the correct statement(s) is (are)
then the correct statement(s) is (are)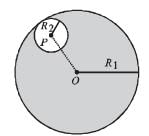
- a)
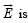 uniform, its magnitude is independent of R2 but its direction depends
uniform, its magnitude is independent of R2 but its direction depends 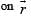
- b)
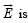 is uniform, its magnitude depends on R2 and its direction depends
is uniform, its magnitude depends on R2 and its direction depends 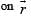
- c)
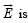 uniform, its magnitude is independent of a but its direction depends on
uniform, its magnitude is independent of a but its direction depends on 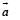
- d)
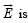 uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on
uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on 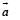
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a uniform spherical charge distribution of radius R1 centred at the origin O. In this distribution, a spherical cavity of radius R2, centred at P with distance OP = a = R1 – R2 (see figure) is made. If the electric field inside the cavity at position 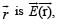 then the correct statement(s) is (are)
then the correct statement(s) is (are)
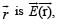 then the correct statement(s) is (are)
then the correct statement(s) is (are)
a)
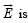 uniform, its magnitude is independent of R2 but its direction depends
uniform, its magnitude is independent of R2 but its direction depends 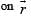
b)
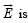 is uniform, its magnitude depends on R2 and its direction depends
is uniform, its magnitude depends on R2 and its direction depends 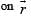
c)
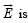 uniform, its magnitude is independent of a but its direction depends on
uniform, its magnitude is independent of a but its direction depends on 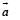
d)
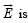 uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on
uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on 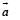
|
|
Anand Kumar answered |

A non-conducting solid sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The magnitude of the electric field due to the sphere at a distance r from its centre- a)increases as r increases, for r < R.
- b)decreases as r increases, for 0 < r < ∞.
- c)decreases as r increases, for R < r < ∞.
- d)is discontinuous at r = R.
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A non-conducting solid sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The magnitude of the electric field due to the sphere at a distance r from its centre
a)
increases as r increases, for r < R.
b)
decreases as r increases, for 0 < r < ∞.
c)
decreases as r increases, for R < r < ∞.
d)
is discontinuous at r = R.
|
|
Neer Shreyansh answered |

Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net charge on the sphere is then- a)negative and distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere
- b)negative and appears only at the point on the sphere closest to the point charge
- c)negative and distributed non-uniformly over the entire surface of the sphere
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net charge on the sphere is then
a)
negative and distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere
b)
negative and appears only at the point on the sphere closest to the point charge
c)
negative and distributed non-uniformly over the entire surface of the sphere
d)
zero

|
Nikhil Sen answered |
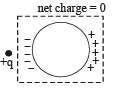
When a positive point charge is placed outside a conducting sphere, a rearrangement of charge takes place on the surface.
But the total charge on the sphere is zero as no charge has left or entered the sphere.
But the total charge on the sphere is zero as no charge has left or entered the sphere.
Charges Q, 2Q and 4Q are uniformly distributed in three dielectric solid spheres 1, 2 and 3 of radii R/2, R and 2R respectively, as shown in figure. If magnitude of the electric fields at point P at a distance R from the centre of sphere 1, 2 and 3 are E1, E2 and E3 respectively, then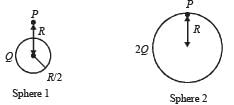
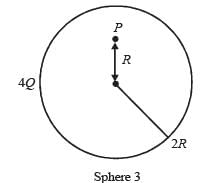
- a)E1 > E2 > E3
- b)E3 > E1 > E2
- c)E2 > E1 > E3
- d)E3 > E2 > E1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Charges Q, 2Q and 4Q are uniformly distributed in three dielectric solid spheres 1, 2 and 3 of radii R/2, R and 2R respectively, as shown in figure. If magnitude of the electric fields at point P at a distance R from the centre of sphere 1, 2 and 3 are E1, E2 and E3 respectively, then


a)
E1 > E2 > E3
b)
E3 > E1 > E2
c)
E2 > E1 > E3
d)
E3 > E2 > E1

|
Roshni Chavan answered |
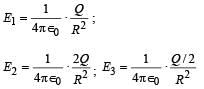
Clearly E2 > E1 > E3 where Q/2 is the charge enclosed in a sphere of radius R concentric with the given sphere.
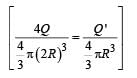
An ellipsoidal cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge q is placed at the centre of the cavity. The points A and B are on the cavity surface as shown in the figure. Then
- a)electric field near A in the cavity = electric field near B in the cavity
- b)charge density at A = charge density at B
- c)potential at A = potential at B
- d)total electric field flux through the surface of the cavity is q/ε0
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
An ellipsoidal cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge q is placed at the centre of the cavity. The points A and B are on the cavity surface as shown in the figure. Then

