GATE Exam > GATE Questions > A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4...
Start Learning for Free
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.
- a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 V
- b)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 V
- c)Open, 4 A, 0 V
- d)Short, ∞ A, 10 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long...
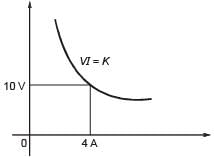
Maximum power transistor of VI product is maximum. If draw the the curve, it intersect (10, 4) that will give maximum power.
The terminal voltage is 10 V (Load voltage) and current is 4 A (Load current).
Load resistance is 10/4 = 2.5Ω.
Most Upvoted Answer
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long...
To find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, we can use the formula for power in a circuit:
P = I^2 * R
To maximize power, we need to maximize the product of current and resistance. Since the benchtop power supply acts as a current source up to 10 V, we can assume that the current is constant at 4 A for resistances below 10 V.
For resistances above 10 V, the power supply acts as a voltage source with a fixed voltage of 10 V. In this case, the current will be determined by the load resistance according to Ohm's Law:
I = V/R
We want to find the load resistance at which the power is maximized. Setting up the equation:
P = I^2 * R
When acting as a current source:
P = (4 A)^2 * R = 16R
When acting as a voltage source:
P = (10 V)^2 / R = 100/R
To find the maximum power, we can set the two equations equal to each other and solve for R:
16R = 100/R
16R^2 = 100
R^2 = 100/16
R^2 = 6.25
R = √6.25
R ≈ 2.5 Ω
Therefore, the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred is approximately 2.5 Ω.
To find the corresponding load voltage and current, we can use the equations:
For resistances below 10 V (current source):
V = I * R = 4 A * 2.5 Ω = 10 V
I = 4 A
For resistances above 10 V (voltage source):
V = 10 V
I = V/R = 10 V / 2.5 Ω = 4 A
Therefore, the load voltage and current at the load resistance of 2.5 Ω are 10 V and 4 A, respectively.
P = I^2 * R
To maximize power, we need to maximize the product of current and resistance. Since the benchtop power supply acts as a current source up to 10 V, we can assume that the current is constant at 4 A for resistances below 10 V.
For resistances above 10 V, the power supply acts as a voltage source with a fixed voltage of 10 V. In this case, the current will be determined by the load resistance according to Ohm's Law:
I = V/R
We want to find the load resistance at which the power is maximized. Setting up the equation:
P = I^2 * R
When acting as a current source:
P = (4 A)^2 * R = 16R
When acting as a voltage source:
P = (10 V)^2 / R = 100/R
To find the maximum power, we can set the two equations equal to each other and solve for R:
16R = 100/R
16R^2 = 100
R^2 = 100/16
R^2 = 6.25
R = √6.25
R ≈ 2.5 Ω
Therefore, the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred is approximately 2.5 Ω.
To find the corresponding load voltage and current, we can use the equations:
For resistances below 10 V (current source):
V = I * R = 4 A * 2.5 Ω = 10 V
I = 4 A
For resistances above 10 V (voltage source):
V = 10 V
I = V/R = 10 V / 2.5 Ω = 4 A
Therefore, the load voltage and current at the load resistance of 2.5 Ω are 10 V and 4 A, respectively.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A benchtop dc power supply acts as an ideal 4 A current source as long as its terminal voltage is below 10 V. Beyond this point, it begins to behave as an ideal 10 V voltage source for all load currents going down to 0 A. When connected to an ideal rheostat, find the load resistance value at which maximum power is transferred, and the corresponding load voltage and current.a)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 10 Vb)2.5 Ω, 4 A, 5 Vc)Open, 4 A, 0 Vd)Short, ∞ A, 10 VCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















