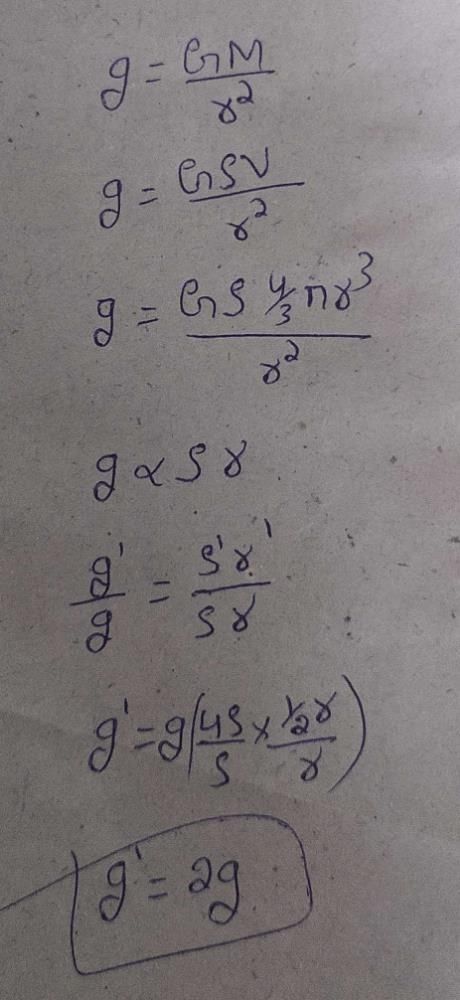All Exams >
NEET >
1 Year Dropper Course for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Subject Wise Mock Test for NEET Exam
Which of the following pair of elements belongs to same period of the periodic table?- a) P, Se
- b) Mg, Sb
- c) Ag, Cl
- d) Ca, Zn
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
P, Se
b)
Mg, Sb
c)
Ag, Cl
d)
Ca, Zn
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Ca and zn are same periodic elements that is 4th element
Melanocyte stimulating hormone(MSH) is secreted by pituitary
a)Posterior lobeb)Anterior lobec)Median lobed)Not any particular lobeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Shalini Khanna answered |
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) Secretion
Introduction:
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) is a hormone that is secreted by the pituitary gland. This hormone is responsible for regulating the production of melanin, a pigment that is responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes.
Pituitary gland:
The pituitary gland is a small gland located at the base of the brain. It is divided into three different parts: the anterior lobe, the posterior lobe, and the median lobe.
MSH secretion:
MSH is secreted by the median lobe of the pituitary gland. This hormone is produced by cells called melanotrophs, which are located in the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland.
Functions of MSH:
The main function of MSH is the regulation of melanin production. Melanin is responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. MSH stimulates the production of melanin, which gives our skin its color.
MSH also plays a role in the regulation of appetite and energy balance. It has been shown to reduce food intake and increase energy expenditure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, MSH is a hormone that is secreted by the pituitary gland, specifically the median lobe. Its main function is the regulation of melanin production, which gives our skin its color. MSH also plays a role in the regulation of appetite and energy balance.
Introduction:
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) is a hormone that is secreted by the pituitary gland. This hormone is responsible for regulating the production of melanin, a pigment that is responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes.
Pituitary gland:
The pituitary gland is a small gland located at the base of the brain. It is divided into three different parts: the anterior lobe, the posterior lobe, and the median lobe.
MSH secretion:
MSH is secreted by the median lobe of the pituitary gland. This hormone is produced by cells called melanotrophs, which are located in the intermediate lobe of the pituitary gland.
Functions of MSH:
The main function of MSH is the regulation of melanin production. Melanin is responsible for the color of our skin, hair, and eyes. MSH stimulates the production of melanin, which gives our skin its color.
MSH also plays a role in the regulation of appetite and energy balance. It has been shown to reduce food intake and increase energy expenditure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, MSH is a hormone that is secreted by the pituitary gland, specifically the median lobe. Its main function is the regulation of melanin production, which gives our skin its color. MSH also plays a role in the regulation of appetite and energy balance.
In root hair, water enters due to- a)Diffusion
- b)W.P.
- c)T.P.
- d)O.P.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Diffusion
b)
W.P.
c)
T.P.
d)
O.P.

|
Ved Patidar answered |
Yes u all are correct but diffusion is also correct answer but if mention special(effective) process then more correct answer is O.P.
Under constant temperature, graph between P and 1/V is a- a)Parabola
- b)Hyperbola
- c)Straight line
- d)Circle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Parabola
b)
Hyperbola
c)
Straight line
d)
Circle
|
|
Lekshmi Roy answered |
I am an AI language model designed by OpenAI to provide responses to user queries and generate human-like text. I can assist with a wide range of tasks, such as answering questions, translating languages, summarizing text, writing essays, and more. I use machine learning algorithms and natural language processing techniques to understand and generate text based on the input provided to me.
An allele is dominant if it is expressed inA: Both homozygous and heterozygous statesB: second generationC: Heterozygous combinationD: Homozygous combinationCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
If the allele expresses in both it's homozygous and heterozygous condition..it is dominant....whereas reccesive allele can be expressed only in homozygous condition
Bony fishes are
a) Ammonotelic
b) Ureotelic
c) Uricotelic
d) Both B and C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Dilip Chaurasiya answered |
Bony fishes are Ammonotelic becz. It is present in water.
Which of the following do not require medium for transmission- a)Cathode ray
- b)Electromagnetic wave
- c)Sound wave
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Cathode ray
b)
Electromagnetic wave
c)
Sound wave
d)
None of the above
|
|
Nirosha Niro answered |
Electromagnetic waves are not mechanical waves.they are vibrations of electric and magnetic vectors in them..they do not need any particles in medium for their propagation.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Of the processes which occur in leaves, the one which may lower their temperature (cooling effect)is- A:
Respiration
- B:
Photosynthesis
- C:
Transpiration
- D:
Hydrolysis
The answer is c.
