NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large pl...
Start Learning for Free
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as
[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]
- a)Ti plasmid
- b)Ri plasmid
- c)Recombinant plasmid
- d)Shine Delgrano sequence
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumo...
A Ti or tumour inducing plasmid is a plasmid that often, but not always, is a part of the genetic equipment that Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Agrobacterium rhizogenes use to transduce their genetic material to plants.
View all questions of this test
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a pathogen of plants using tumor-inducing Ti plasmid to transfer oncogenic DNA. The copy number and conjugal transfer of Ti plasmid are regulated by quorum sensing in A. tumefaciens.
Most Upvoted Answer
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumo...
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - Ti plasmid.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil bacterium that can infect plants and cause the formation of tumors or galls. This ability is due to the presence of a large plasmid called the Ti (tumor-inducing) plasmid. Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
1. Agrobacterium tumefaciens:
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that naturally occurs in the soil. It is known for its ability to transfer a part of its DNA, contained within the Ti plasmid, into the genome of the host plant. This DNA transfer results in the formation of tumors or galls on the infected plant.
2. Tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid:
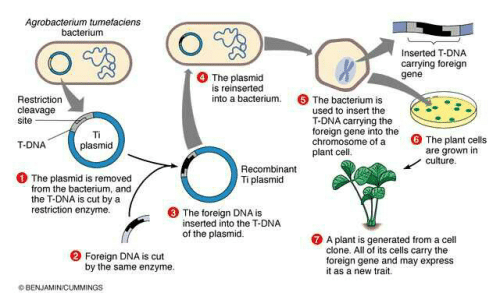
The Ti plasmid is a large circular DNA molecule that is present within Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It contains several regions that are crucial for the bacterium's ability to infect plants and induce tumor formation. The Ti plasmid is responsible for the transfer of a specific piece of DNA, known as the T-DNA (transfer DNA), into the plant's genome.
3. Transfer DNA (T-DNA):
The T-DNA is a specific segment of DNA present within the Ti plasmid. It carries genes that are responsible for the production of plant hormones called auxins and cytokinins. These hormones promote uncontrolled cell division and growth, leading to the formation of tumors or galls in the infected plant.
4. Mechanism of infection:
When Agrobacterium tumefaciens comes into contact with a wounded plant, it attaches to the plant cells and transfers the T-DNA from the Ti plasmid into the plant genome. This transfer is facilitated by a set of genes present on the Ti plasmid called vir genes. The T-DNA integrates into the plant genome and is then expressed, leading to the production of plant hormones and tumor formation.
5. Importance of Ti plasmid in genetic engineering:
The ability of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to transfer DNA into plant cells has been widely used in genetic engineering. Researchers can modify the T-DNA region of the Ti plasmid to carry desired genes and introduce them into plants. This technique, known as Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, allows for the production of genetically modified plants with new traits.
In conclusion, Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid called the Ti plasmid, which is responsible for inducing tumor formation in plants. The Ti plasmid transfers a specific segment of DNA, known as the T-DNA, into the plant genome, leading to uncontrolled cell division and the formation of tumors or galls. This ability of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been harnessed in genetic engineering to introduce new genes into plants.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil bacterium that can infect plants and cause the formation of tumors or galls. This ability is due to the presence of a large plasmid called the Ti (tumor-inducing) plasmid. Here is a detailed explanation of the answer:
1. Agrobacterium tumefaciens:
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that naturally occurs in the soil. It is known for its ability to transfer a part of its DNA, contained within the Ti plasmid, into the genome of the host plant. This DNA transfer results in the formation of tumors or galls on the infected plant.
2. Tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid:
The Ti plasmid is a large circular DNA molecule that is present within Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It contains several regions that are crucial for the bacterium's ability to infect plants and induce tumor formation. The Ti plasmid is responsible for the transfer of a specific piece of DNA, known as the T-DNA (transfer DNA), into the plant's genome.
3. Transfer DNA (T-DNA):
The T-DNA is a specific segment of DNA present within the Ti plasmid. It carries genes that are responsible for the production of plant hormones called auxins and cytokinins. These hormones promote uncontrolled cell division and growth, leading to the formation of tumors or galls in the infected plant.
4. Mechanism of infection:
When Agrobacterium tumefaciens comes into contact with a wounded plant, it attaches to the plant cells and transfers the T-DNA from the Ti plasmid into the plant genome. This transfer is facilitated by a set of genes present on the Ti plasmid called vir genes. The T-DNA integrates into the plant genome and is then expressed, leading to the production of plant hormones and tumor formation.
5. Importance of Ti plasmid in genetic engineering:
The ability of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to transfer DNA into plant cells has been widely used in genetic engineering. Researchers can modify the T-DNA region of the Ti plasmid to carry desired genes and introduce them into plants. This technique, known as Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, allows for the production of genetically modified plants with new traits.
In conclusion, Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid called the Ti plasmid, which is responsible for inducing tumor formation in plants. The Ti plasmid transfers a specific segment of DNA, known as the T-DNA, into the plant genome, leading to uncontrolled cell division and the formation of tumors or galls. This ability of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been harnessed in genetic engineering to introduce new genes into plants.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumo...
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Agrobacterium tumefaciens contains a large plasmid, which induces tumour in the plants it is termed as[Uttaranchal PMT 2004]a)Ti plasmidb)Ri plasmidc)Recombinant plasmidd)Shine Delgrano sequenceCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























