GATE Exam > GATE Questions > A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of...
Start Learning for Free
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will be
- a)12
- b)14
- c)15
- d)18
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa...
Assumption: The expansion process is quasi-equilibrium and spring is linear in the range of interest.
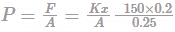
View all questions of this test
V2 = 2V = 2 × 0.05 = 0.1 m3
Displacement of the piston (and of the spring)

=0.5 m
Additional pressure applied by the spring on the gas at final state
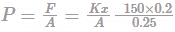
=120 kPa
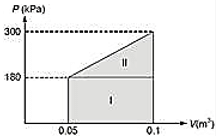
Without the spring, the pressure of the gas would remain constant at 180 kPa while the piston is rising. But under the effect of the spring, the pressure rises linearly from 180 kPa to 180 + 120 = 300 kPa at the final state

Total work done = Work done against the atmosphere + Work done against the spring
= Area I + Area II
= (300 + 180)/2 (0.1 - 0.05).
Alternate:
Total work done by the gas = Work done in expansion + Work saved in the form of potential energy of spring =180(0.1-0.05)+(½)×150×0.22=12 kJ
Most Upvoted Answer
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa...
Given data:
Initial volume of gas, V1 = 0.05 m3
Initial pressure of gas, P1 = 180 kPa
Spring constant, k = 150 kN/m
Cross-sectional area of piston, A = 0.25 m2
Calculations:
Step 1: Initial state
Initial force exerted by the spring, F = k * x (where x is the compression of the spring)
Initial force exerted by the gas, Fgas = P1 * A
Since the spring is just touching the piston, F = Fgas
k * x = P1 * A
150 * x = 180 * 0.25
x = 1.2 m
Step 2: Final state
Final volume of gas, V2 = 2 * V1 = 0.1 m3
Final pressure of gas, P2 = P1 * (V1 / V2) = 180 * (0.05 / 0.1) = 90 kPa
Work done by the gas, W = P2 * (V2 - V1) = 90 * (0.1 - 0.05) = 4.5 kJ
Step 3: Total work done
Total work done by the gas = Work done in compressing the spring + Work done against the pressure
Total work done = 0.5 * k * x^2 + W
Total work done = 0.5 * 150 * 1.2^2 + 4.5
Total work done = 108 + 4.5 = 112.5 kJ ≈ 12 kJ
Therefore, the total work done by the gas is approximately 12 kJ, which is option 'A'.
Initial volume of gas, V1 = 0.05 m3
Initial pressure of gas, P1 = 180 kPa
Spring constant, k = 150 kN/m
Cross-sectional area of piston, A = 0.25 m2
Calculations:
Step 1: Initial state
Initial force exerted by the spring, F = k * x (where x is the compression of the spring)
Initial force exerted by the gas, Fgas = P1 * A
Since the spring is just touching the piston, F = Fgas
k * x = P1 * A
150 * x = 180 * 0.25
x = 1.2 m
Step 2: Final state
Final volume of gas, V2 = 2 * V1 = 0.1 m3
Final pressure of gas, P2 = P1 * (V1 / V2) = 180 * (0.05 / 0.1) = 90 kPa
Work done by the gas, W = P2 * (V2 - V1) = 90 * (0.1 - 0.05) = 4.5 kJ
Step 3: Total work done
Total work done by the gas = Work done in compressing the spring + Work done against the pressure
Total work done = 0.5 * k * x^2 + W
Total work done = 0.5 * 150 * 1.2^2 + 4.5
Total work done = 108 + 4.5 = 112.5 kJ ≈ 12 kJ
Therefore, the total work done by the gas is approximately 12 kJ, which is option 'A'.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A piston-cylinder device contains 0.05 m3 of gas initially at 180 kPa. At this stage, a linear spring that has a spring constant of 150 kN/m is just touching the piston but exerting no force on it. Now the heat is transferred to the gas, causing the piston to rise and to compress the spring until the volume inside the cylinder doubles. If the cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.25 m2, then the total work done (in kJ) by the gas will bea)12b)14c)15d)18Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















