GATE Exam > GATE Questions > In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resist...
Start Learning for Free
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.
- a)Increases
- b)Decreases
- c)Remains same
- d)Remains same but the Q-point shifts
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass ...
The re model of CE transistor.
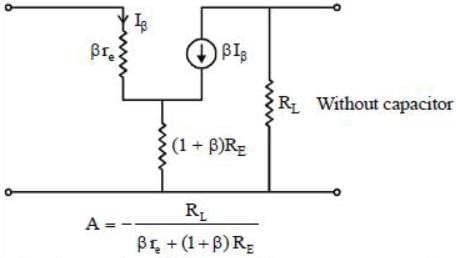
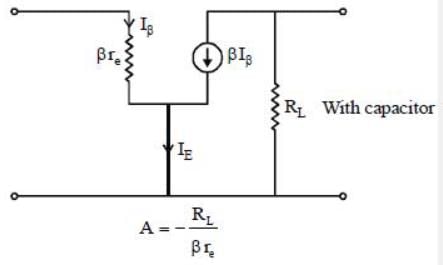
Therefore, gain will decrease if we remove capacitor.


Therefore, gain will decrease if we remove capacitor.
Most Upvoted Answer
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass ...
Explanation:
When a capacitor is used to bypass the emitter resistor in a common emitter (CE) amplifier, it provides a low impedance path for the AC signal to bypass the emitter resistor. This effectively reduces the negative feedback provided by the emitter resistor, resulting in a higher voltage gain for the amplifier.
Effect of Bypass Capacitor:
1. Reduction in emitter resistance: The bypass capacitor, when connected in parallel to the emitter resistor, reduces the effective resistance seen by the AC signal. This is because the reactance of the capacitor decreases with increasing frequency, allowing more AC current to flow through it. As a result, the effective emitter resistance decreases.
2. Increased bypass of AC signal: The bypass capacitor provides a low impedance path for the AC signal, allowing it to bypass the emitter resistor. This means that a significant portion of the AC signal does not have to flow through the emitter resistor, reducing the voltage drop across it.
3. Increased AC voltage gain: The voltage gain of a CE amplifier is given by the equation Av = -gm * (Re || RL), where gm is the transconductance of the transistor, Re is the emitter resistor, and RL is the load resistor. When the bypass capacitor is present, the effective emitter resistance (Re || RL) is reduced, leading to a higher voltage gain for the amplifier.
Effect of Removing Bypass Capacitor:
When the bypass capacitor is removed, the AC signal is forced to flow through the emitter resistor. This increases the effective emitter resistance (Re || RL), resulting in a lower voltage gain for the amplifier.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when the bypass capacitor is removed in a CE amplifier with emitter resistance, the voltage gain of the amplifier decreases. This is because the effective emitter resistance increases, reducing the voltage drop across the emitter resistor and consequently decreasing the voltage gain of the amplifier.
When a capacitor is used to bypass the emitter resistor in a common emitter (CE) amplifier, it provides a low impedance path for the AC signal to bypass the emitter resistor. This effectively reduces the negative feedback provided by the emitter resistor, resulting in a higher voltage gain for the amplifier.
Effect of Bypass Capacitor:
1. Reduction in emitter resistance: The bypass capacitor, when connected in parallel to the emitter resistor, reduces the effective resistance seen by the AC signal. This is because the reactance of the capacitor decreases with increasing frequency, allowing more AC current to flow through it. As a result, the effective emitter resistance decreases.
2. Increased bypass of AC signal: The bypass capacitor provides a low impedance path for the AC signal, allowing it to bypass the emitter resistor. This means that a significant portion of the AC signal does not have to flow through the emitter resistor, reducing the voltage drop across it.
3. Increased AC voltage gain: The voltage gain of a CE amplifier is given by the equation Av = -gm * (Re || RL), where gm is the transconductance of the transistor, Re is the emitter resistor, and RL is the load resistor. When the bypass capacitor is present, the effective emitter resistance (Re || RL) is reduced, leading to a higher voltage gain for the amplifier.
Effect of Removing Bypass Capacitor:
When the bypass capacitor is removed, the AC signal is forced to flow through the emitter resistor. This increases the effective emitter resistance (Re || RL), resulting in a lower voltage gain for the amplifier.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, when the bypass capacitor is removed in a CE amplifier with emitter resistance, the voltage gain of the amplifier decreases. This is because the effective emitter resistance increases, reducing the voltage drop across the emitter resistor and consequently decreasing the voltage gain of the amplifier.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a certain CE amplifier with emitter resistance and emitter by-pass capacitor, if the by-pass capacitor is removed the voltage gain of the amplifier.a)Increasesb)Decreasesc)Remains samed)Remains same but the Q-point shiftsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















