GATE Exam > GATE Questions > A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipe...
Start Learning for Free
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)
Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to cali...
Given: Di = inner diameter = 103 mm.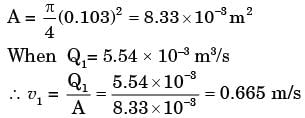
View all questions of this test
Q = 6.311 x 10-4 √h, h = mm of Hg ...(i)
(Volt)2 = a + b (Velocity)1/2...(ii)
E1 = 0.284 V
when h1 = 77 mm Hg
E2 = 0.323 V
when h2 = 154 mm Hg
From equation (i),
when h1 = 77 mm Hg,
Q1 = 6.311 x 10-4 √77 = 5.54 x 10-3 m3/s
when h2 = 154 mm Hg,
Q2 = 6.311 x 10-4 x √154 = 7.83 x 10-3 m3/s
From continuity equation, Q = A.v,
where A = Area v = velocity
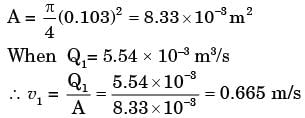
Most Upvoted Answer
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to cali...
Calibrating the Orifice Meter
The orifice meter is calibrated using the pipeline with a known inner diameter (ID) of 103 mm. The readings of the orifice meter are recorded in mm of Hg, and the volume flow rate (Q) of the fluid can be determined using the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10^(-4)√h, where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m^3/s.
Correlating CTA Readings
The readings of the constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA) are correlated with the orifice meter readings using the equation: (volt)^2 = a * b * (velocity)^(1/2), where volt is the voltage reading, velocity is the flow velocity, and a and b are constants to be determined.
Determining the Constants (a) and (b)
To determine the constants (a) and (b), we can use the given voltage readings and their corresponding orifice meter readings.
Given:
Voltage readings (volt): 0.284 V and 0.323 V
Orifice meter readings (h): 77 mm Hg and 154 mm Hg
Using the orifice meter calibration equation, we can determine the flow rates (Q) corresponding to the orifice meter readings:
Q1 = 6.311 x 10^(-4)√77
Q2 = 6.311 x 10^(-4)√154
Now, let's calculate the velocities (v) corresponding to the flow rates using the known inner diameter (ID) of the pipeline:
v1 = Q1 / (π * (ID/2)^2)
v2 = Q2 / (π * (ID/2)^2)
Using the given voltage readings and the equation (volt)^2 = a * b * (velocity)^(1/2), we can set up two equations as follows:
0.284^2 = a * b * (v1)^(1/2)
0.323^2 = a * b * (v2)^(1/2)
Substituting the values of v1 and v2, we get:
0.284^2 = a * b * (Q1 / (π * (ID/2)^2))^(1/4)
0.323^2 = a * b * (Q2 / (π * (ID/2)^2))^(1/4)
Simplifying the equations, we have:
a * b = (0.284^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q1^(1/2)
a * b = (0.323^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q2^(1/2)
Since a and b are constants, we can equate the two equations:
(0.284^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q1^(1/2) = (0.323^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q2^(1/2)
Simplifying further, we get:
a * b = (0.323^2 * Q1^(1/2)) / (0.284^2 * Q2^(1/2))
Now,
The orifice meter is calibrated using the pipeline with a known inner diameter (ID) of 103 mm. The readings of the orifice meter are recorded in mm of Hg, and the volume flow rate (Q) of the fluid can be determined using the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10^(-4)√h, where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m^3/s.
Correlating CTA Readings
The readings of the constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA) are correlated with the orifice meter readings using the equation: (volt)^2 = a * b * (velocity)^(1/2), where volt is the voltage reading, velocity is the flow velocity, and a and b are constants to be determined.
Determining the Constants (a) and (b)
To determine the constants (a) and (b), we can use the given voltage readings and their corresponding orifice meter readings.
Given:
Voltage readings (volt): 0.284 V and 0.323 V
Orifice meter readings (h): 77 mm Hg and 154 mm Hg
Using the orifice meter calibration equation, we can determine the flow rates (Q) corresponding to the orifice meter readings:
Q1 = 6.311 x 10^(-4)√77
Q2 = 6.311 x 10^(-4)√154
Now, let's calculate the velocities (v) corresponding to the flow rates using the known inner diameter (ID) of the pipeline:
v1 = Q1 / (π * (ID/2)^2)
v2 = Q2 / (π * (ID/2)^2)
Using the given voltage readings and the equation (volt)^2 = a * b * (velocity)^(1/2), we can set up two equations as follows:
0.284^2 = a * b * (v1)^(1/2)
0.323^2 = a * b * (v2)^(1/2)
Substituting the values of v1 and v2, we get:
0.284^2 = a * b * (Q1 / (π * (ID/2)^2))^(1/4)
0.323^2 = a * b * (Q2 / (π * (ID/2)^2))^(1/4)
Simplifying the equations, we have:
a * b = (0.284^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q1^(1/2)
a * b = (0.323^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q2^(1/2)
Since a and b are constants, we can equate the two equations:
(0.284^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q1^(1/2) = (0.323^2 * π * (ID/2)^2) / Q2^(1/2)
Simplifying further, we get:
a * b = (0.323^2 * Q1^(1/2)) / (0.284^2 * Q2^(1/2))
Now,

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer?.
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A calibrated orifice meter is used in a pipeline of 103 mm ID to calibrate the probe of a constant temperature hotwire anemometer (CTA). The orifice meter readings are recorded in mm of Hg and the CTA readings in volts. It is independently found that the average velocity in the pipeline is exactly equal to the velocity at its axis, the volume flow rate of the fluid (Q) can be measured from the orifice meter calibration equation: Q = 6.311 x 10-4√h where h is in mm of Hg and Q is in m3/s. The readings of the CTA are correlated in the form : (volt)2 = a + b (velocity)1/2. Determine the constants (a) and (b) in this equation if the voltage readings are 0.284 and 0.323 V respectively when the corresponding orifice meter readings are 77 and 154 mm Hg. (5) (2002)Correct answer is '0.09, 0.252'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















