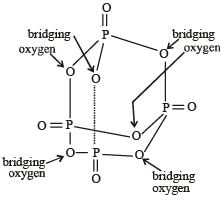
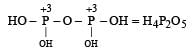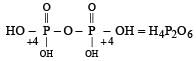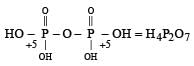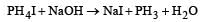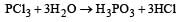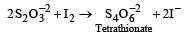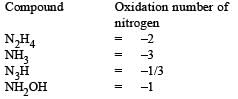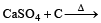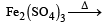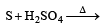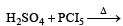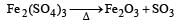All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers >
All Questions
All questions of The p-Block Elements (Group 15, 16, 17 and 18) for NEET Exam
Which is the strongest acid in the following : [NEET 2013]- a)HClO3
- b)HClO4
- c)H2SO3
- d)H2SO4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the strongest acid in the following : [NEET 2013]
a)
HClO3
b)
HClO4
c)
H2SO3
d)
H2SO4

|
Surbhi Das answered |
HClO4 is the strongest acid amongst all because the oxidation state or Cl is maximum (+7).
Which of the following is a polar molecule ? [NEET 2013]- a)SF4
- b)SiF4
- c)XeF4
- d)BF3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a polar molecule ? [NEET 2013]
a)
SF4
b)
SiF4
c)
XeF4
d)
BF3

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
SF4 has 4 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons, sp3d hybridisation leads to irregular shape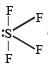 and resultant
and resultant
 and resultant
and resultantμ ≠ 0.
Each of the following is true about white and red phosphorus except that they [1989]- a)Are both soluble in CS2
- b)Can be oxidised by heating in air
- c)Consist of the same kind of atoms
- d)Can be converted into one another
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Each of the following is true about white and red phosphorus except that they [1989]
a)
Are both soluble in CS2
b)
Can be oxidised by heating in air
c)
Consist of the same kind of atoms
d)
Can be converted into one another

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Both white and red phosphorus are not soluble in CS2 only white P is soluble.
Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent? [2009]- a)Br2
- b)I2
- c)Cl2
- d)F2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following which is the strongest oxidising agent? [2009]
a)
Br2
b)
I2
c)
Cl2
d)
F2

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Standard reduction potential of halogens are positive and decreases from fluorine to iodine. Therefore halogens act as strong oxidising agent and their oxidising power decreases from fluorine to iodine.
It is possible to obtain oxygen from air by fractional distillation because [1989]- a)oxygen is in a different group of the periodic table from nitrogen
- b)oxygen is more reactive than nitrogen
- c)oxygen has higher b.p. than nitrogen
- d)oxygen has a lower density than nitrogen.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
It is possible to obtain oxygen from air by fractional distillation because [1989]
a)
oxygen is in a different group of the periodic table from nitrogen
b)
oxygen is more reactive than nitrogen
c)
oxygen has higher b.p. than nitrogen
d)
oxygen has a lower density than nitrogen.

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
Air is liquified by making use of the jouleThomson effect (cooling by expansion of the gas). Water vapour and CO2 are removed by solidification. The remaining constituents of liquid air i.e., liquid oxygen and liquid nitrogen are separated by means of fractional distillation (b.p. of O2 = –183°C : b. P. of N2 = – 195.8°C).
Which of the following is the most basic oxide?- a)Sb2O3
- b)Bi2O3 [2006]
- c)SeO2
- d)Al2O3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the most basic oxide?
a)
Sb2O3
b)
Bi2O3 [2006]
c)
SeO2
d)
Al2O3

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
More the oxidation state of the central atom (metal) more is its acidity. Hence SeO2 (O. S. of Se = +4) is acidic. Further for a given O.S., the basic character of the oxides increases with the increasing size of the central atom.
Thus Al2O3 and Sb2O3 are amphoteric and Bi2O3 is basic.
Thus Al2O3 and Sb2O3 are amphoteric and Bi2O3 is basic.
Noble gases do not react with other elements because [1994]- a)They are mono atomic
- b)They are found in abundance
- c)The size of their atoms is very small
- d)They are completely paired up and stable electron shells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Noble gases do not react with other elements because [1994]
a)
They are mono atomic
b)
They are found in abundance
c)
The size of their atoms is very small
d)
They are completely paired up and stable electron shells

