SSC Exam > SSC Questions > Velocity distribution profile for laminar fl...
Start Learning for Free
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:
- a)Parabolic
- b)Linear
- c)Constant
- d)Logarithmic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plate...
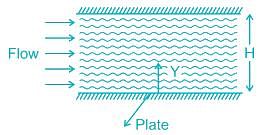
Velocity distribution profile equation is written as:

It is a parabolic equation, So the velocity distribution is parabolic.
Most Upvoted Answer
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plate...
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is parabolic.
Explanation:
Laminar flow refers to the smooth and orderly movement of fluid particles in a straight line, without any turbulence. In the case of laminar flow between parallel plates, the fluid moves in layers with different velocities. The velocity distribution profile describes how the velocity of the fluid varies across the flow cross-section.
The velocity distribution in laminar flow between parallel plates can be derived using the Hagen-Poiseuille equation. This equation relates the velocity of the fluid to the pressure drop across the flow and the dimensions of the flow channel. The Hagen-Poiseuille equation assumes that the flow is fully developed, meaning that the velocity does not change in the direction of flow.
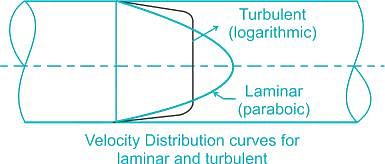
The velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates can be described by a parabolic curve. This means that the velocity is highest at the center of the channel and gradually decreases towards the walls. The maximum velocity occurs at the centerline of the channel, where the fluid particles experience the least resistance to flow. As the fluid particles move closer to the walls, they experience more friction, causing the velocity to decrease.
The parabolic velocity profile can be mathematically represented by the Poiseuille's equation, which states that the velocity at a certain distance from the center of the channel is proportional to the square of that distance. This relationship between velocity and distance from the centerline results in a parabolic velocity distribution profile.
The parabolic velocity profile is a characteristic feature of laminar flow between parallel plates and is commonly observed in various fluid flow applications. It helps in understanding the flow behavior and predicting the fluid dynamics within the flow channel.
In conclusion, the velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is parabolic, with the maximum velocity at the centerline of the channel and gradually decreasing towards the walls. This profile is derived from the Hagen-Poiseuille equation and is an important concept in the study of fluid dynamics.
Explanation:
Laminar flow refers to the smooth and orderly movement of fluid particles in a straight line, without any turbulence. In the case of laminar flow between parallel plates, the fluid moves in layers with different velocities. The velocity distribution profile describes how the velocity of the fluid varies across the flow cross-section.
The velocity distribution in laminar flow between parallel plates can be derived using the Hagen-Poiseuille equation. This equation relates the velocity of the fluid to the pressure drop across the flow and the dimensions of the flow channel. The Hagen-Poiseuille equation assumes that the flow is fully developed, meaning that the velocity does not change in the direction of flow.
The velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates can be described by a parabolic curve. This means that the velocity is highest at the center of the channel and gradually decreases towards the walls. The maximum velocity occurs at the centerline of the channel, where the fluid particles experience the least resistance to flow. As the fluid particles move closer to the walls, they experience more friction, causing the velocity to decrease.
The parabolic velocity profile can be mathematically represented by the Poiseuille's equation, which states that the velocity at a certain distance from the center of the channel is proportional to the square of that distance. This relationship between velocity and distance from the centerline results in a parabolic velocity distribution profile.
The parabolic velocity profile is a characteristic feature of laminar flow between parallel plates and is commonly observed in various fluid flow applications. It helps in understanding the flow behavior and predicting the fluid dynamics within the flow channel.
In conclusion, the velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is parabolic, with the maximum velocity at the centerline of the channel and gradually decreasing towards the walls. This profile is derived from the Hagen-Poiseuille equation and is an important concept in the study of fluid dynamics.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Velocity distribution profile for laminar flow between parallel plates is:a)Parabolicb)Linearc)Constantd)LogarithmicCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















