Verbal Exam > Verbal Questions > Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one ...
Start Learning for Free
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue?
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant t...
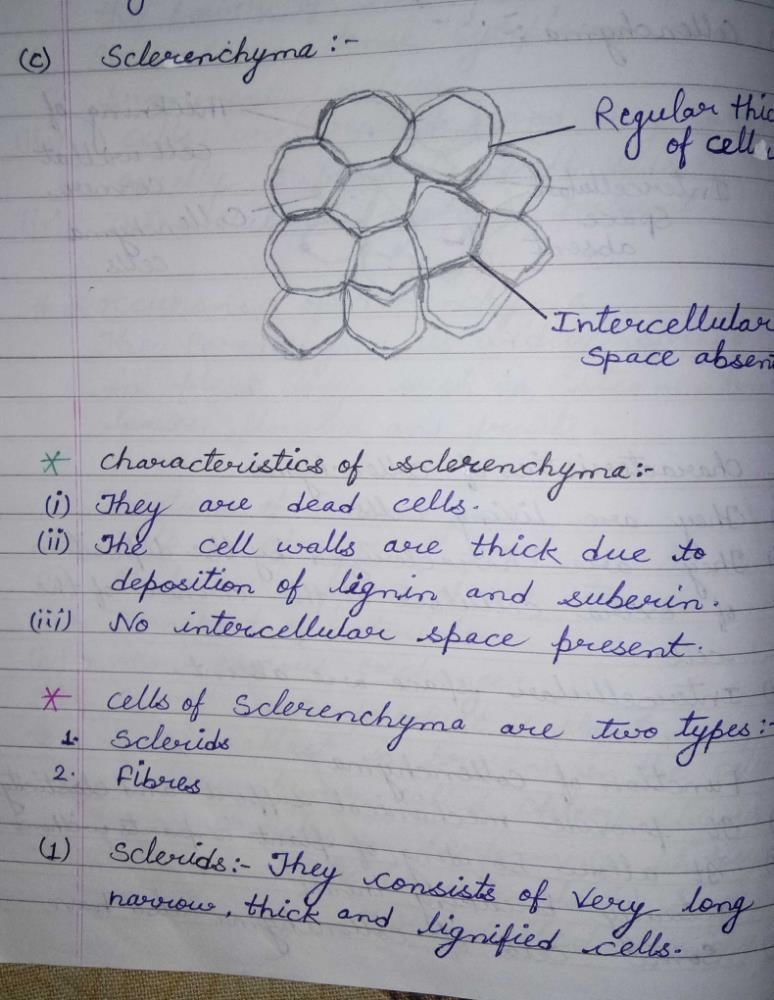
Community Answer
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant t...
Types of Sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma is a type of supportive plant tissue characterized by thick, lignified cell walls. It is primarily involved in providing structural strength and rigidity to various parts of the plant. There are two main types of sclerenchyma: fibers and sclereids.
1. Sclerenchyma Fibers
- Description: Fibers are long, narrow cells that occur in bundles. They have a high tensile strength due to their thick cell walls, making them essential for supporting the plant.
- Function: The primary function of sclerenchyma fibers is to provide mechanical support and flexibility, allowing the plant to withstand various stresses such as wind and gravitational forces.
2. Sclereids
- Description: Sclereids are shorter and irregularly shaped compared to fibers. They can be found throughout the plant, especially in seed coats, fruit shells, and some types of wood.
- Function: Sclereids serve to strengthen and protect the plant tissues, contributing to the hardness of certain parts, such as nutshells and pear fruit, which deters herbivory and enhances seed dispersal.
Overall Importance of Sclerenchyma
- Sclerenchyma plays a crucial role in plant health, ensuring structural support and protection. The presence of this tissue type is vital for the plant's ability to thrive in its environment, enabling it to grow tall and withstand various mechanical stresses.
Understanding these types and their functions is essential in the study of plant physiology and tissue organization.
Sclerenchyma is a type of supportive plant tissue characterized by thick, lignified cell walls. It is primarily involved in providing structural strength and rigidity to various parts of the plant. There are two main types of sclerenchyma: fibers and sclereids.
1. Sclerenchyma Fibers
- Description: Fibers are long, narrow cells that occur in bundles. They have a high tensile strength due to their thick cell walls, making them essential for supporting the plant.
- Function: The primary function of sclerenchyma fibers is to provide mechanical support and flexibility, allowing the plant to withstand various stresses such as wind and gravitational forces.
2. Sclereids
- Description: Sclereids are shorter and irregularly shaped compared to fibers. They can be found throughout the plant, especially in seed coats, fruit shells, and some types of wood.
- Function: Sclereids serve to strengthen and protect the plant tissues, contributing to the hardness of certain parts, such as nutshells and pear fruit, which deters herbivory and enhances seed dispersal.
Overall Importance of Sclerenchyma
- Sclerenchyma plays a crucial role in plant health, ensuring structural support and protection. The presence of this tissue type is vital for the plant's ability to thrive in its environment, enabling it to grow tall and withstand various mechanical stresses.
Understanding these types and their functions is essential in the study of plant physiology and tissue organization.

|
Explore Courses for Verbal exam
|

|
Similar Verbal Doubts
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue?
Question Description
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? for Verbal 2025 is part of Verbal preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Verbal exam syllabus. Information about Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? covers all topics & solutions for Verbal 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue?.
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? for Verbal 2025 is part of Verbal preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Verbal exam syllabus. Information about Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? covers all topics & solutions for Verbal 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue?.
Solutions for Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Verbal.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Verbal Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue?, a detailed solution for Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? has been provided alongside types of Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain types of scllerenchyma and state one function of each. Plant tissue : chapter 6 Tissue? tests, examples and also practice Verbal tests.

|
Explore Courses for Verbal exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















