UPSC Exam > UPSC Questions > The region between the rivers Tigris and Eup...
Start Learning for Free
The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?
- a)Udder valley
- b)Mesopotamia
- c)Sind valley
- d)Sonoma valley
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically calle...
It's a historic region situated within the tigris-Euphrates river system, in modern days roughly corresponding to most of Iraq plus Kuwait, Syria, Turkey.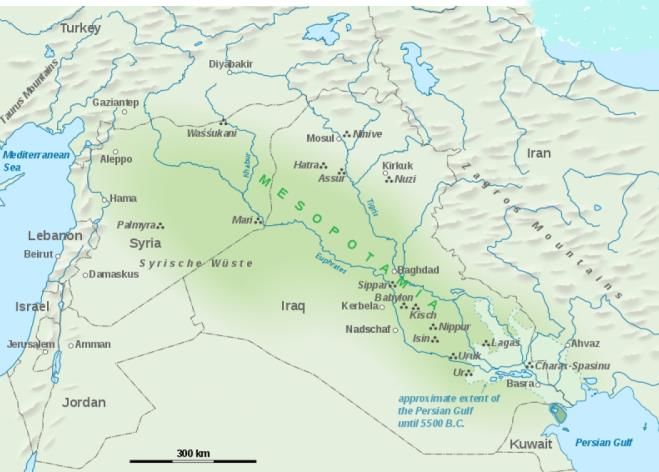

Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically calle...
The historically significant region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates is called Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia is a Greek word that translates to "land between two rivers," referring to the area located in present-day Iraq, Kuwait, and parts of Syria and Turkey. This region is often referred to as the cradle of civilization as it is one of the earliest centers of human civilization.
Mesopotamia was home to several ancient civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. These civilizations developed advanced systems of writing, mathematics, agriculture, and governance, laying the foundation for many aspects of modern society.
Key Features of Mesopotamia:
1. Geographical Location: Mesopotamia is located in the fertile crescent, a region that stretches from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers provided a reliable water source for agriculture, leading to the development of permanent settlements.
2. Agricultural Advancements: The fertile soil of Mesopotamia allowed for the cultivation of crops such as barley, wheat, and dates. To harness the water from the rivers, the ancient Mesopotamians built intricate irrigation systems, including canals and dikes.
3. City-States: Mesopotamia was organized into several city-states, each with its own ruler and government. The city-states were often in competition with one another and engaged in conflicts and alliances.
4. Writing System: The Sumerians of Mesopotamia developed one of the first known writing systems called cuneiform. This system used wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets and was used for administrative, economic, and literary purposes.
5. Legal Systems: The Code of Hammurabi, developed by the Babylonian king Hammurabi, is one of the most famous legal codes from Mesopotamia. It consisted of a set of laws that governed various aspects of society and established the principle of "an eye for an eye."
6. Architectural Achievements: Mesopotamia is known for its impressive architectural achievements, including the ziggurats - towering stepped structures that served as religious temples. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, were also located in Mesopotamia.
7. Trade and Commerce: Mesopotamia was a hub of trade and commerce, facilitated by its central location between different regions. The Mesopotamians traded goods such as textiles, metals, spices, and agricultural products with neighboring societies.
Overall, Mesopotamia played a crucial role in the development of human civilization, contributing to advancements in various fields and leaving a lasting impact on subsequent cultures and societies.
Mesopotamia was home to several ancient civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. These civilizations developed advanced systems of writing, mathematics, agriculture, and governance, laying the foundation for many aspects of modern society.
Key Features of Mesopotamia:
1. Geographical Location: Mesopotamia is located in the fertile crescent, a region that stretches from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers provided a reliable water source for agriculture, leading to the development of permanent settlements.
2. Agricultural Advancements: The fertile soil of Mesopotamia allowed for the cultivation of crops such as barley, wheat, and dates. To harness the water from the rivers, the ancient Mesopotamians built intricate irrigation systems, including canals and dikes.
3. City-States: Mesopotamia was organized into several city-states, each with its own ruler and government. The city-states were often in competition with one another and engaged in conflicts and alliances.
4. Writing System: The Sumerians of Mesopotamia developed one of the first known writing systems called cuneiform. This system used wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets and was used for administrative, economic, and literary purposes.
5. Legal Systems: The Code of Hammurabi, developed by the Babylonian king Hammurabi, is one of the most famous legal codes from Mesopotamia. It consisted of a set of laws that governed various aspects of society and established the principle of "an eye for an eye."
6. Architectural Achievements: Mesopotamia is known for its impressive architectural achievements, including the ziggurats - towering stepped structures that served as religious temples. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, were also located in Mesopotamia.
7. Trade and Commerce: Mesopotamia was a hub of trade and commerce, facilitated by its central location between different regions. The Mesopotamians traded goods such as textiles, metals, spices, and agricultural products with neighboring societies.
Overall, Mesopotamia played a crucial role in the development of human civilization, contributing to advancements in various fields and leaving a lasting impact on subsequent cultures and societies.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Question Description
The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UPSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The region between the rivers Tigris and Euphrates historically called as___?a) Udder valleyb) Mesopotamiac) Sind valleyd) Sonoma valleyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UPSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















