NEET Exam > NEET Questions > If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is ke...
Start Learning for Free
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) is
- a)Tn = 2Ti
- b)Tn = Ti - T
- c)Tn = Ti + T
- d)Tn = Ti/2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot jun...
**Explanation:**
A thermocouple is a device that measures temperature by utilizing the Seebeck effect. It consists of two different metals joined together at one end, known as the hot junction, and the other end is kept at a constant reference temperature, known as the cold junction. When there is a temperature gradient between the two junctions, it generates a voltage proportional to the temperature difference.
The relation between the neutral temperature (Tn) and the temperature of inversion (Ti) is given by the Thomson effect. The Thomson effect states that when a current flows through a homogeneous conductor, heat is absorbed or evolved at the rate of one watt per ampere per degree Celsius change in temperature.
To derive the relation between Tn and Ti, let's consider the following:
1. **Neutral Temperature (Tn):** It is the temperature at which the Seebeck coefficient of the two metals in the thermocouple becomes zero. At this temperature, the thermocouple produces no electromotive force (EMF) when there is no temperature difference between the junctions.
2. **Temperature of Inversion (Ti):** It is the temperature at which the polarity of the EMF produced by the thermocouple changes. Below Ti, the positive terminal of the thermocouple is at the hot junction, and above Ti, the positive terminal is at the cold junction.
Now, let's analyze the given scenario:
- The cold junction is kept at 0°C, which means its temperature is constant.
- The hot junction is kept at ToC, which can vary.
- Since the cold junction temperature is constant, any change in the EMF will be solely due to the temperature difference at the hot junction.
Based on the properties of a thermocouple, we can conclude that:
- The EMF produced by the thermocouple is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the hot and cold junctions.
- The EMF is zero at the neutral temperature (Tn).
To find the relation between Tn and Ti, we need to consider the behavior of the thermocouple when the hot junction's temperature is below or above Ti.
- When the hot junction's temperature is below Ti, the EMF is positive.
- When the hot junction's temperature is above Ti, the EMF is negative.
Therefore, we can conclude that the neutral temperature (Tn) is the average of the temperature of inversion (Ti) and the cold junction temperature.
Mathematically, it can be represented as:
Tn = (Ti + 0)/2
Simplifying the equation, we get:
Tn = Ti/2
Hence, the correct answer is option D: Tn = Ti/2.
A thermocouple is a device that measures temperature by utilizing the Seebeck effect. It consists of two different metals joined together at one end, known as the hot junction, and the other end is kept at a constant reference temperature, known as the cold junction. When there is a temperature gradient between the two junctions, it generates a voltage proportional to the temperature difference.
The relation between the neutral temperature (Tn) and the temperature of inversion (Ti) is given by the Thomson effect. The Thomson effect states that when a current flows through a homogeneous conductor, heat is absorbed or evolved at the rate of one watt per ampere per degree Celsius change in temperature.
To derive the relation between Tn and Ti, let's consider the following:
1. **Neutral Temperature (Tn):** It is the temperature at which the Seebeck coefficient of the two metals in the thermocouple becomes zero. At this temperature, the thermocouple produces no electromotive force (EMF) when there is no temperature difference between the junctions.
2. **Temperature of Inversion (Ti):** It is the temperature at which the polarity of the EMF produced by the thermocouple changes. Below Ti, the positive terminal of the thermocouple is at the hot junction, and above Ti, the positive terminal is at the cold junction.
Now, let's analyze the given scenario:
- The cold junction is kept at 0°C, which means its temperature is constant.
- The hot junction is kept at ToC, which can vary.
- Since the cold junction temperature is constant, any change in the EMF will be solely due to the temperature difference at the hot junction.
Based on the properties of a thermocouple, we can conclude that:
- The EMF produced by the thermocouple is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the hot and cold junctions.
- The EMF is zero at the neutral temperature (Tn).
To find the relation between Tn and Ti, we need to consider the behavior of the thermocouple when the hot junction's temperature is below or above Ti.
- When the hot junction's temperature is below Ti, the EMF is positive.
- When the hot junction's temperature is above Ti, the EMF is negative.
Therefore, we can conclude that the neutral temperature (Tn) is the average of the temperature of inversion (Ti) and the cold junction temperature.
Mathematically, it can be represented as:
Tn = (Ti + 0)/2
Simplifying the equation, we get:
Tn = Ti/2
Hence, the correct answer is option D: Tn = Ti/2.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot jun...
Tn = 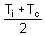 = neutral temperature
= neutral temperature
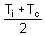 = neutral temperature
= neutral temperatureWhere Tc is cold junction temperature , here Tc = 0
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If the cold junction of a thermo-couple is kept at 0oC and the hot junction is kept at ToC, then the relation between neutral temperature (Tn) and temperature of inversion (Ti) isa)Tn = 2Tib)Tn = Ti - Tc)Tn = Ti + Td)Tn = Ti/2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























