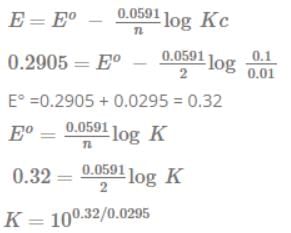All Exams >
NEET >
4 Months Preparation for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Electrochemistry for NEET Exam
Molar conductivity for a compound AB is 145.0 Scm2mol-1 and for CB is 110.1 Scm2mol-1. Limiting molar conductivity for A+ is 73.5 Scm2mol-1. What is limiting molar conductivity for C+?- a)326.6 S cm2 mol-1
- b)38.6 S cm2 mol-1
- c)181.6 S cm2 mol-1
- d)90.8 S cm2 mol-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Molar conductivity for a compound AB is 145.0 Scm2mol-1 and for CB is 110.1 Scm2mol-1. Limiting molar conductivity for A+ is 73.5 Scm2mol-1. What is limiting molar conductivity for C+?
a)
326.6 S cm2 mol-1
b)
38.6 S cm2 mol-1
c)
181.6 S cm2 mol-1
d)
90.8 S cm2 mol-1

|
Priyal answered |

Chemical used in salt bridge isa. KOHb. KCIc. KNO2d. KBrCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anand Saha answered |
KCl is used as salt bridge because it provides positive K+ ions and negative Cl- ions as the salt bridge needs to maintain the neutrality in the system by providing enough negative ions equal to the positive ions during oxidation.
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?- a)A will be a good oxidising agent
- b)A will accept electrons easily
- c)A will undergo reduction easily
- d)A will undergo oxidation easily
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?
a)
A will be a good oxidising agent
b)
A will accept electrons easily
c)
A will undergo reduction easily
d)
A will undergo oxidation easily
|
|
Avantika Dasgupta answered |
Reduction Potential of Element A
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V. This means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons.
Explanation of Options
a) A will be a good oxidising agent - This statement is incorrect. A good oxidizing agent is one that accepts electrons from other species and undergoes reduction. But, since the reduction potential of element A is negative, it indicates that the element A is likely to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, so it is not a good oxidizing agent.
b) A will accept electrons easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to lose electrons and undergo oxidation, rather than accepting electrons and undergoing reduction.
c) A will undergo reduction easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, rather than undergoing reduction and gaining electrons.
d) A will undergo oxidation easily - This statement is correct. The reduction potential value of element A is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. Therefore, element A will undergo oxidation easily.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D'. The reduction potential value of an element indicates its tendency to undergo oxidation or reduction. A negative reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, while a positive reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo reduction and gain electrons.
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V. This means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons.
Explanation of Options
a) A will be a good oxidising agent - This statement is incorrect. A good oxidizing agent is one that accepts electrons from other species and undergoes reduction. But, since the reduction potential of element A is negative, it indicates that the element A is likely to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, so it is not a good oxidizing agent.
b) A will accept electrons easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to lose electrons and undergo oxidation, rather than accepting electrons and undergoing reduction.
c) A will undergo reduction easily - This statement is incorrect. The reduction potential value is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, rather than undergoing reduction and gaining electrons.
d) A will undergo oxidation easily - This statement is correct. The reduction potential value of element A is negative, which means that the element A has a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. The more negative the reduction potential value, the easier it is for the element to undergo oxidation and lose electrons. Therefore, element A will undergo oxidation easily.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'D'. The reduction potential value of an element indicates its tendency to undergo oxidation or reduction. A negative reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo oxidation and lose electrons, while a positive reduction potential value indicates a strong tendency to undergo reduction and gain electrons.
A half cell reaction A- → A + e- has a large negative reduction potential. It follows that :- a)A is easily reduced
- b)A – is easily reduced
- c)A – is easily oxidised
- d)A is easily oxidised
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A half cell reaction A- → A + e- has a large negative reduction potential. It follows that :
a)
A is easily reduced
b)
A – is easily reduced
c)
A – is easily oxidised
d)
A is easily oxidised
|
|
Kalyan Chavan answered |
Can you please provide more details or context about the half-cell reaction you are referring to?
Hydrogen gas is not liberated when the following metal is added to dil. HCl.- a)Mg
- b)Sn
- c)Ag
- d)Zn
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hydrogen gas is not liberated when the following metal is added to dil. HCl.
a)
Mg
b)
Sn
c)
Ag
d)
Zn
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
The metals, present below hydrogen in the electrochemical series, cannot liberate hydrogen from the dilute acids.
Among the given metals only Ag is present below hydrogen in electrochemical series, so it does not evolve hydrogen with dil HCl.
Ag−I−dilHCl ⟶ No reaction
Among the given metals only Ag is present below hydrogen in electrochemical series, so it does not evolve hydrogen with dil HCl.
Ag−I−dilHCl ⟶ No reaction
Temperature for the measurement of standard electrode potential is- a)298K
- b)300K
- c)30?C
- d)310K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Temperature for the measurement of standard electrode potential is
a)
298K
b)
300K
c)
30?C
d)
310K
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The standard electrode potentials are customarily determined at solute concentrations of 1 Molar, gas pressures of 1 atmosphere, and a standard temperature which is usually 25°C i.e, 298 K.
Calculate the standard cell potentials of galvanic cell, ∆rG and equilibrium constant of the reactions if the reaction is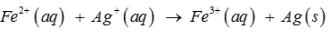
- a)0.01V, – 2.800 kJ mol–1, 3.2
- b)0.03V, – 2.895 kJ mol–1, 3.2
- c)0.02V, – 2.850 kJ mol–1, 3.2
- d)0.04V, – 2.955 kJ mol–1, 3.2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the standard cell potentials of galvanic cell, ∆rG and equilibrium constant of the reactions if the reaction is
a)
0.01V, – 2.800 kJ mol–1, 3.2
b)
0.03V, – 2.895 kJ mol–1, 3.2
c)
0.02V, – 2.850 kJ mol–1, 3.2
d)
0.04V, – 2.955 kJ mol–1, 3.2

