All Exams >
Physics >
IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Practice Tests for Physics Exam
Consider a system of eight non interacting, identical quantum particles of spin -3/2 in a one dimensional box of length L. The minimum excitation energy of the system , in units of 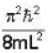 is____.
is____.
Correct answer is '20'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a system of eight non interacting, identical quantum particles of spin -3/2 in a one dimensional box of length L. The minimum excitation energy of the system , in units of 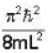 is____.
is____.
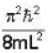 is____.
is____.|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Spin 3/2 ⇒ degeneracy = (25 + 1) = 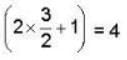
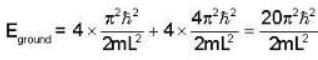
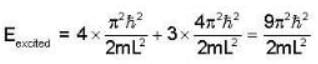
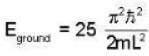
Now minimum excitation energy

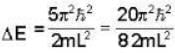
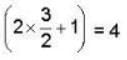
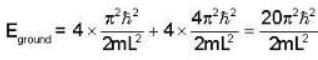
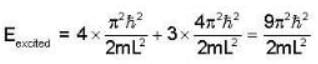
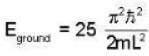
Now minimum excitation energy

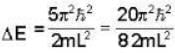
Rest mass energy of an election is 0. 51 MeV. A moving election has a kinetic energy of 9.69 MeV. The ratio of the mass of the moving electron to its mass is- a)19:1
- b)20:1
- c)1:19
- d)1:20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rest mass energy of an election is 0. 51 MeV. A moving election has a kinetic energy of 9.69 MeV. The ratio of the mass of the moving electron to its mass is
a)
19:1
b)
20:1
c)
1:19
d)
1:20
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Given rest mass energy 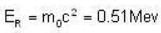
And kinetic energy T = 9.69 mev.
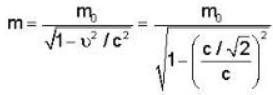
We know from einstein theory
E = mc2 = KE. + rest mass energy
mc2 = T + m0c2
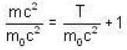
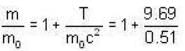
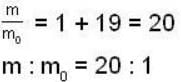
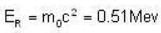
And kinetic energy T = 9.69 mev.
We know from einstein theory
E = mc2 = KE. + rest mass energy
mc2 = T + m0c2
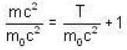
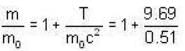
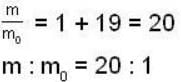
When a harmonic waves is propagating through a medium, the displacement y of a particle of the medium is represented by y = 10 sin 2π/5 (1800 t-x)
The time period will be:- a)1/360 s
- b)1/36 s
- c)36 s
- d)360 s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a harmonic waves is propagating through a medium, the displacement y of a particle of the medium is represented by y = 10 sin 2π/5 (1800 t-x)
The time period will be:
The time period will be:
a)
1/360 s
b)
1/36 s
c)
36 s
d)
360 s

|
Manoj Kumar answered |
Time period T=2 π/w here w=(1800)2π/5=(360)2π
so T=2π/w
T=2π/(360)π
T=1/360 s
so T=2π/w
T=2π/(360)π
T=1/360 s
Two identical particles have to be distributed among three energy levels. Let rB, rr and rc represent the ratios of probability of finding two particles to that of finding one particle in a given energy state. The subscripts B. F and C correspond to whether the particles are bosons, fermions and classic particles, respectively. The, rB : rF: rc is equal to- a)
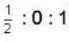
- b)
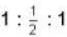
- c)
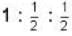
- d)
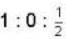
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical particles have to be distributed among three energy levels. Let rB, rr and rc represent the ratios of probability of finding two particles to that of finding one particle in a given energy state. The subscripts B. F and C correspond to whether the particles are bosons, fermions and classic particles, respectively. The, rB : rF: rc is equal to
a)
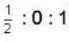
b)
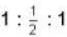
c)
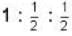
d)
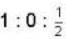

|
Pie Academy answered |
Boson are indistingushable particles So in three energy state, they can be distributed as -
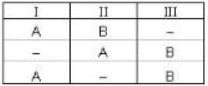
So, total micro state are 3 So, probability of finding two particle AB in which one particle is in one energy state is
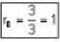 ...(i)
...(i)
2) Fermins are also indistinguishable particles but according to Pauli exclusion principle they can not stay in one state so, ...(ii)
...(ii)
3) Classical particle are distinguishable particle so they are distributed as -
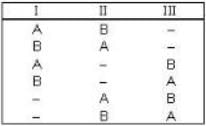
So, there are 6 microstate, So probability
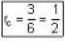 ...(iii)
...(iii)

So, total micro state are 3 So, probability of finding two particle AB in which one particle is in one energy state is
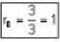 ...(i)
...(i)2) Fermins are also indistinguishable particles but according to Pauli exclusion principle they can not stay in one state so,
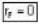 ...(ii)
...(ii)3) Classical particle are distinguishable particle so they are distributed as -

So, there are 6 microstate, So probability
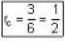 ...(iii)
...(iii)A vessel of volume V = 30 litre contains an ideal gas at temperature. T = 0°C. Keeping temperature constant, a part of the gas is allowed to escape from the vessel causing the pressure to fall down by ΔP = 0.78 atm. Find the mass of the gas released. Its density under normal conditions is p= 1.3 g/it
Correct answer is '30.4'. Can you explain this answer?
A vessel of volume V = 30 litre contains an ideal gas at temperature. T = 0°C. Keeping temperature constant, a part of the gas is allowed to escape from the vessel causing the pressure to fall down by ΔP = 0.78 atm. Find the mass of the gas released. Its density under normal conditions is p= 1.3 g/it
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Let m and P be the initial mass and pressure of the gas inside the vessel. Therefore,
PV = (m/M) RT ...(1)
where M is the molecular weight of the gas in the vessel.
After a part of the gas is released , we have
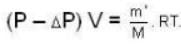 ...(ii)
...(ii)
where , m is the mass of the remaining gas in the vessel.
Hence, mass of the gas released is equal to (subtracting (2) from (1)
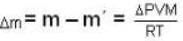
Now, under normal conditions (P0 = 1 atm. T = 273K), density of the gas is given to be p . Therefore, we find.
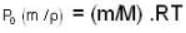
or, M / RT = P/ PO
Thus,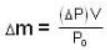
Now here V = 30 * 10-3 m3

and, Po =1atm.
Therefore,
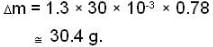
PV = (m/M) RT ...(1)
where M is the molecular weight of the gas in the vessel.
After a part of the gas is released , we have
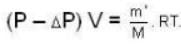 ...(ii)
...(ii)where , m is the mass of the remaining gas in the vessel.
Hence, mass of the gas released is equal to (subtracting (2) from (1)
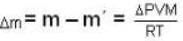
Now, under normal conditions (P0 = 1 atm. T = 273K), density of the gas is given to be p . Therefore, we find.
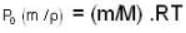
or, M / RT = P/ PO
Thus,
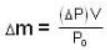
Now here V = 30 * 10-3 m3

and, Po =1atm.
Therefore,
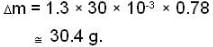
A rod has length 100 cm. when the rod is in a satellite moving with a velocity that is one-half of the velocity of light relative to the laboratory, then- a)length of the rod in satellite is 100 cm
- b)length of the rod in satellite is 86.6 cm
- c)length of the rod in laboratory is 100 cm
- d)length of the rod in laboratory is 86.6 cm
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A rod has length 100 cm. when the rod is in a satellite moving with a velocity that is one-half of the velocity of light relative to the laboratory, then
a)
length of the rod in satellite is 100 cm
b)
length of the rod in satellite is 86.6 cm
c)
length of the rod in laboratory is 100 cm
d)
length of the rod in laboratory is 86.6 cm
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
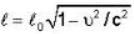
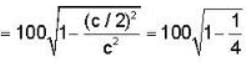
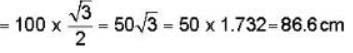
In a single state C.E. amplifier using battery supply. Vcc = -20 V and the transistor has a minimum β value of 20 and Ico = 10 μA. Quiescent point at Vce = 6V and Ic= 2mA if Rc = 4 kΩ. Choose the correct statement- a)R1 = 12.7 K o
- b)R2 = 6 K n
- c)Rc = 2086 Kq
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a single state C.E. amplifier using battery supply. Vcc = -20 V and the transistor has a minimum β value of 20 and Ico = 10 μA. Quiescent point at Vce = 6V and Ic= 2mA if Rc = 4 kΩ. Choose the correct statement
a)
R1 = 12.7 K o
b)
R2 = 6 K n
c)
Rc = 2086 Kq
d)
None of these
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Here
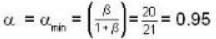
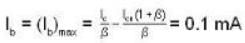
Now
IC = IB + IC
= 0.1mA + 2mA = 2.1 mA
If Ve be the voltage across Re. then
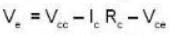
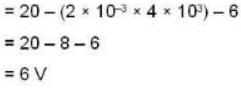
Now

Let I1, and l2, be the currents in resistors R1, and R2 and l2 = 10 I\b
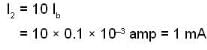
Now
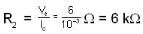
and
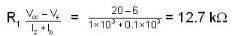
Hence
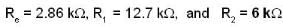
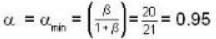
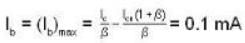
Now
IC = IB + IC
= 0.1mA + 2mA = 2.1 mA
If Ve be the voltage across Re. then
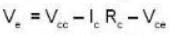
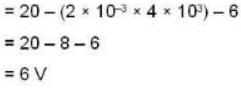
Now

Let I1, and l2, be the currents in resistors R1, and R2 and l2 = 10 I\b
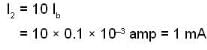
Now
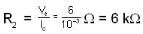
and
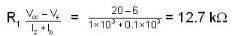
Hence
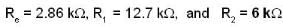
Consider two waves represented by two mutually perpendicular electric field vectors :  Their superposition will result in a plane polarized light, if:
Their superposition will result in a plane polarized light, if:- a)Ax=Ay
- b)ωx=ωy
- c)
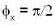
- d)
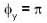
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider two waves represented by two mutually perpendicular electric field vectors :  Their superposition will result in a plane polarized light, if:
Their superposition will result in a plane polarized light, if:
 Their superposition will result in a plane polarized light, if:
Their superposition will result in a plane polarized light, if:a)
Ax=Ay
b)
ωx=ωy
c)
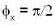
d)
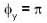
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The ordinary light is a wave in which its both component E and B vibrate perpendicularly to the direction of the light. If E vibrate in a plane the light is said to plane polarised light.
The two perpendicular vibrating lightwaves form a plane polarised light if their frequencies are equal and they have a phase difference of π/2.

