NEET Exam > NEET Questions > A ball is travelling with uniform translatory...
Start Learning for Free
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?
Verified Answer
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?
When a body moves in such a way that the linear distance covered by each particle of the body is same during the motion, then the motion is said to be translatory or translation motion.
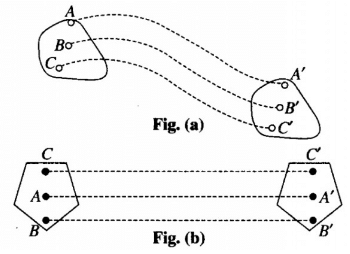
Translatory motion can be, again of two types viz., curvilinear (shown in fig. (a) or rectilinear (shown in fig. (b), accordingly as the paths of every constituent particles are similarly curved or straight line paths. Here it is important that the body does not change its orientation. Here we can also define it further in uniform and non-uniform translatory motion. Here figure
(b) is uniformly translatory motion.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?
A ball traveling with uniform translatory motion refers to the ball moving in a straight line at a constant speed. This type of motion is characterized by three key aspects: direction, speed, and consistency.
Direction:
The ball moves in a straight line, meaning its path does not curve or deviate from a linear trajectory. The direction of the ball's motion remains constant throughout its journey.
Speed:
The speed of the ball remains constant. This implies that the ball covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. For example, if the ball covers 10 meters in 2 seconds, it will cover the same 10 meters in the subsequent 2 seconds and so on.
Consistency:
Uniform translatory motion requires the speed to remain unchanged throughout the ball's journey. There are no variations or fluctuations in the speed of the ball during its movement.
Characteristics:
1. Straight-line path: The ball moves in a straight line without any deviations.
2. Constant speed: The ball maintains a consistent speed, covering equal distances in equal intervals of time.
3. Unchanging direction: The direction of the ball's motion remains constant throughout its journey.
4. No acceleration: Since the speed remains constant, there is no acceleration involved. Acceleration refers to any change in speed or direction, which is absent in this case.
Example:
Imagine a ball rolling on a flat, frictionless surface. Initially, the ball is given a push in a particular direction. Due to the absence of any external forces, the ball starts moving with uniform translatory motion. It continues to move in a straight line, covering equal distances in equal time intervals, and at a constant speed. The direction of its motion remains unchanged unless acted upon by an external force.
Importance:
Understanding uniform translatory motion is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and sports. It allows scientists and engineers to analyze and predict the behavior of objects moving in a straight line at a constant speed. In sports, it helps athletes refine their techniques and strategies by considering the consistent motion of objects such as balls or projectiles.
In conclusion, a ball traveling with uniform translatory motion implies that it moves in a straight line at a constant speed without any changes in direction or acceleration. This concept is significant in understanding the behavior of objects in motion and has practical applications in various fields.
Direction:
The ball moves in a straight line, meaning its path does not curve or deviate from a linear trajectory. The direction of the ball's motion remains constant throughout its journey.
Speed:
The speed of the ball remains constant. This implies that the ball covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. For example, if the ball covers 10 meters in 2 seconds, it will cover the same 10 meters in the subsequent 2 seconds and so on.
Consistency:
Uniform translatory motion requires the speed to remain unchanged throughout the ball's journey. There are no variations or fluctuations in the speed of the ball during its movement.
Characteristics:
1. Straight-line path: The ball moves in a straight line without any deviations.
2. Constant speed: The ball maintains a consistent speed, covering equal distances in equal intervals of time.
3. Unchanging direction: The direction of the ball's motion remains constant throughout its journey.
4. No acceleration: Since the speed remains constant, there is no acceleration involved. Acceleration refers to any change in speed or direction, which is absent in this case.
Example:
Imagine a ball rolling on a flat, frictionless surface. Initially, the ball is given a push in a particular direction. Due to the absence of any external forces, the ball starts moving with uniform translatory motion. It continues to move in a straight line, covering equal distances in equal time intervals, and at a constant speed. The direction of its motion remains unchanged unless acted upon by an external force.
Importance:
Understanding uniform translatory motion is crucial in various fields, including physics, engineering, and sports. It allows scientists and engineers to analyze and predict the behavior of objects moving in a straight line at a constant speed. In sports, it helps athletes refine their techniques and strategies by considering the consistent motion of objects such as balls or projectiles.
In conclusion, a ball traveling with uniform translatory motion implies that it moves in a straight line at a constant speed without any changes in direction or acceleration. This concept is significant in understanding the behavior of objects in motion and has practical applications in various fields.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?
Question Description
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?.
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?.
Solutions for A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that?, a detailed solution for A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? has been provided alongside types of A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A ball is travelling with uniform translatory motion. This mean that? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