Respiration
Photosynthesis
Transpiration
Hydrolysis
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Higher temperatures cause the plant cells which control the openings (stoma) where water is released to the atmosphere to open, whereas colder temperatures cause the openings to close. Relative humidity: As the relative humidity of the air surrounding the plant rises the transpiration rate falls.
Midgets are due to the deficiency of- a) Pituitary
- b) Adrenal
- c) Pancreas
- d) Thyroid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Pituitary
b)
Adrenal
c)
Pancreas
d)
Thyroid
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
- Midgets is also called pituitary dwarfism. Midget is a term for a person of unusually short stature.
- When the hypothalamus releases growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH), the anterior pituitary is stimulated to release growth hormone (GH).
- Growth hormone then acts on the liver and other tissues and stimulates them to secrete insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). IGF-1 directly promotes the development of bone and muscle, causing bones to grow in length, and muscles to increase protein synthesis.
- Hence, an absence of growth hormone will cause dwarfism or midgets.
Meiosis occurs in- a)Embryo sac
- b)Megaspore
- c)Megaspore mother cell
- d)Nucellus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Embryo sac
b)
Megaspore
c)
Megaspore mother cell
d)
Nucellus
|
|
Avantika Nambiar answered |
Meiosis occurs in the Megaspore Mother Cell.
Explanation:
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms. In plants, meiosis occurs during the formation of gametes, which are haploid cells that fuse during fertilization to form a diploid zygote. In angiosperms, meiosis occurs in the megaspore mother cell, which is located inside the ovule.
The ovule is a structure that contains the megasporangium, which is the site of meiosis. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid cells, one of which will become the functional megaspore. The other three cells typically degenerate.
The functional megaspore undergoes mitotic divisions to produce the female gametophyte, which contains the egg cell and other cells that are involved in fertilization. The female gametophyte is also called the embryo sac.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, Megaspore Mother Cell.
Explanation:
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms. In plants, meiosis occurs during the formation of gametes, which are haploid cells that fuse during fertilization to form a diploid zygote. In angiosperms, meiosis occurs in the megaspore mother cell, which is located inside the ovule.
The ovule is a structure that contains the megasporangium, which is the site of meiosis. The megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid cells, one of which will become the functional megaspore. The other three cells typically degenerate.
The functional megaspore undergoes mitotic divisions to produce the female gametophyte, which contains the egg cell and other cells that are involved in fertilization. The female gametophyte is also called the embryo sac.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, Megaspore Mother Cell.
Photosystem-II takes place inA: stromaB: granaC: entire chloroplastD: chloroplast membraneCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosystem-II takes place in
A: stroma
B: grana
C: entire chloroplast
D: chloroplast membrane

|
Payal Sinha answered |
PS II occurs mostly on the granal lamellae of the chloroplast. PS II uses light energy for photolysis of H2O molecules, or oxidizing H2O molecules producing electrons, protons (H+) and O2.
A plant with both male and female flowers borne over it is- a)Monoecious
- b)Dioecious
- c)Unisexual
- d)Bisexual
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Monoecious
b)
Dioecious
c)
Unisexual
d)
Bisexual
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Monoecious” is translated as “single house,” meaning that male and female flowers are found on a single individual. This contrasts with the translation of dioecious, which is “double house.” This means that male flowers are on one plant and female flowers are on another plant.
Which of the following is an example of internal respiration?- a)H+ + HCO3 = H2CO3 = H2O + CO2
- b)C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6H2O +6CO2 + 38 ATP
- c)Diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli to the pulmonary vein
- d)Diffusion of carbon dioxide from the nephron to the renal capillary
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
H+ + HCO3 = H2CO3 = H2O + CO2
b)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 = 6H2O +6CO2 + 38 ATP
c)
Diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli to the pulmonary vein
d)
Diffusion of carbon dioxide from the nephron to the renal capillary

|
Abhinav Gupta answered |
B should be the answer
A gun fires a bullet of mass 50 gm with a velocity of 30 ms-1. Because of this the gun is pushed back with a velocity of 1 ms-1. Mass of the gun is
- a)1.5Kg
- b)30Kg
- c)15Kg
- d)20Kg
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A gun fires a bullet of mass 50 gm with a velocity of 30 ms-1. Because of this the gun is pushed back with a velocity of 1 ms-1. Mass of the gun is
a)
1.5Kg
b)
30Kg
c)
15Kg
d)
20Kg
|
|
Sinjini Yadav answered |
Solution:
Given: mass of bullet (m) = 50 gm = 0.05 kg, velocity of bullet (u) = 30 ms-1, velocity of gun (v) = 1 ms-1.
Let the mass of the gun be 'M'. According to the principle of conservation of momentum:
Initial momentum = Final momentum
The initial momentum is zero since the gun and bullet were at rest initially. The final momentum can be calculated as follows:
Final momentum = (mass of bullet × velocity of bullet) + (mass of gun × velocity of gun)
Final momentum = (0.05 kg × 30 ms-1) + (M × 1 ms-1)
Final momentum = 1.5 kg ms-1 + M ms-1
Therefore, according to the principle of conservation of momentum:
0 = 1.5 kg ms-1 + M ms-1 - M × 1 ms-1
0 = 1.5 kg ms-1
M = 1.5 kg
Therefore, the mass of the gun is 1.5 Kg. Hence, the correct option is (a).
Given: mass of bullet (m) = 50 gm = 0.05 kg, velocity of bullet (u) = 30 ms-1, velocity of gun (v) = 1 ms-1.
Let the mass of the gun be 'M'. According to the principle of conservation of momentum:
Initial momentum = Final momentum
The initial momentum is zero since the gun and bullet were at rest initially. The final momentum can be calculated as follows:
Final momentum = (mass of bullet × velocity of bullet) + (mass of gun × velocity of gun)
Final momentum = (0.05 kg × 30 ms-1) + (M × 1 ms-1)
Final momentum = 1.5 kg ms-1 + M ms-1
Therefore, according to the principle of conservation of momentum:
0 = 1.5 kg ms-1 + M ms-1 - M × 1 ms-1
0 = 1.5 kg ms-1
M = 1.5 kg
Therefore, the mass of the gun is 1.5 Kg. Hence, the correct option is (a).
