SSC Exam > SSC Questions > A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at ...
Start Learning for Free
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.
The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)
- a)804.7
- b)953.2
- c)981.7
- d)1012.2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This...
Work done for an isothermal process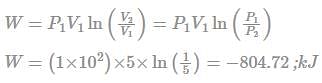
View all questions of this test
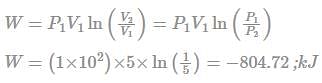
The work required is 804.72 kJ.
Most Upvoted Answer
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This...
Given:
- Volume of gas (V1) = 5 m^3
- Initial pressure of gas (P1) = 1 bar
- Final pressure of gas (P2) = 5 bar
- Natural logarithm of 5 (ln 5) = 1.609
To find:
- Work done in the process (W)
Assumption:
- The gas is assumed to be an ideal gas.
- The process is assumed to be reversible and isothermal.
Explanation:
1. Isothermal Process:
In an isothermal process, the temperature of the gas remains constant. This means that the product of pressure and volume (PV) of the gas remains constant throughout the process.
P1V1 = P2V2
2. Calculating Final Volume (V2):
Using the given values, we can rearrange the equation to find the final volume (V2).
V2 = (P1V1) / P2
V2 = (1 * 5) / 5
V2 = 1 m^3
3. Work done (W):
The work done in an isothermal process can be calculated using the following equation:
W = nRT * ln(V2 / V1)
Where:
- n = number of moles of gas
- R = ideal gas constant
- T = temperature of the gas (constant in this case)
- ln = natural logarithm function
4. Calculating Number of Moles (n):
To calculate the number of moles, we need to use the ideal gas equation:
PV = nRT
Rearranging the equation, we get:
n = PV / RT
5. Calculating Work done (W):
Substituting the values into the equation for work done:
W = nRT * ln(V2 / V1)
W = (PV / RT) * RT * ln(V2 / V1)
W = P * V * ln(V2 / V1)
W = 1 * 5 * ln(1 / 5)
W = 5 * ln(0.2)
W = 5 * (-1.609)
W = -8.045 kJ
6. Final Answer:
Since work done is a scalar quantity, the negative sign indicates that work is done on the gas. Taking the absolute value, the work done in this process is approximately 8.045 kJ.
The correct answer is option A) 804.7.
- Volume of gas (V1) = 5 m^3
- Initial pressure of gas (P1) = 1 bar
- Final pressure of gas (P2) = 5 bar
- Natural logarithm of 5 (ln 5) = 1.609
To find:
- Work done in the process (W)
Assumption:
- The gas is assumed to be an ideal gas.
- The process is assumed to be reversible and isothermal.
Explanation:
1. Isothermal Process:
In an isothermal process, the temperature of the gas remains constant. This means that the product of pressure and volume (PV) of the gas remains constant throughout the process.
P1V1 = P2V2
2. Calculating Final Volume (V2):
Using the given values, we can rearrange the equation to find the final volume (V2).
V2 = (P1V1) / P2
V2 = (1 * 5) / 5
V2 = 1 m^3
3. Work done (W):
The work done in an isothermal process can be calculated using the following equation:
W = nRT * ln(V2 / V1)
Where:
- n = number of moles of gas
- R = ideal gas constant
- T = temperature of the gas (constant in this case)
- ln = natural logarithm function
4. Calculating Number of Moles (n):
To calculate the number of moles, we need to use the ideal gas equation:
PV = nRT
Rearranging the equation, we get:
n = PV / RT
5. Calculating Work done (W):
Substituting the values into the equation for work done:
W = nRT * ln(V2 / V1)
W = (PV / RT) * RT * ln(V2 / V1)
W = P * V * ln(V2 / V1)
W = 1 * 5 * ln(1 / 5)
W = 5 * ln(0.2)
W = 5 * (-1.609)
W = -8.045 kJ
6. Final Answer:
Since work done is a scalar quantity, the negative sign indicates that work is done on the gas. Taking the absolute value, the work done in this process is approximately 8.045 kJ.
The correct answer is option A) 804.7.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A cylinder contains 5 m3 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process until its pressure increases to 5 bar.The work in kJ required for this process is _____ (take ln 5= 1.609)a)804.7b)953.2c)981.7d)1012.2Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















