NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and...
Start Learning for Free
Nylon-66 is a polyamide of
- a)Vinylchloride and formaldehyde
- b)Adipic acid and methyl amine
- c)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine
- d)Formaldehyde and melamine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic aci...
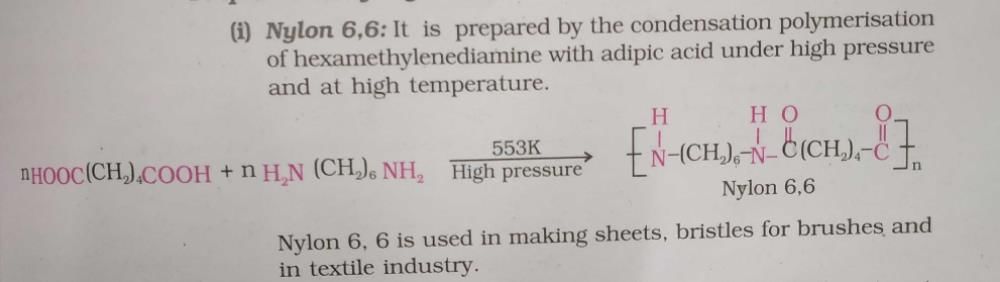
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic aci...
Nylon-66 is a polyamide that is formed from the condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine. It is a synthetic material that possesses high strength, durability, and heat resistance. Nylon-66 is widely used in various applications such as textile fibers, engineering plastics, and industrial products.
Below is a detailed explanation of the process and components involved in the formation of Nylon-66:
Polymerization Process:
1. Condensation Polymerization: Nylon-66 is formed through a condensation polymerization reaction. In this process, two monomers, adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine, react together to form a polymer chain.
Components of Nylon-66:
1. Adipic Acid: Adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid that contains two carboxyl groups (-COOH) at its ends. It is a white crystalline powder and is commonly used in the production of nylon polymers.
2. Hexamethylene Diamine: Hexamethylene diamine is an organic compound that contains two amine groups (-NH2) at its ends. It is a colorless liquid and is widely used as a building block in the production of nylon polymers.
Formation of Nylon-66:
1. Step 1: Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine are mixed together in a reaction vessel.
2. Step 2: The carboxyl groups of adipic acid react with the amine groups of hexamethylene diamine through a condensation reaction, resulting in the formation of amide bonds (-CO-NH-) between the monomers.
3. Step 3: The condensation reaction continues, and the polymer chain grows as more monomers join together, forming a long, repeating chain structure.
4. Step 4: The reaction mixture is heated and allowed to cool, leading to the solidification of the polymer.
5. Step 5: The solid polymer is then processed further to obtain the desired form, such as fibers or plastic pellets.
Properties and Applications of Nylon-66:
1. High Strength and Durability: Nylon-66 exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and toughness, making it suitable for applications that require strength and durability.
2. Heat Resistance: Nylon-66 has good heat resistance, allowing it to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation.
3. Chemical Resistance: Nylon-66 is resistant to many chemicals, oils, and solvents, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
4. Textile Fibers: Nylon-66 is commonly used in the textile industry to produce strong and resilient fibers, which are used in clothing, carpets, and other textile products.
5. Engineering Plastics: Nylon-66 is employed in the manufacturing of engineering plastics, which are used in automotive components, electrical connectors, and mechanical parts.
6. Industrial Products: Nylon-66 is utilized in the production of various industrial products, such as bearings, gears, and conveyor belts, due to its excellent mechanical properties.
In conclusion, Nylon-66 is a polyamide formed from the condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine. It possesses high strength, durability, and heat resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as textiles, plastics, and manufacturing.
Below is a detailed explanation of the process and components involved in the formation of Nylon-66:
Polymerization Process:
1. Condensation Polymerization: Nylon-66 is formed through a condensation polymerization reaction. In this process, two monomers, adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine, react together to form a polymer chain.
Components of Nylon-66:
1. Adipic Acid: Adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid that contains two carboxyl groups (-COOH) at its ends. It is a white crystalline powder and is commonly used in the production of nylon polymers.
2. Hexamethylene Diamine: Hexamethylene diamine is an organic compound that contains two amine groups (-NH2) at its ends. It is a colorless liquid and is widely used as a building block in the production of nylon polymers.
Formation of Nylon-66:
1. Step 1: Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine are mixed together in a reaction vessel.
2. Step 2: The carboxyl groups of adipic acid react with the amine groups of hexamethylene diamine through a condensation reaction, resulting in the formation of amide bonds (-CO-NH-) between the monomers.
3. Step 3: The condensation reaction continues, and the polymer chain grows as more monomers join together, forming a long, repeating chain structure.
4. Step 4: The reaction mixture is heated and allowed to cool, leading to the solidification of the polymer.
5. Step 5: The solid polymer is then processed further to obtain the desired form, such as fibers or plastic pellets.
Properties and Applications of Nylon-66:
1. High Strength and Durability: Nylon-66 exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and toughness, making it suitable for applications that require strength and durability.
2. Heat Resistance: Nylon-66 has good heat resistance, allowing it to withstand high temperatures without significant degradation.
3. Chemical Resistance: Nylon-66 is resistant to many chemicals, oils, and solvents, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
4. Textile Fibers: Nylon-66 is commonly used in the textile industry to produce strong and resilient fibers, which are used in clothing, carpets, and other textile products.
5. Engineering Plastics: Nylon-66 is employed in the manufacturing of engineering plastics, which are used in automotive components, electrical connectors, and mechanical parts.
6. Industrial Products: Nylon-66 is utilized in the production of various industrial products, such as bearings, gears, and conveyor belts, due to its excellent mechanical properties.
In conclusion, Nylon-66 is a polyamide formed from the condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine. It possesses high strength, durability, and heat resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in industries such as textiles, plastics, and manufacturing.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Nylon-66 is a polyamide ofa)Vinylchloride and formaldehydeb)Adipic acid and methyl aminec)Adipic acid and hexamethylene diamined)Formaldehyde and melamine Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