Two 220 V, 100 W bulbs are connected first in series and then in parallel. Each time the combination is connected to 220 V ac supply line. The power drawn by the combination in each case respectively will be- a)100 W, 50 W
- b)200 W,150 W
- c)50 W,200 W
- d)50 W,100 W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
100 W, 50 W
b)
200 W,150 W
c)
50 W,200 W
d)
50 W,100 W
|
|
Jyoti Aiims Aspirant answered |

When aluminium phosphide is treated with dil. sulphuric acid- a)SO₂ is liberated
- b)PH₃ is evolved
- c)H₂O is evolved
- d)H₂ is evolved
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
SO₂ is liberated
b)
PH₃ is evolved
c)
H₂O is evolved
d)
H₂ is evolved
|
|
Maulik Chakraborty answered |
Explanation:
Aluminium phosphide is a highly toxic, colorless, and flammable gas that is used as a fumigant for stored grain and other agricultural products. When it is treated with dilute sulfuric acid, the following reaction takes place:
AlP + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H3PO4 + PH3
The main product of this reaction is phosphine gas (PH3), which is highly toxic and can cause severe respiratory and neurological effects if inhaled. The other products of the reaction are aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)3) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4).
The reaction can be explained in terms of the reactivity of aluminum phosphide and the acidity of sulfuric acid. Aluminum phosphide is a reactive compound that readily reacts with acids to produce phosphine gas. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that can donate protons to the aluminum phosphide, leading to the formation of aluminum sulfate and phosphoric acid. The phosphoric acid can further react with the remaining sulfuric acid to form more aluminum sulfate and water.
In summary, when aluminum phosphide is treated with dilute sulfuric acid, phosphine gas is evolved as the main product, along with aluminum sulfate and phosphoric acid. It is important to handle aluminum phosphide and its derivatives with caution, as they are highly toxic and pose a significant risk to human health and the environment.
Aluminium phosphide is a highly toxic, colorless, and flammable gas that is used as a fumigant for stored grain and other agricultural products. When it is treated with dilute sulfuric acid, the following reaction takes place:
AlP + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H3PO4 + PH3
The main product of this reaction is phosphine gas (PH3), which is highly toxic and can cause severe respiratory and neurological effects if inhaled. The other products of the reaction are aluminum sulfate (Al2(SO4)3) and phosphoric acid (H3PO4).
The reaction can be explained in terms of the reactivity of aluminum phosphide and the acidity of sulfuric acid. Aluminum phosphide is a reactive compound that readily reacts with acids to produce phosphine gas. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid that can donate protons to the aluminum phosphide, leading to the formation of aluminum sulfate and phosphoric acid. The phosphoric acid can further react with the remaining sulfuric acid to form more aluminum sulfate and water.
In summary, when aluminum phosphide is treated with dilute sulfuric acid, phosphine gas is evolved as the main product, along with aluminum sulfate and phosphoric acid. It is important to handle aluminum phosphide and its derivatives with caution, as they are highly toxic and pose a significant risk to human health and the environment.
A transformer is employed to reduce 220 V to 11 V. The primary draws a current of 5 A and the secondary 90 A. The efficiency of the transformer is- a)20%
- b)40%
- c)70%
- d)90%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A transformer is employed to reduce 220 V to 11 V. The primary draws a current of 5 A and the secondary 90 A. The efficiency of the transformer is
a)
20%
b)
40%
c)
70%
d)
90%

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
A transformer is employed to reduce 220 V to 11 V. The primary draws a current of 5 A and the secondary 90 A. The efficiency of the transformer is
An organic compound X give a red precipitate on heating with Fehling's solution. Which one of the following reactions yields X as a major product?- a)
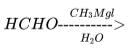
- b)
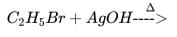
- c)
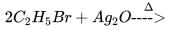
- d)
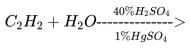
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic compound X give a red precipitate on heating with Fehling's solution. Which one of the following reactions yields X as a major product?
a)
b)
c)
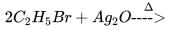
d)
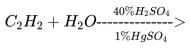
|
|
Ramakrishna Sarlana answered |
Fehlings test is given by aldehydes the only option which gives aldehyde is option D.so,the correct answer is option D.In option A) primary alcohol is formed and In option B)ethyl alcohol is formed and In option C) dieťhyl ether is formed.
Blood is brought to the glomerulus by the- a)Renal vein
- b)Afferent arteriole
- c)Efferent arteriole
- d)Peritubular capillaries
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Renal vein
b)
Afferent arteriole
c)
Efferent arteriole
d)
Peritubular capillaries
|
|
DREAM AIIMS answered |
Blood enters the glomerulus through an afferent arteriole, and exits via an efferent arteriole.
Blockages in which of the following blood vessels reduces blood flow to the heart muscle?- a)Aorta
- b)Carotid artery
- c)Coronary artery
- d)Pulmonary artery
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Aorta
b)
Carotid artery
c)
Coronary artery
d)
Pulmonary artery
|
|
Srestha Mehta answered |
Coronary Artery Blockage and Reduced Blood Flow to the Heart Muscle
Coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. When these arteries become blocked or narrowed due to plaque buildup, it can lead to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, which can result in chest pain (angina), heart attack, or even death.
Explanation:
• Aortais the largest artery in the body that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Blockages in the aorta can cause problems in different parts of the body and not specifically to the heart muscle.
• Carotid artery is a major blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain, face, and neck. Blockages in the carotid artery can lead to stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), but they do not affect the blood flow to the heart muscle.
• Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation. Blockages in the pulmonary artery can cause pulmonary embolism or other lung-related problems, but they do not affect the blood flow to the heart muscle.
• Coronary artery supplies oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. When these arteries become blocked or narrowed due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), it can cause reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. This condition is known as coronary artery disease (CAD).
• CAD can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attack, or even death. Risk factors for CAD include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, family history, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Conclusion:
Thus, blockages in the coronary artery reduce blood flow to the heart muscle, which can lead to various heart-related problems. It is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage risk factors to prevent or manage coronary artery disease.
Coronary arteries are the blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. When these arteries become blocked or narrowed due to plaque buildup, it can lead to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, which can result in chest pain (angina), heart attack, or even death.
Explanation:
• Aortais the largest artery in the body that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Blockages in the aorta can cause problems in different parts of the body and not specifically to the heart muscle.
• Carotid artery is a major blood vessel that supplies blood to the brain, face, and neck. Blockages in the carotid artery can lead to stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), but they do not affect the blood flow to the heart muscle.
• Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation. Blockages in the pulmonary artery can cause pulmonary embolism or other lung-related problems, but they do not affect the blood flow to the heart muscle.
• Coronary artery supplies oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. When these arteries become blocked or narrowed due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), it can cause reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. This condition is known as coronary artery disease (CAD).
• CAD can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, heart attack, or even death. Risk factors for CAD include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, family history, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Conclusion:
Thus, blockages in the coronary artery reduce blood flow to the heart muscle, which can lead to various heart-related problems. It is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle and manage risk factors to prevent or manage coronary artery disease.
Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude  are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be
are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be
- a)zero
- b)q/ε₀
- c)8q/ε₀
- d)16q/ε₀
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Eight dipoles of charges of magnitude  are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be
are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be
 are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will be
are placed inside a cube. The total electric flux coming out of the cube will bea)
zero
b)
q/ε₀
c)
8q/ε₀
d)
16q/ε₀

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Explanation:
- Electric Flux: The electric flux through a closed surface is given by the total electric field passing through that surface.
- Gauss's Law: According to Gauss's Law, the total electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed by that surface divided by the permittivity of free space (ε₀).
- Given Situation: In this case, there are eight dipoles of charges inside a cube. Since dipoles consist of equal and opposite charges separated by a distance, the total charge enclosed by the cube is zero.
- Total Electric Flux: Therefore, the total electric flux coming out of the cube is zero as there is no net charge enclosed.
- Therefore, the correct answer is A: zero.
According to their modes of nutrition, the fungi are classified into- a)one category
- b)two categories
- c)four categories
- d)six categories
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
one category
b)
two categories
c)
four categories
d)
six categories

|
Anshika Sharmaa answered |
Two special categories are parasitic and saprophytic form.
Which part of the reproductive structure produces both enzymes and hormones?- a)Archegonium
- b)Middle layer
- c)Tapetum
- d)Endothecium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Archegonium
b)
Middle layer
c)
Tapetum
d)
Endothecium

|
Rajni Kokate answered |
Tapetum synthesizes callase enzyme which dissolves callose. it produces many hormones ,amino acids and nutritious substances that are needed for pollen grains.
Which is the chiral molecule?- a)CH₃Cl
- b)CH₂Cl₂
- c)CHBr₃
- d)CHClBrI
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
CH₃Cl
b)
CH₂Cl₂
c)
CHBr₃
d)
CHClBrI
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
CHClBrI is a chiral molecule as all the four groups attached to the carbon are diff...option D
The winged pollen grains of Pinus sp. are produced in-- a)Pollen chamber
- b)Tapetum
- c)Anther
- d)Microsporangium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Pollen chamber
b)
Tapetum
c)
Anther
d)
Microsporangium
|
|
Kaneez Fatima answered |
These pollen grains or microgametophytes are born through meiotic division of the microsporocytes or pollen mother cells within the microsporangium.
A 5000 kg rocket is set for vertical firing. The exhaust speed is 800 ms⁻1. To give an initial upward accleration of 20 ms⁻2. the amount of gas ejected per second to supply the needed thrust will be (g=10 ms⁻2)- a)127.5 kg s⁻1
- b)187.5 kg s⁻1
- c)185.5 kg s⁻1
- d)137.5 kg s⁻1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 5000 kg rocket is set for vertical firing. The exhaust speed is 800 ms⁻1. To give an initial upward accleration of 20 ms⁻2. the amount of gas ejected per second to supply the needed thrust will be (g=10 ms⁻2)
a)
127.5 kg s⁻1
b)
187.5 kg s⁻1
c)
185.5 kg s⁻1
d)
137.5 kg s⁻1
|
|
Shatabdi Malik answered |

During DNA replication, the strands separate by- a)DNA polymerase
- b)Topoisomerase
- c)Unwindase/Helicase
- d)Gyrase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
DNA polymerase
b)
Topoisomerase
c)
Unwindase/Helicase
d)
Gyrase

|
Smrity answered |
Helicase is enzyme which uses energy and break the hydrogen bonds and create replication fork. and hence separate DNA strands.
Benzene is used in the preparation of- a) Polythene
- b) Gammaxene
- c) Chloroform
- d) Vinegar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Polythene
b)
Gammaxene
c)
Chloroform
d)
Vinegar
|
|
Krithika Sharma answered |
Benzene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H6. It is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet odor. Benzene is extensively used in the chemical industry as a solvent, as a starting material for the synthesis of various chemicals, and as a raw material for the manufacture of plastics, synthetic fibers, rubber, dyes, and pharmaceuticals.
Preparation of Gammaxene from Benzene:
Gammaxene is a type of insecticide that is derived from benzene. It is prepared by the following steps:
1. Nitration: Benzene is first nitrated with a mixture of concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids to form nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2).
2. Reduction: The nitro group in nitrobenzene is then reduced by using metallic zinc and hydrochloric acid to form aniline (C6H5NH2).