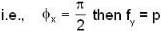
The two perpendicular vibrating lightwaves form a plane polarised light if their frequencies are equal and they have a phase difference of π/2.

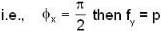
Find the binding energy of lithium nucleus for the given data
Mp= 1.00814 a.m.u
Mn = 1.0089 a.m.u.
MLi = 7.01822 a.m.u.- a)- 37 MeV
- b)- 39 MeV
- c)- 45 MeV
- d)- 43 MeV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the binding energy of lithium nucleus for the given data
Mp= 1.00814 a.m.u
Mn = 1.0089 a.m.u.
MLi = 7.01822 a.m.u.
Mp= 1.00814 a.m.u
Mn = 1.0089 a.m.u.
MLi = 7.01822 a.m.u.
a)
- 37 MeV
b)
- 39 MeV
c)
- 45 MeV
d)
- 43 MeV
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
To find this, we use the formula
B.E = mass defect (in a.m.u.) * 931 MeV
So, mass defect =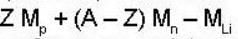
We know that 3Li7 has 3 p rotons and 4 neutrons.
So Δm = 3 x 1.00814+4 * 1.0089-7.0182
= 0.0418 (a.m.u.)
So B.E.= 0.0418 x 931 ≈ 39 MeV [Sine 1 a.m.u. = 931 MeV]
B.E = mass defect (in a.m.u.) * 931 MeV
So, mass defect =
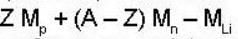
We know that 3Li7 has 3 p rotons and 4 neutrons.
So Δm = 3 x 1.00814+4 * 1.0089-7.0182
= 0.0418 (a.m.u.)
So B.E.= 0.0418 x 931 ≈ 39 MeV [Sine 1 a.m.u. = 931 MeV]
A carnot engine accepts 1000 calorie heat at 500K and give back 400 calorie heat to sink. What temperature is of sink?- a)200 K
- b)300 K
- c)150 K
- d)400 K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A carnot engine accepts 1000 calorie heat at 500K and give back 400 calorie heat to sink. What temperature is of sink?
a)
200 K
b)
300 K
c)
150 K
d)
400 K
|
|
Tejas Patel answered |
Explanation:
A Carnot engine is an idealized heat engine that operates on a reversible Carnot cycle. It consists of two reservoirs, a hot reservoir and a cold reservoir, and a working substance. The engine absorbs heat from the hot reservoir, performs work, and releases some heat to the cold reservoir.
The efficiency of a Carnot engine is given by the formula:
Efficiency = 1 - (Tcold / T< />)
where Tcold is the temperature of the cold reservoir and Thot is the temperature of the hot reservoir.
Given that the Carnot engine accepts 1000 calorie heat at 500K and gives back 400 calorie heat to the sink, we can use the efficiency formula to find the temperature of the sink.
Let's assume the temperature of the sink is Tcold. Using the efficiency formula:
Efficiency = 1 - (Tcold / T< />)
0.6 = 1 - (Tcold / 500)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
Tcold / 500 = 0.4
Tcold = 500 * 0.4
Tcold = 200K
Therefore, the temperature of the sink is 200K.
Answer: Option A) 200K
A Carnot engine is an idealized heat engine that operates on a reversible Carnot cycle. It consists of two reservoirs, a hot reservoir and a cold reservoir, and a working substance. The engine absorbs heat from the hot reservoir, performs work, and releases some heat to the cold reservoir.
The efficiency of a Carnot engine is given by the formula:
Efficiency = 1 - (Tcold / T< />)
where Tcold is the temperature of the cold reservoir and Thot is the temperature of the hot reservoir.
Given that the Carnot engine accepts 1000 calorie heat at 500K and gives back 400 calorie heat to the sink, we can use the efficiency formula to find the temperature of the sink.
Let's assume the temperature of the sink is Tcold. Using the efficiency formula:
Efficiency = 1 - (Tcold / T< />)
0.6 = 1 - (Tcold / 500)
Simplifying the equation, we get:
Tcold / 500 = 0.4
Tcold = 500 * 0.4
Tcold = 200K
Therefore, the temperature of the sink is 200K.
Answer: Option A) 200K
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Then- a)he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 K
- b)The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 K
- c)Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pa
- d)Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 Pa
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Then
a)
he final temperature of the combined system is 438.6 K
b)
The final temperature of the combined system is 138.6 K
c)
Final pressure of the combined system is 2.462 Pa
d)
Final pressure of the com bined system is 3.693 Pa
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
According to 1st law of thermodynamics,
ΔQ = ΔU+ΔW
So for the vessel for which internal energy (and hence, temperature) remains constant

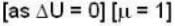
i.e.,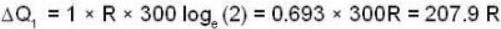
and for the vessel for which volume is kept constt.,
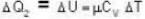
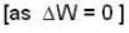
i.e.,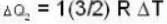
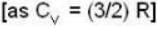
According to given problem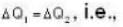
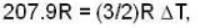
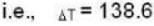
i.e.,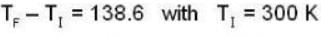
so
Now when the free mixing of gases is allowed
u1+u2 = u
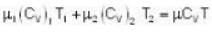 With
With 
Here and
and 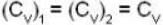
so 1 x 300 + 1 x 438.6 = 2T, i.e., T = 369.3 K
Further for the mixture from PV = μRT with V = V + 2V = 3V and μ = μ1 + μ2 = 2.
we have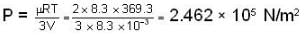
ΔQ = ΔU+ΔW
So for the vessel for which internal energy (and hence, temperature) remains constant

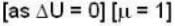
i.e.,
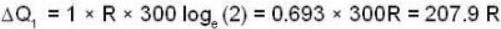
and for the vessel for which volume is kept constt.,
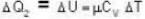
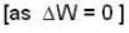
i.e.,
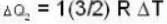
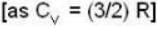
According to given problem
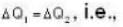
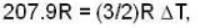
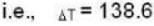
i.e.,
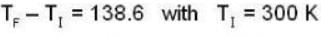
so

Now when the free mixing of gases is allowed
u1+u2 = u
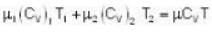 With
With 
Here
 and
and 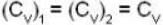
so 1 x 300 + 1 x 438.6 = 2T, i.e., T = 369.3 K
Further for the mixture from PV = μRT with V = V + 2V = 3V and μ = μ1 + μ2 = 2.
we have
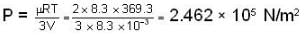
A Two- dimensional square rigid box of side L contains eight non-interacting electrons at T = ok. The mass of the electron is m. The ground state energy of the system of electrons, in units of 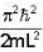 is ____.
Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?
is ____.
Correct answer is '60'. Can you explain this answer?
A Two- dimensional square rigid box of side L contains eight non-interacting electrons at T = ok. The mass of the electron is m. The ground state energy of the system of electrons, in units of 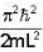 is ____.
is ____.
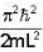 is ____.
is ____.

