NEET Exam > NEET Questions > An oil immersion objective of a light microsc...
Start Learning for Free
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is?
Most Upvoted Answer
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical apert...
**Oil Immersion Objective and Numerical Aperture:**
An oil immersion objective is a specialized lens used in light microscopy that requires the use of immersion oil between the objective lens and the specimen. This oil has a refractive index close to that of glass, which helps to minimize the loss of light due to refraction.
Numerical aperture (NA) is a measure of the light-gathering ability and resolving power of an objective lens. It is determined by the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the specimen, and the angle of the cone of light entering the lens. A higher numerical aperture indicates a greater resolving power of the lens.
**Abbé Equation:**
The Abbé equation is used to calculate the maximum theoretical resolving power (R) of a microscope. It is given by the formula:
R = (0.61 * λ) / NA
Where:
R = Resolving power (in nm)
λ = Wavelength of light used (in nm)
NA = Numerical aperture of the objective lens
**Calculating Resolving Power:**
In this case, we are given that the numerical aperture of the oil immersion objective is 1.25, and the wavelength of the blue light used is 450 nm. We can substitute these values into the Abbé equation to calculate the resolving power:
R = (0.61 * 450) / 1.25
R = 275.4 / 1.25
R ≈ 220.32 nm
Therefore, the maximum theoretical resolving power of the microscope with this oil immersion objective and blue light is approximately 220.32 nm.
**Explanation:**
The resolving power of a microscope determines its ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects. It is influenced by factors such as the numerical aperture of the objective lens and the wavelength of light used. A higher numerical aperture and a shorter wavelength of light result in a greater resolving power.
In this case, the oil immersion objective has a numerical aperture of 1.25, which is relatively high. The numerical aperture affects the angle of the cone of light entering the lens, allowing for better light-gathering and increased resolving power.
The wavelength of blue light used is 450 nm, which is shorter than the wavelength of visible light. Shorter wavelengths enable higher resolution because the distance between two points that can be distinguished decreases as the wavelength decreases.
By substituting the given values into the Abbé equation, we can calculate the maximum theoretical resolving power of the microscope, which is approximately 220.32 nm. This means that the microscope can distinguish between two points that are at least 220.32 nm apart.
In summary, the oil immersion objective with a numerical aperture of 1.25 and blue light with a wavelength of 450 nm provides a maximum theoretical resolving power of approximately 220.32 nm. This allows for high-resolution imaging and the ability to distinguish fine details in the specimen being observed.
An oil immersion objective is a specialized lens used in light microscopy that requires the use of immersion oil between the objective lens and the specimen. This oil has a refractive index close to that of glass, which helps to minimize the loss of light due to refraction.
Numerical aperture (NA) is a measure of the light-gathering ability and resolving power of an objective lens. It is determined by the refractive index of the medium between the lens and the specimen, and the angle of the cone of light entering the lens. A higher numerical aperture indicates a greater resolving power of the lens.
**Abbé Equation:**
The Abbé equation is used to calculate the maximum theoretical resolving power (R) of a microscope. It is given by the formula:
R = (0.61 * λ) / NA
Where:
R = Resolving power (in nm)
λ = Wavelength of light used (in nm)
NA = Numerical aperture of the objective lens
**Calculating Resolving Power:**
In this case, we are given that the numerical aperture of the oil immersion objective is 1.25, and the wavelength of the blue light used is 450 nm. We can substitute these values into the Abbé equation to calculate the resolving power:
R = (0.61 * 450) / 1.25
R = 275.4 / 1.25
R ≈ 220.32 nm
Therefore, the maximum theoretical resolving power of the microscope with this oil immersion objective and blue light is approximately 220.32 nm.
**Explanation:**
The resolving power of a microscope determines its ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects. It is influenced by factors such as the numerical aperture of the objective lens and the wavelength of light used. A higher numerical aperture and a shorter wavelength of light result in a greater resolving power.
In this case, the oil immersion objective has a numerical aperture of 1.25, which is relatively high. The numerical aperture affects the angle of the cone of light entering the lens, allowing for better light-gathering and increased resolving power.
The wavelength of blue light used is 450 nm, which is shorter than the wavelength of visible light. Shorter wavelengths enable higher resolution because the distance between two points that can be distinguished decreases as the wavelength decreases.
By substituting the given values into the Abbé equation, we can calculate the maximum theoretical resolving power of the microscope, which is approximately 220.32 nm. This means that the microscope can distinguish between two points that are at least 220.32 nm apart.
In summary, the oil immersion objective with a numerical aperture of 1.25 and blue light with a wavelength of 450 nm provides a maximum theoretical resolving power of approximately 220.32 nm. This allows for high-resolution imaging and the ability to distinguish fine details in the specimen being observed.
Community Answer
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical apert...
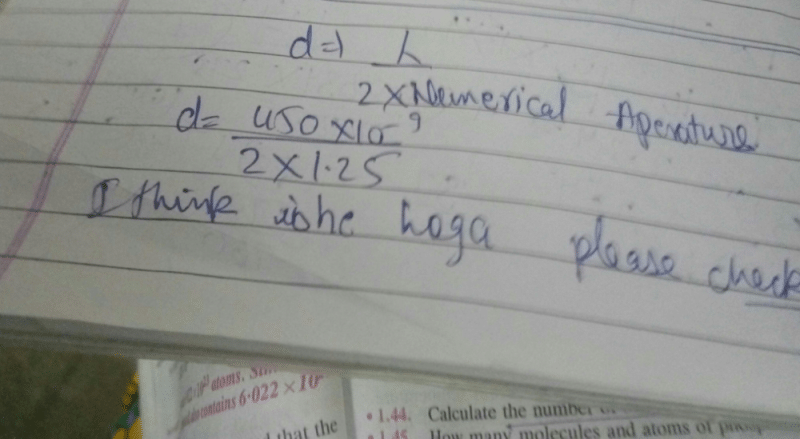
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is?
Question Description
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is?.
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is?.
Solutions for An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is?, a detailed solution for An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? has been provided alongside types of An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An oil immersion objective of a light microscope has a numerical aperture of 1.25. Using the Abbé equation, the maximum theoretical resolving power (in nm) of the microscope with this objective and blue light (wavelength = 450 nm) is? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























