NEET Exam > NEET Questions > A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.1...
Start Learning for Free
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).
- a)0.049 m
- b)0.087 m
- c)0.137 m
- d)0.172 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically...
Given,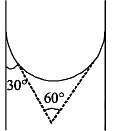
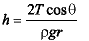
Angle of contact θ = 30°
Surface tension, T = 0.05 Nm-1
Radius of capillary tube, r = 0.15 m m = 0.15 x 10-3m
Density of ethylene iodide, ⍴ = 667 kgm-3

Capillary Rise,
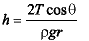
= 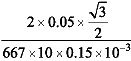
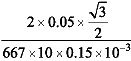
= 0.087 m
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically...
Given data:
Radius of the capillary tube, r = 0.15 mm = 0.15 × 10^(-3) m
Surface tension of methylene iodide, σ = 0.05 Nm^(-1)
Density of methylene iodide, ρ = 667 kg m^(-3)
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 ms^(-2)
Angle between the tangents, θ = 60°
We need to find the height, h, to which the methylene iodide rises in the capillary tube.
Let's analyze the situation using the concept of capillary rise.
Capillary Rise:
When a capillary tube is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises in the tube due to the combination of adhesive and cohesive forces.
Adhesive forces:
Adhesive forces are the forces of attraction between the liquid molecules and the molecules of the capillary tube. These forces tend to pull the liquid up the capillary tube.
Cohesive forces:
Cohesive forces are the forces of attraction between the molecules of the liquid itself. These forces tend to hold the liquid molecules together.
Balance between adhesive and cohesive forces:
For the liquid to rise in the capillary tube, the adhesive forces must be greater than the cohesive forces. The capillary rise can be calculated using the formula:
h = (2σcosθ) / (ρgr)
where h is the height to which the liquid rises, σ is the surface tension, θ is the angle between the tangents, ρ is the density of the liquid, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and r is the radius of the capillary tube.
Calculating the height:
Substituting the given values into the formula, we have:
h = (2 × 0.05 × cos60°) / (667 × 10 × 0.15 × 10^(-3))
h = (0.1) / (0.10005 × 6.67 × 0.15)
h ≈ 0.087 m
Therefore, the height to which the methylene iodide rises in the capillary tube is approximately 0.087 m.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Radius of the capillary tube, r = 0.15 mm = 0.15 × 10^(-3) m
Surface tension of methylene iodide, σ = 0.05 Nm^(-1)
Density of methylene iodide, ρ = 667 kg m^(-3)
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 ms^(-2)
Angle between the tangents, θ = 60°
We need to find the height, h, to which the methylene iodide rises in the capillary tube.
Let's analyze the situation using the concept of capillary rise.
Capillary Rise:
When a capillary tube is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises in the tube due to the combination of adhesive and cohesive forces.
Adhesive forces:
Adhesive forces are the forces of attraction between the liquid molecules and the molecules of the capillary tube. These forces tend to pull the liquid up the capillary tube.
Cohesive forces:
Cohesive forces are the forces of attraction between the molecules of the liquid itself. These forces tend to hold the liquid molecules together.
Balance between adhesive and cohesive forces:
For the liquid to rise in the capillary tube, the adhesive forces must be greater than the cohesive forces. The capillary rise can be calculated using the formula:
h = (2σcosθ) / (ρgr)
where h is the height to which the liquid rises, σ is the surface tension, θ is the angle between the tangents, ρ is the density of the liquid, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and r is the radius of the capillary tube.
Calculating the height:
Substituting the given values into the formula, we have:
h = (2 × 0.05 × cos60°) / (667 × 10 × 0.15 × 10^(-3))
h = (0.1) / (0.10005 × 6.67 × 0.15)
h ≈ 0.087 m
Therefore, the height to which the methylene iodide rises in the capillary tube is approximately 0.087 m.
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A capillary tube made of glass of radius 0.15 mm is dipped vertically in a beaker filled with methylene iodide (surface tension = 0.05 Nm–1, density = 667 kg m–3) which rises to height h in the tube. It is observed that the two tangents drawn from liquid-glass interfaces (from opp. sides of the capillary) make an angle of 60° with one another. Then h is close to (g = 10 ms–2).a)0.049 mb)0.087 mc)0.137 md)0.172 mCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























