SSC Exam > SSC Questions > In order to avoid separation in the Venturi ...
Start Learning for Free
In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kept
- a)10° to 15°
- b)15° to 20°
- c)5° to 7°
- d)7° to 10°
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of diver...
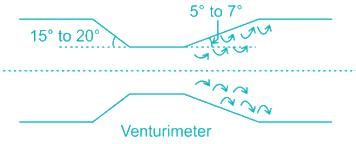
In the diverging portion, there is a decrease in velocity & a subsequent increase in pressure. If the divergence angle is very large, then backpressure will increase by a great extent & eddies formation will take place, resulting in flow separation. Thus, to avoid flow separation, the divergence angle must not exceed more than 7°, and the range should be around 5 - 7°.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of diver...
Explanation:
The Venturi meter is a device used to measure the flow rate of fluid flowing through a pipe. It consists of a converging section, a throat, and a diverging section. The converging section narrows down the flow area, causing an increase in flow velocity. The throat is the narrowest point of the meter, where the flow velocity is at its maximum. The diverging section then gradually increases the flow area, causing a decrease in flow velocity.
In order to accurately measure the flow rate using a Venturi meter, it is important to ensure that there is no separation of flow occurring in the diverging section. Separation of flow refers to the detachment of the fluid streamlines from the wall of the meter, resulting in turbulent and unpredictable flow patterns. This can lead to inaccurate measurements and reduced meter efficiency.
To avoid separation of flow in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kept within a specific range. The correct answer, option C, states that the angle of divergence is kept between 5° to 7°.
Reasoning:
The angle of divergence plays a crucial role in maintaining smooth and streamlined flow through the meter. If the angle of divergence is too large, it can create a sudden expansion of flow area, leading to separation and turbulence. On the other hand, if the angle is too small, it can cause a gradual expansion of flow area, resulting in reduced flow velocity and inaccuracies in flow measurement.
By keeping the angle of divergence between 5° to 7°, a smooth and gradual expansion of flow area is achieved. This allows the fluid streamlines to remain attached to the wall of the meter, minimizing separation and turbulence. The flow remains streamlined and predictable, ensuring accurate flow rate measurements.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the angle of divergence in a Venturi meter is kept between 5° to 7° in order to avoid separation of flow and maintain accurate flow rate measurements. This range of angle ensures that the flow remains smooth and streamlined, minimizing turbulence and unpredictability.
The Venturi meter is a device used to measure the flow rate of fluid flowing through a pipe. It consists of a converging section, a throat, and a diverging section. The converging section narrows down the flow area, causing an increase in flow velocity. The throat is the narrowest point of the meter, where the flow velocity is at its maximum. The diverging section then gradually increases the flow area, causing a decrease in flow velocity.
In order to accurately measure the flow rate using a Venturi meter, it is important to ensure that there is no separation of flow occurring in the diverging section. Separation of flow refers to the detachment of the fluid streamlines from the wall of the meter, resulting in turbulent and unpredictable flow patterns. This can lead to inaccurate measurements and reduced meter efficiency.
To avoid separation of flow in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kept within a specific range. The correct answer, option C, states that the angle of divergence is kept between 5° to 7°.
Reasoning:
The angle of divergence plays a crucial role in maintaining smooth and streamlined flow through the meter. If the angle of divergence is too large, it can create a sudden expansion of flow area, leading to separation and turbulence. On the other hand, if the angle is too small, it can cause a gradual expansion of flow area, resulting in reduced flow velocity and inaccuracies in flow measurement.
By keeping the angle of divergence between 5° to 7°, a smooth and gradual expansion of flow area is achieved. This allows the fluid streamlines to remain attached to the wall of the meter, minimizing separation and turbulence. The flow remains streamlined and predictable, ensuring accurate flow rate measurements.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the angle of divergence in a Venturi meter is kept between 5° to 7° in order to avoid separation of flow and maintain accurate flow rate measurements. This range of angle ensures that the flow remains smooth and streamlined, minimizing turbulence and unpredictability.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Question Description
In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2025 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2025 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In order to avoid separation in the Venturi meter, the angle of divergence is kepta)10° to 15°b)15° to 20°c)5° to 7°d)7° to 10°Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