|
Abhishek Desai answered |
On account of highly stable ns2 np6 configuration in the valence shell. These elements have no tendency either to lose gain or share electrons with atoms of other elements i.e., their combining capacity or valency is zero. Further all the orbitals in the atoms of these elements are doubly occupied i.e electrons are not available for sharing.
In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order: [2009]- a)MF > MCl > MBr > MI
- b)MF > MCl > MI > MBr
- c)MI > MBr > MCl > MF
- d)MCl > MI > MBr > MF
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the case of alkali metals, the covalent character decreases in the order: [2009]
a)
MF > MCl > MBr > MI
b)
MF > MCl > MI > MBr
c)
MI > MBr > MCl > MF
d)
MCl > MI > MBr > MF

|
Ruchi Chopra answered |
MI > MBr > MCl > MF. As the size of the anion decreases covalency decreases.
The formula for calcium chlorite is [1994]- a)Ca(ClO4)2
- b)Ca(ClO3)2
- c)CaClO2
- d)Ca(ClO2)2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for calcium chlorite is [1994]
a)
Ca(ClO4)2
b)
Ca(ClO3)2
c)
CaClO2
d)
Ca(ClO2)2
|
|
Shraddha Choudhury answered |
The formula for calcium chlorite is Ca(ClO2)2. Let's break down the components of this compound to understand why this is the correct formula.
Calcium:
- Calcium is a metal with a +2 charge. It is represented by the symbol Ca in the periodic table.
Chlorite:
- Chlorite is a polyatomic ion with the formula ClO2-. It consists of one chlorine atom (Cl) bonded to two oxygen atoms (O), and it carries a -1 charge.
Formation of calcium chlorite:
- When calcium reacts with chlorite, the calcium ion (Ca2+) combines with two chlorite ions (ClO2-) to form calcium chlorite (Ca(ClO2)2).
- The calcium ion has a +2 charge, while each chlorite ion has a -1 charge. To balance the charges, two chlorite ions are needed for every calcium ion.
Explanation of options:
a) Ca(ClO4)2:
- This formula represents calcium perchlorate, not calcium chlorite. Perchlorate is a different polyatomic ion that consists of one chlorine atom and four oxygen atoms.
b) Ca(ClO3)2:
- This formula represents calcium chlorate, not calcium chlorite. Chlorate is another polyatomic ion that consists of one chlorine atom and three oxygen atoms.
c) CaClO2:
- This formula represents calcium hypochlorite, not calcium chlorite. Hypochlorite is a different polyatomic ion that consists of one chlorine atom and two oxygen atoms.
d) Ca(ClO2)2:
- This formula represents calcium chlorite, which is the correct compound. It consists of one calcium ion (Ca2+) bonded to two chlorite ions (ClO2-).
In summary, the correct formula for calcium chlorite is Ca(ClO2)2, as it consists of one calcium ion bonded to two chlorite ions.
Calcium:
- Calcium is a metal with a +2 charge. It is represented by the symbol Ca in the periodic table.
Chlorite:
- Chlorite is a polyatomic ion with the formula ClO2-. It consists of one chlorine atom (Cl) bonded to two oxygen atoms (O), and it carries a -1 charge.
Formation of calcium chlorite:
- When calcium reacts with chlorite, the calcium ion (Ca2+) combines with two chlorite ions (ClO2-) to form calcium chlorite (Ca(ClO2)2).
- The calcium ion has a +2 charge, while each chlorite ion has a -1 charge. To balance the charges, two chlorite ions are needed for every calcium ion.
Explanation of options:
a) Ca(ClO4)2:
- This formula represents calcium perchlorate, not calcium chlorite. Perchlorate is a different polyatomic ion that consists of one chlorine atom and four oxygen atoms.
b) Ca(ClO3)2:
- This formula represents calcium chlorate, not calcium chlorite. Chlorate is another polyatomic ion that consists of one chlorine atom and three oxygen atoms.
c) CaClO2:
- This formula represents calcium hypochlorite, not calcium chlorite. Hypochlorite is a different polyatomic ion that consists of one chlorine atom and two oxygen atoms.
d) Ca(ClO2)2:
- This formula represents calcium chlorite, which is the correct compound. It consists of one calcium ion (Ca2+) bonded to two chlorite ions (ClO2-).
In summary, the correct formula for calcium chlorite is Ca(ClO2)2, as it consists of one calcium ion bonded to two chlorite ions.
Oxygen will directly react with each of th e following elements except [1989]- a)P
- b)Cl
- c)Na
- d)S.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen will directly react with each of th e following elements except [1989]
a)
P
b)
Cl
c)
Na
d)
S.

|
Surbhi Das answered |
 (burns with blue light)
(burns with blue light) (burns with yellow light)
(burns with yellow light)
Chlorine does not react directly with oxygen.
The bleaching action of chlorine is due to [1991]- a)Reduction
- b)Hydrogenation
- c)Chlorination
- d)Oxidation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The bleaching action of chlorine is due to [1991]
a)
Reduction
b)
Hydrogenation
c)
Chlorination
d)
Oxidation

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Bleaching action of chlorine is due to oxidation in presence of moisture. It is permanent
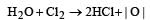
Colouring matter + | O | → colourless matter
Which one of the following arrangements does not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it ? [2008]- a)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidizing power
- b)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electron gain enthalpy
- c)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
- d)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity.
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements does not give the correct picture of the trends indicated against it ? [2008]
a)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidizing power
b)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electron gain enthalpy
c)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
d)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity.
|
|
Nisha Pillai answered |
From the given options we find option (a) is correct. The oxidising power of halogens follow the order F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 . Option (b) is incorrect because it in not the correct order of electron gain enthalpy of halogens. The correct order is Cl2 > F2 > Br2 > I2 . The low value of F2 than Cl2 is due to its small size. Option (c) is incorrect. The correct order of bond dissociation energies of halogens is Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2 . Option (d) is correct. It is the correct order of electronegativity values of halogens. Thus option (b) and (c) are incorrect.
Which one of the following arrangements does not truly represent the property indicated against it?[2000]- a)Br2 < Cl2 < F2 : Electronegativity
- b)Br2 < F2 < Cl2 : Electron affinity
- c)Br2 < Cl2 < F2 : Bond energy
- d)Br2 < Cl2 < F2 : Oxidising power
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following arrangements does not truly represent the property indicated against it?[2000]
a)
Br2 < Cl2 < F2 : Electronegativity
b)
Br2 < F2 < Cl2 : Electron affinity
c)
Br2 < Cl2 < F2 : Bond energy
d)
Br2 < Cl2 < F2 : Oxidising power

|
Krish Khanna answered |
The bond energy of F2 < Cl2 due to more repulsion in between non-bonding electrons (2p) of F2 in comparision to non- bonding pair (3p) repulsion in Cl2, the bond energy of F2 < Cl2.
Bond energy (kJ mol–1) :
Bond energy (kJ mol–1) :

