NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Why does the torque become unstable at 180 de...
Start Learning for Free
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field?
Most Upvoted Answer
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is pl...
**Introduction**
When a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, it experiences a torque due to the interaction between the electric field and the dipole moment. The torque tends to align the dipole moment with the electric field, resulting in stable equilibrium. However, at 180 degrees, the torque becomes unstable, causing the dipole to rotate.
**Explanation**
1. **Dipole in an Electric Field**: A dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges separated by a distance. When placed in a uniform electric field, the charges experience forces in opposite directions. The force on one charge is stronger than the other, leading to a net force acting on the dipole.
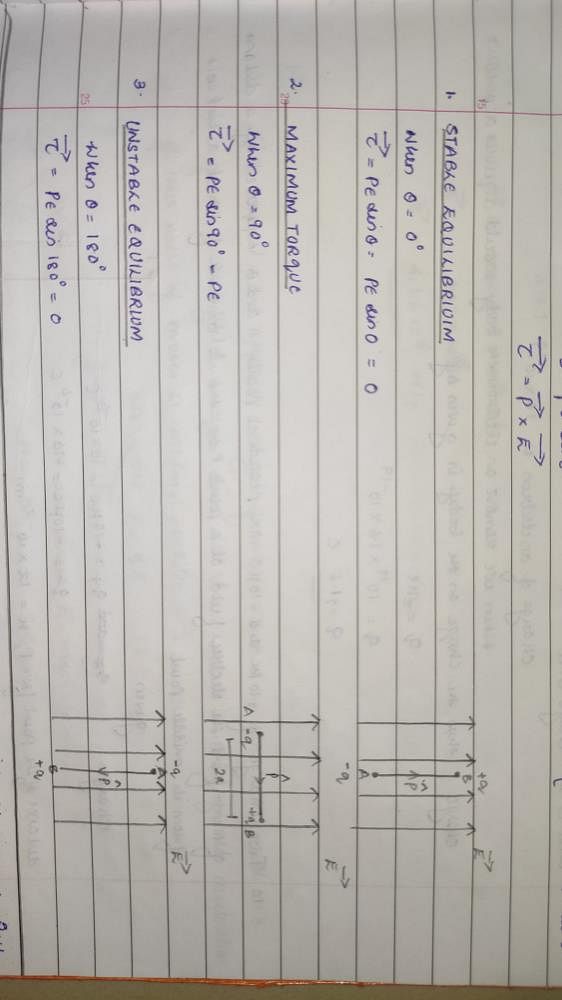
2. **Torque on a Dipole**: The torque on a dipole in an electric field is given by the equation: τ = pEsinθ, where τ is the torque, p is the dipole moment, E is the electric field strength, and θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
3. **Stable Equilibrium**: When the dipole is aligned with the electric field (θ = 0 degrees), the torque is zero. This corresponds to stable equilibrium, as there is no rotational tendency. The dipole remains in this position unless disturbed.
4. **Unstable Equilibrium**: At 180 degrees (θ = 180 degrees), the torque becomes maximum. This occurs because the sine of 180 degrees is also maximum (sin180 = 1). The torque is given by τ = pEsinθ = pEsin180 = pE. The dipole experiences a maximum rotational tendency to align itself with the electric field.
5. **Rotational Motion**: When the dipole is slightly displaced from the stable equilibrium position (θ ≠ 0), the torque acts to restore the dipole to its stable position. However, when the dipole is displaced from the unstable equilibrium position (θ ≠ 180 degrees), the torque acts to further rotate the dipole away from the unstable position.
6. **Energy Considerations**: At 180 degrees, the dipole has maximum potential energy (U = -pEcosθ). Any deviation from this position results in a decrease in potential energy, driving the dipole to rotate away from the unstable equilibrium.
7. **Dynamic Equilibrium**: The dipole oscillates back and forth around the stable equilibrium position due to the torque. It does not settle at 180 degrees due to the unstable nature of that equilibrium.
In conclusion, the torque becomes unstable at 180 degrees when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field due to the maximum rotational tendency and the associated increase in potential energy. This causes the dipole to rotate away from the unstable equilibrium position.
When a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, it experiences a torque due to the interaction between the electric field and the dipole moment. The torque tends to align the dipole moment with the electric field, resulting in stable equilibrium. However, at 180 degrees, the torque becomes unstable, causing the dipole to rotate.
**Explanation**
1. **Dipole in an Electric Field**: A dipole consists of two equal and opposite charges separated by a distance. When placed in a uniform electric field, the charges experience forces in opposite directions. The force on one charge is stronger than the other, leading to a net force acting on the dipole.
2. **Torque on a Dipole**: The torque on a dipole in an electric field is given by the equation: τ = pEsinθ, where τ is the torque, p is the dipole moment, E is the electric field strength, and θ is the angle between the dipole moment and the electric field.
3. **Stable Equilibrium**: When the dipole is aligned with the electric field (θ = 0 degrees), the torque is zero. This corresponds to stable equilibrium, as there is no rotational tendency. The dipole remains in this position unless disturbed.
4. **Unstable Equilibrium**: At 180 degrees (θ = 180 degrees), the torque becomes maximum. This occurs because the sine of 180 degrees is also maximum (sin180 = 1). The torque is given by τ = pEsinθ = pEsin180 = pE. The dipole experiences a maximum rotational tendency to align itself with the electric field.
5. **Rotational Motion**: When the dipole is slightly displaced from the stable equilibrium position (θ ≠ 0), the torque acts to restore the dipole to its stable position. However, when the dipole is displaced from the unstable equilibrium position (θ ≠ 180 degrees), the torque acts to further rotate the dipole away from the unstable position.
6. **Energy Considerations**: At 180 degrees, the dipole has maximum potential energy (U = -pEcosθ). Any deviation from this position results in a decrease in potential energy, driving the dipole to rotate away from the unstable equilibrium.
7. **Dynamic Equilibrium**: The dipole oscillates back and forth around the stable equilibrium position due to the torque. It does not settle at 180 degrees due to the unstable nature of that equilibrium.
In conclusion, the torque becomes unstable at 180 degrees when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field due to the maximum rotational tendency and the associated increase in potential energy. This causes the dipole to rotate away from the unstable equilibrium position.
Community Answer
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is pl...
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field?
Question Description
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field?.
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field?.
Solutions for Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field?, a detailed solution for Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? has been provided alongside types of Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Why does the torque become unstable at 180 degree, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