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The standard emf of a galvanic cell involving 3 moles of electrons in its redox reaction is 0.59V.
Eºcell = 0.59V
n=3
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of the cell is given by the expression: ln K = RT nFEºcell
ln K = 8.314 × 298 × 3 × 96500 × 0.59 = 68.9
K≈1030
n=3
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of the cell is given by the expression: ln K = RT nFEºcell
ln K = 8.314 × 298 × 3 × 96500 × 0.59 = 68.9
K≈1030
The equilibrium constant for the reaction of the cell is 1030.
The standard reduction potential at 298 K for the following half cells are given: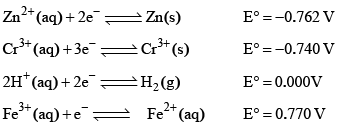 Which is the strongest reducing agent:
Which is the strongest reducing agent:- a)Zn(s)
- b)Cr(s)
- c)H2(g)
- d)Fe2+ (aq)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard reduction potential at 298 K for the following half cells are given:
Which is the strongest reducing agent:
a)
Zn(s)
b)
Cr(s)
c)
H2(g)
d)
Fe2+ (aq)
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Zn has minimum reduction potential it means Zn is strong reducing agent. Hence A is correct.
An electrochemical cell consists of two half-cell reactions.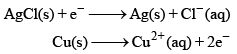 The mass of copper (in grams) dissolved on passing 0.5 A current for 1h is [Given, atomic mass of Cu is 63.6, F = 96500 C mol–1]
The mass of copper (in grams) dissolved on passing 0.5 A current for 1h is [Given, atomic mass of Cu is 63.6, F = 96500 C mol–1]- a)0.88
- b)1.18
- c)0.29
- d)0.59
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An electrochemical cell consists of two half-cell reactions.
The mass of copper (in grams) dissolved on passing 0.5 A current for 1h is [Given, atomic mass of Cu is 63.6, F = 96500 C mol–1]
a)
0.88
b)
1.18
c)
0.29
d)
0.59
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
m/E = Q/F
m/(63.6/2) = (0.5 x 60 x 60)/96500
m = (1800 x 63.6)/(96500 x 2)
m = 0.59
m/(63.6/2) = (0.5 x 60 x 60)/96500
m = (1800 x 63.6)/(96500 x 2)
m = 0.59
The standard reduction potentials E°, for the half reactions are as: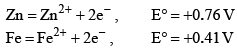 The emf for the cell reaction,
The emf for the cell reaction,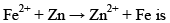
- a)–0.35 V
- b)+0.35 V
- c)+1.17 V
- d)–1.17 V
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard reduction potentials E°, for the half reactions are as:
The emf for the cell reaction,
a)
–0.35 V
b)
+0.35 V
c)
+1.17 V
d)
–1.17 V

