SSC Exam > SSC Questions > Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases ...
Start Learning for Free
Lacing of compound steel columns-
- a)increases the load-carrying capacity
- b)assures unified behaviour
- c)decreases overall buckling of the column
- d)decreases the chances of local buckling
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacit...
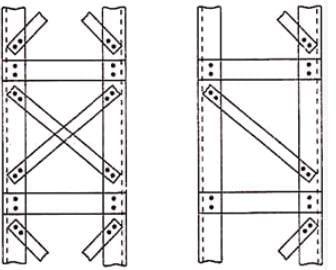
Double laced and Single Laced System Combined with Cross members.
Most Upvoted Answer
Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacit...
Lacing of compound steel columns is a technique used to enhance the stability and load-carrying capacity of columns in steel structures. It involves the use of diagonal braces or plates that are connected to the flanges and webs of the columns. The main purpose of lacing is to provide additional support to the column against buckling and bending under external loads.
The correct answer is option B, which states that lacing assures unified behavior. This means that the use of lacing ensures that the column behaves as a single unit rather than individual components. The following are the reasons why lacing assures unified behavior:
1. Reduces the Risk of Local Buckling: Lacing provides additional support to the column, which reduces the risk of local buckling. Local buckling occurs when a section of the column is subjected to high compressive stress, causing it to deform or buckle. Lacing helps to distribute the stress evenly across the column, thereby preventing local buckling.
2. Increases the Load-carrying Capacity: Lacing increases the load-carrying capacity of the column by providing additional support against external loads. The diagonal braces or plates used in lacing are designed to resist tensile and compressive stresses, which enhances the strength and stiffness of the column.
3. Enhances the Stability of the Column: Lacing enhances the stability of the column by reducing the overall buckling of the column. Buckling occurs when a column becomes unstable and fails under compressive stress. Lacing helps to distribute the stress evenly across the column, thereby enhancing its stability.
In conclusion, lacing is an effective technique used to enhance the stability and load-carrying capacity of compound steel columns. It assures unified behavior by reducing the risk of local buckling, increasing the load-carrying capacity, and enhancing the stability of the column.
The correct answer is option B, which states that lacing assures unified behavior. This means that the use of lacing ensures that the column behaves as a single unit rather than individual components. The following are the reasons why lacing assures unified behavior:
1. Reduces the Risk of Local Buckling: Lacing provides additional support to the column, which reduces the risk of local buckling. Local buckling occurs when a section of the column is subjected to high compressive stress, causing it to deform or buckle. Lacing helps to distribute the stress evenly across the column, thereby preventing local buckling.
2. Increases the Load-carrying Capacity: Lacing increases the load-carrying capacity of the column by providing additional support against external loads. The diagonal braces or plates used in lacing are designed to resist tensile and compressive stresses, which enhances the strength and stiffness of the column.
3. Enhances the Stability of the Column: Lacing enhances the stability of the column by reducing the overall buckling of the column. Buckling occurs when a column becomes unstable and fails under compressive stress. Lacing helps to distribute the stress evenly across the column, thereby enhancing its stability.
In conclusion, lacing is an effective technique used to enhance the stability and load-carrying capacity of compound steel columns. It assures unified behavior by reducing the risk of local buckling, increasing the load-carrying capacity, and enhancing the stability of the column.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Lacing of compound steel columns-a)increases the load-carrying capacityb)assures unified behaviourc)decreases overall buckling of the columnd)decreases the chances of local bucklingCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