3. Diazotization: Aniline is diazotized with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid to form diazonium chloride.
4. Coupling: The diazonium chloride is then coupled with gamma-resorcylaldehyde to form gammaxene (C18H12O2N2).
Thus, benzene is used in the preparation of gammaxene by a series of chemical reactions.
Preparation of Gammaxene from Benzene:
Gammaxene is a type of insecticide that is derived from benzene. It is prepared by the following steps:
1. Nitration: Benzene is first nitrated with a mixture of concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids to form nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2).
2. Reduction: The nitro group in nitrobenzene is then reduced by using metallic zinc and hydrochloric acid to form aniline (C6H5NH2).
3. Diazotization: Aniline is diazotized with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid to form diazonium chloride.
4. Coupling: The diazonium chloride is then coupled with gamma-resorcylaldehyde to form gammaxene (C18H12O2N2).
Thus, benzene is used in the preparation of gammaxene by a series of chemical reactions.
Which of the following type of reproduction occurs in sponges?
- a)Fission
- b)Budding
- c)Fragmentation
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following type of reproduction occurs in sponges?
a)
Fission
b)
Budding
c)
Fragmentation
d)
None of these
|
|
Vandana Chakraborty answered |
Fragmentation is the type of reproduction that occurs in sponges.
Explanation:
Sponges are multicellular aquatic animals that belong to the phylum Porifera. They are sessile and exhibit a wide range of body forms. Sponges reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction in sponges can occur by fragmentation.
In fragmentation, a sponge breaks up into small pieces due to physical disturbances such as wave action or predation. These small pieces are called fragments, and each fragment is capable of regenerating into a complete individual sponge. The process of regeneration involves the reorganization of the cells and tissues of the fragment into a new sponge.
Fragmentation is a common mode of reproduction in sponges, especially in species that have a high degree of flexibility and can withstand physical disturbances. It allows sponges to colonize new areas quickly and efficiently.
In addition to fragmentation, sponges can also reproduce asexually by budding, which involves the development of new individuals from outgrowths of the parent sponge. However, budding is less common in sponges than fragmentation.
Overall, fragmentation is the primary mode of asexual reproduction in sponges, and it plays an important role in their ecology and evolution.
Explanation:
Sponges are multicellular aquatic animals that belong to the phylum Porifera. They are sessile and exhibit a wide range of body forms. Sponges reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction in sponges can occur by fragmentation.
In fragmentation, a sponge breaks up into small pieces due to physical disturbances such as wave action or predation. These small pieces are called fragments, and each fragment is capable of regenerating into a complete individual sponge. The process of regeneration involves the reorganization of the cells and tissues of the fragment into a new sponge.
Fragmentation is a common mode of reproduction in sponges, especially in species that have a high degree of flexibility and can withstand physical disturbances. It allows sponges to colonize new areas quickly and efficiently.
In addition to fragmentation, sponges can also reproduce asexually by budding, which involves the development of new individuals from outgrowths of the parent sponge. However, budding is less common in sponges than fragmentation.
Overall, fragmentation is the primary mode of asexual reproduction in sponges, and it plays an important role in their ecology and evolution.
Mitotic anaphase differs from metaphase in possessing- a)Same number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
- b)Half number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
- c)Half number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
- d)Same number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Same number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
b)
Half number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
c)
Half number of chromosomes and same number of chromatids
d)
Same number of chromosomes and half number of chromatids
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
D) Same number of chromosome and half number of chromatids - each chromosome separates into its two chromatids at anaphase.
Which conformation for ethane has the lowest potential energy?- a) eclipsed
- b) staggered
- c) skew
- d) all have equal Potential Energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
eclipsed
b)
staggered
c)
skew
d)
all have equal Potential Energy
|
|
Vandana Yadav answered |
Explanation:
Ethane is a hydrocarbon that consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. The carbon-carbon bond in ethane is a single bond, which allows for free rotation around the axis of the bond. This free rotation leads to different conformations of ethane, which are defined by the orientation of the hydrogen atoms relative to each other.
The three most common conformations of ethane are eclipsed, staggered, and skew. The potential energy of each conformation is related to the repulsion between the electron clouds of the atoms in the molecule.
Staggered conformation has the lowest potential energy:
The staggered conformation is the most stable conformation of ethane. In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms on one carbon atom are oriented in the opposite direction to the hydrogen atoms on the other carbon atom. This orientation leads to the lowest possible electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Eclipsed conformation has higher potential energy:
The eclipsed conformation is the least stable conformation of ethane. In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms on one carbon atom are oriented directly above the hydrogen atoms on the other carbon atom. This orientation leads to the highest possible electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Skew conformation has intermediate potential energy:
The skew conformation is an intermediate conformation between the staggered and eclipsed conformations. In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms on one carbon atom are oriented at a 60-degree angle to the hydrogen atoms on the other carbon atom. This orientation leads to an intermediate level of electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the staggered conformation has the lowest potential energy because it has the lowest electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms. The eclipsed conformation has the highest potential energy because it has the highest electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms. The skew conformation has an intermediate potential energy because it has an intermediate level of electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Ethane is a hydrocarbon that consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. The carbon-carbon bond in ethane is a single bond, which allows for free rotation around the axis of the bond. This free rotation leads to different conformations of ethane, which are defined by the orientation of the hydrogen atoms relative to each other.
The three most common conformations of ethane are eclipsed, staggered, and skew. The potential energy of each conformation is related to the repulsion between the electron clouds of the atoms in the molecule.
