NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted i...
Start Learning for Free
Name the embryonic stage that gets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.
- a)Blastocyst
- b)Embryo
- c)Gastrula
- d)Morula
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a h...
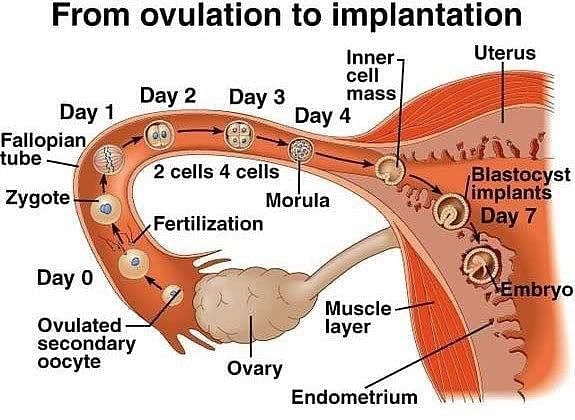
Implantation is a process in which a developing embryo, moving as a blastocyst through a uterus, makes contact with the uterine wall and remains attached to it until birth. The lining of the uterus (endometrium) prepares for the developing blastocyst to attach to it via many internal changes.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a h...
Implantation of the embryo is a crucial step in the development of a human fetus. The correct answer to the given question is option 'A', blastocyst. Now let's understand why blastocyst is the correct answer.
Introduction to implantation:
Implantation is the process in which the fertilized egg, also known as the zygote, attaches itself to the uterine wall for further development. It occurs approximately 6-7 days after fertilization and is a critical step in the establishment of pregnancy.
Explanation:
The human embryo goes through several stages of development before it reaches the implantation stage. These stages include fertilization, cleavage, morula, and blastocyst.
1. Fertilization:
Fertilization occurs when the sperm fertilizes the egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote. This process takes place in the fallopian tubes.
2. Cleavage:
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of rapid cell divisions called cleavage. During this stage, the zygote divides into smaller cells called blastomeres. Cleavage continues until the embryo reaches the morula stage.
3. Morula:
The morula is a solid ball of cells formed by the division of the zygote. It consists of about 16-32 cells and resembles a mulberry. The morula continues to divide and develop further.
4. Blastocyst:
As the morula continues to divide, it undergoes changes that lead to the formation of a blastocyst. The blastocyst stage typically occurs around day 5-6 after fertilization. It consists of two distinct cell populations: the inner cell mass (ICM) and the outer trophoblast cells.
- Inner Cell Mass (ICM): The ICM is a cluster of cells located within the blastocyst. It eventually develops into the embryo itself.
- Trophoblast Cells: The trophoblast cells surround the ICM and play a crucial role in implantation. They are responsible for the formation of the placenta and facilitate the attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall.
Implantation:
Once the blastocyst is formed, it travels through the fallopian tubes and reaches the uterus. It then attaches itself to the thickened and enriched uterine lining, known as the endometrium. This attachment is called implantation. The trophoblast cells secrete enzymes that help in the invasion of the uterine wall and facilitate the establishment of a connection between the maternal blood supply and the developing embryo.
Conclusion:
In summary, the blastocyst is the embryonic stage that gets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female. It is a crucial stage in the development of the fetus as it marks the beginning of pregnancy and the formation of the placenta. Implantation occurs approximately 6-7 days after fertilization and involves the attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine lining.
Introduction to implantation:
Implantation is the process in which the fertilized egg, also known as the zygote, attaches itself to the uterine wall for further development. It occurs approximately 6-7 days after fertilization and is a critical step in the establishment of pregnancy.
Explanation:
The human embryo goes through several stages of development before it reaches the implantation stage. These stages include fertilization, cleavage, morula, and blastocyst.
1. Fertilization:
Fertilization occurs when the sperm fertilizes the egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote. This process takes place in the fallopian tubes.
2. Cleavage:
After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of rapid cell divisions called cleavage. During this stage, the zygote divides into smaller cells called blastomeres. Cleavage continues until the embryo reaches the morula stage.
3. Morula:
The morula is a solid ball of cells formed by the division of the zygote. It consists of about 16-32 cells and resembles a mulberry. The morula continues to divide and develop further.
4. Blastocyst:
As the morula continues to divide, it undergoes changes that lead to the formation of a blastocyst. The blastocyst stage typically occurs around day 5-6 after fertilization. It consists of two distinct cell populations: the inner cell mass (ICM) and the outer trophoblast cells.
- Inner Cell Mass (ICM): The ICM is a cluster of cells located within the blastocyst. It eventually develops into the embryo itself.
- Trophoblast Cells: The trophoblast cells surround the ICM and play a crucial role in implantation. They are responsible for the formation of the placenta and facilitate the attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine wall.
Implantation:
Once the blastocyst is formed, it travels through the fallopian tubes and reaches the uterus. It then attaches itself to the thickened and enriched uterine lining, known as the endometrium. This attachment is called implantation. The trophoblast cells secrete enzymes that help in the invasion of the uterine wall and facilitate the establishment of a connection between the maternal blood supply and the developing embryo.
Conclusion:
In summary, the blastocyst is the embryonic stage that gets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female. It is a crucial stage in the development of the fetus as it marks the beginning of pregnancy and the formation of the placenta. Implantation occurs approximately 6-7 days after fertilization and involves the attachment of the blastocyst to the uterine lining.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Name the embryonic stage thatgets implanted in the uterine wall of a human female.a)Blastocystb)Embryoc)Gastrulad)MorulaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