|
Asf Institute answered |
Fe2++2e−⟶Fe; 20mmE∘=−0.41V
20mm Zn⟶Zn2++2e−; E∘=+0.76V
⇒Fe2++Zn⟶Zn2++Fe; E∘=+0.35V
20mm Zn⟶Zn2++2e−; E∘=+0.76V
⇒Fe2++Zn⟶Zn2++Fe; E∘=+0.35V
Salt bridge is indicated in the cell representation by :- a)I
- b)!!
- c)((
- d)II
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Salt bridge is indicated in the cell representation by :
a)
I
b)
!!
c)
((
d)
II
|
|
Khushi Pandey answered |
Indicàted by Twø parallel linés (||)
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:- a)Velocity of K+ and NO3– are same
- b)Velocity of NO3– is greater than that of K+
- c)Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3–
- d)KNO3 is highly soluble in water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:
a)
Velocity of K+ and NO3– are same
b)
Velocity of NO3– is greater than that of K+
c)
Velocity of K+ is greater than that of NO3–
d)
KNO3 is highly soluble in water
|
|
Riya Agarwal answered |
Velocities of both should be same to balance the amount of both ions in the soln. if the vel of any of them is more...then its ions will release more
The equilibrium constant of the reaction: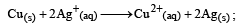 E° = 0.46 V at 298 K is [2007]
E° = 0.46 V at 298 K is [2007]- a)2.0 × 1010
- b)4.0 × 1010
- c)4.0 × 1015
- d)2.4 × 1010
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant of the reaction:
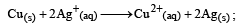
E° = 0.46 V at 298 K is [2007]
a)
2.0 × 1010
b)
4.0 × 1010
c)
4.0 × 1015
d)
2.4 × 1010

|
Harshitha Chavan answered |
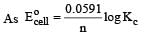
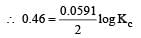
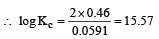
or Kc = Antilog 15.57 = 3.7 × 1015 ≈ 4 × 1015
Consider the following reaction which of the following statement is true for this cell reaction.
(Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu)- a)Zn2+ ions are oxidized to Zn
- b)Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ ions
- c)Zn is reduced to Zn2+ ions
- d)Cu2+ ions are oxidized to Cu
-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction which of the following statement is true for this cell reaction.
(Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu)
(Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu)
a)
Zn2+ ions are oxidized to Zn
b)
Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ ions
c)
Zn is reduced to Zn2+ ions
d)
Cu2+ ions are oxidized to Cu
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- For the reaction Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu, Zn is oxidized to Zn2+ while Cu2+ is reduced to Cu
- In a redox reaction, the reactant that loses electrons (is oxidized) causes a reduction and is called a reducing agent. In the example above, zinc metal is the reducing agent; it loses two electrons (is oxidized) and becomes Zn2+ ion.
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?- a)A will be a good oxidising agent
- b)A will accept electrons easily
- c)A will undergo reduction easily
- d)A will undergo oxidation easily
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential of an element A is -2.71V.What can be concluded from this?
a)
A will be a good oxidising agent
b)
A will accept electrons easily
c)
A will undergo reduction easily
d)
A will undergo oxidation easily

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Reduction potential means to accept electrons to reduce oneself.
A + e- → A- ∆Ereduction = +ve value
Since, the reduction potential is negative, it means that the reaction will reverse to make ∆E value +ve. So the reaction becomes,
A → A+ + e-
This becomes oxidation of A. So oxidation of A will be easy.
A + e- → A- ∆Ereduction = +ve value
Since, the reduction potential is negative, it means that the reaction will reverse to make ∆E value +ve. So the reaction becomes,
A → A+ + e-
This becomes oxidation of A. So oxidation of A will be easy.
Galvanization is applying a coating of:- a)Pb
- b)Cr
- c)Cu
- d)Zn
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Galvanization is applying a coating of:
a)
Pb
b)
Cr
c)
Cu
d)
Zn

|
Akash Kulkarni answered |
Galvanization is the process of coating a metal object with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The correct answer is option 'D' which is Zinc.
Zinc as a coating material:
Zinc is a highly reactive metal and has a strong affinity towards oxygen. When exposed to air, it reacts with oxygen to form a thin layer of zinc oxide on its surface. This layer acts as a barrier between the metal and the air, preventing further oxidation. Zinc is also very ductile and can be easily shaped and molded to fit any object. These properties make it an ideal coating material for metal objects.
Galvanization process:
The galvanization process involves coating a metal object with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The process can be carried out using one of two methods: hot-dip galvanizing or electroplating.
Hot-dip galvanizing:
In hot-dip galvanizing, the metal object is first cleaned and then dipped into a bath of molten zinc. The high temperature of the zinc bath causes the zinc to react with the surface of the metal, forming a layer of zinc-iron alloy. The object is then removed from the bath and allowed to cool, forming a layer of pure zinc on its surface.
Electroplating:
In electroplating, the metal object is first cleaned and then placed in a solution containing zinc ions. A direct current is then passed through the solution, causing the zinc ions to be deposited onto the surface of the metal object. The object is then removed from the solution and rinsed to remove any excess zinc.
Advantages of galvanization:
Galvanization provides several benefits, including:
1. Corrosion resistance: Zinc is a highly corrosion-resistant material that protects the underlying metal from rust and other forms of corrosion.
2. Longevity: Galvanized objects have a long lifespan and can last for decades without needing to be replaced.
3. Low maintenance: Galvanized objects require very little maintenance, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, galvanization is the process of coating a metal object with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. Zinc is an ideal coating material due to its high reactivity, ability to form a protective oxide layer, and ductility. Galvanization provides several benefits, including corrosion resistance, longevity, and low maintenance.
Zinc as a coating material:
Zinc is a highly reactive metal and has a strong affinity towards oxygen. When exposed to air, it reacts with oxygen to form a thin layer of zinc oxide on its surface. This layer acts as a barrier between the metal and the air, preventing further oxidation. Zinc is also very ductile and can be easily shaped and molded to fit any object. These properties make it an ideal coating material for metal objects.
Galvanization process:
The galvanization process involves coating a metal object with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. The process can be carried out using one of two methods: hot-dip galvanizing or electroplating.
Hot-dip galvanizing:
In hot-dip galvanizing, the metal object is first cleaned and then dipped into a bath of molten zinc. The high temperature of the zinc bath causes the zinc to react with the surface of the metal, forming a layer of zinc-iron alloy. The object is then removed from the bath and allowed to cool, forming a layer of pure zinc on its surface.
Electroplating:
In electroplating, the metal object is first cleaned and then placed in a solution containing zinc ions. A direct current is then passed through the solution, causing the zinc ions to be deposited onto the surface of the metal object. The object is then removed from the solution and rinsed to remove any excess zinc.
Advantages of galvanization:
Galvanization provides several benefits, including:
1. Corrosion resistance: Zinc is a highly corrosion-resistant material that protects the underlying metal from rust and other forms of corrosion.
2. Longevity: Galvanized objects have a long lifespan and can last for decades without needing to be replaced.
3. Low maintenance: Galvanized objects require very little maintenance, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, galvanization is the process of coating a metal object with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. Zinc is an ideal coating material due to its high reactivity, ability to form a protective oxide layer, and ductility. Galvanization provides several benefits, including corrosion resistance, longevity, and low maintenance.
The reduction potential of an element A is 1.71 V. What can be concluded from this?- a)A will lose electrons easily
- b)A will undergo reduction easily
- c)A will undergo oxidation easily
- d)A will be a good reducing agent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The reduction potential of an element A is 1.71 V. What can be concluded from this?
a)
A will lose electrons easily
b)
A will undergo reduction easily
c)
A will undergo oxidation easily
d)
A will be a good reducing agent
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The standard reduction potential is the tendency for a chemical species to be reduced, and is measured in volts at standard conditions. The more positive the potential is the more likely it will be reduced. Hence, A will undergo reduction easily.
In an electrolytic cell current flows from -- a)Cathode to anode in outer circuit
- b)Anode to cathode outside the cell
- c)Cathode to anode inside the cell
- d)Anode to cathode inside the cell
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In an electrolytic cell current flows from -
a)
Cathode to anode in outer circuit
b)
Anode to cathode outside the cell
c)
Cathode to anode inside the cell
d)
Anode to cathode inside the cell
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In an electrolytic cell, current flows from cathode to anode in outer circuit and in daniell cell, it is the reverse direction of flow of current from anode to cathode in outer circuit.
In the electrolytic cell, flow of electrons is from:- a)Cathode to anode in solution
- b)Cathode to anode through external supply
- c)Cathode to anode through internal supply
- d)Anode to cathode through internal supply
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the electrolytic cell, flow of electrons is from:
a)
Cathode to anode in solution
b)
Cathode to anode through external supply
c)
Cathode to anode through internal supply
d)
Anode to cathode through internal supply

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
Flow of Electrons in an Electrolytic Cell
In an electrolytic cell, the flow of electrons is from: Anode to Cathode through Internal Supply
This means that option B is correct. Here's why:
In an electrolytic cell, the flow of electrons is from: Anode to Cathode through Internal Supply
This means that option B is correct. Here's why:
- Anode: This is where oxidation takes place in an electrolytic cell. During oxidation, a substance loses electrons. This means that the anode is the source of electrons.
- Cathode: This is where reduction takes place in an electrolytic cell. During reduction, a substance gains electrons, meaning that the cathode is where electrons are received.
- Flow of electrons: Since electrons are produced at the anode (through oxidation) and consumed at the cathode (through reduction), the flow of electrons is from the anode to the cathode.
- Internal supply: In an electrolytic cell, the power supply is connected to the anode and cathode, creating an electric current within the cell. This current forces the electrons to move from the anode to the cathode, hence the term "through internal supply".
In summary, in an electrolytic cell, the flow of electrons is from anode to cathode through internal supply as a result of the oxidation and reduction reactions taking place at the anode and cathode, respectively.
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential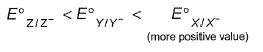 then,
then,- a)Y will oxidise X and not Z
- b)Y will oxidise Z and not X
- c)Y will oxidise both X and Z
- d)Z- will reduce both X and Y
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 M Y- and 1 M Z- at 298 K.If the standard reduction potential
then,
a)
Y will oxidise X and not Z
b)
Y will oxidise Z and not X
c)
Y will oxidise both X and Z
d)
Z- will reduce both X and Y
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
In ECS, pair with more negative values of E°red reducing agent is above oxidising agent.
Thus, Z/Z- is the best reducing agent
Thus, Z- will reduce both X and Y and itself will be oxidised to Z .
At 300K molar conductivity of solution A is 350 units, and at infinite dilution the molar conductivity of the same sample is 480 unit. Predict the percentage dissociation of the electrolyte.- a)73.0%
- b)37.0%
- c)63.0%
- d)137.0%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At 300K molar conductivity of solution A is 350 units, and at infinite dilution the molar conductivity of the same sample is 480 unit. Predict the percentage dissociation of the electrolyte.
a)
73.0%
b)
37.0%
c)
63.0%
d)
137.0%

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
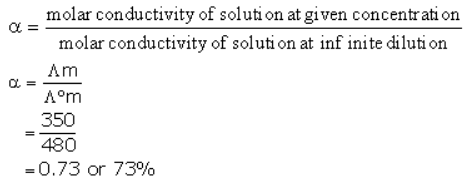
Stronger the oxidizing agent, greater is the:- a)Reactivity
- b)Ionic behaviour
- c)Oxidation potential
- d)Reduction potential
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stronger the oxidizing agent, greater is the:
a)
Reactivity
b)
Ionic behaviour
c)
Oxidation potential
d)
Reduction potential
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Lithium is strongest Reducing agent because of lowest standard reduction potential. When something is oxidized, it reduces another substance, becoming a reducing agent. Hence lithium is the strongest reducing agent. remember, Li is the strongest reducing agent and F is the strongest oxidizing agent!
On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing agent is: 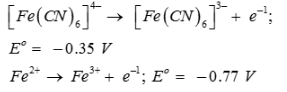
- a)[Fe(CN)6]4-
- b)Fe2+
- c)Fe3+
- d)[Fe(CN)6]3-
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing agent is:
a)
[Fe(CN)6]4-
b)
Fe2+
c)
Fe3+
d)
[Fe(CN)6]3-

|
Dishani Kulkarni answered |
Strongest oxidizing agent is one having more positive or less negative reduction potential.
Which of the following solutions has the highest equivalent conductance ?- a)0.01M NaCl
- b)0.050 M NaCl
- c)0.005M NaCl
- d)0.02M NaCl
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following solutions has the highest equivalent conductance ?
a)
0.01M NaCl
b)
0.050 M NaCl
c)
0.005M NaCl
d)
0.02M NaCl
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Higher the dilution higher will be the equivalent conductance
Correct arrangement of Al, Cu, Fe, Mg and Zn in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts is- a)Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Cu
- b)Mg, Al, Zn, Cu, Fe
- c)Mg, Al, Cu, Fe, Zn
- d)Cu, Al, Zn, Fe, Mg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct arrangement of Al, Cu, Fe, Mg and Zn in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts is
a)
Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Cu
b)
Mg, Al, Zn, Cu, Fe
c)
Mg, Al, Cu, Fe, Zn
d)
Cu, Al, Zn, Fe, Mg

|
Mehul Choudhary answered |
Reactivity series.
The electrode potential measures the :- a)tendency of a cell reaction to occur
- b)current carried by an elelctrode
- c)tendency of the electrode to gain or lose electrons
- d)difference in the ionisation of electrode and metal ion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrode potential measures the :
a)
tendency of a cell reaction to occur
b)
current carried by an elelctrode
c)
tendency of the electrode to gain or lose electrons
d)
difference in the ionisation of electrode and metal ion
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The tendency of an electrode to lose or gain electrons when it is in contact with its own ions in solution is called electrode potential.
Since the tendency to lose electrons means also the tendency to get oxidised, this tendency is called oxidation potential. Similarly, the tendency to gain electrons means the tendency to get reduced. Hence this tendency is called reduction potential.
Kohlrausch’s Law shows that:- a)at infinite dilution the ionic conductivity of ions is additive.
- b)at infinite dilution the ionic conductivity of all the ions of the electrolyte become equal.
- c)at infinite dilution the concentration of the electrolyte becomes unity.
- d)at infinite dilution the concentration of ions increases.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Kohlrausch’s Law shows that:
a)
at infinite dilution the ionic conductivity of ions is additive.
b)
at infinite dilution the ionic conductivity of all the ions of the electrolyte become equal.
c)
at infinite dilution the concentration of the electrolyte becomes unity.
d)
at infinite dilution the concentration of ions increases.
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The correct answer is option A
Kohlrausch's law states that the equivalent conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of the conductances of the anions and cations. If a salt is dissolved in water, the conductivity of the solution is the sum of the conductances of the anions and cations.
Hence, at infinite dilution the ionic conductivity of ions is additive.
Hence, at infinite dilution the ionic conductivity of ions is additive.
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:- a)Salt bridge
- b)Electrolyte
- c)Anode
- d)Cathode
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:
a)
Salt bridge
b)
Electrolyte
c)
Anode
d)
Cathode
|
|
Sargam Singh answered |
A substance with lower reduction potential has more tendency to oxidize .in a electrochemical cell anode performs oxidation reaction hence the electrode will function as a anode
The variation of equivalent conductance vs decrease in concentration of a strong electrolyte is correctly given in the plot -- a) A
- b) A
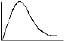
- c)A

- d) A

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The variation of equivalent conductance vs decrease in concentration of a strong electrolyte is correctly given in the plot -
a)
A
b)
A
c)
A
d)
A
|
|
Om Desai answered |
On decreasing the value of M will increase but increase will be hyberbolic.
One of the simplest methods of preventing corrosion is to prevent the surface of the metallic object to come in contact with atmosphere. This can be done- a)by covering the surface with oil
- b)by covering the surface with salt
- c)by covering the surface with citric acid
- d)by covering the surface with paint or by some chemicals
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the simplest methods of preventing corrosion is to prevent the surface of the metallic object to come in contact with atmosphere. This can be done
a)
by covering the surface with oil
b)
by covering the surface with salt
c)
by covering the surface with citric acid
d)
by covering the surface with paint or by some chemicals
|
|
Rajesh Chatterjee answered |
Preventing corrosion is essential to ensure the longevity and integrity of metallic objects. One of the simplest and most effective methods to prevent corrosion is by covering the surface of the object with paint or certain chemicals. This method creates a protective barrier between the metal surface and the atmosphere, preventing contact and thereby reducing the chances of corrosion.
Here is a detailed explanation of why covering the surface with paint or chemicals is an effective method of preventing corrosion:
1. Creation of a Barrier: By covering the surface of the metallic object with paint or chemicals, a physical barrier is created between the metal and the surrounding atmosphere. This barrier prevents the metal from coming into direct contact with oxygen, moisture, and other corrosive elements present in the air.
2. Protection from Moisture: Moisture is one of the primary causes of corrosion. When metal comes into contact with moisture, it undergoes a chemical reaction known as oxidation, leading to the formation of rust. By covering the surface, the paint or chemicals act as a waterproof layer, preventing moisture from reaching the metal surface and reducing the chances of corrosion.
3. Prevention of Oxygen Exposure: Oxygen is another key component in the corrosion process. By covering the surface, the paint or chemicals act as a barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching the metal surface. This helps in inhibiting the oxidation reaction and reducing the chances of corrosion.
4. Chemical Protection: Some paints and chemicals used for covering the surface of metallic objects contain corrosion inhibitors. These inhibitors are chemicals that actively work to prevent or slow down the corrosion process. They form a protective layer on the metal surface, hindering the reaction between the metal and corrosive elements.
5. Flexibility and Ease of Application: Paints and chemicals offer the advantage of being flexible and easy to apply on different types of metal surfaces. They can be brushed, sprayed, or dipped, allowing for complete coverage and protection against corrosion.
It is important to note that the choice of paint or chemical coating depends on the specific requirements of the metal object, the environment it will be exposed to, and the type of corrosion it is susceptible to. Consulting with experts or conducting thorough research is recommended to ensure the most suitable protective coating is applied.
Here is a detailed explanation of why covering the surface with paint or chemicals is an effective method of preventing corrosion:
1. Creation of a Barrier: By covering the surface of the metallic object with paint or chemicals, a physical barrier is created between the metal and the surrounding atmosphere. This barrier prevents the metal from coming into direct contact with oxygen, moisture, and other corrosive elements present in the air.
2. Protection from Moisture: Moisture is one of the primary causes of corrosion. When metal comes into contact with moisture, it undergoes a chemical reaction known as oxidation, leading to the formation of rust. By covering the surface, the paint or chemicals act as a waterproof layer, preventing moisture from reaching the metal surface and reducing the chances of corrosion.
3. Prevention of Oxygen Exposure: Oxygen is another key component in the corrosion process. By covering the surface, the paint or chemicals act as a barrier, preventing oxygen from reaching the metal surface. This helps in inhibiting the oxidation reaction and reducing the chances of corrosion.
4. Chemical Protection: Some paints and chemicals used for covering the surface of metallic objects contain corrosion inhibitors. These inhibitors are chemicals that actively work to prevent or slow down the corrosion process. They form a protective layer on the metal surface, hindering the reaction between the metal and corrosive elements.
5. Flexibility and Ease of Application: Paints and chemicals offer the advantage of being flexible and easy to apply on different types of metal surfaces. They can be brushed, sprayed, or dipped, allowing for complete coverage and protection against corrosion.
It is important to note that the choice of paint or chemical coating depends on the specific requirements of the metal object, the environment it will be exposed to, and the type of corrosion it is susceptible to. Consulting with experts or conducting thorough research is recommended to ensure the most suitable protective coating is applied.
The electrochemical cell shown below is a concentration cell.
M|M2+ (saturated solut ion of a sparingly so luble salt, MX2 || M2+ (0.001 mol dm–3)| M.
The emf of the cell depends on the difference in concentration of M2+ ions at the two electrodes. The emf of the cell at 298 is 0.059 V.Q. The value of ΔG (kJ mol-1) for the given cell is (take 1 F = 96500 C mol-1)- a)–5.7
- b)5.7
- c)11.4
- d)–11.4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The electrochemical cell shown below is a concentration cell.
M|M2+ (saturated solut ion of a sparingly so luble salt, MX2 || M2+ (0.001 mol dm–3)| M.
The emf of the cell depends on the difference in concentration of M2+ ions at the two electrodes. The emf of the cell at 298 is 0.059 V.
M|M2+ (saturated solut ion of a sparingly so luble salt, MX2 || M2+ (0.001 mol dm–3)| M.
The emf of the cell depends on the difference in concentration of M2+ ions at the two electrodes. The emf of the cell at 298 is 0.059 V.
Q.
The value of ΔG (kJ mol-1) for the given cell is (take 1 F = 96500 C mol-1)
a)
–5.7
b)
5.7
c)
11.4
d)
–11.4
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
At cathode:M+2(aq)+2e−→M(s)
At anode:M(s)+2X−(aq)→MX2(aq)+2e−
n - factor of the cell reaction is 2.
At anode:M(s)+2X−(aq)→MX2(aq)+2e−
n - factor of the cell reaction is 2.
ΔG=−nFEcell
= −2×96500×0.059
= −11.4 kJmole−1
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at cathode is:- a)Hydrolysis
- b)Reduction
- c)Oxidation
- d)Neutralization
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at cathode is:
a)
Hydrolysis
b)
Reduction
c)
Oxidation
d)
Neutralization
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
The electrode at which oxidation takes place is known as the anode, while the electrode at which reduction take place is called the cathode. If you see galvanic cell reduction take place at the left electrode, so the left one is the cathode. Oxidation takes place at the right electrode, so the right one is the anode.
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 Ω. What is the cell constant if conductivity of 0.001M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.146 × 10-3 S cm-1.- a)0.219 cm-1
- b)0.239 cm-1
- c)0.229 cm-1
- d)0.209 cm-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 Ω. What is the cell constant if conductivity of 0.001M KCl solution at 298 K is 0.146 × 10-3 S cm-1.
a)
0.219 cm-1
b)
0.239 cm-1
c)
0.229 cm-1
d)
0.209 cm-1
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Κ = G x cell constant and G = 1/R.
The standard electrode potential is measured by- a)Galvanometer
- b)Voltmeter
- c)Electrometer
- d)Pyrometer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard electrode potential is measured by
a)
Galvanometer
b)
Voltmeter
c)
Electrometer
d)
Pyrometer