Staggered conformation has the lowest potential energy:
The staggered conformation is the most stable conformation of ethane. In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms on one carbon atom are oriented in the opposite direction to the hydrogen atoms on the other carbon atom. This orientation leads to the lowest possible electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Eclipsed conformation has higher potential energy:
The eclipsed conformation is the least stable conformation of ethane. In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms on one carbon atom are oriented directly above the hydrogen atoms on the other carbon atom. This orientation leads to the highest possible electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Skew conformation has intermediate potential energy:
The skew conformation is an intermediate conformation between the staggered and eclipsed conformations. In this conformation, the hydrogen atoms on one carbon atom are oriented at a 60-degree angle to the hydrogen atoms on the other carbon atom. This orientation leads to an intermediate level of electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the staggered conformation has the lowest potential energy because it has the lowest electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms. The eclipsed conformation has the highest potential energy because it has the highest electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms. The skew conformation has an intermediate potential energy because it has an intermediate level of electron cloud repulsion between the two carbon atoms.
The force constant of a weightless spring is 16 N/m. A body of mass 1.0 Kg suspended from it is pulled down through 5 cm and then released. The maximum kinetic energy of the system will be- a)2 x 10⁻2 J
- b)4 x 10⁻2 J
- c)8 x 10⁻2 J
- d)16 x 10⁻2 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The force constant of a weightless spring is 16 N/m. A body of mass 1.0 Kg suspended from it is pulled down through 5 cm and then released. The maximum kinetic energy of the system will be
a)
2 x 10⁻2 J
b)
4 x 10⁻2 J
c)
8 x 10⁻2 J
d)
16 x 10⁻2 J
|
|
Shatabdi Malik answered |
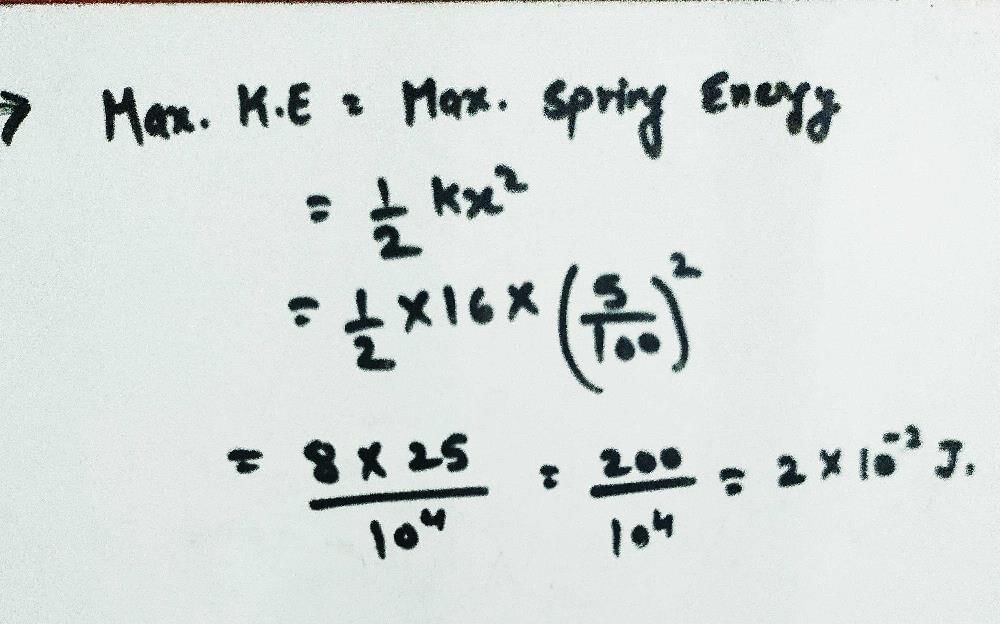
The IUPAC name of the compound having the molecular formula Cl₃C-CH₂CHO is- a)3,3,3-Trichloropropanal
- b)1,1,1-Trichloropropanal
- c)2,2,2-Trichloropropanal
- d)Chloral
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
3,3,3-Trichloropropanal
b)
1,1,1-Trichloropropanal
c)
2,2,2-Trichloropropanal
d)
Chloral
|
|
Sai Nikhil answered |
According to the IUPAC nomenclature we give preference to the functional group so no. should be from right to left at 1st position CHO gp mean aldehyde give 'al'at last position 3C so propanal at 3rd position cl go is present so name is''3,3,3trichloropropanal
Mitosis can be studied in- a)Onion root tip
- b)Garlic root tip
- c)Tendril tip
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Onion root tip
b)
Garlic root tip
c)
Tendril tip
d)
All the above
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
► Cell division is the basic requirement for the growth and development of the body, if the cells top dividing the body will eventually die.
There are two types of cell divisions:
- One occurs in the gamete cell and is necessary for reproduction as this cell division leads to genetic material exchange, this is meiosis or the reductional division.
- The other one is mitosis also known as Equational division which occurs in the somatic cells of the body and this cell division is employed in the repair of the body and increasing the number of cells for growth and development.
► In plants, mitosis occurs in the meristems which have the ability to divide continuously.
Meristems in plants are of two types:
- Apical meristems which are present on the tips of roots and shoots and they help in the elongation of length of the plant.
- The other is lateral meristem which helps in increasing the width of the plant.
Plants don’t repair or replace their damaged parts like leaves, branches but for new ones due to the continuous production of new cells in the meristems.
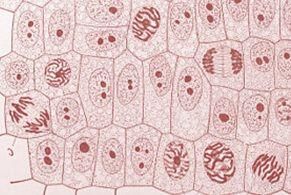
Mitosis in Onion Root Tips:
Three resistors each of 2 ohm are connected together in a triangular shape. The resistance between any two vertices will be- a) 4/3 ohm
- b) 3/4 ohm
- c) 3 ohm
- d) 6 ohm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
4/3 ohm
b)
3/4 ohm
c)
3 ohm
d)
6 ohm
|
|
Tajamul Akhter answered |
4/3 ohm....two are in series and 3rd one is parallel...m
If only 2% of the main current is to be passed through a galvanometer of resistance G, then the resistance of shunt will be- a)G/50
- b)G/49
- c)50 G
- d)49 G
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
G/50
b)
G/49
c)
50 G
d)
49 G
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Let total current through the circuit be I.
Then, 0.02I current is to be passed through galvanometer of resistance G.
Let the resistance of shunt is Rs .
∵ Shunt are in parallel combination with Galvanometer.
∴ 0.02I X G = (1 - 0.02)I X Rs
⇒0.02G = 0.98 X Rs
⇒Rs = 0.02G/0.98 = G/49
Hence answer is G/49
Water falls from a height of 210 m. Assuming whole of energy due to fall is converted into heat the rise in temperature of water would be (J = 4.3 Joule/cal)- a)42oC
- b)49oC
- c)0.49oC
- d)4.9oC
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Water falls from a height of 210 m. Assuming whole of energy due to fall is converted into heat the rise in temperature of water would be (J = 4.3 Joule/cal)
a)
42oC
b)
49oC
c)
0.49oC
d)
4.9oC
|
|
Stuti Sen answered |
Given:
Height of water fall, h = 210 m
Energy due to fall is converted into heat.
J = 4.3 Joule/cal
To find: Rise in temperature of water
Solution:
The potential energy of water at height h is given by the formula,
Potential Energy = mgh
where m is the mass of water, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of water fall.
According to the question, the potential energy of water is converted into heat energy. The heat energy required to raise the temperature of water by ΔT is given by the formula,
Heat Energy = mCΔT
where C is the specific heat capacity of water.
Equating the potential energy and heat energy, we get
mgh = mCΔT
Simplifying the above equation, we get
ΔT = gh/C
Substituting the given values, we get
ΔT = (210 x 9.8)/(1 x 4.3 x 10^3)
ΔT = 0.49°C
Therefore, the rise in temperature of water is 0.49°C.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Height of water fall, h = 210 m
Energy due to fall is converted into heat.
J = 4.3 Joule/cal
To find: Rise in temperature of water
Solution:
The potential energy of water at height h is given by the formula,
Potential Energy = mgh
where m is the mass of water, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of water fall.
According to the question, the potential energy of water is converted into heat energy. The heat energy required to raise the temperature of water by ΔT is given by the formula,
Heat Energy = mCΔT
where C is the specific heat capacity of water.
Equating the potential energy and heat energy, we get
mgh = mCΔT
Simplifying the above equation, we get
ΔT = gh/C
Substituting the given values, we get
ΔT = (210 x 9.8)/(1 x 4.3 x 10^3)
ΔT = 0.49°C
Therefore, the rise in temperature of water is 0.49°C.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
The current flowing through a wire depends on time as I = 3t2 + 2t +5. The charge flowing through the cross-section of the wire in time from t = 0 to t = 2 sec. is
- a)22C
- b)20C
- c)18C
- d)5C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The current flowing through a wire depends on time as I = 3t2 + 2t +5. The charge flowing through the cross-section of the wire in time from t = 0 to t = 2 sec. is
a)
22C
b)
20C
c)
18C
d)
5C

|
Top Rankers answered |
Explanation:
Given:
- Current flowing through the wire: I = 3t2 + 2t + 5
- Time interval: t = 0 to t = 2 sec
Charge Flowing Through the Cross-Section of the Wire:
- The charge flowing through the wire is given by the integral of current with respect to time.
- Q = ∫(3t2 + 2t + 5) dt
- Q = [t3 + t2 + 5t] evaluated from t = 0 to t = 2 sec
- Q = [(2)3 + (2)2 + 5(2)] - [(0)3 + (0)2 + 5(0)]
- Q = [8 + 4 + 10] - [0 + 0 + 0]
- Q = 22 C
Therefore, the charge flowing through the cross-section of the wire from t = 0 to t = 2 sec is 22 Coulombs. Hence, the correct answer is A: 22C.
Given:
- Current flowing through the wire: I = 3t2 + 2t + 5
- Time interval: t = 0 to t = 2 sec
Charge Flowing Through the Cross-Section of the Wire:
- The charge flowing through the wire is given by the integral of current with respect to time.
- Q = ∫(3t2 + 2t + 5) dt
- Q = [t3 + t2 + 5t] evaluated from t = 0 to t = 2 sec
- Q = [(2)3 + (2)2 + 5(2)] - [(0)3 + (0)2 + 5(0)]
- Q = [8 + 4 + 10] - [0 + 0 + 0]
- Q = 22 C
Therefore, the charge flowing through the cross-section of the wire from t = 0 to t = 2 sec is 22 Coulombs. Hence, the correct answer is A: 22C.
During which phase of meiosis homologous chromosomes separate ?- a)metaphase-I
- b)anaphase-I
- c)prophase-II
- d)telophase-II
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
metaphase-I
b)
anaphase-I
c)
prophase-II
d)
telophase-II
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Answer: B. Anaphase-I
Explanation:
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate during Anaphase-I. Meiosis is a two-step process, consisting of Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
Meiosis I:
- Prophase-I: Chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes pair up, and crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids.
- Metaphase-I: Homologous chromosome pairs align at the equatorial plate.
- Anaphase-I: Homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
- This is the phase where the answer lies, as homologous chromosomes separate during this phase.
- Telophase-I: Chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, nuclear envelope reforms, and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Meiosis II:
- Prophase-II: Chromosomes condense again, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase-II: Individual chromosomes align at the equatorial plate.
- Anaphase-II: Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase-II: Chromatids reach the poles of the cell, nuclear envelope reforms, and the cells divide, resulting in four genetically unique haploid cells.
Explanation:
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate during Anaphase-I. Meiosis is a two-step process, consisting of Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
Meiosis I:
- Prophase-I: Chromosomes condense, homologous chromosomes pair up, and crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids.
- Metaphase-I: Homologous chromosome pairs align at the equatorial plate.
- Anaphase-I: Homologous chromosomes separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
- This is the phase where the answer lies, as homologous chromosomes separate during this phase.
- Telophase-I: Chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, nuclear envelope reforms, and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Meiosis II:
- Prophase-II: Chromosomes condense again, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase-II: Individual chromosomes align at the equatorial plate.
- Anaphase-II: Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase-II: Chromatids reach the poles of the cell, nuclear envelope reforms, and the cells divide, resulting in four genetically unique haploid cells.
Muscles immune to fatigue are- a) Cardiac
- b) Eye muscles
- c) Unstriated
- d) Skeletal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Cardiac
b)
Eye muscles
c)
Unstriated
d)
Skeletal
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Cardiac muscle resists fatigue so well because it's got more mitochondria than skeletal muscle. With so many power plants at its disposal, the heart doesn't need to stop and chill out. It also has a steady supply of blood bringing it oxygen and nutrients.
The first ionisation potentials of four consecutive elements, present in the second period of the periodic table are 8.3, 11.3, 14.5 and 13.6 eV respectively. Which one of the following is the first ionisation potential (in eV) of nitrogen?- a) 13.6
- b) 11.3
- c) 8.3
- d) 14.5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
13.6
b)
11.3
c)
8.3
d)
14.5

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
Nitrogen has highest ionization potential so 14.5 eV will be the first ionization enthalpy of Nitrogen.
Light energy is changed to chemical energy in the process of- a) Bioluminescence
- b) Photosynthesis
- c) Both A and B
- d) Photorespiration
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bioluminescence
b)
Photosynthesis
c)
Both A and B
d)
Photorespiration
|
|
Debanshi Pillai answered |
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy that can be used to fuel cellular activities. It is the only process by which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and oxygen is released into the environment.
The process of photosynthesis can be broken down into two stages:
1. Light-dependent reactions: In this stage, light energy is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These energy-rich molecules are used to power the next stage of photosynthesis.
2. Light-independent reactions: In this stage, also known as the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules such as glucose using the energy stored in ATP and NADPH. This process occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts and does not require light.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option B, photosynthesis. Bioluminescence is a different process in which living organisms produce light through chemical reactions. Photorespiration is a process that occurs in plants when there is a shortage of carbon dioxide and excess oxygen in the environment. It is not related to the conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
The process of photosynthesis can be broken down into two stages:
1. Light-dependent reactions: In this stage, light energy is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These energy-rich molecules are used to power the next stage of photosynthesis.
2. Light-independent reactions: In this stage, also known as the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is fixed into organic molecules such as glucose using the energy stored in ATP and NADPH. This process occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts and does not require light.
Therefore, the correct answer to the given question is option B, photosynthesis. Bioluminescence is a different process in which living organisms produce light through chemical reactions. Photorespiration is a process that occurs in plants when there is a shortage of carbon dioxide and excess oxygen in the environment. It is not related to the conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
Which of the following has molecular weight of 92?
- a)Toluene
- b)Benzene
- c)Methylene
- d)Propene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has molecular weight of 92?
a)
Toluene
b)
Benzene
c)
Methylene
d)
Propene

|
Himanshu Dubey answered |
Toluene has formula c7h8 or c6h5ch3
mass of c is 12 and h is 1
hence 12×7=84 &8×1=8
84+8=92
mass of c is 12 and h is 1
hence 12×7=84 &8×1=8
84+8=92
Cellular structure which always disappears during mitosis and meiosis is- a)Plastids
- b)Nucleolus and nuclear envelope
- c)Plasma membrane
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Plastids
b)
Nucleolus and nuclear envelope
c)
Plasma membrane
d)
None of the above
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Explanation:The correct answer is B: Nucleolus and nuclear envelope. During mitosis and meiosis, the cellular structure that always disappears is the nucleolus and nuclear envelope. This is because these structures need to break down to allow the chromosomes to separate and be distributed to the new cells formed during cell division.Here's a brief overview of their roles and what happens during cell division:Nucleolus:- It is a small, dense structure within the nucleus of a cell.- Its primary function is to produce ribosomes, which are essential for protein synthesis.- During the prophase of mitosis and meiosis, the nucleolus disassembles, and its components are dispersed throughout the cell.Nuclear envelope:- It is a double membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell.- It separates the genetic material within the nucleus from the cytoplasm of the cell.- During the prophase of mitosis and meiosis, the nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing the chromosomes to be accessed by the spindle fibers that will separate them during cell division.In summary, the nucleolus and nuclear envelope are cellular structures that always disappear during mitosis and meiosis to facilitate the process of cell division.
The most stable hydride is- a)NH₃
- b)PH₃
- c)AsH₃
- d)SbH₃
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
NH₃
b)
PH₃
c)
AsH₃
d)
SbH₃
|
|
Raiyan Zaib answered |
See---
is the most stable hydride among the hydrides of group 15 elements because the strength of E-H (Here E = N, P, As, Sb, or Br) bond decreases down the group due to increase in size of the central atom
es NH3 is more basic than PH3 as NH3 has more density of electron. Owing it to the small size of nitrogen and small P orbitals it has the ability to form stronger bonds due to effective overlap. In PH3 however, the large size of P results in the P orbitals becoming diffused preventing effective
is the most stable hydride among the hydrides of group 15 elements because the strength of E-H (Here E = N, P, As, Sb, or Br) bond decreases down the group due to increase in size of the central atom
es NH3 is more basic than PH3 as NH3 has more density of electron. Owing it to the small size of nitrogen and small P orbitals it has the ability to form stronger bonds due to effective overlap. In PH3 however, the large size of P results in the P orbitals becoming diffused preventing effective
Two bodies having same mass 40 kg are moving in opposite directions, one with a velocity of 10 m/s and the other with 7 m/s. If they collide elastically and move as one body, the velocity of the combination is- a)10 m/s
- b)7 m/s
- c)3 m/s
- d)1.5 m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
10 m/s
b)
7 m/s
c)
3 m/s
d)
1.5 m/s
|
|
Yashnavi Jamhoriya answered |

Chapter doubts & questions for Subject Wise Mock Test - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Subject Wise Mock Test - 1 Year Dropper Course for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup