SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The available moisture of the soil is equal ...
Start Learning for Free
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -
- a)field capacity
- b)saturation capacity
- c)moisture content at wilting point
- d)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb...
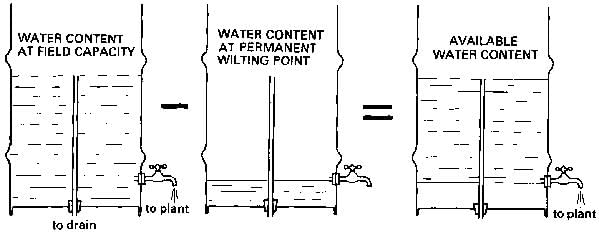
The amount of water actually available to the plant is the amount of water stored in the soil at field capacity minus the water that will remain in the soil at permanent wilting point.
Most Upvoted Answer
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb...
Soil Moisture and its Available Capacity
Soil moisture is the amount of water present in the soil. It is important for plant growth and is affected by various factors such as climate, soil type, vegetation, and land use.
The available moisture of the soil is defined as the water that is available for plant growth, and it is equal to the difference between the field capacity and the permanent wilting point within the root zone of plants.
Field Capacity
Field capacity is the maximum amount of water that soil can hold against the force of gravity after it has been saturated and excess water has drained away. At field capacity, the soil is moist but not saturated, and plant roots can easily extract water from the soil.
Permanent Wilting Point
The permanent wilting point is the point at which plants can no longer extract water from the soil, and they wilt and eventually die. At this point, the soil is completely dry, and water is held tightly by soil particles and unavailable for plant uptake.
Available Moisture
The available moisture is the difference between the field capacity and the permanent wilting point within the root zone of plants. It represents the amount of water that plants can use for growth and development.
Importance of Available Moisture
The available moisture is an important factor in determining plant growth and yield. If the soil moisture level is too low, plants will wilt and eventually die. If the soil moisture level is too high, plants may suffer from root rot and other diseases.
Therefore, it is important to maintain soil moisture at an optimal level for plant growth by using irrigation, mulching, and other management practices.
Soil moisture is the amount of water present in the soil. It is important for plant growth and is affected by various factors such as climate, soil type, vegetation, and land use.
The available moisture of the soil is defined as the water that is available for plant growth, and it is equal to the difference between the field capacity and the permanent wilting point within the root zone of plants.
Field Capacity
Field capacity is the maximum amount of water that soil can hold against the force of gravity after it has been saturated and excess water has drained away. At field capacity, the soil is moist but not saturated, and plant roots can easily extract water from the soil.
Permanent Wilting Point
The permanent wilting point is the point at which plants can no longer extract water from the soil, and they wilt and eventually die. At this point, the soil is completely dry, and water is held tightly by soil particles and unavailable for plant uptake.
Available Moisture
The available moisture is the difference between the field capacity and the permanent wilting point within the root zone of plants. It represents the amount of water that plants can use for growth and development.
Importance of Available Moisture
The available moisture is an important factor in determining plant growth and yield. If the soil moisture level is too low, plants will wilt and eventually die. If the soil moisture level is too high, plants may suffer from root rot and other diseases.
Therefore, it is important to maintain soil moisture at an optimal level for plant growth by using irrigation, mulching, and other management practices.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb...
Moisture equivalent is defined as the percentage of water which a soil can retain in opposition to a centrifugal force 1000 times that of gravity. It is measured by saturating sample of soil 1 cm thick, and subjecting it to a centrifugal force of 1000 times gravity for 30 min.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The available moisture of the soil is equal to its -a)field capacityb)saturation capacityc)moisture content at wilting pointd)difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point within the root of plantsCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