Bleaching powder reacts with a few drops of dilute HCl to give [1989]- a)chlorine
- b)hypochlorous acid
- c)calcium oxide
- d)oxygen
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bleaching powder reacts with a few drops of dilute HCl to give [1989]
a)
chlorine
b)
hypochlorous acid
c)
calcium oxide
d)
oxygen
|
|
Abhijeet Menon answered |
Bleaching powder, also known as calcium hypochlorite, is a chemical compound that is widely used as a bleaching agent and disinfectant. It reacts with a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) to produce chlorine gas (Cl2). Let's understand the reaction in detail:
1. Chemical equation:
Ca(OCl)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + Cl2
2. Reactants:
- Bleaching powder (Ca(OCl)2): It contains calcium hypochlorite, which is the active ingredient. It is a yellowish-white powder that is highly soluble in water.
- Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl): It is a strong acid commonly used in laboratories. It is a clear, colorless liquid with a pungent odor.
3. Reaction process:
- When bleaching powder is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, the following reaction takes place:
Ca(OCl)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + Cl2
- The calcium hypochlorite in bleaching powder reacts with hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride (CaCl2), water (H2O), and chlorine gas (Cl2).
- This reaction is a redox reaction, where calcium hypochlorite acts as the reducing agent by losing electrons, and hydrochloric acid acts as the oxidizing agent by gaining electrons.
4. Chlorine gas production:
- The main product of the reaction is chlorine gas (Cl2).
- Chlorine gas is a greenish-yellow gas with a strong odor and is highly toxic.
- It is widely used in water treatment, disinfection, and as a bleaching agent for textiles, paper, and other materials.
Therefore, when bleaching powder reacts with a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid, it produces chlorine gas as the main product. Chlorine (option A) is the correct answer.
1. Chemical equation:
Ca(OCl)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + Cl2
2. Reactants:
- Bleaching powder (Ca(OCl)2): It contains calcium hypochlorite, which is the active ingredient. It is a yellowish-white powder that is highly soluble in water.
- Dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl): It is a strong acid commonly used in laboratories. It is a clear, colorless liquid with a pungent odor.
3. Reaction process:
- When bleaching powder is added to dilute hydrochloric acid, the following reaction takes place:
Ca(OCl)2 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + Cl2
- The calcium hypochlorite in bleaching powder reacts with hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride (CaCl2), water (H2O), and chlorine gas (Cl2).
- This reaction is a redox reaction, where calcium hypochlorite acts as the reducing agent by losing electrons, and hydrochloric acid acts as the oxidizing agent by gaining electrons.
4. Chlorine gas production:
- The main product of the reaction is chlorine gas (Cl2).
- Chlorine gas is a greenish-yellow gas with a strong odor and is highly toxic.
- It is widely used in water treatment, disinfection, and as a bleaching agent for textiles, paper, and other materials.
Therefore, when bleaching powder reacts with a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid, it produces chlorine gas as the main product. Chlorine (option A) is the correct answer.
Hypo is used in photography to [1988]- a)Reduce AgBr grains to metallic silver
- b)Convert metallic silver to silver salt
- c)Remove undecomposed silver bromide as a soluble complex
- d)Remove reduced silver
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hypo is used in photography to [1988]
a)
Reduce AgBr grains to metallic silver
b)
Convert metallic silver to silver salt
c)
Remove undecomposed silver bromide as a soluble complex
d)
Remove reduced silver

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
Undecomposed AgBr forms a soluble complex with hypo
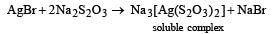
It is washed with water and the image is fixed
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]- a)Hydrogen iodide
- b)Sulphur dioxide
- c)chlorine
- d)Iodine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution of potassium bromide is treated with each of the following. Which one would liberate bromine ? [1993]
a)
Hydrogen iodide
b)
Sulphur dioxide
c)
chlorine
d)
Iodine

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
A stronger oxidising agent (Cl2) displaces a weaker oxidising agent (Br2) from its salt solution.
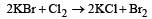
Polyanion formation is maximum in [1994]- a)Nitrogen
- b)Oxygen
- c)Sulphur
- d)Boron
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Polyanion formation is maximum in [1994]
a)
Nitrogen
b)
Oxygen
c)
Sulphur
d)
Boron

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Due to greater tendency for catenation, sulphur shows property of polyanion formation to a greater extent. For example, in polysulphides such as 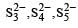
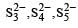
Which of the following oxy-acids has the maximum number of hydrogens directly attached to phosphorus? [1999]- a)H4P2O7
- b)H3PO2
- c)H3PO3
- d)H3PO4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following oxy-acids has the maximum number of hydrogens directly attached to phosphorus? [1999]
a)
H4P2O7
b)
H3PO2
c)
H3PO3
d)
H3PO4
|
|
Smrity answered |
In option a )no hydrogen attached directly to p
in option b) two H directly attached to P
in option c) one H directly attached to P
and in option d) no any hydrogen directly attached to P
so correct option is b
in option b) two H directly attached to P
in option c) one H directly attached to P
and in option d) no any hydrogen directly attached to P
so correct option is b
Which would quickly absorb oxygen ? [1991, 92]- a)Alkaline solution of pyrogallol
- b)Conc. H2SO4
- c)Lime water
- d)Alkaline solution of CuSO4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which would quickly absorb oxygen ? [1991, 92]
a)
Alkaline solution of pyrogallol
b)
Conc. H2SO4
c)
Lime water
d)
Alkaline solution of CuSO4

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Alkaline solution of pyrogallol absorbs oxygen quickly.
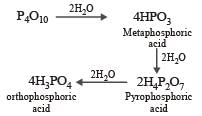
P2O5 is heated with water to give [1991]- a)Hypophosphorous acid
- b)Phosphorous acid
- c)Hypophosphoric acid
- d)Orthophosphoric acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
P2O5 is heated with water to give [1991]
a)
Hypophosphorous acid
b)
Phosphorous acid
c)
Hypophosphoric acid
d)
Orthophosphoric acid

|
Surbhi Das answered |
P2O5 have great affinity for water. The final product is orthophosphoric acid.
Pure nitrogen is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of [1991]- a)NH4OH + NaCl
- b)NH4 NO3 + NaCl
- c)NH4 Cl + NaOH
- d)NH4 Cl + NaNO2.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pure nitrogen is prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of [1991]
a)
NH4OH + NaCl
b)
NH4 NO3 + NaCl
c)
NH4 Cl + NaOH
d)
NH4 Cl + NaNO2.
|
|
Jhanvi Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Nitrogen gas (N2) is prepared in the laboratory by the decomposition of ammonium nitrite (NH4NO2). This can be achieved by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
The reaction involved is:
2NH4Cl + 2NaNO2 → N2 + 2NaCl + 4H2O
Step-by-Step Explanation:
1. Start with a mixture of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2) in a reaction vessel.
2. Heat the mixture to a high temperature, typically around 300-400°C. This provides the energy needed to drive the decomposition reaction.
3. The ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) decomposes into ammonia gas (NH3) and hydrogen chloride gas (HCl) according to the following reaction:
NH4Cl → NH3 + HCl
4. The sodium nitrite (NaNO2) decomposes into sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2) according to the following reaction:
2NaNO2 → 2NaNO3 + N2O
5. The nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2) further decomposes into nitrogen gas (N2) and oxygen gas (O2) according to the following reaction:
2NO2 → 2NO + O2
2NO → N2 + O2
6. The nitrogen gas (N2) is collected and can be used for various applications.
Key Points:
- Pure nitrogen gas (N2) can be prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
- The reaction involves the decomposition of both ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite, resulting in the formation of nitrogen gas, sodium chloride, and water.
- The decomposition reactions are driven by the high temperature provided during the heating process.
- Nitrogen gas is collected and can be used for various purposes.
Nitrogen gas (N2) is prepared in the laboratory by the decomposition of ammonium nitrite (NH4NO2). This can be achieved by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
The reaction involved is:
2NH4Cl + 2NaNO2 → N2 + 2NaCl + 4H2O
Step-by-Step Explanation:
1. Start with a mixture of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2) in a reaction vessel.
2. Heat the mixture to a high temperature, typically around 300-400°C. This provides the energy needed to drive the decomposition reaction.
3. The ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) decomposes into ammonia gas (NH3) and hydrogen chloride gas (HCl) according to the following reaction:
NH4Cl → NH3 + HCl
4. The sodium nitrite (NaNO2) decomposes into sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2) according to the following reaction:
2NaNO2 → 2NaNO3 + N2O
5. The nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2) further decomposes into nitrogen gas (N2) and oxygen gas (O2) according to the following reaction:
2NO2 → 2NO + O2
2NO → N2 + O2
6. The nitrogen gas (N2) is collected and can be used for various applications.
Key Points:
- Pure nitrogen gas (N2) can be prepared in the laboratory by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
- The reaction involves the decomposition of both ammonium chloride and sodium nitrite, resulting in the formation of nitrogen gas, sodium chloride, and water.
- The decomposition reactions are driven by the high temperature provided during the heating process.
- Nitrogen gas is collected and can be used for various purposes.
Bleaching powder is obtained by the action of chlorine gas and [1988]- a)dilute solution of Ca(OH)2
- b)concentrated solution of Ca(OH)2
- c)dry CaO
- d)dry slaked lime
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Bleaching powder is obtained by the action of chlorine gas and [1988]
a)
dilute solution of Ca(OH)2
b)
concentrated solution of Ca(OH)2
c)
dry CaO
d)
dry slaked lime

|
Ishaan Menon answered |
Cl2 gas reacts with drys laked lime, Ca (OH)2 at 40°C to give bleaching powder
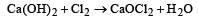
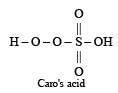
The acid which has a peroxy linkage is [1994]- a)Sulphurous acid
- b)Pyrosulphuric acid
- c)Dithionic acid
- d)Caro’s acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The acid which has a peroxy linkage is [1994]
a)
Sulphurous acid
b)
Pyrosulphuric acid
c)
Dithionic acid
d)
Caro’s acid

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
Caro’s acid is H2SO5 which contains one S – O – O – H peroxy linkage. It is also known as permonosulphuric acids.
Which one of the following substance is used in the laboratory for fast drying of neutral gases?[1992]- a)Phosphorus pentoxide
- b)Active charcoal
- c)Anhydrous calcium chloride
- d)Na3PO4.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following substance is used in the laboratory for fast drying of neutral gases?[1992]
a)
Phosphorus pentoxide
b)
Active charcoal
c)
Anhydrous calcium chloride
d)
Na3PO4.

|
Subhankar Datta answered |
Phosphorus pentoxide has great affinity for water. It forms ortho phosphoric acid on absorbing water
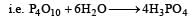
It is thus used as a powerful dehydrating or drying agent.
Which of the following statements is false ? [1994]- a)Radon is obtained from the decay of radium
- b)Helium is inert gas
- c)Xenon is the most reactive among the rare gases
- d)The most abundant rare gas found in the atmosphere is helium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is false ? [1994]
a)
Radon is obtained from the decay of radium
b)
Helium is inert gas
c)
Xenon is the most reactive among the rare gases
d)
The most abundant rare gas found in the atmosphere is helium

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
The most abundant rare gas found in the atmosphere is argon and not helium.
Which of the following statements is not valid for oxoacids of phosphorus? [2012]- a)Orthophosphoric acid is used in the manufacture of triple superphosphate.
- b)Hypophosphorous acid is a diprotic acid.
- c)All oxoacidscontaintetrahedral four coordinated phosphorus.
- d)All oxoacids contain atleast one P = O and one P — OH group.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not valid for oxoacids of phosphorus? [2012]
a)
Orthophosphoric acid is used in the manufacture of triple superphosphate.
b)
Hypophosphorous acid is a diprotic acid.
c)
All oxoacidscontaintetrahedral four coordinated phosphorus.
d)
All oxoacids contain atleast one P = O and one P — OH group.

|
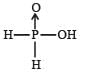
Subham Chavan answered |
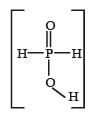 Hypophosphorous acid
Hypophosphorous acid(H3PO2) is a monobasic acid. i.e., it has only one ionisable hydrogen atom or one OH is present
Nitrogen is relatively in active element because [1992]- a)Its atom has a stable electronic configuration
- b)It has low atomic radius
- c)Its electronegativity is fairly high
- d)Dissociation energy of its molecule is fairly high
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitrogen is relatively in active element because [1992]
a)
Its atom has a stable electronic configuration
b)
It has low atomic radius
c)
Its electronegativity is fairly high
d)
Dissociation energy of its molecule is fairly high

|
Pankaj Banerjee answered |
N2 molecule contains triple bond between N atoms having very high dissociation energy (946 kJ mol–1) due to which it is relatively inactive.
Number of electrons shared in the formation of nitrogen molecule is [1992]- a)6
- b)10
- c)2
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of electrons shared in the formation of nitrogen molecule is [1992]
a)
6
b)
10
c)
2
d)
8

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Nitrogen molecule is diatomic containing a triple bond between two N atoms,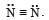
Therefore, nitrogen molecule is formed by sharing six electrons.
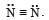
Therefore, nitrogen molecule is formed by sharing six electrons.
Which one of the following compounds does not exist ?[1989]- a)NCl5
- b)AsF5
- c)SbCl5
- d)PF5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following compounds does not exist ?[1989]
a)
NCl5
b)
AsF5
c)
SbCl5
d)
PF5

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
As Nitrogen does not have d-orbital in its valence shell its maximum covalency is 3 while in the case of other elements the maximum covalency is 5.
During its reactions, ozone [1999]- a)can only combine with hydrogen atoms
- b)accepts electrons
- c)loses electrons
- d)shows the role of electrons to be irrelevant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During its reactions, ozone [1999]
a)
can only combine with hydrogen atoms
b)
accepts electrons
c)
loses electrons
d)
shows the role of electrons to be irrelevant
|
|
Abhijeet Menon answered |
Answer:
Ozone (O3) is a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. It is formed in the atmosphere through a series of chemical reactions involving oxygen molecules (O2) and ultraviolet radiation. Ozone is an important component of the Earth's atmosphere as it plays a crucial role in absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
During its reactions, ozone can undergo various processes, including the following:
1. Ozone can combine with hydrogen atoms:
Ozone can react with hydrogen atoms to form water molecules. This reaction is known as hydrogenation, and it occurs under specific conditions. However, it is important to note that ozone can also react with other elements and compounds, not just hydrogen atoms.
2. Ozone accepts electrons:
Ozone is an oxidizing agent, meaning it has the ability to accept electrons from other substances. In many chemical reactions, ozone acts as an electron acceptor, gaining electrons to form stable compounds. This process is part of its role as an oxidant.
3. Ozone loses electrons:
While ozone can accept electrons, it can also lose electrons in certain reactions. When ozone loses an electron, it forms an oxygen molecule (O2). This process is known as reduction, where ozone acts as a reducing agent.
4. The role of electrons is relevant:
The statement that ozone shows the role of electrons to be irrelevant is incorrect. In fact, the role of electrons is crucial in ozone reactions. Electrons are involved in the transfer of charge, which allows ozone to act as an oxidizing or reducing agent. The gain or loss of electrons determines the outcome of the reaction and the formation of new compounds.
In summary, ozone can undergo various reactions, including combining with hydrogen atoms, accepting electrons, and losing electrons. The role of electrons is essential in these reactions, as they determine the behavior of ozone as an oxidizing or reducing agent. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - ozone can only combine with hydrogen atoms.
Ozone (O3) is a molecule composed of three oxygen atoms. It is formed in the atmosphere through a series of chemical reactions involving oxygen molecules (O2) and ultraviolet radiation. Ozone is an important component of the Earth's atmosphere as it plays a crucial role in absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
During its reactions, ozone can undergo various processes, including the following:
1. Ozone can combine with hydrogen atoms:
Ozone can react with hydrogen atoms to form water molecules. This reaction is known as hydrogenation, and it occurs under specific conditions. However, it is important to note that ozone can also react with other elements and compounds, not just hydrogen atoms.
2. Ozone accepts electrons:
Ozone is an oxidizing agent, meaning it has the ability to accept electrons from other substances. In many chemical reactions, ozone acts as an electron acceptor, gaining electrons to form stable compounds. This process is part of its role as an oxidant.
3. Ozone loses electrons:
While ozone can accept electrons, it can also lose electrons in certain reactions. When ozone loses an electron, it forms an oxygen molecule (O2). This process is known as reduction, where ozone acts as a reducing agent.
4. The role of electrons is relevant:
The statement that ozone shows the role of electrons to be irrelevant is incorrect. In fact, the role of electrons is crucial in ozone reactions. Electrons are involved in the transfer of charge, which allows ozone to act as an oxidizing or reducing agent. The gain or loss of electrons determines the outcome of the reaction and the formation of new compounds.
In summary, ozone can undergo various reactions, including combining with hydrogen atoms, accepting electrons, and losing electrons. The role of electrons is essential in these reactions, as they determine the behavior of ozone as an oxidizing or reducing agent. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - ozone can only combine with hydrogen atoms.
Which of the following statements is not true ? [2003]- a)HF is a stronger acid than HCl
- b)Among halide ions, iodide is the most powerful reducing agent
- c)Fluorine is the only halogen that does not show a variable oxidation state
- d)HOCl is a stronger acid than HOBr
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true ? [2003]
a)
HF is a stronger acid than HCl
b)
Among halide ions, iodide is the most powerful reducing agent
c)
Fluorine is the only halogen that does not show a variable oxidation state
d)
HOCl is a stronger acid than HOBr

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
F is more electronegative than Cl therefore HF bond is stronger than HCl and hence proton is not given off easily and hence HF is a weakest acid.
Which of the following statements is not correct for nitrogen ? [1990]- a)Its electronegativity is very high
- b)d-orbitals are available for bonding
- c)It is a typical non-metal
- d)Its molecular size is small
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct for nitrogen ? [1990]
a)
Its electronegativity is very high
b)
d-orbitals are available for bonding
c)
It is a typical non-metal
d)
Its molecular size is small

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
In case of nitrogen, d-orbitals are not available.
By passing H2S gas in acidified KMnO4 solution, we get [1995]- a)S
- b)K2S
- c)MnO2
- d)K2SO3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
By passing H2S gas in acidified KMnO4 solution, we get [1995]
a)
S
b)
K2S
c)
MnO2
d)
K2SO3

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |

Thus in this reaction sulphur (S) is produced.
Which of the following oxides will be the least acidic?[1996]- a)As4O6
- b)As4O10
- c)P4O10
- d)P4O6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following oxides will be the least acidic?[1996]
a)
As4O6
b)
As4O10
c)
P4O10
d)
P4O6

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
As th e O.N of the central atom of the compounds increases acidic strength of that compound also increases and on moving from top to bottom in groups acidic strength of oxides also decrease due to decreasing electronegativity in groups.
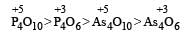
The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following species are : [2010]- a)
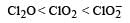
- b)
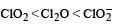
- c)
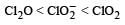
- d)
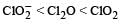
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct order of increasing bond angles in the following species are : [2010]
a)
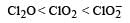
b)
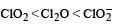
c)
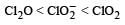
d)
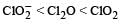

|
Yash Saha answered |
The correct order of increasing bond angle is 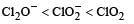
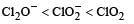
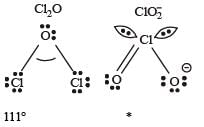
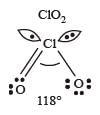
* In ClO2– there are 2 lone pairs of electrons present on the central chlorine atom. Therefore the bond angle in ClO2– is less than 118° which is the bond angle in ClO2 which has less number of electrons on chlorine.
Which one of the following orders correctly represents the increasing acid strengths of the given acids? [2007]- a)HOClO < HOCl < HOClO3 < HOClO2
- b)HOClO2 < HOClO3 < HOClO < HOCl
- c)HOClO3 < HOClO2 < HOClO < HOCl
- d)HOCl < HOClO < HOClO2 < HOClO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following orders correctly represents the increasing acid strengths of the given acids? [2007]
a)
HOClO < HOCl < HOClO3 < HOClO2
b)
HOClO2 < HOClO3 < HOClO < HOCl
c)
HOClO3 < HOClO2 < HOClO < HOCl
d)
HOCl < HOClO < HOClO2 < HOClO3
|
|
Poulomi Desai answered |
The correct order of increasing acid strength is:
d) HCOOH < ch3cooh="" />< hno3="" />< hclo4.="" />
d) HCOOH < ch3cooh="" />< hno3="" />< hclo4.="" />
Aqueous solution of ammonia consists of- a)H+
- b)OH– [1991]
- c)NH4+
- d)NH4+and OH–
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Aqueous solution of ammonia consists of
a)
H+
b)
OH– [1991]
c)
NH4+
d)
NH4+and OH–

|
Rohan Unni answered |
Aqueous solution of ammonia is obtained by passing NH3 in H2O which gives NH4+ and OH– ions.
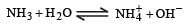
In which of the following arrangements the given sequence is not strictly according to the property indicated against it ? [2012 M]- a)HF < HCl < HBr < HI : increasing acidic strength
- b)H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te : increasing pKa values
- c)NH3 < PH3 < AsH3 < SbH3 : increasing acidic character
- d)CO2 < SiO2 < SnO2 < PbO2 : increasing oxidising power
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following arrangements the given sequence is not strictly according to the property indicated against it ? [2012 M]
a)
HF < HCl < HBr < HI : increasing acidic strength
b)
H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te : increasing pKa values
c)
NH3 < PH3 < AsH3 < SbH3 : increasing acidic character
d)
CO2 < SiO2 < SnO2 < PbO2 : increasing oxidising power
|
|
Abhijeet Sharma answered |
The property and sequence given are not mentioned in the question, so it is impossible to determine which arrangement does not strictly follow the property indicated. Please provide more information or clarify the question.
Which one of the following orders is not in accordance with the property stated against is ? [2006]- a)HI > HBr > HCl > HF : Acidic property in water
- b)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity
- c)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
- d)F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidising power
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following orders is not in accordance with the property stated against is ? [2006]
a)
HI > HBr > HCl > HF : Acidic property in water
b)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Electronegativity
c)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Bond dissociation energy
d)
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 : Oxidising power

|
Shalini Saha answered |
Bond dissociation energy of fluorine is less because of its small size and repulsion between electrons of two atoms. So option (c) is wrong order. The correct order is [Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2]
Chapter doubts & questions for The p-Block Elements (Group 15, 16, 17 and 18) - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The p-Block Elements (Group 15, 16, 17 and 18) - Chemistry 31 Years NEET Chapterwise Solved Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily