SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The degree of reaction for an impulse steam ...
Start Learning for Free
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:
- a)0.5
- b)1
- c)0
- d)-2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-...
Degree of reaction 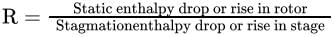
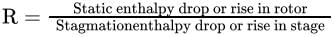

In the case of an impulse turbine, there is no change in the enthalpy in rotor, so degree of reaction is zero.
R=0
And for Parson's turbine or 50% reaction turbine R=0.5 and for
Hero's turbine
Most Upvoted Answer
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-...
Understanding the Degree of Reaction in Impulse Steam Turbines
The degree of reaction (R) is a crucial parameter in turbine design, particularly in distinguishing between impulse and reaction turbines.
Definition of Degree of Reaction
- The degree of reaction is defined as the ratio of the static enthalpy drop across the rotor to the total enthalpy drop across both the rotor and the stator.
Impulse vs. Reaction Turbines
- In an impulse turbine, the steam expands entirely in the nozzle before reaching the rotor.
- The rotor only converts the kinetic energy of the steam into mechanical energy, with no pressure drop occurring within it.
Degree of Reaction for Impulse Turbines
- For impulse turbines, the steam does not experience any pressure drop across the rotor.
- Theoretical calculations show that the enthalpy drop across the rotor (h2 – h3) is zero.
Mathematical Expression
- The formula for the degree of reaction (R) can be expressed as:
R = (h2 - h3) / (h1 - h4)
Where:
- h1 is the enthalpy at the inlet (stator)
- h2 is the enthalpy at the outlet of the rotor
- h3 is the enthalpy at the inlet of the rotor
- h4 is the enthalpy at the outlet (stator)
- Since h2 = h3 in an impulse turbine, the numerator becomes zero, leading to:
R = 0 / (h1 - h4) = 0
Conclusion
- Thus, the degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is 0, indicating that the entire enthalpy drop occurs in the nozzles, not in the rotor.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
The degree of reaction (R) is a crucial parameter in turbine design, particularly in distinguishing between impulse and reaction turbines.
Definition of Degree of Reaction
- The degree of reaction is defined as the ratio of the static enthalpy drop across the rotor to the total enthalpy drop across both the rotor and the stator.
Impulse vs. Reaction Turbines
- In an impulse turbine, the steam expands entirely in the nozzle before reaching the rotor.
- The rotor only converts the kinetic energy of the steam into mechanical energy, with no pressure drop occurring within it.
Degree of Reaction for Impulse Turbines
- For impulse turbines, the steam does not experience any pressure drop across the rotor.
- Theoretical calculations show that the enthalpy drop across the rotor (h2 – h3) is zero.
Mathematical Expression
- The formula for the degree of reaction (R) can be expressed as:
R = (h2 - h3) / (h1 - h4)
Where:
- h1 is the enthalpy at the inlet (stator)
- h2 is the enthalpy at the outlet of the rotor
- h3 is the enthalpy at the inlet of the rotor
- h4 is the enthalpy at the outlet (stator)
- Since h2 = h3 in an impulse turbine, the numerator becomes zero, leading to:
R = 0 / (h1 - h4) = 0
Conclusion
- Thus, the degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is 0, indicating that the entire enthalpy drop occurs in the nozzles, not in the rotor.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The degree of reaction for an impulse steam turbine is:a)0.5b)1c)0d)-2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















