NEET Exam > NEET Questions > what is true friut Related: Edible parts of ...
Start Learning for Free
what is true friut
? Related: Edible parts of fruits
Most Upvoted Answer
what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits?
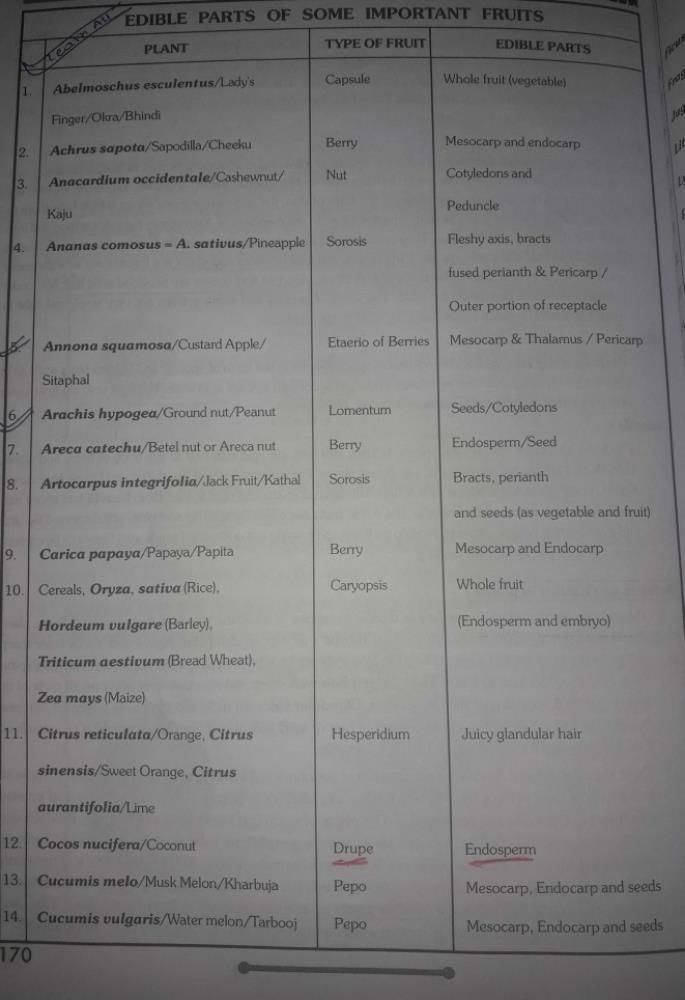
Community Answer
what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits?
True Fruits Explained
True fruits develop from the ovary of a flower after fertilization. They are classified based on their structure and the number of ovaries involved in their formation.
Types of True Fruits
- Simple Fruits: Formed from a single ovary. Examples include:
- Drupes (e.g., cherries, peaches)
- Berries (e.g., tomatoes, grapes)
- Pomes (e.g., apples, pears)
- Aggregate Fruits: Develop from multiple ovaries of a single flower. Examples include:
- Raspberries
- Blackberries
- Strawberries
- Multiple Fruits: Form from the ovaries of multiple flowers that grow closely together. Examples include:
- Pineapples
- Figs
- Mulberries
Edible Parts of Fruits
The edible parts of fruits vary widely but generally include:
- Flesh: The juicy part of the fruit that is often sweet or sour, providing essential nutrients.
- Seeds: Some seeds are edible (e.g., sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds), while others may be toxic (e.g., apple seeds).
- Skin: The outer layer, which can be rich in fiber and antioxidants (e.g., apple skin, grape skin).
- Core: Present in certain fruits like apples and pears, which may or may not be consumed.
- Pith: The white, spongy tissue found in citrus fruits, providing fiber and flavor.
Understanding the structure and edible parts of true fruits enhances appreciation for their nutritional values and culinary uses.
True fruits develop from the ovary of a flower after fertilization. They are classified based on their structure and the number of ovaries involved in their formation.
Types of True Fruits
- Simple Fruits: Formed from a single ovary. Examples include:
- Drupes (e.g., cherries, peaches)
- Berries (e.g., tomatoes, grapes)
- Pomes (e.g., apples, pears)
- Aggregate Fruits: Develop from multiple ovaries of a single flower. Examples include:
- Raspberries
- Blackberries
- Strawberries
- Multiple Fruits: Form from the ovaries of multiple flowers that grow closely together. Examples include:
- Pineapples
- Figs
- Mulberries
Edible Parts of Fruits
The edible parts of fruits vary widely but generally include:
- Flesh: The juicy part of the fruit that is often sweet or sour, providing essential nutrients.
- Seeds: Some seeds are edible (e.g., sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds), while others may be toxic (e.g., apple seeds).
- Skin: The outer layer, which can be rich in fiber and antioxidants (e.g., apple skin, grape skin).
- Core: Present in certain fruits like apples and pears, which may or may not be consumed.
- Pith: The white, spongy tissue found in citrus fruits, providing fiber and flavor.
Understanding the structure and edible parts of true fruits enhances appreciation for their nutritional values and culinary uses.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits?.
what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits?.
Solutions for what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits?, a detailed solution for what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? has been provided alongside types of what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is true friut Related: Edible parts of fruits? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