a)
electric field near A in the cavity = electric field near B in the cavity
b)
charge density at A = charge density at B
c)
potential at A = potential at B
d)
total electric field flux through the surface of the cavity is q/ε0

|
Pankaj Sengupta answered |
When two points are connected with a conducting path in electrostatic condition, then the potential of the two points is equal. Thus potential at A = Potential at B (c) is the correct option.
Option (d) is a result of Gauss's law
Option (d) is a result of Gauss's law
Total electric flux through cavity 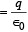
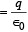
Option (a) and (b) are dependent on the curvature which is different at points A and B.
If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respectively is φ1 and φ2 , the electric charge inside the surface will be- a)(φ2 - φ1) εo
- b)(φ1 + φ2) / εo
- c)(φ2 - φ1) / εo
- d)(φ1 + φ2) εo
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the electric flux entering and leaving an enclosed surface respectively is φ1 and φ2 , the electric charge inside the surface will be
a)
(φ2 - φ1) εo
b)
(φ1 + φ2) / εo
c)
(φ2 - φ1) / εo
d)
(φ1 + φ2) εo

|
Sarthak Khanna answered |
The flux entering an en closed sur face is taken as negative and the flux leaving the surface is taken as positive, by convention. Therefore the net flux leaving the enclosed surface = φ2 -φ1
∴ the charge enclosed in the surface by Gauss’s law is q = ∈0 (φ2 -φ1)
Two points P and Q are maintained at the potentials of 10 V and – 4 V, respectively. The work done in moving 100 electrons from P to Q is :- a)9.60 × 10–17J
- b)–2.24 × 10–16 J
- c)2.24 × 10–16 J
- d)–9.60× 10–17 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two points P and Q are maintained at the potentials of 10 V and – 4 V, respectively. The work done in moving 100 electrons from P to Q is :
a)
9.60 × 10–17J
b)
–2.24 × 10–16 J
c)
2.24 × 10–16 J
d)
–9.60× 10–17 J

|
Gauri Chauhan answered |
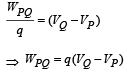
= (– 100 × 1.6 × 10–19) (– 4 – 10)
= +2.24 × 10–16J
= +2.24 × 10–16J
A parallel plate air capacitor is connected to a battery. The quantities charge, voltage, electric field and energy associated with this capacitor are given by Q0, V0, E0 and U0 respectively. A dielectric slab is now introduced to fill the space between the plates with battery still in connection.
The corresponding quantities now given by Q, V, E and U are related to th e previous one as- a)Q > Q0
- b)V > V0
- c)E > E0
- d)U > U0
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate air capacitor is connected to a battery. The quantities charge, voltage, electric field and energy associated with this capacitor are given by Q0, V0, E0 and U0 respectively. A dielectric slab is now introduced to fill the space between the plates with battery still in connection.
The corresponding quantities now given by Q, V, E and U are related to th e previous one as
The corresponding quantities now given by Q, V, E and U are related to th e previous one as
a)
Q > Q0
b)
V > V0
c)
E > E0
d)
U > U0
|
|
Arka Rane answered |
= Q0, V = V0, E = E0, U = U0
b)Q > Q0, V = V0, E > E0, U > U0
c)Q > Q0, V < v0,="" e="" /> E0, U = U0
d)Q > Q0, V > V0, E > E0, U > U0
b)Q > Q0, V = V0, E > E0, U > U0
c)Q > Q0, V < v0,="" e="" /> E0, U = U0
d)Q > Q0, V > V0, E > E0, U > U0
A positively charged thin metal ring of radius R is fixed in the xy plane with its centre at the origin O. A negatively charged particle P is released from rest at the point (0, 0, z0) where z0 > 0. Then the motion of P is- a)periodic, for all values of z0 satisfying 0 < z0 < ∞
- b)simple harmonic, for all values of z0 satisfying 0 < z0 < R
- c)approximately simple harmonic, provided z0 < < R
- d)such that P crosses O and continues to move along the negative z axis towards z = ∞
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A positively charged thin metal ring of radius R is fixed in the xy plane with its centre at the origin O. A negatively charged particle P is released from rest at the point (0, 0, z0) where z0 > 0. Then the motion of P is
a)
periodic, for all values of z0 satisfying 0 < z0 < ∞
b)
simple harmonic, for all values of z0 satisfying 0 < z0 < R
c)
approximately simple harmonic, provided z0 < < R
d)
such that P crosses O and continues to move along the negative z axis towards z = ∞
|
|
Vaishnavi Iyer answered |
Let Q be the charge on the ring, the negative charge – q is released from point P (0, 0, Z0). The electric field at P due to the charged ring will be along positive z-axis and its magnitude will be
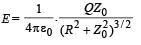
Therefore, force on charge P will be towards centre as shown, and its magnitude is
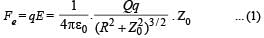
Similarly, when it crosses the origin, the force is again towards centre O.
Thus the motion of the particle is periodic for all values of Z0 lying between 0 and ∞.
Thus the motion of the particle is periodic for all values of Z0 lying between 0 and ∞.
Secondly if 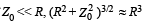
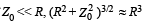
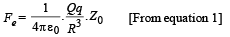
i.e. the restoring force Fe∝ – Z0. Hence the motion of the particle will be simple harmonic. (Here negative sign implies that the force is towards its mean position)
Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two massless strings of length l are initially a distance d(d << l) apart because of their mutual repulsion.
The charge begins to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result charges approach each other with a velocity v. Then as a function of distance x between them,- a)v ∝ x–1
- b)v ∝ x½
- c)v ∝ x
- d)v ∝ x–½
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two massless strings of length l are initially a distance d(d << l) apart because of their mutual repulsion.
The charge begins to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result charges approach each other with a velocity v. Then as a function of distance x between them,
The charge begins to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate. As a result charges approach each other with a velocity v. Then as a function of distance x between them,
a)
v ∝ x–1
b)
v ∝ x½
c)
v ∝ x
d)
v ∝ x–½

