SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical...
Start Learning for Free
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given by
- a)dp/dz = g
- b)dp/dz = 0
- c)dp/dz = ρg
- d)dp/dz = −ρg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y a...
The pressure at any point in a fluid at rest is obtained by the Hydrostatic Law, which states that the rate of increase of pressure in a vertically downward direction must be equal to the specific weight of the fluid at that point.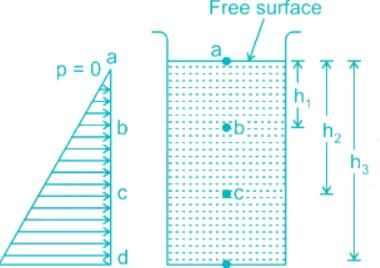
View all questions of this test

p = ρgh
Pressure distribution profile
dp/dz = -ω = -pg
dp = -ω.dz
It indicates that a negative pressure gradient exists upward along any vertical.
Thus, the pressure decreases in the upward direction and increases in the downward direction with a magnitude equal to a specific weight.
Most Upvoted Answer
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y a...
The pressure at any point in a fluid at rest is obtained by the Hydrostatic Law, which states that the rate of increase of pressure in a vertically downward direction must be equal to the specific weight of the fluid at that point.

p = ρgh
Pressure distribution profile
dp/dz = -ω = -pg
dp = -ω.dz
It indicates that a negative pressure gradient exists upward along any vertical.
Thus, the pressure decreases in the upward direction and increases in the downward direction with a magnitude equal to a specific weight.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y a...
The correct answer to the question is option 'D': dp/dz = -ρg. Let's break down and explain this answer in detail.
Understanding the Fluid Static Pressure Variation:
- Fluid static pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest. It is the pressure exerted by the fluid due to the weight of the fluid column above a certain point.
- The pressure in a fluid increases with depth. The deeper you go into a fluid, the higher the pressure will be.
- The pressure variation in a fluid is caused by the weight of the fluid itself. The weight of the fluid column above a certain point creates a pressure on that point.
Pressure Variation Equation:
The pressure variation equation in a fluid is given by the hydrostatic pressure equation:
dp/dz = -ρg
Explanation of the Pressure Variation Equation:
- dp/dz: This represents the rate of change of pressure with respect to the depth. It indicates how the pressure changes as we move vertically in the fluid.
- ρ: This is the density of the fluid. Density refers to the mass per unit volume of the fluid. It is a measure of how closely packed the molecules in the fluid are.
- g: This represents the acceleration due to gravity. It is a constant and has a value of approximately 9.8 m/s².
- The negative sign (-) in the equation indicates that the pressure increases with decreasing depth. As we move deeper into the fluid, the pressure increases.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option D):
Option D, dp/dz = -ρg, is the correct answer because it accurately represents the pressure variation in a fluid. The pressure in a fluid increases with depth, and this is captured by the negative sign in the equation. The density of the fluid and the acceleration due to gravity are also important factors in determining the pressure variation.
In summary, the correct answer to the given question is option 'D': dp/dz = -ρg. This equation represents the pressure variation in a fluid, where the pressure increases with depth. The density of the fluid and the acceleration due to gravity play important roles in determining the magnitude of the pressure variation.
Understanding the Fluid Static Pressure Variation:
- Fluid static pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest. It is the pressure exerted by the fluid due to the weight of the fluid column above a certain point.
- The pressure in a fluid increases with depth. The deeper you go into a fluid, the higher the pressure will be.
- The pressure variation in a fluid is caused by the weight of the fluid itself. The weight of the fluid column above a certain point creates a pressure on that point.
Pressure Variation Equation:
The pressure variation equation in a fluid is given by the hydrostatic pressure equation:
dp/dz = -ρg
Explanation of the Pressure Variation Equation:
- dp/dz: This represents the rate of change of pressure with respect to the depth. It indicates how the pressure changes as we move vertically in the fluid.
- ρ: This is the density of the fluid. Density refers to the mass per unit volume of the fluid. It is a measure of how closely packed the molecules in the fluid are.
- g: This represents the acceleration due to gravity. It is a constant and has a value of approximately 9.8 m/s².
- The negative sign (-) in the equation indicates that the pressure increases with decreasing depth. As we move deeper into the fluid, the pressure increases.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option D):
Option D, dp/dz = -ρg, is the correct answer because it accurately represents the pressure variation in a fluid. The pressure in a fluid increases with depth, and this is captured by the negative sign in the equation. The density of the fluid and the acceleration due to gravity are also important factors in determining the pressure variation.
In summary, the correct answer to the given question is option 'D': dp/dz = -ρg. This equation represents the pressure variation in a fluid, where the pressure increases with depth. The density of the fluid and the acceleration due to gravity play important roles in determining the magnitude of the pressure variation.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Question Description
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2025 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2025 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The depth of a fluid is measured in vertical Z – direction; X and Y are the other two directions and are mutually perpendicular. The static pressure variation in the fluid is given bya)dp/dz = gb)dp/dz = 0c)dp/dz = ρgd)dp/dz = −ρgCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