|
Gauri Khanna answered |
Voltmeter measures the potential.
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:- a)Reduction
- b)Neutralization
- c)Hydrolysis
- d)Oxidation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:
a)
Reduction
b)
Neutralization
c)
Hydrolysis
d)
Oxidation
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Oxidation takes place at the right electrode, so the right one is the anode. While in electrolytic cell reduction takes place at the right electrode, so right one is the cathode. Oxidation takes place at the left electrode, so the left one is the anode.
A conductance cell was filled with a 0.02 M KCl solution which has a specific conductance of 2.768 × 10-3 ohm-1 cm-1. If its resistance is 82.4 ohm at 25ºC, the cell constant is-- a)0.2182 cm-1
- b)0.2281 cm-1
- c)0.2821 cm-1
- d)0.2381 cm-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A conductance cell was filled with a 0.02 M KCl solution which has a specific conductance of 2.768 × 10-3 ohm-1 cm-1. If its resistance is 82.4 ohm at 25ºC, the cell constant is-
a)
0.2182 cm-1
b)
0.2281 cm-1
c)
0.2821 cm-1
d)
0.2381 cm-1
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
K = G. L/A
10–3 × 2.768 = 1/R ×L/A
L/A = 228.08 × 10–3
= 0.2281 cm–1
10–3 × 2.768 = 1/R ×L/A
L/A = 228.08 × 10–3
= 0.2281 cm–1
Consider the following relations for emf of a electrochemical cell: [2010]
(i) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iii) emf of cell = (Reduction potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iv) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?- a)(ii) and (iv)
- b)(iii) and (i)
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following relations for emf of a electrochemical cell: [2010]
(i) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iii) emf of cell = (Reduction potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iv) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?
(i) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iii) emf of cell = (Reduction potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iv) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?
a)
(ii) and (iv)
b)
(iii) and (i)
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)

|
Prisha Singh answered |
Option (b) and (d) are correct
∴ Correct choice : (a)
∴ Correct choice : (a)
In the electrolysis of CuSO4, the reaction :Cu2+ + 2e¯ → Cu, takes place at :- a)Anode
- b)Cathode
- c)In solution
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the electrolysis of CuSO4, the reaction :
Cu2+ + 2e¯ → Cu, takes place at :
a)
Anode
b)
Cathode
c)
In solution
d)
None
|
|
Ananya Singh answered |
Cu²⁺ reduces to Cu. Because of reduction of Cu²⁺, reaction takes place at cathode.Read NCERT book for more clear
Based on the data given blow strongest oxidizing agent will be:
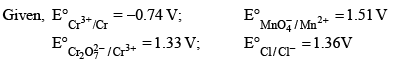
- a)Cl
- b)Cr3+
- c)Mn2+
- d)MnO4–
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the data given blow strongest oxidizing agent will be:
a)
Cl
b)
Cr3+
c)
Mn2+
d)
MnO4–
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
As MnO4- has highest reduction potential among them so it is strongest oxidizing agent.
The cell representation of the given reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)- a)Zn|zn2+||Cu2+|Cu
- b)Cu2+|Cu||Zn|zn2+
- c)Zn|zn2+||Cu|Cu2+
- d)Cu|Cu2+||zn2+|Zn
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell representation of the given reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)
Zn(s) + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu(s)
a)
Zn|zn2+||Cu2+|Cu
b)
Cu2+|Cu||Zn|zn2+
c)
Zn|zn2+||Cu|Cu2+
d)
Cu|Cu2+||zn2+|Zn
|
|
Atishay Jain answered |
Answer is A because Zn oxidized in Zn+2 and Cu+2 reduced in Cu.So Zn is anode and Cu is cathode.
One mole of electron passes through each of the solution of AgNO3, CuSO4 and AlCl3 when Ag, Cu and Al are deposited at cathode. The molar ratio of Ag, Cu and Al deposited are- a)1 : 1 : 1
- b)6 : 3 : 2
- c)6 : 3 : 1
- d)1 : 3 : 6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of electron passes through each of the solution of AgNO3, CuSO4 and AlCl3 when Ag, Cu and Al are deposited at cathode. The molar ratio of Ag, Cu and Al deposited are
a)
1 : 1 : 1
b)
6 : 3 : 2
c)
6 : 3 : 1
d)
1 : 3 : 6
|
|
Anisha Bose answered |
Molar ratio
All have the same equivalent
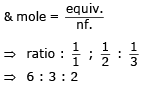
All have the same equivalent
Salts of A (atomic weight = 7), B (atomic weight = 27) and C (atomic weight = 48) were electrolysed under identical conditions using the same quantity of electricity. It was found that when 2.1 g of A was deposited, the weights of B and C deposited were 2.7 and 7.2 g. The valencies of A, B and C respectively are- a)3, 1 and 2
- b)1, 3 and 2
- c)3, 1 and 3
- d)2, 3 and 2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Salts of A (atomic weight = 7), B (atomic weight = 27) and C (atomic weight = 48) were electrolysed under identical conditions using the same quantity of electricity. It was found that when 2.1 g of A was deposited, the weights of B and C deposited were 2.7 and 7.2 g. The valencies of A, B and C respectively are
a)
3, 1 and 2
b)
1, 3 and 2
c)
3, 1 and 3
d)
2, 3 and 2
|
|
Roshni Desai answered |
If x = 1 ⇒ y = 3, z = 2
The density of Cu is 8.94 g cm–3. The quantity of electricity needed to plate an area 10 cm × 10cm to a thickness of 10-2 cm using CuSO4 solution would be- a)13586 C
- b)27172 C
- c)40758 C
- d)20348 C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The density of Cu is 8.94 g cm–3. The quantity of electricity needed to plate an area 10 cm × 10cm to a thickness of 10-2 cm using CuSO4 solution would be
a)
13586 C
b)
27172 C
c)
40758 C
d)
20348 C
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Volume : 10 × 10 × 10–2 = 1 cm3
mass of Cu = 8.94 g
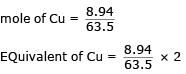
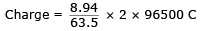
= 27172 C
mass of Cu = 8.94 g
= 27172 C
Chapter doubts & questions for Electrochemistry - 4 Months Preparation for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electrochemistry - 4 Months Preparation for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup