NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all a...
Start Learning for Free
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please?
Most Upvoted Answer
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't...
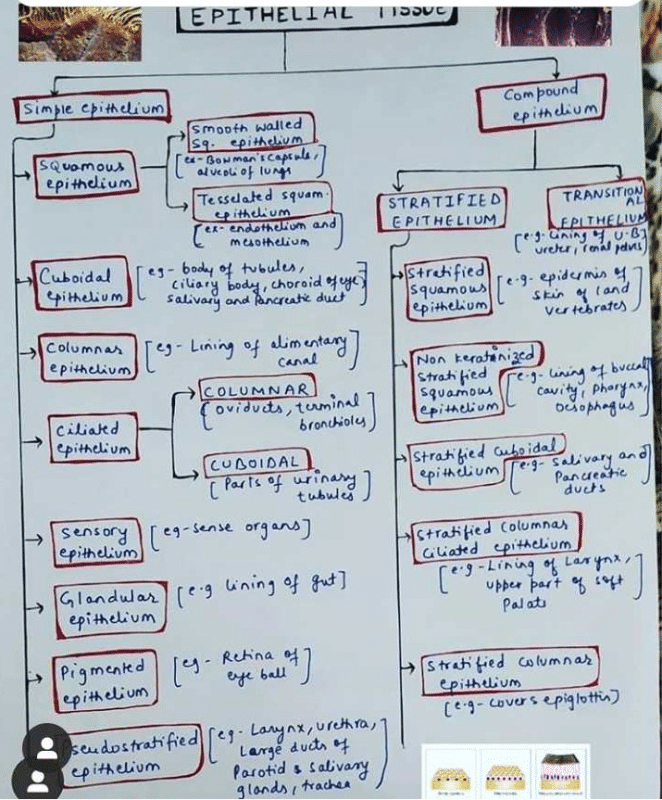
Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, that covers the surfaces of the body, lines the internal cavities, and forms glands. It is composed of closely packed cells that are arranged in sheets or layers. This tissue has several functions, such as protection, absorption, excretion, secretion, and sensation. Here is a flow chart of epithelial tissue:
Types of Epithelial Tissue:
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: thin, flat cells that allow for diffusion and filtration.
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: cube-shaped cells that secrete and absorb substances.
- Simple Columnar Epithelium: tall, narrow cells that secrete mucus and absorb nutrients.
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: appears layered, but all cells touch the basement membrane; secretes and moves mucus.
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium: layers of flat cells that protect against abrasion and dehydration.
- Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: layers of cube-shaped cells that protect and secrete.
- Stratified Columnar Epithelium: layers of tall, narrow cells that protect and secrete.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue:
- Protection: provides a barrier against physical, chemical, and biological damage.
- Absorption: absorbs nutrients, water, and ions from the environment.
- Excretion: eliminates waste products from the body.
- Secretion: produces and releases substances such as hormones, enzymes, and mucus.
- Sensation: contains sensory receptors that detect touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue:
- Avascular: lacks blood vessels and receives nutrients by diffusion from underlying tissues.
- Basement Membrane: a thin layer of extracellular matrix that anchors the epithelium to the underlying connective tissue.
- Apical Surface: faces the external environment or internal cavity and may have specialized structures such as cilia or microvilli.
- Lateral Surface: faces neighboring cells and may have intercellular junctions.
- Regeneration: has a high rate of cell division and can regenerate quickly after injury.
In conclusion, epithelial tissue is a vital component of the body that performs a variety of functions. Understanding its types, functions, and characteristics can help in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that affect this tissue.
Types of Epithelial Tissue:
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: thin, flat cells that allow for diffusion and filtration.
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: cube-shaped cells that secrete and absorb substances.
- Simple Columnar Epithelium: tall, narrow cells that secrete mucus and absorb nutrients.
- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: appears layered, but all cells touch the basement membrane; secretes and moves mucus.
- Stratified Squamous Epithelium: layers of flat cells that protect against abrasion and dehydration.
- Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: layers of cube-shaped cells that protect and secrete.
- Stratified Columnar Epithelium: layers of tall, narrow cells that protect and secrete.
Functions of Epithelial Tissue:
- Protection: provides a barrier against physical, chemical, and biological damage.
- Absorption: absorbs nutrients, water, and ions from the environment.
- Excretion: eliminates waste products from the body.
- Secretion: produces and releases substances such as hormones, enzymes, and mucus.
- Sensation: contains sensory receptors that detect touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue:
- Avascular: lacks blood vessels and receives nutrients by diffusion from underlying tissues.
- Basement Membrane: a thin layer of extracellular matrix that anchors the epithelium to the underlying connective tissue.
- Apical Surface: faces the external environment or internal cavity and may have specialized structures such as cilia or microvilli.
- Lateral Surface: faces neighboring cells and may have intercellular junctions.
- Regeneration: has a high rate of cell division and can regenerate quickly after injury.
In conclusion, epithelial tissue is a vital component of the body that performs a variety of functions. Understanding its types, functions, and characteristics can help in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that affect this tissue.
Community Answer
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't...
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please?
Question Description
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Solutions for Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please?, a detailed solution for Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? has been provided alongside types of Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Flow chart of epithelial tissue // it's all about to help you so don't answer please? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