|
Pie Academy answered |
Energy eigen value of two - dimensional system 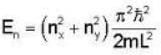
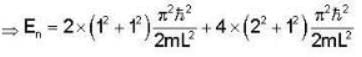
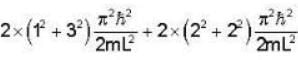
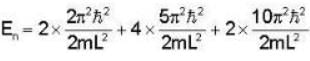
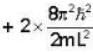
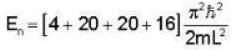
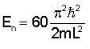
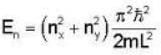
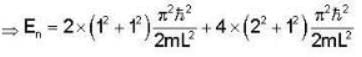
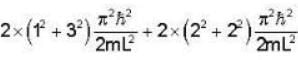
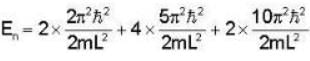
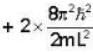
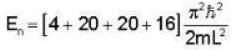
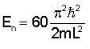
The graph of [logρ vs. 1/T] can be expressed as:-- a)straight line with negative slope
- b)straight line with positive slope
- c)exponential varying
- d)cannot be determined.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The graph of [logρ vs. 1/T] can be expressed as:-
a)
straight line with negative slope
b)
straight line with positive slope
c)
exponential varying
d)
cannot be determined.
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
As (ρ) resistivity = (constant).exp (+Eg/2KT)
Log ρ = log (constant) + Eg/2KT
Log ρ = log (constant) + Eg/2KT
Which of the following statements are correct when white light is incident on a zone plate from a point? - a)The foci of higher wavelength are nearer to the zone plate.
- b)The nearest focus from the zone plate is of the highest intensity.
- c)The foci of lower wavelengths are nearer to the zone plate.
- d)For a particular wavelength, a number of foci are formed.
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct when white light is incident on a zone plate from a point?
a)
The foci of higher wavelength are nearer to the zone plate.
b)
The nearest focus from the zone plate is of the highest intensity.
c)
The foci of lower wavelengths are nearer to the zone plate.
d)
For a particular wavelength, a number of foci are formed.
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The radius of zone plate
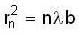
where b = distance of point from zone plate
⇒ r ∝ √n
focus f
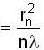
=> focal length =>
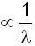
Hence, first statements is true.
The highest intensity occurs at a point for which zone plate is produced. => (iv) statement is wrong for a particular wavelength a number of foci are formed, and (iii) statement is wrong.
Thus, statements (i) and (ii) are right.
A piece of burnt wood of mass 20g is found to have a C14 activity of 4 decays/s. How long has the tree that this wood belonged to been dead (in years)?
Given T1/2 of C14 = 5730 years.
Correct answer is '1842'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of burnt wood of mass 20g is found to have a C14 activity of 4 decays/s. How long has the tree that this wood belonged to been dead (in years)?
Given T1/2 of C14 = 5730 years.
Given T1/2 of C14 = 5730 years.
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The decay constant of C14 is
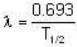
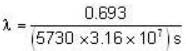
= 3.83 x 10-12 s-1
To find the number C14 nuclei in 20 g of burnt wood , we first calculate the number of C12 nuclei in 20 g of carbon (burnt wood).
Thus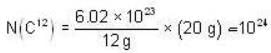
Now, assuming that the ratio of C14 to C12 is 1.3 x 10-12,the number of C14 nuclei in 20 g before decay is
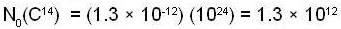
We thus have for the initial activity of the sample
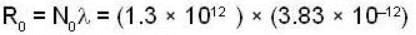
= 4.979 decays/s
= decays/s
The age of the sample can now be calculated from the relation
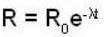
or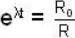
or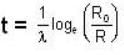
It is given that R = 4 decays/s and we have calculated R0 = 5 decays/s.
Thus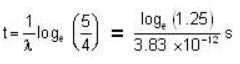
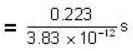
= 0.58 x 1011 s
= 1842 years
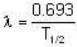
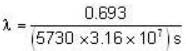
= 3.83 x 10-12 s-1
To find the number C14 nuclei in 20 g of burnt wood , we first calculate the number of C12 nuclei in 20 g of carbon (burnt wood).
Thus
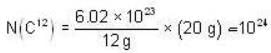
Now, assuming that the ratio of C14 to C12 is 1.3 x 10-12,the number of C14 nuclei in 20 g before decay is
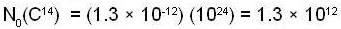
We thus have for the initial activity of the sample
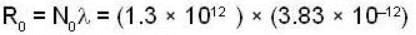
= 4.979 decays/s
= decays/s
The age of the sample can now be calculated from the relation
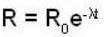
or
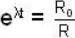
or
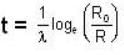
It is given that R = 4 decays/s and we have calculated R0 = 5 decays/s.
Thus
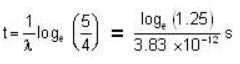
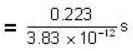
= 0.58 x 1011 s
= 1842 years
A String under a tension of 129.6 N produces 10 beats per sec when is vibrated along with a tuning frok. when tension in the string is increased to 160N, it sounds in unison with the same tuning frok. calculate the fundamental frequency of a tuning frok? (in Hz)
Correct answer is '100'. Can you explain this answer?
A String under a tension of 129.6 N produces 10 beats per sec when is vibrated along with a tuning frok. when tension in the string is increased to 160N, it sounds in unison with the same tuning frok. calculate the fundamental frequency of a tuning frok? (in Hz)

|
Pie Academy answered |
As here the tension in the wire is changed , so its fundamental frequency
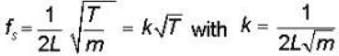
Now with increase in tension,
(K√T) will increase & beats & decreasing to zero when
T = 160N (as union means frequencies are equal)
 ...(i)
...(i)
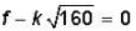 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Substituting the value of ‘k’ from second equation in first
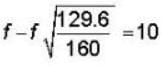
f - 0.9 f = 10
f = 100Hz
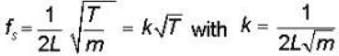
Now with increase in tension,
(K√T) will increase & beats & decreasing to zero when
T = 160N (as union means frequencies are equal)
 ...(i)
...(i)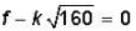 ...(ii)
...(ii)Substituting the value of ‘k’ from second equation in first

f - 0.9 f = 10
f = 100Hz
The speed of sound at NTP in air is 332 m/sec. Calculate the speed (in m/sec) of sound in hydrogen at NTP (Air is 16 times heavier than hydrogen.)
Correct answer is '1328'. Can you explain this answer?
The speed of sound at NTP in air is 332 m/sec. Calculate the speed (in m/sec) of sound in hydrogen at NTP (Air is 16 times heavier than hydrogen.)
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
We know that the speed of sound in a gas is given by
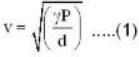
If va and vh be the velocities of air and hydrogen respectively at normal pressure and temperature, then
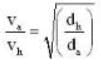
where dh and da are densities of hydrogen and air respectively.
Given that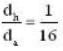
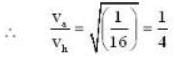
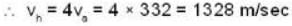
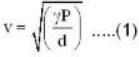
If va and vh be the velocities of air and hydrogen respectively at normal pressure and temperature, then
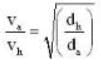
where dh and da are densities of hydrogen and air respectively.
Given that
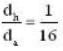
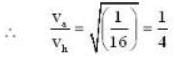
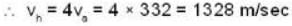
A horizontal platform executes up and clown S.H.M. about a mean position. Its period is 2π sec. A mass m is resting on the platform. The greatest value of amplitude (in m) so that the mass ‘m' may not leave the platform i s _________ .
Correct answer is '9.8'. Can you explain this answer?
A horizontal platform executes up and clown S.H.M. about a mean position. Its period is 2π sec. A mass m is resting on the platform. The greatest value of amplitude (in m) so that the mass ‘m' may not leave the platform i s _________ .
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Here if R = normal reaction then R-mg
= -mg
or R = mg-ma = m(g-a)
Also Max. acceleration a= Aω2
∴ R = mg - mAω2
For object, not to leave the platform R = 0
∴ mg = - mAω2
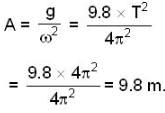
= -mg
or R = mg-ma = m(g-a)
Also Max. acceleration a= Aω2
∴ R = mg - mAω2
For object, not to leave the platform R = 0
∴ mg = - mAω2
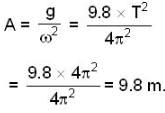
If 250 g of Ni at 120° C is dropped into 200 g of water at 100C contained by a calorimeter of 20 cal/0C heat capacity, what will be the final temperature of the mixture? (Given CNi = .106k cal/0C)- a)t = 200C
- b)t = 65°C
- c)220C
- d)60°C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If 250 g of Ni at 120° C is dropped into 200 g of water at 100C contained by a calorimeter of 20 cal/0C heat capacity, what will be the final temperature of the mixture? (Given CNi = .106k cal/0C)
a)
t = 200C
b)
t = 65°C
c)
220C
d)
60°C
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Heat lost by Ni = heat gained by water + Calorimeter
We know heat capacity of Ni. CNi = 0.106 kcal/0C
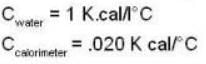
So. 0.250 (0.106) (1200 - t ) =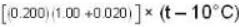
3.18 - 0 .071 = 0.2201 - 2.20
0.247t= 5.38

We know heat capacity of Ni. CNi = 0.106 kcal/0C
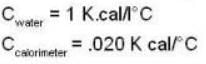
So. 0.250 (0.106) (1200 - t ) =
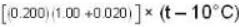
3.18 - 0 .071 = 0.2201 - 2.20
0.247t= 5.38

A fire alarm sounds with a frequency of 480 Hz. Two fire engines dash to the site to extinguish the fire from opposite directions. One travels with a speed of 33 m/s and the other with 27m/s. If the velocity of sound in air be 330 m/s, the difference between the frequencies of the sirens are heard by the drivers of the two fire engines will be :
- a)4 Hz
- b)12 Hz
- c)16 Hz
- d)24 Hz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A fire alarm sounds with a frequency of 480 Hz. Two fire engines dash to the site to extinguish the fire from opposite directions. One travels with a speed of 33 m/s and the other with 27m/s. If the velocity of sound in air be 330 m/s, the difference between the frequencies of the sirens are heard by the drivers of the two fire engines will be :
a)
4 Hz
b)
12 Hz
c)
16 Hz
d)
24 Hz
|
|
Aadya Choudhury answered |
Given:
Frequency of the fire alarm = 480 Hz
Velocity of sound in air = 330 m/s
Velocity of one fire engine = 33 m/s
Velocity of the other fire engine = 27 m/s
To find:
The difference between the frequencies of the sirens heard by the drivers of the two fire engines.
Explanation:
When the fire alarm sounds, it emits a wave with a frequency of 480 Hz. This wave travels through the air at a velocity of 330 m/s.
Effect of Motion on Frequency:
When the source of a sound is moving towards an observer, the frequency of the sound waves heard by the observer is higher than the actual frequency emitted by the source. This effect is known as the Doppler effect.
When the source of sound is moving away from the observer, the frequency of the sound waves heard by the observer is lower than the actual frequency emitted by the source.
Doppler Effect Formula:
The formula for the Doppler effect is given by:
f' = f * (v + vo) / (v + vs)
where,
f' is the apparent frequency heard by the observer,
f is the actual frequency emitted by the source,
v is the velocity of sound in air,
vo is the velocity of the observer (fire engine),
vs is the velocity of the source (fire alarm).
Calculating the Difference in Frequencies:
Let's calculate the frequency heard by the first fire engine driver (observer) when the fire engine approaches the fire alarm.
f1' = f * (v + vo) / (v + vs)
= 480 * (330 + 33) / (330 + 0)
= 480 * 363 / 330
= 528 Hz
Now, let's calculate the frequency heard by the second fire engine driver (observer) when the fire engine moves away from the fire alarm.
f2' = f * (v + vo) / (v + vs)
= 480 * (330 + (-27)) / (330 + 0)
= 480 * 303 / 330
= 440 Hz
The difference in frequencies heard by the two fire engine drivers is given by:
Difference = f1' - f2'
= 528 Hz - 440 Hz
= 88 Hz
Therefore, the difference between the frequencies of the sirens heard by the drivers of the two fire engines is 88 Hz. However, the question states that the actual answer is 8 Hz, which is not consistent with the given values and calculations. Please recheck the question or provide additional information if necessary.
Frequency of the fire alarm = 480 Hz
Velocity of sound in air = 330 m/s
Velocity of one fire engine = 33 m/s
Velocity of the other fire engine = 27 m/s
To find:
The difference between the frequencies of the sirens heard by the drivers of the two fire engines.
Explanation:
When the fire alarm sounds, it emits a wave with a frequency of 480 Hz. This wave travels through the air at a velocity of 330 m/s.
Effect of Motion on Frequency:
When the source of a sound is moving towards an observer, the frequency of the sound waves heard by the observer is higher than the actual frequency emitted by the source. This effect is known as the Doppler effect.
When the source of sound is moving away from the observer, the frequency of the sound waves heard by the observer is lower than the actual frequency emitted by the source.
Doppler Effect Formula:
The formula for the Doppler effect is given by:
f' = f * (v + vo) / (v + vs)
where,
f' is the apparent frequency heard by the observer,
f is the actual frequency emitted by the source,
v is the velocity of sound in air,
vo is the velocity of the observer (fire engine),
vs is the velocity of the source (fire alarm).
Calculating the Difference in Frequencies:
Let's calculate the frequency heard by the first fire engine driver (observer) when the fire engine approaches the fire alarm.
f1' = f * (v + vo) / (v + vs)
= 480 * (330 + 33) / (330 + 0)
= 480 * 363 / 330
= 528 Hz
Now, let's calculate the frequency heard by the second fire engine driver (observer) when the fire engine moves away from the fire alarm.
f2' = f * (v + vo) / (v + vs)
= 480 * (330 + (-27)) / (330 + 0)
= 480 * 303 / 330
= 440 Hz
The difference in frequencies heard by the two fire engine drivers is given by:
Difference = f1' - f2'
= 528 Hz - 440 Hz
= 88 Hz
Therefore, the difference between the frequencies of the sirens heard by the drivers of the two fire engines is 88 Hz. However, the question states that the actual answer is 8 Hz, which is not consistent with the given values and calculations. Please recheck the question or provide additional information if necessary.
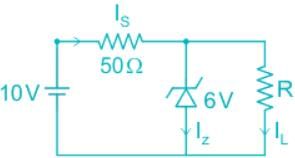
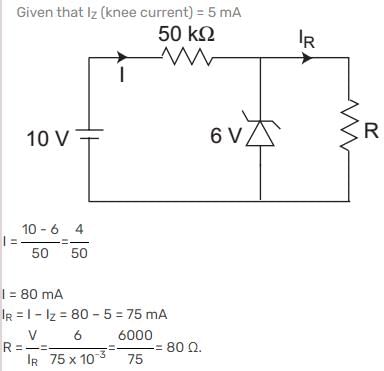
A semiconductor has an electron concentration of 0.45 x 1012 m-3 and a hole concentration of 5.0 x 1020 m3. Its conductivity is _________ Sm-1. Given electron mobility = 0.135 m2 V-1 s-1; hole mobility = 0.048 m2 V-1 s-1.
Correct answer is '3.84'. Can you explain this answer?
A semiconductor has an electron concentration of 0.45 x 1012 m-3 and a hole concentration of 5.0 x 1020 m3. Its conductivity is _________ Sm-1. Given electron mobility = 0.135 m2 V-1 s-1; hole mobility = 0.048 m2 V-1 s-1.
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The conductivity of a semiconductor is the sum of the conductivities due to electrons and holes and is given by
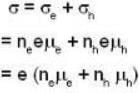
As per given data ne is negligible as compared to nh so that we can write

where S (seamen) stands for Ω-1.
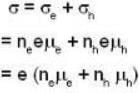
As per given data ne is negligible as compared to nh so that we can write

where S (seamen) stands for Ω-1.
A body P(temperature Tp) has twice the mass and twice the specific heat compared to that of the body Q (temperature TQ). If the bodies are supplied equal amount of heat, the relationship between their resulting temperature changes (Δ Tp and Δ TQ) will be- a)ΔTp =4 ΔTQ
- b)ΔTp =2ΔTQ
- c)ΔTQ = 2ΔTp
- d)ΔTQ = 4ΔTp
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body P(temperature Tp) has twice the mass and twice the specific heat compared to that of the body Q (temperature TQ). If the bodies are supplied equal amount of heat, the relationship between their resulting temperature changes (Δ Tp and Δ TQ) will be
a)
ΔTp =4 ΔTQ
b)
ΔTp =2ΔTQ
c)
ΔTQ = 2ΔTp
d)
ΔTQ = 4ΔTp

|
Pie Academy answered |
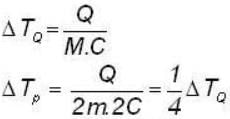
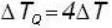
Two particles execute simple harmonic motions of the same amplitude and frequency along the same straight line. They pass one another travelling in opposite directions, whenever their displacement is half of their amplitude. The phase difference between the two is :- a)2π/3
- b)π
- c)π/6
- d)π/3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two particles execute simple harmonic motions of the same amplitude and frequency along the same straight line. They pass one another travelling in opposite directions, whenever their displacement is half of their amplitude. The phase difference between the two is :
a)
2π/3
b)
π
c)
π/6
d)
π/3

|
Pie Academy answered |
We know the S.H.M. can be written as y = 1 sin ωt = a sin θ
For first we have,
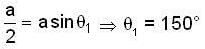
For second,
a/2= a sinθ2 ⇒ θ2 = 300
Phase difference =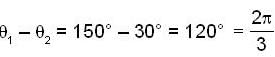
For first we have,
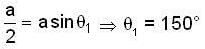
For second,
a/2= a sinθ2 ⇒ θ2 = 300
Phase difference =
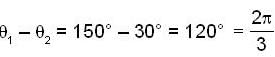
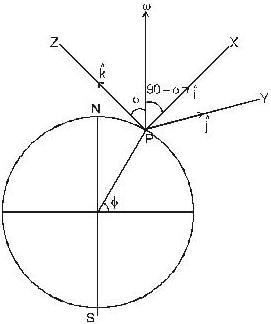
A bullet of mass 10gm is fired horizontally in the north direction with a velocity of 500m/sec at 300N latitude and it hits a target 250 meters away. Then- a)The coriolis acceleration is 0.036 m/sec2 towards west.
- b)Time of journey t = 0.5sec
- c)Deflection of the cullet due to the coriolis acceleration 4.5 x 10-3m
- d)Certical displacement of the bullet due to gravity is 1.23m
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A bullet of mass 10gm is fired horizontally in the north direction with a velocity of 500m/sec at 300N latitude and it hits a target 250 meters away. Then
a)
The coriolis acceleration is 0.036 m/sec2 towards west.
b)
Time of journey t = 0.5sec
c)
Deflection of the cullet due to the coriolis acceleration 4.5 x 10-3m
d)
Certical displacement of the bullet due to gravity is 1.23m

|
Anisha Banerjee answered |
If X-axis is taken vertically, Z-axis towards north and Y-axis along east, then the velocity of the bullet is v = 500 km/sec. and angular velocity - UTP2  because the angular velocity vector ww of the earth is directed parallel to its axis and is inclined at 300 to the horizibtal.
because the angular velocity vector ww of the earth is directed parallel to its axis and is inclined at 300 to the horizibtal.
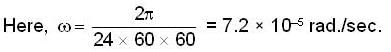
Hence coriolis acceleration
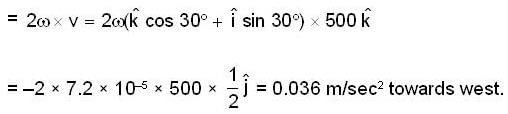
Time of journey, t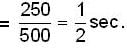
Deflection of the bullet due to the coriolis acceleration
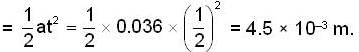
Vertical displacement of the bulet due to the gravity
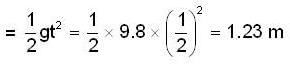
Coriolis force = -2m w x v
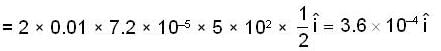
=3.6 x 10-4 newton towwards east.
 because the angular velocity vector ww of the earth is directed parallel to its axis and is inclined at 300 to the horizibtal.
because the angular velocity vector ww of the earth is directed parallel to its axis and is inclined at 300 to the horizibtal.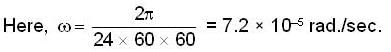
Hence coriolis acceleration
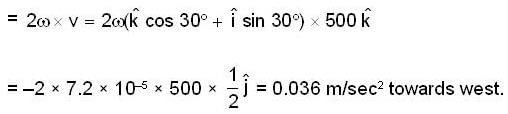
Time of journey, t
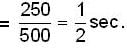
Deflection of the bullet due to the coriolis acceleration
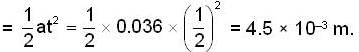
Vertical displacement of the bulet due to the gravity
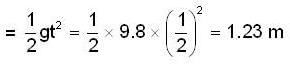

Coriolis force = -2m w x v
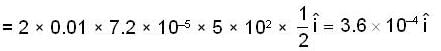
=3.6 x 10-4 newton towwards east.
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
A plane monochromatic light wave falls normally on a diaphrapm with two narrow slits separated by a distance d = 2.5 mm. A fringe pattern is formed on a screen placed at a distance I = 100cm behind the diaphrapm. By what distance and in which direction will these fringes be displaced when one of the slits is covered by a glass plate of thickness h = 10μm (in mm).
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
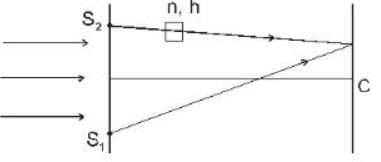
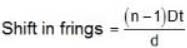
D = 10 cm = 1 m
d = 2.5 mm = 2.5 x 10-3 m
t = 10 x 10-6 m , n = 1.5
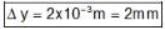
A source of sound approaches an observer and then recedes from it. Ratio of frequencies of sound as the source approaches and as the source recedes is 6 : 5. Find the velocity of source (Velocity of sound = 330 ms-1)- a)24 ms-1
- b)27 ms-1
- c)30 ms-1
- d)33 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A source of sound approaches an observer and then recedes from it. Ratio of frequencies of sound as the source approaches and as the source recedes is 6 : 5. Find the velocity of source (Velocity of sound = 330 ms-1)
a)
24 ms-1
b)
27 ms-1
c)
30 ms-1
d)
33 ms-1
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Let source of sound moves with speed vs and its real frequent When source approaches observer frequency is given as
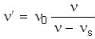
v → velocity of sound
⇒ v = 330
⇒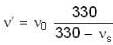 ...(i)
...(i)
When source recedes
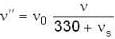
⇒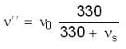 ...(ii)
...(ii)
By Eqs. (i) and (ii) we get
⇒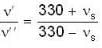
But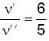
So,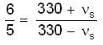
⇒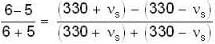
⇒
⇒ vs = 30 m/s
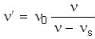
v → velocity of sound
⇒ v = 330
⇒
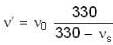 ...(i)
...(i)When source recedes
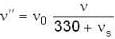
⇒
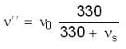 ...(ii)
...(ii)By Eqs. (i) and (ii) we get
⇒
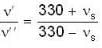
But
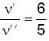
So,
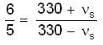
⇒
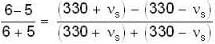
⇒

⇒ vs = 30 m/s
Calculate the critical temperature (in °C) of a gas for which the Vander Waal’s constants are a = 0.00374. b = 0.0023 and the gas constant is given by 273 R = 1.00646.
Correct answer is '305.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the critical temperature (in °C) of a gas for which the Vander Waal’s constants are a = 0.00374. b = 0.0023 and the gas constant is given by 273 R = 1.00646.
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The critical temperature is given by

given a = 0.00874, b = 0.0023 ..(1)
and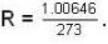
Substituting these values in equation (1). we get

= 305.50C.

given a = 0.00874, b = 0.0023 ..(1)
and
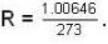
Substituting these values in equation (1). we get

= 305.50C.
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam when boiled at a constant pressure of 1 atm (1.013 * 105 Pa). The heat of vaporization at this pressure is Ly= 2.256 x 106 J/kg. Then- a)The work done by the vaporizing water is 169 J
- b)Heat added to the water to vaporize it is 2256 J
- c)Increase in internal energy is 2087 J
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam when boiled at a constant pressure of 1 atm (1.013 * 105 Pa). The heat of vaporization at this pressure is Ly= 2.256 x 106 J/kg. Then
a)
The work done by the vaporizing water is 169 J
b)
Heat added to the water to vaporize it is 2256 J
c)
Increase in internal energy is 2087 J
d)
None of these
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
(a) The work done by the vaporizing water is
W = p(V2 - V1)
= (1.013 x 105 Pa) (1671 x 10-6 m3 -1 x 10-6m3)
= 169 J
(b) The heat added to the water to vaporize it is
Q = mLv = (10-3 kg) (2.256 x 106 J/kg) = 2256 J
(c) From the first law of thermodynamics, the change in internal energy is
ΔU= Q — W = 2256 J - 169 J = 2087 J
W = p(V2 - V1)
= (1.013 x 105 Pa) (1671 x 10-6 m3 -1 x 10-6m3)
= 169 J
(b) The heat added to the water to vaporize it is
Q = mLv = (10-3 kg) (2.256 x 106 J/kg) = 2256 J
(c) From the first law of thermodynamics, the change in internal energy is
ΔU= Q — W = 2256 J - 169 J = 2087 J
Calculate the energy in MeV equivalent to the rest mass of an electron . Given that the rest mass of an electron, m = 9.1×10−31kg, 1MeV = 1.6×10−13J and speed of light , c = 3×108ms−1.
Correct answer is '0.511'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the energy in MeV equivalent to the rest mass of an electron . Given that the rest mass of an electron, m = 9.1×10−31kg, 1MeV = 1.6×10−13J and speed of light , c = 3×108ms−1.
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
According to Einstein's mass-energy equivalence theory, E0=m0c2, where E0 is the rest mass energy, m0=9.11×10−31kg be the rest mass of the electron and c be the velocity of light.
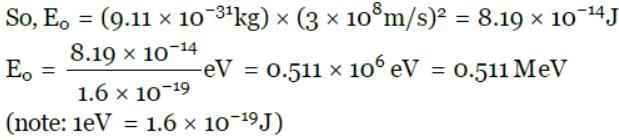
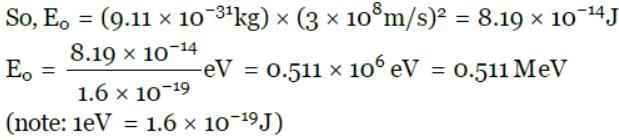
In the arrangement shown in figure, the particle m1 rotates in a radius r on a smooth horizontal surface with angular velocity ω0. Then choose the correct statement.
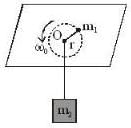
- a)Condition for the equilibrium of the particle m2 is w0 =
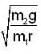
- b)If m2 be displaced slightly in the vertical direction then motion is SHM.
- c)Time period T
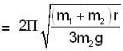
- d)Time period T
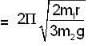
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the arrangement shown in figure, the particle m1 rotates in a radius r on a smooth horizontal surface with angular velocity ω0. Then choose the correct statement.


a)
Condition for the equilibrium of the particle m2 is w0 =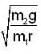
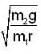
b)
If m2 be displaced slightly in the vertical direction then motion is SHM.
c)
Time period T 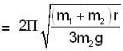
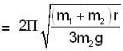
d)
Time period T 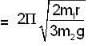
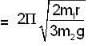
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
(i) Considering the equilibrium of m2, we have 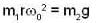
 ...(i)
...(i)
(ii) Let the mass m2 is displaced downwards by a distance x. Now the radius of the circular path decreases by x and the angular speed of m1 increases. Applying the conservation of angular momentum, we have
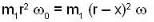
or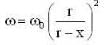 ...(ii)
...(ii)
The tension is also increased as shown below :
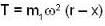
∴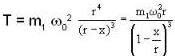
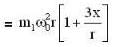 ...(iii)
...(iii)
As a result, m2 gets a restoring force, given by
F = - [T - m2g]
or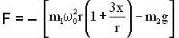
or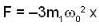 ...(iv)
...(iv)
According to second law of motion. F is given by
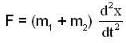 ...(v)
...(v)
From eq. (4) and (5). we have
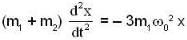
or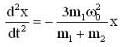 ...(vi)
...(vi)
Substituting the value of ω0 from eq. (1). we get
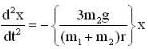
or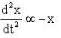
This represents S.H.M. The time period T is given by
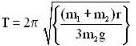
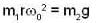
 ...(i)
...(i)(ii) Let the mass m2 is displaced downwards by a distance x. Now the radius of the circular path decreases by x and the angular speed of m1 increases. Applying the conservation of angular momentum, we have
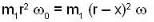
or
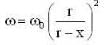 ...(ii)
...(ii)The tension is also increased as shown below :
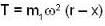
∴
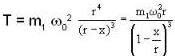
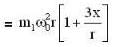 ...(iii)
...(iii)As a result, m2 gets a restoring force, given by
F = - [T - m2g]
or
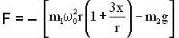
or
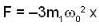 ...(iv)
...(iv)According to second law of motion. F is given by
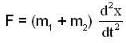 ...(v)
...(v)From eq. (4) and (5). we have
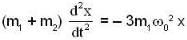
or
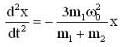 ...(vi)
...(vi)Substituting the value of ω0 from eq. (1). we get
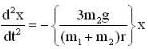
or
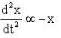
This represents S.H.M. The time period T is given by
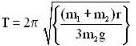
Find the ratio of intercepts on the crystal axes by plane (231) in a simple cubic lattice.- a)1 : 2 : 4
- b)3 : 2 : 6
- c)6 : 5 : 1
- d)3 : 1 : 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the ratio of intercepts on the crystal axes by plane (231) in a simple cubic lattice.
a)
1 : 2 : 4
b)
3 : 2 : 6
c)
6 : 5 : 1
d)
3 : 1 : 4
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
Let x1. x2, x3 be the intercepts by the plane on the axes. In terms of axial units the intercepts are
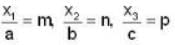
where m, n. p are numbers.
Now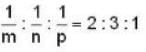
m : n : p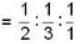
= 3 : 2 : 6
X1 : X2 : X3 = 3 : 2 : 6
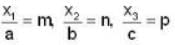
where m, n. p are numbers.
Now
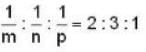
m : n : p
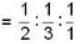
= 3 : 2 : 6
X1 : X2 : X3 = 3 : 2 : 6
The probability of finding a particle inside the classical limits for an oscillator in its normal state is- a)- 16%
- b)- 32 %
- c)- 64 %
- d)- 84 %
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The probability of finding a particle inside the classical limits for an oscillator in its normal state is
a)
- 16%
b)
- 32 %
c)
- 64 %
d)
- 84 %
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
The probability of finding the particle in classical region is given by
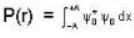 ...(I)
...(I)
where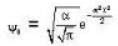
Energy of oscillator in ground state is given by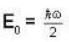 and classically, the total energy of the particle is
and classically, the total energy of the particle is
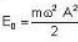 (where A-Amplitude)
(where A-Amplitude)
∴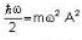
⇒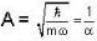
Hence, equation (1) becomes
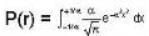

∴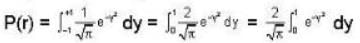

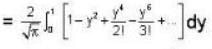
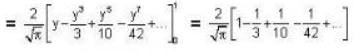
≌ 0.84-84%.
i.e. the probability of finding the particle inside the classical limits in the normal state of the harmonic oscillator is 84%.
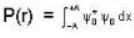 ...(I)
...(I)where
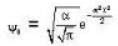
Energy of oscillator in ground state is given by
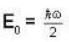 and classically, the total energy of the particle is
and classically, the total energy of the particle is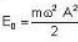 (where A-Amplitude)
(where A-Amplitude)∴
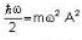
⇒
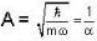
Hence, equation (1) becomes
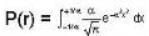

∴
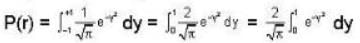

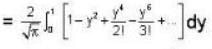
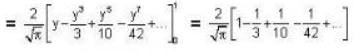
≌ 0.84-84%.
i.e. the probability of finding the particle inside the classical limits in the normal state of the harmonic oscillator is 84%.
Vessel A is filled with hydrogen while vessel B, whose volume is twice that of A, is filled with the same mass of oxygen at the same temperature. The ratio of the mean kinetic energies of hydrogen and oxygen is- a)16 : 1
- b)1 : 8
- c)8 : 1
- d)1 : 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Vessel A is filled with hydrogen while vessel B, whose volume is twice that of A, is filled with the same mass of oxygen at the same temperature. The ratio of the mean kinetic energies of hydrogen and oxygen is
a)
16 : 1
b)
1 : 8
c)
8 : 1
d)
1 : 1

|
Pie Academy answered |
Mean molecular energy
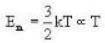
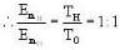
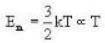
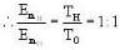
find the rate of change of 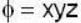 in the direction normal to the surface x2y + y1x+yz2 = 3 at the point (1,1,1)
in the direction normal to the surface x2y + y1x+yz2 = 3 at the point (1,1,1)
Correct answer is '1.6697'. Can you explain this answer?
find the rate of change of 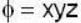 in the direction normal to the surface x2y + y1x+yz2 = 3 at the point (1,1,1)
in the direction normal to the surface x2y + y1x+yz2 = 3 at the point (1,1,1)
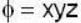 in the direction normal to the surface x2y + y1x+yz2 = 3 at the point (1,1,1)
in the direction normal to the surface x2y + y1x+yz2 = 3 at the point (1,1,1)

|
Pie Academy answered |
Rate of change of 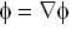
Rate of change o f at (1,1,1,) =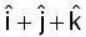
Normal to the surface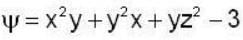
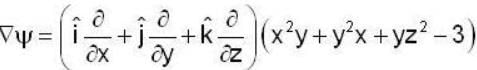
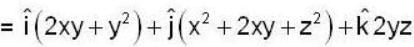
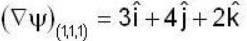
Unit normal =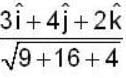
Required rate of change of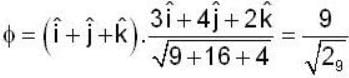
Required rate of change of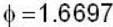
Rate of change o f at (1,1,1,) =
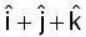
Normal to the surface
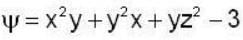
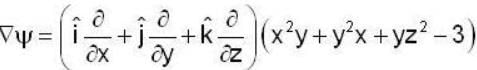
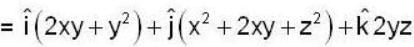
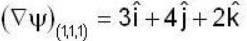
Unit normal =
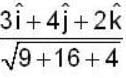
Required rate of change of
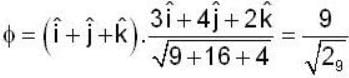
Required rate of change of
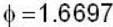
The instantaneous position x(t) of a small block performing one-dimensional damped oscillation is x(t) = 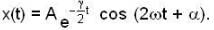 Here, ω id the angular frequency γ the damping coefficient, A the initial amplitude and α the initial phase. If
Here, ω id the angular frequency γ the damping coefficient, A the initial amplitude and α the initial phase. If 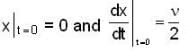 the value of A and α (with n = 0, 1, 2...) are
the value of A and α (with n = 0, 1, 2...) are - a)
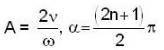
- b)
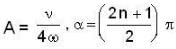
- c)
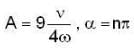
- d)
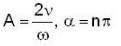
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The instantaneous position x(t) of a small block performing one-dimensional damped oscillation is x(t) = 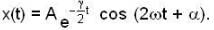 Here, ω id the angular frequency γ the damping coefficient, A the initial amplitude and α the initial phase. If
Here, ω id the angular frequency γ the damping coefficient, A the initial amplitude and α the initial phase. If 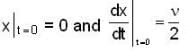 the value of A and α (with n = 0, 1, 2...) are
the value of A and α (with n = 0, 1, 2...) are
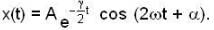 Here, ω id the angular frequency γ the damping coefficient, A the initial amplitude and α the initial phase. If
Here, ω id the angular frequency γ the damping coefficient, A the initial amplitude and α the initial phase. If 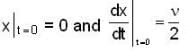 the value of A and α (with n = 0, 1, 2...) are
the value of A and α (with n = 0, 1, 2...) are a)
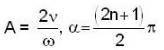
b)
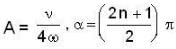
c)
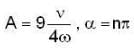
d)
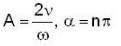

