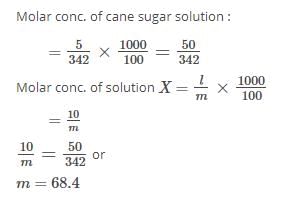All Exams >
NEET >
Chemistry Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of Solutions for NEET Exam
When the solvent is in solid state, solution is- a)Solid solution
- b)Gaseous solution
- c)Solution
- d)Liquid solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the solvent is in solid state, solution is
a)
Solid solution
b)
Gaseous solution
c)
Solution
d)
Liquid solution

|
Aditi answered |
When both the solute and solvent are in solid state ,then the solution is called as solid solution or solid sol .
Molality is expressed in- a)mol/kg
- b)mol/L
- c)L/mol
- d)g/L
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Molality is expressed in
a)
mol/kg
b)
mol/L
c)
L/mol
d)
g/L

|
Siddharth Abimanyu answered |
Molality=moles of solute/kg of solvent... so option A
the molarity ofa solution obtained by mixing 750 ml of 0.5(M) hcl with 250ml of 2(M) hcl will be?- a)1.25 M
- b)2.5 M
- c)1.00 M
- d)0.875 M
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
the molarity ofa solution obtained by mixing 750 ml of 0.5(M) hcl with 250ml of 2(M) hcl will be?
a)
1.25 M
b)
2.5 M
c)
1.00 M
d)
0.875 M
|
|
Vilas Kumar answered |
M = M1V1+ M2V2 / V1+V2. M = 750*0.5+250*2 / 750+250. M = 875 / 1000. M = 0.875
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at the given temperature and pressure is called a- a)Unsaturated solution
- b)Dilute solution
- c)Solid solution
- d)Saturated solution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at the given temperature and pressure is called a
a)
Unsaturated solution
b)
Dilute solution
c)
Solid solution
d)
Saturated solution
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The correct answer is option D
In a saturated solution, more solute cannot be dissolved at a given temperature.
This is because, the solute dissolves in a solvent because of space between particles of solvent but on continuous addition of solute, the space between the solvent particles gets fulfilled. Thus no more solute particle can dissolve in a solvent.
In a saturated solution, more solute cannot be dissolved at a given temperature.
This is because, the solute dissolves in a solvent because of space between particles of solvent but on continuous addition of solute, the space between the solvent particles gets fulfilled. Thus no more solute particle can dissolve in a solvent.
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.
- A:
0.03, Ethyl chloride
- B:
0.08, cannot be determined
- C:
0.03, Methanol
- D:
0.08, Ethyl chloride
The answer is d.
Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.
0.03, Ethyl chloride
0.08, cannot be determined
0.03, Methanol
0.08, Ethyl chloride

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Mole fraction of third component is 1 - (0.6 + 0.32) = 0.08.
Since ethyl chloride has highest mole fraction so it is the solvent.
Since ethyl chloride has highest mole fraction so it is the solvent.
The number of moles of KCl in 3 L of 3 M solution is- a)27 moles
- b)1 moles
- c)9 moles
- d)3 moles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of moles of KCl in 3 L of 3 M solution is
a)
27 moles
b)
1 moles
c)
9 moles
d)
3 moles
|
|
Om Desai answered |
In 3M there will be 3 moles per litre therefore in 3 litres there will be 9 moles.
Which is correct about Henry's law- a)The gas in contact with the liquid should behave as an ideal gas
- b)There should not be any chemical interaction between the gas and liquid
- c)The pressure applied should be high
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is correct about Henry's law
a)
The gas in contact with the liquid should behave as an ideal gas
b)
There should not be any chemical interaction between the gas and liquid
c)
The pressure applied should be high
d)
All of these
|
|
Sri Suhas answered |
Yes, because if the gases in the mixture or solution will react then there will be partly solution and partly compound due to which the solution concentration will change and we will not get a proper Henry constant to the solution.
Hope this helps you. If you find an answer to this never hesitate to put it in the answer box.
Mole fraction of glycerine, C3H5(OH)3 in a solution containing 36 gm of water and 46 gm of glycerine is:- a)0.40
- b)0.20
- c)0.46
- d)0.36
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Mole fraction of glycerine, C3H5(OH)3 in a solution containing 36 gm of water and 46 gm of glycerine is:
a)
0.40
b)
0.20
c)
0.46
d)
0.36
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
No. of moles of glycerine= 46/92 (where 92 is M.M. of glycerine)
= 0.5moles
no. of moles of water= 36/18(where 18 is M.M. of water)
= 2moles
so mole fraction oh glycerine = No. of moles of glycerine/No. of moles of glycerine + No. of moles of water
= 0.5/2 + 0.5
= 0.20
Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.- a)0.03, Ethyl chloride
- b)0.08, cannot be determined
- c)0.03, Methanol
- d)0.08, Ethyl chloride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mole fraction of ethyl chloride and methanol in a ternary solution is 0.6 and 0.32 respectively. What is the mole fraction of third component. Also identify the solvent in this ternary solution.
a)
0.03, Ethyl chloride
b)
0.08, cannot be determined
c)
0.03, Methanol
d)
0.08, Ethyl chloride

|
Anu answered |
•sum of mole fractions are always 1.so mole fraction of 3rd component =1-(0.6+0.32)=0.8 • solvent is the component of a solution that is present in the greatest amount. so ethyl chloride is solvent
The level of contamination of chloroform was found to be 15 ppm. It means 15 g of chloroform is present in how many grams of solution?- a)1000 g
- b)106 g
- c)100 g
- d)1.0 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The level of contamination of chloroform was found to be 15 ppm. It means 15 g of chloroform is present in how many grams of solution?
a)
1000 g
b)
106 g
c)
100 g
d)
1.0 g
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
1 ppm is equivalent to 1 part out of 1 million (106) parts.
∴ Mass percent of 15 ppm chloroform in water
∴ Mass percent of 15 ppm chloroform in water

⇒ 1.5 x 10-3 g chloroform present in 100 g water
Thus, 15g chloroform will be present in water
Thus, 15g chloroform will be present in water

When common salt is dissolved in water:- a)Melting point of solution increases
- b)Boiling point of solution increases
- c)Boiling point of solution decreases
- d)both melting .point and boiling point decreases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When common salt is dissolved in water:
a)
Melting point of solution increases
b)
Boiling point of solution increases
c)
Boiling point of solution decreases
d)
both melting .point and boiling point decreases
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
So the boiling point of water will increase. When salt is added to water, then the intermolecular forces between water molecules gets altered due to dissociation of NaCl into sodium and chloride ions.
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is- a)
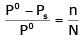
- b)
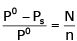
- c)
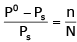
- d)
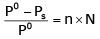
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
EduRev Support answered |
The exact mathematical expression of Raoult's law is 
Here, Po represents the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, P represents the vapour pressure of the solution, n represents the number of moles of solute and N represents the number of moles of the solvent.
Here, Po represents the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, P represents the vapour pressure of the solution, n represents the number of moles of solute and N represents the number of moles of the solvent.
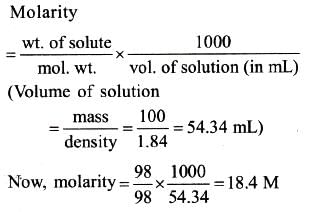
Can you explain the answer of this question below: Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?
- A:
2.85m
- B:
3.15m
- C:
1.45m
- D:
2.50m
The answer is c.
Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?
2.85m
3.15m
1.45m
2.50m
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
12.5% w/w means 12.5 g in 100 g of solution.
Weight of solvent = 100 g – 12.5 g= 87.5 g. Number of moles of sulphuric acid = 12.5/ 98 =0.127 mol
So molality = 0.127 X 1000/87.5 = 1.45 m
The mass of sodium chloride in 2.5 M solution is- a)37.80 g
- b)146.25 g
- c)117 .00g
- d)58.50 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of sodium chloride in 2.5 M solution is
a)
37.80 g
b)
146.25 g
c)
117 .00g
d)
58.50 g
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
For preparing one molar solution we are required to dissolve one mole of the NaCl ( 58.5g) , for 2.5 mol we require 2.5 * 58.5= 146.25 g
Which of the two has lower freezing point, 2m NaCl or 5m NaCl aqueous solution?- a)2m NaCl solution
- b)Both have same freezing point
- c)5m NaCl solution
- d)The solutions cannot freeze
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the two has lower freezing point, 2m NaCl or 5m NaCl aqueous solution?
a)
2m NaCl solution
b)
Both have same freezing point
c)
5m NaCl solution
d)
The solutions cannot freeze
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The correct answer is option C
ΔTf= Kf x m Since ΔTf for 5m NaCl will be higher than for 2m, 5m NaCl solution freezes at a lower temperature.
ΔTf= Kf x m Since ΔTf for 5m NaCl will be higher than for 2m, 5m NaCl solution freezes at a lower temperature.
The molal elevation constant is the elevation in boiling point of- a)1M solution
- b)1m solution
- c)1N solution
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The molal elevation constant is the elevation in boiling point of
a)
1M solution
b)
1m solution
c)
1N solution
d)
None of the above
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Molal elevation constant is a characteristic constant for a given solvent. It is the elevation of boiling point produced when one mole of solute is dissolved in 1 kg of solvent. The proportionality constant, Kb, is called the molal boiling point elevation constant. It is a constant that is equal to the change in the boiling point for a 1-molal solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute.
Molal elevation constant is a characteristic constant for a given solvent. It is the elevation of boiling point produced when one mole of solute is dissolved in 1 kg of solvent. The proportionality constant, Kb, is called the molal boiling point elevation constant. It is a constant that is equal to the change in the boiling point for a 1-molal solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute.
If the vapour pressure of pure solvent A is 17.5 mm and lowering of vapour pressure of solution formed by adding a non-volatile electrolyte is 0.0175 mm then what is the relative lowering of vapour pressure?- a)0.1
- b)1.01
- c)0.001
- d)0.01
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the vapour pressure of pure solvent A is 17.5 mm and lowering of vapour pressure of solution formed by adding a non-volatile electrolyte is 0.0175 mm then what is the relative lowering of vapour pressure?
a)
0.1
b)
1.01
c)
0.001
d)
0.01
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is option C
Relative lowering of vapour pressure:
= lowering of vapour pressure of solution/ vapour pressure of pure solvent
=0.0175/17.5=0.001
Relative lowering of vapour pressure:
= lowering of vapour pressure of solution/ vapour pressure of pure solvent
=0.0175/17.5=0.001
1 M, 2.5 litre NaOH solution is mixed with another 0.5 M, 3 litre NaOH solution. Then find out the molarity of resultant solution [2002]- a)0.80 M
- b)1.0 M
- c)0.73 M
- d)0.50 M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
1 M, 2.5 litre NaOH solution is mixed with another 0.5 M, 3 litre NaOH solution. Then find out the molarity of resultant solution [2002]
a)
0.80 M
b)
1.0 M
c)
0.73 M
d)
0.50 M
|
|
User5881746 answered |
M = M1V1+M2V2 / V1+V2. M = 1*2.5+0.5*3 / 2.5+3.
M = 4 / 5.5. M = 0.73
M = 4 / 5.5. M = 0.73
Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?- a)2.85m
- b)3.15m
- c)1.45m
- d)2.50m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the molality of 12.5% w/w sulphuric acid?
a)
2.85m
b)
3.15m
c)
1.45m
d)
2.50m
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
12.5% w/w means 12.5 g in 100 g of solution.
Weight of solvent = 100 g – 12.5 g= 87.5 g. Number of moles of sulphuric acid = 12.5/ 98 =0.127 mol
So molality = 0.127x1000/87.5 = 1.45 m
A sample of 300.0 g of drinking water is found to contain 38 mg Pb. What this concentration in parts per million?- a)3 x 102 ppm
- b)6.5 m
- c)130 ppm Pb
- d)21 ppm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sample of 300.0 g of drinking water is found to contain 38 mg Pb. What this concentration in parts per million?
a)
3 x 102 ppm
b)
6.5 m
c)
130 ppm Pb
d)
21 ppm
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
We use parts per million to express the concentrations of solutions that contain very, very small amounts, often called trace amounts, of a given solute.
More specifically, a solution's concentration in parts per millions tells you the number of parts of solute present for every
10^6=1,000,000
parts of solution. You can thus say that a 1 ppm
solution will contain exactly 1 g of solute for every 10^6g of solution.
In this case, you know that you have
38 mg Pb x (1 g/10^3 mg) = 3.8 x 10^-2 g Pb
in exactly
300.0 g = 3.000 x 10^2 g solution
This means that you can use this known composition as a conversion factor to scale up the mass of the solution to
10^6 g solution x (3.8 x 10^-2 g Pb/3.000 x 10^2 g solution)
= 130 g solution
Since this represents the mass of lead present in exactly 10^6 g of solution, you can say that the solution has a concentration of:
concentration (ppm) = 130 ppm Pb
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
An unopened soda has an aqueous concentration of C02 at 25° C equal to 0.0506 molal. Thus, pressure of C02 gas in the can is (KH = 0.034 mol/kg bar) - a)0.671 bar
- b)1.49 bar
- c)1.20 bar
- d)1.71 bar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
This section contains 11 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct
An unopened soda has an aqueous concentration of C02 at 25° C equal to 0.0506 molal. Thus, pressure of C02 gas in the can is (KH = 0.034 mol/kg bar)
a)
0.671 bar
b)
1.49 bar
c)
1.20 bar
d)
1.71 bar
|
|
Abhijeet Sharma answered |
Which of the following is a colligative property?- a)Molality
- b)Viscosity
- c)Relative lowering of vapour pressure
- d)Surface tension
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a colligative property?
a)
Molality
b)
Viscosity
c)
Relative lowering of vapour pressure
d)
Surface tension
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Colligative properties- The properties that depend upon the ratio of the number of solute molecules and total molecules not upon the nature of solute molecules named as colligative properties.
Example- Osmotic pressure, elevation of boiling point, depression in freezing point and relative lowering of vapour pressure.
Which of the following unit of concertration is independent of temperature?- a)Molarity
- b)Molality
- c)Mole fraction
- d)all
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following unit of concertration is independent of temperature?
a)
Molarity
b)
Molality
c)
Mole fraction
d)
all

|
Kritika Singh answered |
Those concentration terms which involve volume are temperature dependent while those which not involve volume are temperature independent....
The vapour pressure of a solvent decreased by 10mm of mercury when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent. The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2. What should be the mole fraction of the solvent if the decrease in the vapour pressure is to be 20mm of mercury?- a)0.8
- b)0.6 [1998]
- c)0.4
- d)0.2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The vapour pressure of a solvent decreased by 10mm of mercury when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent. The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2. What should be the mole fraction of the solvent if the decrease in the vapour pressure is to be 20mm of mercury?
a)
0.8
b)
0.6 [1998]
c)
0.4
d)
0.2
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |

A solution was made by dissolving 2 g of a solute in 100 g of acetone. The solution boiled at 56.95° C. The boiling point of pure acetone is 55.95° C, and the Kb =1.71°C/m. What is the molecular weight of the solute?- a)22 g
- b)34.2 g
- c)42.3 g
- d)30 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution was made by dissolving 2 g of a solute in 100 g of acetone. The solution boiled at 56.95° C. The boiling point of pure acetone is 55.95° C, and the Kb =1.71°C/m. What is the molecular weight of the solute?
a)
22 g
b)
34.2 g
c)
42.3 g
d)
30 g
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
∆Tb =(Kb × 1000 × W2) / M2 × W1
⇒ M2 = (Kb × 1000 × W2) / ∆Tb × W1
= (1.71 × 1000 × 2) / 1 × 100
= 34.2g
∆Tb =(Kb × 1000 × W2) / M2 × W1
⇒ M2 = (Kb × 1000 × W2) / ∆Tb × W1
= (1.71 × 1000 × 2) / 1 × 100
= 34.2g
The colligative properties of a solution are- a)Proportional to the number of solute particles present
- b)Proportional to percentage of solute
- c)Proportional to normality of solution
- d)Proportional to volume of solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The colligative properties of a solution are
a)
Proportional to the number of solute particles present
b)
Proportional to percentage of solute
c)
Proportional to normality of solution
d)
Proportional to volume of solution

|
Swara Mukherjee answered |
It is also a colligative property and depends on the number of solute molecules and not their identity. For dilute solutions, osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the molarity (C) of the solution at a given temperature (T).
All form ideal solution except [1988]- a)C6H6 and C6H5 CH3
- b)C2H6 and C2H5I
- c)C6H5Cl and C6H5 Br
- d)C2H5 I and C2H5 OH.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All form ideal solution except [1988]
a)
C6H6 and C6H5 CH3
b)
C2H6 and C2H5I
c)
C6H5Cl and C6H5 Br
d)
C2H5 I and C2H5 OH.
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
C2H5I and C2H5OH form non-ideal solution.
If 18 gram of glucose (C6H12O6) is present in 1000 gram of an aqueous solution of glucose it is said to be-- a)39.2 gram
- b)1.1 molal
- c)0.5 molal
- d)0.1 molal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If 18 gram of glucose (C6H12O6) is present in 1000 gram of an aqueous solution of glucose it is said to be-
a)
39.2 gram
b)
1.1 molal
c)
0.5 molal
d)
0.1 molal
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
18 gm of glucose means 0.1mole of glucose as it present in 1000 gm of solvent so it is 0.1 mole
A complex containing K+, Pt (IV) and Cl- is 100% ionised giving i = 3. Thus, complex is- a)K2 [PtCl4]
- b)K2[PtCl6]
- c)K3[PtCl5]
- d)K[PtCl3]
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A complex containing K+, Pt (IV) and Cl- is 100% ionised giving i = 3. Thus, complex is
a)
K2 [PtCl4]
b)
K2[PtCl6]
c)
K3[PtCl5]
d)
K[PtCl3]
|
|
Dipika Rane answered |
In option (B) oxidaton state of platinum is (iv)
x – 6 = –2
x = + 4
x – 6 = –2
x = + 4
Which of the following aqueous solution has minimum freezing point ? [1991]- a)0.01 m NaCl
- b)0.005 m C2H5OH
- c)0.005 m MgI2
- d)0.005 m MgSO4.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following aqueous solution has minimum freezing point ? [1991]
a)
0.01 m NaCl
b)
0.005 m C2H5OH
c)
0.005 m MgI2
d)
0.005 m MgSO4.

|
Swara Desai answered |
ΔTf = i × Kf × m Van't Hoff factor, i = 2 for NaCl, hence ΔTf = 0.02 Kf which is maximum in the present case.
Hence ΔTf is maximum or freezing point is minimum.
Hence ΔTf is maximum or freezing point is minimum.
Concentration of C02 (in mole fraction) in fat when partial pressure of C02 is 55 kPa at 25° C, is (Henry’s law constant of C02 = 8.6 x 104 torr)- a)1.6 x 10-4
- b)4.8 x 10-3
- c)8.6 x 10-4
- d)2.4 x 10-3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Concentration of C02 (in mole fraction) in fat when partial pressure of C02 is 55 kPa at 25° C, is (Henry’s law constant of C02 = 8.6 x 104 torr)
a)
1.6 x 10-4
b)
4.8 x 10-3
c)
8.6 x 10-4
d)
2.4 x 10-3
|
|
Preethi Kulkarni answered |
Note: Kh (Henry’s law constant) is in pressure unit, hence we use relation, Concentration xKH = Pressure
Vapour pressure of benzene at 30°C is 121.8 mm.When 15 g of a non volatile solute is dissolved in 250 g of benzene its vapour pressure decreased to 120.2 mm. The molecular weight of the solute (Mo. wt. of solvent = 78) [1995]- a)356.2
- b)456.8
- c)530.1
- d)656.7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vapour pressure of benzene at 30°C is 121.8 mm.When 15 g of a non volatile solute is dissolved in 250 g of benzene its vapour pressure decreased to 120.2 mm. The molecular weight of the solute (Mo. wt. of solvent = 78) [1995]
a)
356.2
b)
456.8
c)
530.1
d)
656.7

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Give vapour pressure of pur e solute (P0) = 121.8 mm;
Weight of solute (w) = 15 g
Weight of solvent (W) = 250 g;
Vapour pressure of pure solvent (P) = 120.2 mm and Molecular weight of solvent (M) = 78 From Raoult’s law
Weight of solute (w) = 15 g
Weight of solvent (W) = 250 g;
Vapour pressure of pure solvent (P) = 120.2 mm and Molecular weight of solvent (M) = 78 From Raoult’s law
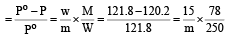
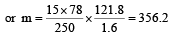
The Van't Hoff factor for a dilute aqueous solution of glucose is- a)zero
- b)1.0
- c)1.5
- d)2.0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Van't Hoff factor for a dilute aqueous solution of glucose is
a)
zero
b)
1.0
c)
1.5
d)
2.0

|
Ayesha Princess answered |
Glucose neither of Associate nor dissociate in aqueous soln.... for this type of molecules vant haff factor is 1...
A mixture contains 1 mole of volatile liquid A ( = 100 mm Hg) and 3 moles of volatile liquid B(= 80 mmHg). If solution behaves ideally, the total vapour pressure of the distillate is- a)5 mm Hg
- b)85.88 mmHg
- c)90 mm Hg
- d)92 mm Hg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A mixture contains 1 mole of volatile liquid A ( = 100 mm Hg) and 3 moles of volatile liquid B(= 80 mmHg). If solution behaves ideally, the total vapour pressure of the distillate is
a)
5 mm Hg
b)
85.88 mmHg
c)
90 mm Hg
d)
92 mm Hg
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
= 85.88 mm Hg
The information that is/are needed to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute is/are- a)The amount of solute used in the experiment
- b)The molal boiling or freezing constant value of the solvent
- c)The amount of solvent used in the experiment
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The information that is/are needed to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute is/are
a)
The amount of solute used in the experiment
b)
The molal boiling or freezing constant value of the solvent
c)
The amount of solvent used in the experiment
d)
All the above

|
Sidharth Gupta answered |
Ya d is right answer as in formula of elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point these all terms required
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)Passage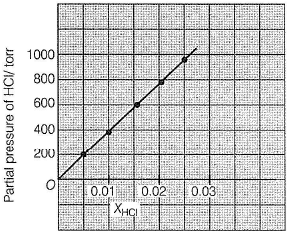 Q.Henry’s law constant for HCI gas is (in torr)
Q.Henry’s law constant for HCI gas is (in torr)- a) 4 x 104
- b) 2x 104
- c)1 x 104
- d)001 x 104
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage
Q.
Henry’s law constant for HCI gas is (in torr)
a)
4 x 104
b)
2x 104
c)
1 x 104
d)
001 x 104
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
Based on given figure, pressure of 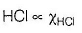
Consider following solutions -I : 1 M a glucose II. : 1 M a sodium chlorideIII. : 1 M benzoic acid in benzene IV. : 1 M ammonium phosphateSelect incorrect statement -- a)All are isotonic solutions
- b)III is hypotonic of I, II, IV
- c)I, II, IV are hypertonic of III
- d)IV is hypertonic of I, II, III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider following solutions -
I : 1 M a glucose II. : 1 M a sodium chloride
III. : 1 M benzoic acid in benzene IV. : 1 M ammonium phosphate
Select incorrect statement -
a)
All are isotonic solutions
b)
III is hypotonic of I, II, IV
c)
I, II, IV are hypertonic of III
d)
IV is hypertonic of I, II, III
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
(A) All solutions are not isotonic because all solution are not at equal concentration so (A) is incorrect
(B) As benzoic acid dimerises so III is hypotonic of I, II, IV
(C) Is also correct as I, II & IV are hypertonic of III
(D) As ammoniun sulphate has maximum number of particale so it will be hypertonic of I, II, III
(B) As benzoic acid dimerises so III is hypotonic of I, II, IV
(C) Is also correct as I, II & IV are hypertonic of III
(D) As ammoniun sulphate has maximum number of particale so it will be hypertonic of I, II, III
Which of the following aqueous solution will show maximum vapour pressure at 300 K?- a)1 M NaCl
- b)1 M CaCl2
- c)1 M AlCl3
- d)1 M C12H22O11
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following aqueous solution will show maximum vapour pressure at 300 K?
a)
1 M NaCl
b)
1 M CaCl2
c)
1 M AlCl3
d)
1 M C12H22O11
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
less no of particle of solute means maximum vapour pressure.
For an ideal solution with pA > pB, which of the following is true?
- a)(xA)liquid = (xB)vapour
- b)(xA)liquid > (xB)vapour
- c)(xA)liquid < (xB)vapour
- d)(xA)liquid and (xB)vapour do not bear any relationship with each other
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For an ideal solution with pA > pB, which of the following is true?
a)
(xA)liquid = (xB)vapour
b)
(xA)liquid > (xB)vapour
c)
(xA)liquid < (xB)vapour
d)
(xA)liquid and (xB)vapour do not bear any relationship with each other
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Since the vapor pressure of A is more than B so the mole fraction of A is more in vapor phase than liquid phase as A is more volatile hence vapor phase would be richer in A. Thus the correct option is (xA)liquid < (xB)Vapor
Beckmann thermometers are used to measure- a)boiling point of solution
- b)elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point
- c)any temperature
- d)freezing point of solution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Beckmann thermometers are used to measure
a)
boiling point of solution
b)
elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point
c)
any temperature
d)
freezing point of solution
|
|
Srishti Chavan answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that Beckmann thermometers are used to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point.
Here's a detailed explanation of why this is the correct answer:
Beckmann Thermometer:
A Beckmann thermometer is a type of liquid-in-glass thermometer that is specifically designed to measure small temperature differences accurately. It is named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann who invented it in the late 19th century.
Measurement of Elevation in Boiling Point or Depression in Freezing Point:
The Beckmann thermometer is primarily used to measure the elevation in boiling point or the depression in freezing point of a solution. This is achieved by comparing the boiling or freezing point of the solution with that of a pure solvent.
Elevation in Boiling Point:
When a solute is added to a solvent, the boiling point of the resulting solution increases. This is known as the elevation in boiling point. The degree of elevation depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this elevation in boiling point.
Depression in Freezing Point:
Similarly, when a solute is added to a solvent, the freezing point of the resulting solution decreases. This is known as the depression in freezing point. Again, the degree of depression depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this depression in freezing point.
Working Principle of a Beckmann Thermometer:
The Beckmann thermometer consists of a long capillary tube filled with a special liquid, usually mercury. The liquid expands or contracts with temperature changes, and the expansion or contraction is measured by a scale attached to the thermometer.
Calibration:
To use a Beckmann thermometer, it needs to be calibrated. This is done by measuring the temperature difference between the thermometer bulb and the end of the mercury column. This calibration is essential to ensure accurate measurements.
Applications:
The Beckmann thermometer finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmaceuticals. It is commonly used to determine the molecular weight of substances, as well as to measure the concentration of solutes in solutions.
In conclusion, Beckmann thermometers are specifically designed to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point of solutions. This makes them a valuable tool in various scientific disciplines.
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that Beckmann thermometers are used to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point.
Here's a detailed explanation of why this is the correct answer:
Beckmann Thermometer:
A Beckmann thermometer is a type of liquid-in-glass thermometer that is specifically designed to measure small temperature differences accurately. It is named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann who invented it in the late 19th century.
Measurement of Elevation in Boiling Point or Depression in Freezing Point:
The Beckmann thermometer is primarily used to measure the elevation in boiling point or the depression in freezing point of a solution. This is achieved by comparing the boiling or freezing point of the solution with that of a pure solvent.
Elevation in Boiling Point:
When a solute is added to a solvent, the boiling point of the resulting solution increases. This is known as the elevation in boiling point. The degree of elevation depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this elevation in boiling point.
Depression in Freezing Point:
Similarly, when a solute is added to a solvent, the freezing point of the resulting solution decreases. This is known as the depression in freezing point. Again, the degree of depression depends on the concentration of the solute. The Beckmann thermometer can accurately measure this depression in freezing point.
Working Principle of a Beckmann Thermometer:
The Beckmann thermometer consists of a long capillary tube filled with a special liquid, usually mercury. The liquid expands or contracts with temperature changes, and the expansion or contraction is measured by a scale attached to the thermometer.
Calibration:
To use a Beckmann thermometer, it needs to be calibrated. This is done by measuring the temperature difference between the thermometer bulb and the end of the mercury column. This calibration is essential to ensure accurate measurements.
Applications:
The Beckmann thermometer finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmaceuticals. It is commonly used to determine the molecular weight of substances, as well as to measure the concentration of solutes in solutions.
In conclusion, Beckmann thermometers are specifically designed to measure the elevation in boiling point or depression in freezing point of solutions. This makes them a valuable tool in various scientific disciplines.
CO(g)is dissolved in H2Oat 25°C and 0.010 atm. Henry’s law constant for this system is 5.80 x104 atm. Thus, mole fraction of CO(g)is- a)1.72 x 10-7
- b)8.28 x 10-7
- c)0.99
- d)0.01
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
CO(g)is dissolved in H2Oat 25°C and 0.010 atm. Henry’s law constant for this system is 5.80 x104 atm. Thus, mole fraction of CO(g)is
a)
1.72 x 10-7
b)
8.28 x 10-7
c)
0.99
d)
0.01
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The mole fraction of a gas in solution is related to partial pressure of the gas above the solution by Henry’s law.
During osmosis, flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane [2006]
- a)from both sides of semipermeable membrane with equal flow rates
- b)from solution having lower concentration only
- c)from both sides of semipermeable membrane with unequal flow rates
- d)from solution having higher concentration only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During osmosis, flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane [2006]
a)
from both sides of semipermeable membrane with equal flow rates
b)
from solution having lower concentration only
c)
from both sides of semipermeable membrane with unequal flow rates
d)
from solution having higher concentration only

|
Anjana Dasgupta answered |
During osmosis water flows through semipermeable membrane from lower concnetration to higher concentration.
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure in Torr of a mixture of volatile components A and B is given by
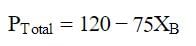
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
- a)120, 75
- b)120, 195
- c)120, 45
- d)75, 45
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At a given temperature, total vapour pressure in Torr of a mixture of volatile components A and B is given by
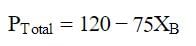
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
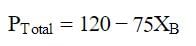
hence, vapour pressure of pure A and B respectively (in Torr) are -
a)
120, 75
b)
120, 195
c)
120, 45
d)
75, 45
|
|
Om Desai answered |

According to Raoult's law, relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to [1995- a)moles of solute
- b)moles of solvent
- c)mole fraction of solute
- d)mole fraction of solvent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Raoult's law, relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to [1995
a)
moles of solute
b)
moles of solvent
c)
mole fraction of solute
d)
mole fraction of solvent
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
Since relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property, therefore it depends upon the number of solute particles or mole fraction of solute.
How many grams of concentrated nitric acid solution should be used to prepare 250 mL of 2.0M HNO3 ? The concentrated acid is 70% HNO3 [NEET 2013]- a)90.0 g conc. HNO3
- b)70.0 g conc. HNO3
- c)54.0 g conc. HNO3
- d)45.0 g conc. HNO3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many grams of concentrated nitric acid solution should be used to prepare 250 mL of 2.0M HNO3 ? The concentrated acid is 70% HNO3 [NEET 2013]
a)
90.0 g conc. HNO3
b)
70.0 g conc. HNO3
c)
54.0 g conc. HNO3
d)
45.0 g conc. HNO3

|
Mamali . answered |
The required number of Moles =(250/1000)2=0•5 moles
(no of Moles = molarity×vol.)
so reqd.mass of HNO3 =0•5×63
=31•5
given mass = no of moles × molar mass
Given,
70gms of HNO3 are present in 100 gms of the Sol.
so,1gm will be present in 100/70 gms of sol.
hense, 31•5 gms will be present in
100/70 × 31•5 gms of sol.
so amount of concentrated nitric acid solution used is 45 gms.
(no of Moles = molarity×vol.)
so reqd.mass of HNO3 =0•5×63
=31•5
given mass = no of moles × molar mass
Given,
70gms of HNO3 are present in 100 gms of the Sol.
so,1gm will be present in 100/70 gms of sol.
hense, 31•5 gms will be present in
100/70 × 31•5 gms of sol.
so amount of concentrated nitric acid solution used is 45 gms.
Chapter doubts & questions for Solutions - Chemistry Class 12 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Solutions - Chemistry Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup