GATE Exam > GATE Questions > In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requir...
Start Learning for Free
In a DRAM,
- a)periodic refreshing is not required
- b)information is stored in a capacitor
- c)information is stored in a latch
- d)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneously
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored...
Explanation:
DRAM:
DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. It is a type of volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices for storing and accessing data. DRAM is based on a storage cell called a capacitor, which can store a small amount of electrical charge.
Information Storage in a Capacitor:
In a DRAM, information is stored in a capacitor. Each bit of data is stored as an electrical charge in a capacitor within the memory cell. The presence or absence of charge represents the binary values 1 and 0, respectively.
Periodic Refreshing:
Unlike other types of memory, such as SRAM (Static Random Access Memory), DRAM requires periodic refreshing of its memory cells. This is because the electrical charge stored in the capacitors tends to leak away over time due to the inherent properties of the capacitor. If the charge is not refreshed, the data stored in the memory cells will be lost.
Read and Write Operations:
Both read and write operations can be performed in a DRAM. To read data from a specific memory cell, the charge stored in the capacitor is sensed and amplified, and then the data is outputted. To write data into a specific memory cell, the charge in the capacitor is changed to represent the desired data value.
Simultaneous Read and Write:
Simultaneous read and write operations are not possible in a DRAM. When a read operation is performed, the charge in the capacitor is read and the data is outputted. During a write operation, the charge in the capacitor is changed to store the desired data value. These operations cannot be performed simultaneously on the same memory cell.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, in a DRAM, information is stored in a capacitor, and periodic refreshing is required. Both read and write operations can be performed, but not simultaneously on the same memory cell.
DRAM:
DRAM stands for Dynamic Random Access Memory. It is a type of volatile memory used in computers and other electronic devices for storing and accessing data. DRAM is based on a storage cell called a capacitor, which can store a small amount of electrical charge.
Information Storage in a Capacitor:
In a DRAM, information is stored in a capacitor. Each bit of data is stored as an electrical charge in a capacitor within the memory cell. The presence or absence of charge represents the binary values 1 and 0, respectively.
Periodic Refreshing:
Unlike other types of memory, such as SRAM (Static Random Access Memory), DRAM requires periodic refreshing of its memory cells. This is because the electrical charge stored in the capacitors tends to leak away over time due to the inherent properties of the capacitor. If the charge is not refreshed, the data stored in the memory cells will be lost.
Read and Write Operations:
Both read and write operations can be performed in a DRAM. To read data from a specific memory cell, the charge stored in the capacitor is sensed and amplified, and then the data is outputted. To write data into a specific memory cell, the charge in the capacitor is changed to represent the desired data value.
Simultaneous Read and Write:
Simultaneous read and write operations are not possible in a DRAM. When a read operation is performed, the charge in the capacitor is read and the data is outputted. During a write operation, the charge in the capacitor is changed to store the desired data value. These operations cannot be performed simultaneously on the same memory cell.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, in a DRAM, information is stored in a capacitor, and periodic refreshing is required. Both read and write operations can be performed, but not simultaneously on the same memory cell.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored...
In a DRAM, a capacitor to store a bit of data is used along with a MOSFET (transfer device) which acts as a switch. The circuit is as shown –
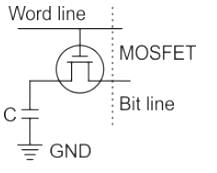
In a DRAM:
- Periodic refreshing is required.
- The information is stored in a capacitor.
- Both read and write operations cannot be performed simultaneously.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Question Description
In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a DRAM,a)periodic refreshing is not requiredb)information is stored in a capacitorc)information is stored in a latchd)both read and write operations can be performed simultaneouslyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