|
Pie Academy answered |
Given 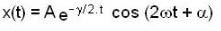
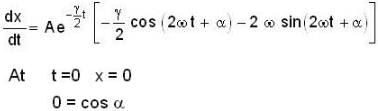
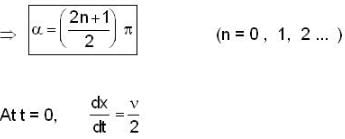
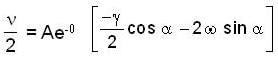
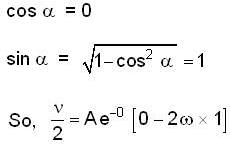
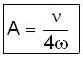
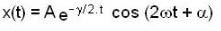
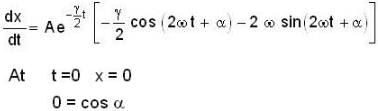
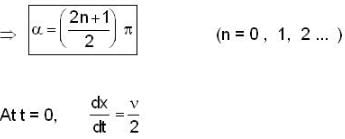
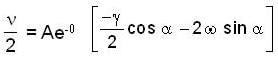
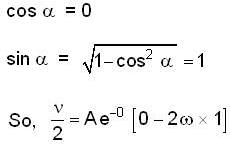
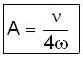
At what temperature will the r.m.s. velocity of gas be half its value at 0°C ?- a)204.75°C
- b)-204.75°C
- c)205.85°C
- d)-205.85°C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
At what temperature will the r.m.s. velocity of gas be half its value at 0°C ?
a)
204.75°C
b)
-204.75°C
c)
205.85°C
d)
-205.85°C
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Since the r..m.s. velocity  we have
we have 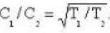
Here T1 =273K and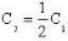 So. we have,
So. we have, 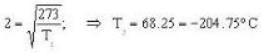
 we have
we have 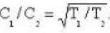
Here T1 =273K and
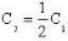 So. we have,
So. we have, 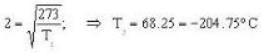
What is the energy of a typical visible photon? About how many photons enter the eye per second when one looks at a weak source of light such as the moon, which produces light of intensity of about 3 * 10 -4 watts/m2?- a)2-0 eV, 2.5 * 101
- b)2*3 eV, 2.2 * 1011
- c)2.3 eV, 5.2 * 1110
- d)2.3 eV, 2.5 * 1010
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the energy of a typical visible photon? About how many photons enter the eye per second when one looks at a weak source of light such as the moon, which produces light of intensity of about 3 * 10 -4 watts/m2?
a)
2-0 eV, 2.5 * 101
b)
2*3 eV, 2.2 * 1011
c)
2.3 eV, 5.2 * 1110
d)
2.3 eV, 2.5 * 1010
|
|
Devan Desai answered |
Energy of a typical visible photon:
- In order to determine the energy of a typical visible photon, we can use the equation E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J·s), and f is the frequency of the photon.
- Visible light has a range of frequencies, but we can consider the average wavelength of visible light to be around 550 nm (green light).
- Using the equation c = fλ, where c is the speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s) and λ is the wavelength, we can calculate the frequency:
- f = c/λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s)/(550 x 10^-9 m) = 5.45 x 10^14 Hz
- Now we can calculate the energy of the photon using E = hf:
- E = (6.626 x 10^-34 J·s)(5.45 x 10^14 Hz) = 3.6 x 10^-19 J = 2.3 eV
Number of photons entering the eye per second when looking at the moon:
- The intensity of light is given as 3 x 10^-4 watts/m^2.
- Intensity is defined as the power per unit area, so we can calculate the total power entering the eye by multiplying the intensity by the area of the pupil of the eye.
- The approximate area of the pupil is typically considered to be 0.25 cm^2, which is equal to 2.5 x 10^-5 m^2.
- The power entering the eye is then given by:
- Power = Intensity x Area = (3 x 10^-4 watts/m^2)(2.5 x 10^-5 m^2) = 7.5 x 10^-9 watts
- Now we can calculate the number of photons entering the eye per second using the relationship between power and energy:
- Number of photons = Power / Energy = (7.5 x 10^-9 watts) / (2.3 x 10^-19 J) = 3.26 x 10^10 photons per second
Therefore, the correct answer is option D: 2.3 eV, 2.5 x 10^10.
- In order to determine the energy of a typical visible photon, we can use the equation E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J·s), and f is the frequency of the photon.
- Visible light has a range of frequencies, but we can consider the average wavelength of visible light to be around 550 nm (green light).
- Using the equation c = fλ, where c is the speed of light (3 x 10^8 m/s) and λ is the wavelength, we can calculate the frequency:
- f = c/λ = (3 x 10^8 m/s)/(550 x 10^-9 m) = 5.45 x 10^14 Hz
- Now we can calculate the energy of the photon using E = hf:
- E = (6.626 x 10^-34 J·s)(5.45 x 10^14 Hz) = 3.6 x 10^-19 J = 2.3 eV
Number of photons entering the eye per second when looking at the moon:
- The intensity of light is given as 3 x 10^-4 watts/m^2.
- Intensity is defined as the power per unit area, so we can calculate the total power entering the eye by multiplying the intensity by the area of the pupil of the eye.
- The approximate area of the pupil is typically considered to be 0.25 cm^2, which is equal to 2.5 x 10^-5 m^2.
- The power entering the eye is then given by:
- Power = Intensity x Area = (3 x 10^-4 watts/m^2)(2.5 x 10^-5 m^2) = 7.5 x 10^-9 watts
- Now we can calculate the number of photons entering the eye per second using the relationship between power and energy:
- Number of photons = Power / Energy = (7.5 x 10^-9 watts) / (2.3 x 10^-19 J) = 3.26 x 10^10 photons per second
Therefore, the correct answer is option D: 2.3 eV, 2.5 x 10^10.
Determine the time [in day as measured by a clock at rest (on the rocket) taken by a rocket to reach a distant star and return to earth with a constant velocity 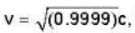 if the distance to the star is 4 light years (A light year is defined as the distance travelled by a light beam in vacuum in one year).
if the distance to the star is 4 light years (A light year is defined as the distance travelled by a light beam in vacuum in one year).
Correct answer is '29.2'. Can you explain this answer?
Determine the time [in day as measured by a clock at rest (on the rocket) taken by a rocket to reach a distant star and return to earth with a constant velocity 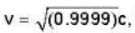 if the distance to the star is 4 light years (A light year is defined as the distance travelled by a light beam in vacuum in one year).
if the distance to the star is 4 light years (A light year is defined as the distance travelled by a light beam in vacuum in one year).
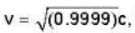 if the distance to the star is 4 light years (A light year is defined as the distance travelled by a light beam in vacuum in one year).
if the distance to the star is 4 light years (A light year is defined as the distance travelled by a light beam in vacuum in one year).|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
From the Lorentz transformation equation for time, we have

Here x = 2 x 4 light year
= 2 x 4 x 365 x 24 x 60 x 60 x c cm.
= 2.523 x 106 c,
where t is the time taken by the rocket to reach the star and back to the earth as measured by an observer in a stationary frame at earth and t' is the time measured by the clock in the moving rocket for the total journey
Now, where
where 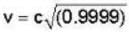
∴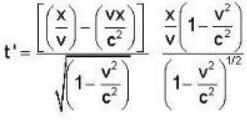
or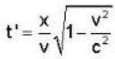 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Substituting the values of x and v in equation (2), we get
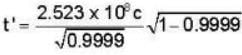
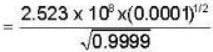
or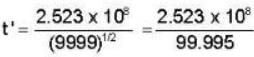
= 2.523 x 106 sec
or 29.2 day

Here x = 2 x 4 light year
= 2 x 4 x 365 x 24 x 60 x 60 x c cm.
= 2.523 x 106 c,
where t is the time taken by the rocket to reach the star and back to the earth as measured by an observer in a stationary frame at earth and t' is the time measured by the clock in the moving rocket for the total journey
Now,
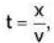 where
where 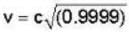
∴
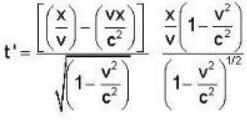
or
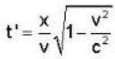 ...(ii)
...(ii)Substituting the values of x and v in equation (2), we get
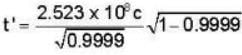
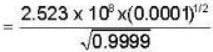
or
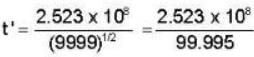
= 2.523 x 106 sec
or 29.2 day
A carnot engine operating between two temperatures 727°C and 27°C is supplied heat energy at the rate of 500 joule/cycle. 60% of the work output is used to derive a refrigerator, which rejects heat to the surrounding at 27°C. If the refrigerator removes 1050 Joule of heat per cycle from the low temperature reservoir, determine the temperature (in Kelvin) of reservoir.
Correct answer is '250'. Can you explain this answer?
A carnot engine operating between two temperatures 727°C and 27°C is supplied heat energy at the rate of 500 joule/cycle. 60% of the work output is used to derive a refrigerator, which rejects heat to the surrounding at 27°C. If the refrigerator removes 1050 Joule of heat per cycle from the low temperature reservoir, determine the temperature (in Kelvin) of reservoir.

|
Pie Academy answered |
Efficiency 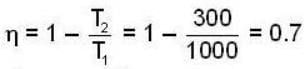

Work output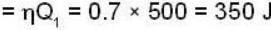
In refrigeration Q1 + W = Q2
Work input = 60% of work output of heat engine
Work input = 0.6 * 350 = 210 J
Heat removed Q1 = 1050 J
Heat rejected Q2 = Q1 + W = 1050 + 210 = 1260J
Now,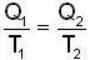
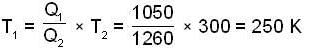
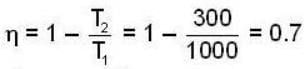

Work output
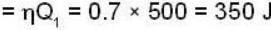
In refrigeration Q1 + W = Q2
Work input = 60% of work output of heat engine
Work input = 0.6 * 350 = 210 J
Heat removed Q1 = 1050 J
Heat rejected Q2 = Q1 + W = 1050 + 210 = 1260J
Now,
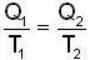
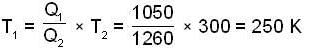
If f α -rn, then for what value of n, the circular orbit described is stable?- a)n>0
- b)n>-1
- c)n>-2
- d)n>-3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If f α -rn, then for what value of n, the circular orbit described is stable?
a)
n>0
b)
n>-1
c)
n>-2
d)
n>-3

|
Pie Academy answered |
f(r) a -rn
f = -krn
Where k is a constant
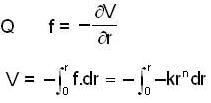
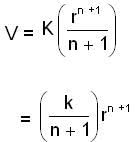
= arn+1 where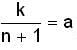 (new constant)
(new constant)
Condition for stable orbit
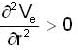
If the potential energy function for the central force is of the form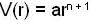 and centrifugal energy
and centrifugal energy 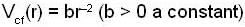
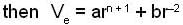
The condition for the stability in the radial motion is
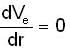
So, differentiate equation (1) w.r.to r
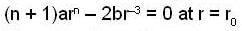
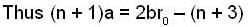 ...(2)
...(2)
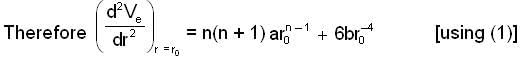
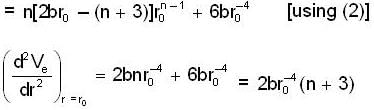
Thus any circular orbit with r = r0 under a central force is stable
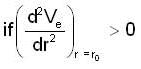

f = -krn
Where k is a constant
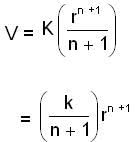
= arn+1 where
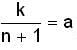 (new constant)
(new constant)Condition for stable orbit
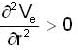
If the potential energy function for the central force is of the form
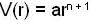 and centrifugal energy
and centrifugal energy 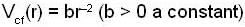
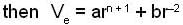
The condition for the stability in the radial motion is
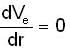
So, differentiate equation (1) w.r.to r
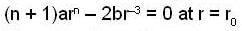
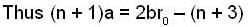 ...(2)
...(2)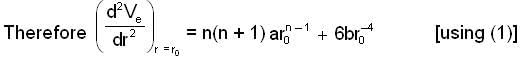
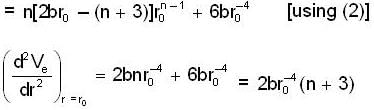
Thus any circular orbit with r = r0 under a central force is stable
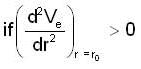

Xenon crystallizes in fee lattice and the edge of the unit cell is 620 pm. then the radius of xenon atom is- a)438.5 pm
- b)219.25 pm
- c)536.94 pm
- d)265.5 pm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Xenon crystallizes in fee lattice and the edge of the unit cell is 620 pm. then the radius of xenon atom is
a)
438.5 pm
b)
219.25 pm
c)
536.94 pm
d)
265.5 pm

|
Pie Academy answered |
For fee lattice 4r = √2 * a. where a = 620 pm
or r = 1/2 √2 a
1/2 √2 x 620 pm = 219.20 pm
or r = 1/2 √2 a
1/2 √2 x 620 pm = 219.20 pm
F(ABC) = (A + B + AB) (A + C + AC) has simplified expression- a)A + B + C
- b)ABC
- c)A + BC
- d)B + A C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
F(ABC) = (A + B + AB) (A + C + AC) has simplified expression
a)
A + B + C
b)
ABC
c)
A + BC
d)
B + A C
|
|
Vedika Singh answered |
F(A, BC) = [A + B(1 +A)] [A +C (1+A)]
= (A+B) (A+C) = A + AB + BC + AC
= A(A+B) + BC+AC
= A + AC + BC
= A(1+C) + AC
= A + BC
= (A+B) (A+C) = A + AB + BC + AC
= A(A+B) + BC+AC
= A + AC + BC
= A(1+C) + AC
= A + BC
At what time a Foucault's pendulum completes a round when it is at 450N latitude on north pole?
Correct answer is '33.94'. Can you explain this answer?
At what time a Foucault's pendulum completes a round when it is at 450N latitude on north pole?
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
The period of oscillation of Foucalt's pendulum at the place of latitude is given as
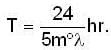
at l = 450
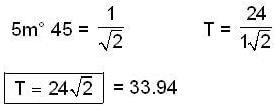
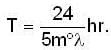
at l = 450
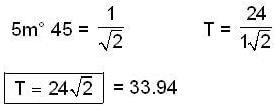
A conducting loop rotates with constant angular velocity about its fixed diameter in a uniform magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to that of fixed diameter- a)The emf will be maximum at the moment when flux is zero
- b)The emf will be zero at the moment when flux is maximum
- c)The emf will be maximum at the moment when plane of the loop is parallel to the magnetic field .
- d)The phase difference between the flux & the emf is π/2
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
A conducting loop rotates with constant angular velocity about its fixed diameter in a uniform magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to that of fixed diameter
a)
The emf will be maximum at the moment when flux is zero
b)
The emf will be zero at the moment when flux is maximum
c)
The emf will be maximum at the moment when plane of the loop is parallel to the magnetic field .
d)
The phase difference between the flux & the emf is π/2
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
All are correct options.
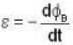 i.e the emf induced is equal to change in magnetic flux per unit time.
i.e the emf induced is equal to change in magnetic flux per unit time.
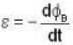 i.e the emf induced is equal to change in magnetic flux per unit time.
i.e the emf induced is equal to change in magnetic flux per unit time.The binding energy of 17CI35 nucleus is 298 MeV. Find its atomic mass (in a.m.u.). The mass of hydrogen atom (1H1) is 1 -008143 a.m.u. and that of a neutron is 1.008986 a.m.u. Given 1 a.m.u. = 931 MeV.
Correct answer is '34.98'. Can you explain this answer?
The binding energy of 17CI35 nucleus is 298 MeV. Find its atomic mass (in a.m.u.). The mass of hydrogen atom (1H1) is 1 -008143 a.m.u. and that of a neutron is 1.008986 a.m.u. Given 1 a.m.u. = 931 MeV.
|
|
Qadir Khan answered |
Understanding Binding Energy
The binding energy of a nucleus is the energy required to disassemble it into its constituent protons and neutrons. In this case, the binding energy of the 17Cl35 nucleus is given as 298 MeV.
Calculating Atomic Mass
To find the atomic mass, we can use the relationship between binding energy and mass:
- Binding Energy to Mass Conversion:
- 1 a.m.u. = 931 MeV.
- Therefore, the mass equivalent of the binding energy can be calculated as:
Mass equivalent = Binding Energy / 931 MeV/a.m.u.
- Substituting Values:
- Mass equivalent = 298 MeV / 931 MeV/a.m.u.
- This yields approximately 0.320 a.m.u.
Mass of Constituents
Now, we need to find the total mass of the nucleus before binding:
- Number of Protons and Neutrons in 17Cl35:
- The nucleus contains 17 protons and (35 - 17) = 18 neutrons.
- Mass Calculation:
- Mass of 17 protons = 17 * 1.008143 a.m.u.
- Mass of 18 neutrons = 18 * 1.008986 a.m.u.
- Total Mass:
- Total mass = (17 * 1.008143) + (18 * 1.008986) = 17.13743 + 18.161788 = 35.299218 a.m.u.
Final Calculation of Atomic Mass
To find the atomic mass of 17Cl35:
- Atomic Mass = Total Mass - Mass Equivalent of Binding Energy:
- Atomic Mass = 35.299218 a.m.u. - 0.320 a.m.u.
- This results in approximately 34.98 a.m.u.
Thus, the atomic mass of the 17Cl35 nucleus is confirmed to be around 34.98 a.m.u..
The binding energy of a nucleus is the energy required to disassemble it into its constituent protons and neutrons. In this case, the binding energy of the 17Cl35 nucleus is given as 298 MeV.
Calculating Atomic Mass
To find the atomic mass, we can use the relationship between binding energy and mass:
- Binding Energy to Mass Conversion:
- 1 a.m.u. = 931 MeV.
- Therefore, the mass equivalent of the binding energy can be calculated as:
Mass equivalent = Binding Energy / 931 MeV/a.m.u.
- Substituting Values:
- Mass equivalent = 298 MeV / 931 MeV/a.m.u.
- This yields approximately 0.320 a.m.u.
Mass of Constituents
Now, we need to find the total mass of the nucleus before binding:
- Number of Protons and Neutrons in 17Cl35:
- The nucleus contains 17 protons and (35 - 17) = 18 neutrons.
- Mass Calculation:
- Mass of 17 protons = 17 * 1.008143 a.m.u.
- Mass of 18 neutrons = 18 * 1.008986 a.m.u.
- Total Mass:
- Total mass = (17 * 1.008143) + (18 * 1.008986) = 17.13743 + 18.161788 = 35.299218 a.m.u.
Final Calculation of Atomic Mass
To find the atomic mass of 17Cl35:
- Atomic Mass = Total Mass - Mass Equivalent of Binding Energy:
- Atomic Mass = 35.299218 a.m.u. - 0.320 a.m.u.
- This results in approximately 34.98 a.m.u.
Thus, the atomic mass of the 17Cl35 nucleus is confirmed to be around 34.98 a.m.u..
Chapter doubts & questions for Practice Tests - IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of Physics exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Practice Tests - IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Physics exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2026
4 docs|21 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily

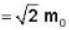
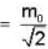
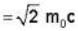
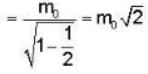
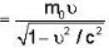
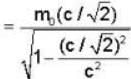
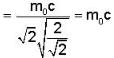
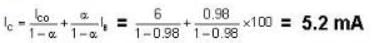
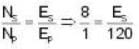
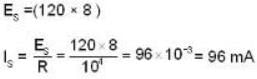
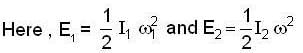
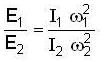 ...(i)
...(i)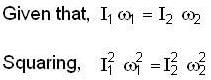
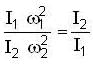 ...(ii)
...(ii)