|
Rohan Chakraborty answered |
Ans.



Option (d)
When charge begins to leak from both the spheres at a constant rate, then
This question contains Statement-1 and Statement-2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements. Statement-1 : For a charged particle moving from point P to point Q, the net work done by an electrostatic field on the particle is independent of the path connecting point P to point Q.Statement-2 : The net work done by a conservative force on an object moving along a closed loop is zero.- a)Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is the correct explanation of Statement-1.
- b)Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is not the correct explanation of Statement-1.
- c)Statement-1 is false, Statement-2 is true.
- d)Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
This question contains Statement-1 and Statement-2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements.
Statement-1 : For a charged particle moving from point P to point Q, the net work done by an electrostatic field on the particle is independent of the path connecting point P to point Q.
Statement-2 : The net work done by a conservative force on an object moving along a closed loop is zero.
a)
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is the correct explanation of Statement-1.
b)
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is not the correct explanation of Statement-1.
c)
Statement-1 is false, Statement-2 is true.
d)
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.

|
Tejas Chawla answered |
Statement 1 is true.
Statement 2 is true and is the correct explanation of (1)
Statement 2 is true and is the correct explanation of (1)
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q will- a)execute simple harmonic motion about the origin
- b)move to the origin remain at rest
- c)move to infinity
- d)execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q will
a)
execute simple harmonic motion about the origin
b)
move to the origin remain at rest
c)
move to infinity
d)
execute oscillatory but not simple harmonic motion
|
|
Sarthak Chauhan answered |
Let us consider the positive charge Q at any instant of time t at a distance x from the origin. It is under the influence of two forces 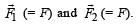 On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
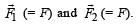 On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force isFR = 2F cos θ
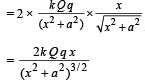
Since FR is not proportional to x, the motion is NOT simple harmonic. The charge Q will accelerate till the origin and gain velocity. At the origin the net force is zero but due to momentum it will cross the origin and more towards left. As it comes on negative x-axis, the force is again towards the origin.
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is connected to a battery and is charged to a potential difference V. Another capacitor of capacitance 2C is similarly charged to a potential difference 2V. The charging battery is now disconnected and the capacitors are connected in parallel to each other in such a way that the positive terminal of one is connected to the negative terminal of the other. The final energy of the configuration is- a)zero
- b)

- c)
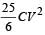
- d)
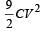
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is connected to a battery and is charged to a potential difference V. Another capacitor of capacitance 2C is similarly charged to a potential difference 2V. The charging battery is now disconnected and the capacitors are connected in parallel to each other in such a way that the positive terminal of one is connected to the negative terminal of the other. The final energy of the configuration is
a)
zero
b)

c)
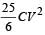
d)
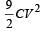

|
Bhavya Joshi answered |
C and 2C are in parallel to each other.
∴ Resultant capacity = (2C + C)
CR = 3C
Net potential = 2V – V
VR = V
CR = 3C
Net potential = 2V – V
VR = V
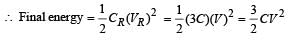
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?- a)If the electric field due to a point charge varies as r –2.5 instead of r–2, then the Gauss law will still be valid.
- b)The Gauss law can be used to calcula te the field distribution around an electric dipole.
- c)If the electric field between two point charges is zero somewhere, then the sign of the two charges is the same.
- d)Th e work done by the external for ce in moving a unit positive charge from point A at potential VA to point B at potential VB is (VB- VA).
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
a)
If the electric field due to a point charge varies as r –2.5 instead of r–2, then the Gauss law will still be valid.
b)
The Gauss law can be used to calcula te the field distribution around an electric dipole.
c)
If the electric field between two point charges is zero somewhere, then the sign of the two charges is the same.
d)
Th e work done by the external for ce in moving a unit positive charge from point A at potential VA to point B at potential VB is (VB- VA).

|
Mira Roy answered |
(a) is not correct because it is valid only when E ∝ r–2
(b) is not correct
(c) is correct as between two point charges we will get a point where the electric field due to the two point charges cancel out each other.
(d) is correct when the work done is without accelerating the charge.
(b) is not correct
(c) is correct as between two point charges we will get a point where the electric field due to the two point charges cancel out each other.
(d) is correct when the work done is without accelerating the charge.
Two identical metal plates are given positive charges Q1 and Q2 (<Q1) respectively. If they are now brought close together to form a parallel plate capacitor with capacitance C, the potential difference between them is- a)(Q1+Q2)/(2C)
- b)(Q1+Q2) / C
- c)(Q1– Q2) /C
- d)(Q1– Q2) /(2C)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical metal plates are given positive charges Q1 and Q2 (<Q1) respectively. If they are now brought close together to form a parallel plate capacitor with capacitance C, the potential difference between them is
a)
(Q1+Q2)/(2C)
b)
(Q1+Q2) / C
c)
(Q1– Q2) /C
d)
(Q1– Q2) /(2C)

|
Atharva Pillai answered |
Within the capacitor,
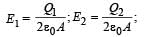
where A = area of each plate
d = separation between two plate
d = separation between two plate
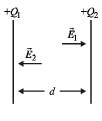
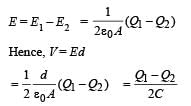
Two equal point charges are fixed at x = – a and x = + a on the x-axis. Another point charge Q is placed at the origin.
The change in the electrical potential energy of Q, when it is displaced by a small distance x along the x-axis, is approximately proportional to- a)x
- b)x2
- c)x3
- d)1/x
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two equal point charges are fixed at x = – a and x = + a on the x-axis. Another point charge Q is placed at the origin.
The change in the electrical potential energy of Q, when it is displaced by a small distance x along the x-axis, is approximately proportional to
The change in the electrical potential energy of Q, when it is displaced by a small distance x along the x-axis, is approximately proportional to
a)
x
b)
x2
c)
x3
d)
1/x

|
Dipanjan Majumdar answered |
Ans.
Option (b)
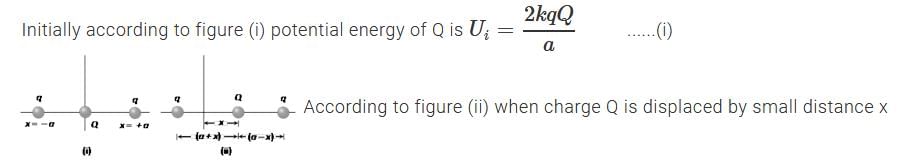
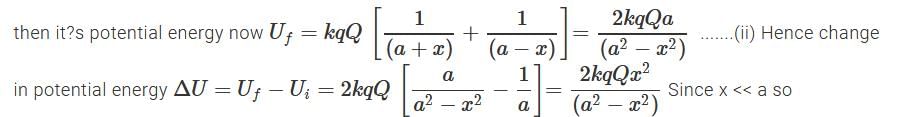
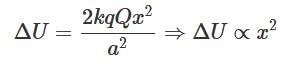
A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge of – 3Q, the new potential difference between the same two surfaces is :- a)V
- b)2V
- c)4V
- d)– 2V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge of – 3Q, the new potential difference between the same two surfaces is :
a)
V
b)
2V
c)
4V
d)
– 2V
|
|
Puja Banerjee answered |
The potential inside the shell will be the sa me everywhere as on its surface. As we add – 3Q charge on the surface, the potential on the surface changes by the same amount as that inside. Therefore the potential difference remains the same.
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° to a nonuniform electric field. The dipole will experience- a)a translational force only in the direction of the field
- b)a translational force only in a direction normal to the direction of the field
- c)a torque as well as a translational force
- d)a torque only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° to a nonuniform electric field. The dipole will experience
a)
a translational force only in the direction of the field
b)
a translational force only in a direction normal to the direction of the field
c)
a torque as well as a translational force
d)
a torque only

|
Sagarika Ahuja answered |
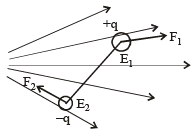
The electric field will be different at the location of the two charges. Therefore the two forces will be unequal.
This will result in a force as well as torque.
This will result in a force as well as torque.
A thin semi-circular ring of radius r has a positive charge q distributed uniformly over it. The net field 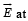 the centre is
the centre is 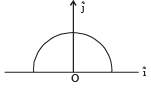
- a)
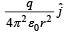
- b)
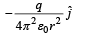
- c)
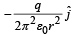
- d)
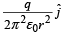
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A thin semi-circular ring of radius r has a positive charge q distributed uniformly over it. The net field 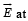 the centre is
the centre is
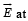 the centre is
the centre is 
a)
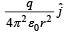
b)
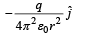
c)
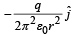
d)
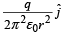
|
|
Vivek answered |
FORMULA USED :
E = λ/(2πε0r)
EXPLANATION :
+ve charge of magnitude q is distributed uniformly over the surface. As the charge is on the surface only we can consider it a line charge. so λ = q/πr.
Now see that the electric field lines due to to the positive charge on the surface are directed towards the centre that is in downwards direction. therefore in vector notation, (-j) will be used.
Now substituting the value in the formula,
E = -q/(2πε0r(πr)) j^
=> E = - q/2π²ε0r² j^
E = λ/(2πε0r)
EXPLANATION :
+ve charge of magnitude q is distributed uniformly over the surface. As the charge is on the surface only we can consider it a line charge. so λ = q/πr.
Now see that the electric field lines due to to the positive charge on the surface are directed towards the centre that is in downwards direction. therefore in vector notation, (-j) will be used.
Now substituting the value in the formula,
E = -q/(2πε0r(πr)) j^
=> E = - q/2π²ε0r² j^
Two identical capacitors, have the same capacitance C. One of them is charged to potential V1 and the other V2. The negative ends of the capacitors are connected together.
When the positive ends are also connected, the decrease in energy of the combined system is- a)
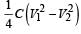
- b)
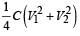
- c)
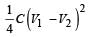
- d)
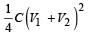
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical capacitors, have the same capacitance C. One of them is charged to potential V1 and the other V2. The negative ends of the capacitors are connected together.
When the positive ends are also connected, the decrease in energy of the combined system is
When the positive ends are also connected, the decrease in energy of the combined system is
a)
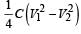
b)
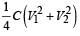
c)
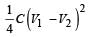
d)
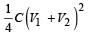

|
Akshay Sharma answered |
Initially we know that
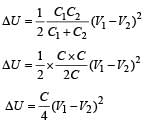
Two capacitors C1 and C2 are charged to 120 V and 200 V respectively. It is found that connecting them together the potential on each one can be made zero. Then- a)5C1 = 3C2
- b)3C1 = 5C2
- c)3C1 + 5C2 = 0
- d)9C1 = 4C2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two capacitors C1 and C2 are charged to 120 V and 200 V respectively. It is found that connecting them together the potential on each one can be made zero. Then
a)
5C1 = 3C2
b)
3C1 = 5C2
c)
3C1 + 5C2 = 0
d)
9C1 = 4C2
|
|
Sarthak Chauhan answered |
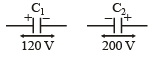
For potential to be made zero, after connection
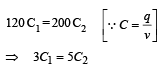
Three concentric metallic spherical shells of radii R, 2R, 3R, are given charges Q1, Q2, Q3, respectively. It is found that the surface charge densities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal. Then, the ratio of the charges given to the shells, Q1 : Q2 : Q3, is- a)1 : 2 : 3
- b)1 : 3 : 5
- c)1 : 4 : 9
- d)1 : 8 : 18
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Three concentric metallic spherical shells of radii R, 2R, 3R, are given charges Q1, Q2, Q3, respectively. It is found that the surface charge densities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal. Then, the ratio of the charges given to the shells, Q1 : Q2 : Q3, is
a)
1 : 2 : 3
b)
1 : 3 : 5
c)
1 : 4 : 9
d)
1 : 8 : 18

|
Bhavana Das answered |
The charges on the surfaces of the metallic spheres are shown in the diagram. It is given that the surface charge densities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal.
Therefore
Therefore
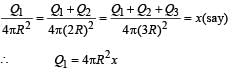
Q1 + Q2 = 4π(2R)2k = 4[4πR2x]
⇒ Q2 = 4[4πR2 x] - Q1
= 4[4πR2x] -4πR2x = 3[4πR2x]
Also Q1 + Q2+ Q3 = 4π(3R)2 x = 9[4πR2x]
∴ Q3 = 9[4πR2x] - Q1 - Q2 = 9[4πR2x] - [4πR2x] -3[4πR2x] = 5[4πR2x]
Also Q1 + Q2+ Q3 = 4π(3R)2 x = 9[4πR2x]
∴ Q3 = 9[4πR2x] - Q1 - Q2 = 9[4πR2x] - [4πR2x] -3[4πR2x] = 5[4πR2x]
⇒ Q1 : Q2 :Q3 = 1 :3 :5
A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has capacitance of 9 pF. The separation between its plates is ‘d’. The space between the plates is now filled with two dielectrics. One of the dielectrics has dielectric constant k1 = 3 and thickness d/3 while the other one has dielectric constant k2 = 6 and thickness 2d/3. Capacitance of the capacitor is now- a)1.8 pF
- b)45 pF
- c)40.5 pF
- d)20.25 pF
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has capacitance of 9 pF. The separation between its plates is ‘d’. The space between the plates is now filled with two dielectrics. One of the dielectrics has dielectric constant k1 = 3 and thickness d/3 while the other one has dielectric constant k2 = 6 and thickness 2d/3. Capacitance of the capacitor is now
a)
1.8 pF
b)
45 pF
c)
40.5 pF
d)
20.25 pF

|
Rohit Yadav answered |
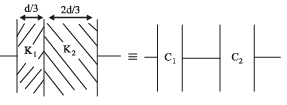
The given capacitance is equal to two capacitances connected in series where
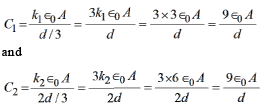
The equivalent capacitance Ceq is
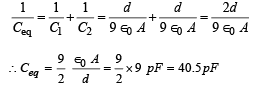
A spherical metal shell A of radius RA and a solid metal sphere B of radius RB(< RA) are kept far apart and each is given charge ‘+Q’. Now they are connected by a thin metal wire. Then- a)
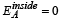
- b)QA > QB
- c)
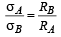
- d)
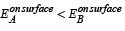
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A spherical metal shell A of radius RA and a solid metal sphere B of radius RB(< RA) are kept far apart and each is given charge ‘+Q’. Now they are connected by a thin metal wire. Then
a)
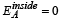
b)
QA > QB
c)
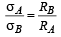
d)
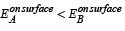

|
Lekshmi Basu answered |
Electric field inside a spherical metallic shell with charge on the surface is always zero. Therefore option [a] is correct.
When the shells are connected with a thin metal wire then electric potentials will be equal, say V.
When the shells are connected with a thin metal wire then electric potentials will be equal, say V.
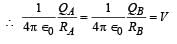
As RA > RB therefore QA > AB. option [b] is also correct.
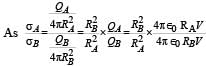
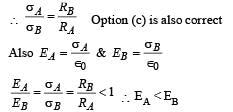
Option (d) is also correct
If gE and gM are the accelerations due to gravity on the surfaces of the earth and the moon respectively and if Millikan’s oil drop experiment could be performed on the two surfaces, one will find the ratio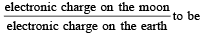
- a)gM /gE
- b)1
- c)0
- d)g E /gM
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If gE and gM are the accelerations due to gravity on the surfaces of the earth and the moon respectively and if Millikan’s oil drop experiment could be performed on the two surfaces, one will find the ratio
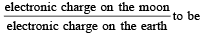
a)
gM /gE
b)
1
c)
0
d)
g E /gM

|
Rishika Mishra answered |
Electronic charge does not depend on acceleration due to gravity as it is a universal constant.
So, electronic charge on earth = electronic charge on moon
So, electronic charge on earth = electronic charge on moon
∴ Required ratio = 1.
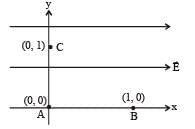
A uniform electric field pointing in positive x-direction exists in a region. Let A be the origin, B be the point on the x-axis at x = +1 cm and C be the point on the y-axis at y = +1 cm. Then the potentials at the points A, B and C satisfy:- a)VA < VB
- b)VA > VB
- c)VA < VC
- d)VA > VC
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A uniform electric field pointing in positive x-direction exists in a region. Let A be the origin, B be the point on the x-axis at x = +1 cm and C be the point on the y-axis at y = +1 cm. Then the potentials at the points A, B and C satisfy:
a)
VA < VB
b)
VA > VB
c)
VA < VC
d)
VA > VC

|
Krish Ghoshal answered |
NOTE : As we move along the direction of electric field the potential decreases.
∴ VA > VB
A long, hollow conducting cylinder is kept coaxially inside another long, hollow conducting cylinder of larger radius.
Both the cylinders are initially electrically neutral. - a)A potential difference appears between the two cylinders when a charge density is given to the inner cylinder.
- b)A potential difference appears between the two cylinders when a charge density is given to the outer cylinder.
- c)No potential difference appears between the two cylinders when a uniform line charge is kept along the axis of the cylinders
- d)No potential difference appears between the two cylinders when same charge density is given to both the cylinders.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A long, hollow conducting cylinder is kept coaxially inside another long, hollow conducting cylinder of larger radius.
Both the cylinders are initially electrically neutral.
Both the cylinders are initially electrically neutral.
a)
A potential difference appears between the two cylinders when a charge density is given to the inner cylinder.
b)
A potential difference appears between the two cylinders when a charge density is given to the outer cylinder.
c)
No potential difference appears between the two cylinders when a uniform line charge is kept along the axis of the cylinders
d)
No potential difference appears between the two cylinders when same charge density is given to both the cylinders.

|
Rithika Mishra answered |
When a charge density is given to the inner cylinder, the potential developed at its surface is different from that on the outer cylinder. This is because the potential decreases with distance for a charged conducting cylinder when the point of consideration is outside the cylinder.
But when a charge density is given to the outer cylinder, it will change its potential by the same amount as that of the inner cylinder. Therefore no potential difference will be produced between the cylinders in this case.
But when a charge density is given to the outer cylinder, it will change its potential by the same amount as that of the inner cylinder. Therefore no potential difference will be produced between the cylinders in this case.
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased by 100%. Due to the consequent decrease in diameter the change in the resistance of the wire will be- a)200%
- b)100%
- c)50%
- d)300%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased by 100%. Due to the consequent decrease in diameter the change in the resistance of the wire will be
a)
200%
b)
100%
c)
50%
d)
300%

|
Nishanth Verma answered |
Rf = n2Ri
Here n = 2 (length becomes twice)
∴ Rf = 4Ri
New reresistance = 400 of Ri
∴ Increase = 300%
The potential at a point x (measured in μ m) due to some charges situated on the x-axis is given by V(x) = 20/(x2 – 4) voltThe electric field E at x = 4 m m is given by- a)(10/9) volt/ m m and in the +ve x direction
- b)(5/3) volt/ m m and in the –ve x direction
- c)(5/3) volt/ m m and in the +ve x direction
- d)(10/9) volt/ m m and in the –ve x direction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The potential at a point x (measured in μ m) due to some charges situated on the x-axis is given by V(x) = 20/(x2 – 4) volt
The electric field E at x = 4 m m is given by
a)
(10/9) volt/ m m and in the +ve x direction
b)
(5/3) volt/ m m and in the –ve x direction
c)
(5/3) volt/ m m and in the +ve x direction
d)
(10/9) volt/ m m and in the –ve x direction

|
Pragati Dey answered |
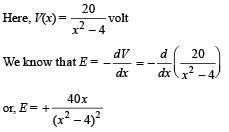
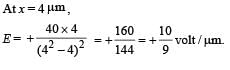
Positive sign indicates tha  -direction.
-direction.
 -direction.
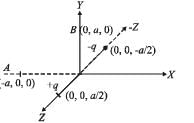
-direction.Positive and negative point charges of equal magnitude are kept at 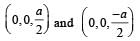 respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is- a)positive
- b)negative
- c)zero
- d)depends on the path connecting the initial and final positions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Positive and negative point charges of equal magnitude are kept at 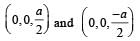 respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
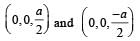 respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) isa)
positive
b)
negative
c)
zero
d)
depends on the path connecting the initial and final positions

|
Bhavya Joshi answered |
The charges make an electric dipole. A and B points lie on the equatorial plane of the dipole.
Therefore, potential at A = potential at B = 0
Therefore, potential at A = potential at B = 0
W = q (VA – VB) = q × 0 = 0
A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field of strength 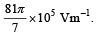 When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is
When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is - a)1.6 × 10–19 C
- b)3.2 × 10 –19 C
- c)4.8 × 10–19 C
- d)8.0 × 10–19 C
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field of strength 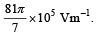 When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is
When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is
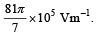 When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is
When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is a)
1.6 × 10–19 C
b)
3.2 × 10 –19 C
c)
4.8 × 10–19 C
d)
8.0 × 10–19 C
|
|
Ankita Mishra answered |
When the electric field is on
Force due to electric field = weight
Force due to electric field = weight
qE = mg
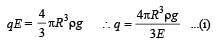
When the electric field is switched off Weight = viscous drag force
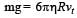
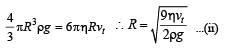
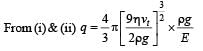
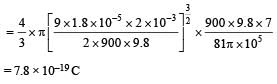
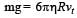
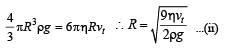
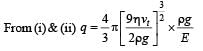
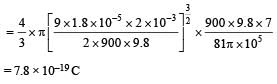
A combination of capacitors is set up as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the electric field, due to a point charge Q (having a charge equal to the sum of the charges on the 4 μF and 9 μF capacitors), at a point distance 30 m from it, would equal :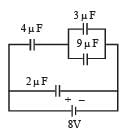
- a)420 N/C
- b)480 N/C
- c)240 N/C
- d)360 N/C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A combination of capacitors is set up as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the electric field, due to a point charge Q (having a charge equal to the sum of the charges on the 4 μF and 9 μF capacitors), at a point distance 30 m from it, would equal :

a)
420 N/C
b)
480 N/C
c)
240 N/C
d)
360 N/C

|
Anshika Rane answered |
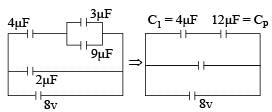
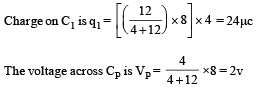
∴ Voltage across 9μF is also 2V
∴ Charge on 9μF capacitor = 9 × 2 = 18μC
∴ Total charge on 4 μF and 9μF = 42μc 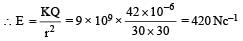
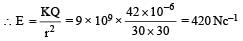
Assume that an electric field 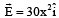 exists in space. Then the potential difference VA - VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is:
exists in space. Then the potential difference VA - VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is:- a)120 J/C
- b)-120 J/C
- c)-80 J/C
- d)80 J/C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that an electric field 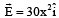 exists in space. Then the potential difference VA - VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is:
exists in space. Then the potential difference VA - VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is:
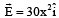 exists in space. Then the potential difference VA - VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is:
exists in space. Then the potential difference VA - VO, where VO is the potential at the origin and VA the potential at x = 2 m is:a)
120 J/C
b)
-120 J/C
c)
-80 J/C
d)
80 J/C

|
Nandini Choudhury answered |
Poten tial difference between any two poin ts in an electric field is given by,
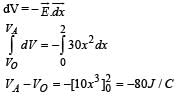
Chapter doubts & questions for Electrostatics - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electrostatics - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
347 docs|185 tests
|
Related JEE Content
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup