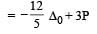All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Coordination Compounds for NEET Exam
If zeise’s salt has the formula [Pt(C2H4)CI3]-. In this, platinum primary and secondary valency are- a)+ 1 and 3
- b)+ 1 and 4
- c)+ 3 and 4
- d)+ 4 and 6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If zeise’s salt has the formula [Pt(C2H4)CI3]-. In this, platinum primary and secondary valency are
a)
+ 1 and 3
b)
+ 1 and 4
c)
+ 3 and 4
d)
+ 4 and 6
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Let the oxidation state of pt be x.
Oxidation state of cl is -1.
So x + 0 – (1*3) must be equal to -1 since the charge of the whole compound is -1.
x + 0 – (1*3) = -1
x -3 = -1
x = -1 + 3
x = +2
So the oxidation state of platinum is +2.
Secondary is due to legend there are mono deadened legend
then 1×4= 4
Oxidation state of cl is -1.
So x + 0 – (1*3) must be equal to -1 since the charge of the whole compound is -1.
x + 0 – (1*3) = -1
x -3 = -1
x = -1 + 3
x = +2
So the oxidation state of platinum is +2.
Secondary is due to legend there are mono deadened legend
then 1×4= 4
The correct IUPAC name of the complex Fe(C5H5)2 is _- a)Cyclopentadienyl iron (II)
- b)Bis (cyclopentadienyl) iron (II)
- c)Dicyclopentadiency ferrate (II)
- d)Ferrocene
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of the complex Fe(C5H5)2 is _
a)
Cyclopentadienyl iron (II)
b)
Bis (cyclopentadienyl) iron (II)
c)
Dicyclopentadiency ferrate (II)
d)
Ferrocene
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
The iron complex may be treated as cationic part, and C5H5- is a bidentate ligand therefore name can be assigned as follows “dicyclopentadienyl Iron (II) cation”.
In the complex PtCl4 . 5NH3 if coordination number of platinum is 6, number of chloride ions precipitated by adding AgNO3 are
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex PtCl4 . 5NH3 if coordination number of platinum is 6, number of chloride ions precipitated by adding AgNO3 are
|
|
Poulomi Desai answered |
Coordination number of platinum is 6.
∴ Number of chloride ions precipitated by adding AgCI are 3.
∴ Number of chloride ions precipitated by adding AgCI are 3.
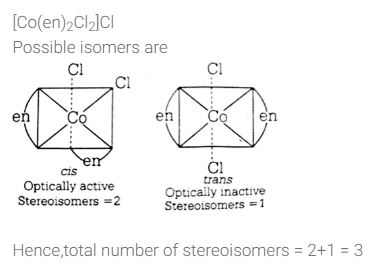
Type of bonding in K4 [Fe(CN)6] is/a- a)ionic
- b)covalent
- c)metallic
- d)coordinate covalent
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Type of bonding in K4 [Fe(CN)6] is/a
a)
ionic
b)
covalent
c)
metallic
d)
coordinate covalent
|
|
Shubham Jain answered |
The complex K4[Fe(CN)6] whose formula can be written like that of double salt. Fe(CN)2 . 4KCN, dissociates to give K+ and [Fe(CN)6]4- ions in the aqueous solution.
The magnetic moment of [Ru(H2O)6]2+ corresponds to the presence of ...... unpaired electrons.
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic moment of [Ru(H2O)6]2+ corresponds to the presence of ...... unpaired electrons.

|
Anuj Iyer answered |
Ru2+ =[Kr] 4d6. This forms outer complex. Hence, unpaired electrons are 4.
The IUPAC name of [Ni(PPh3)2CI2]2+ is- a)bis dichloro(triphenylphosphine) nickel (II) ion
- b)dichloro bis (triphenylphosphine) nickel (ll)ion
- c)dichloro triphenylphosphine nickel (II) ion
- d)triphenylphosphine nickel (ll)dichloride
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of [Ni(PPh3)2CI2]2+ is
a)
bis dichloro(triphenylphosphine) nickel (II) ion
b)
dichloro bis (triphenylphosphine) nickel (ll)ion
c)
dichloro triphenylphosphine nickel (II) ion
d)
triphenylphosphine nickel (ll)dichloride
|
|
Aravind Rane answered |
The IUPAC name of [Ni(PPh3)CI2]2+ is dichlo ro bis (triphenylphosphine) nickel (II) ion.
Earth's atmosphere is richest in :- a)ultraviolet
- b)infrared
- c)X-rays
- d)microwaves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Earth's atmosphere is richest in :
a)
ultraviolet
b)
infrared
c)
X-rays
d)
microwaves
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Earth 's atmosphere is richest in infrared radiation or IR.
* The earth emits huge amounts of infrared radiation and thereby makes the atmosphere richest in infrared rays.
* When sunlight (solar radiation) hits the earth, some of the energy is absorbed by the earth that ultimately heats up the earth.
* This heat gets radiated by the earth in the form of infrared radiation.
Earth 's atmosphere is richest in infrared radiation or IR.
* The earth emits huge amounts of infrared radiation and thereby makes the atmosphere richest in infrared rays.
* When sunlight (solar radiation) hits the earth, some of the energy is absorbed by the earth that ultimately heats up the earth.
* This heat gets radiated by the earth in the form of infrared radiation.
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following- a)[Cu(NH3)4]2+
- b)[Ni(CN)4]2–
- c)TiCl4
- d)[CoCl6]4–
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnetic moment of 1.73 BM will be shown by one among the following
a)
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
b)
[Ni(CN)4]2–
c)
TiCl4
d)
[CoCl6]4–
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
Electronic configuration of Cu2+ ion in [Cu(NH3)4]2+.
Cu2+ ion =[Ar]3d94s0.
∴Cu2+ ion has one unpaired electron.
Magnetic moment of [Cu(NH3)4]2+ (μ) =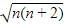 BM
BM
where, n = no. of unpaired electrons
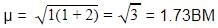
Whereas Ni2+ in [Ni(CN)4]2− , Ti4+ in TiCl4 and Co2+ ion [COCl6]4− has 2,0 and 3 unpaired electrons respectively.
Electronic configuration of Cu2+ ion in [Cu(NH3)4]2+.
Cu2+ ion =[Ar]3d94s0.
∴Cu2+ ion has one unpaired electron.
Magnetic moment of [Cu(NH3)4]2+ (μ) =
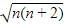 BM
BMwhere, n = no. of unpaired electrons
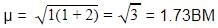
Whereas Ni2+ in [Ni(CN)4]2− , Ti4+ in TiCl4 and Co2+ ion [COCl6]4− has 2,0 and 3 unpaired electrons respectively.
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following complexes have correct name?- a)K [Pt(NH3)CI5] = potassiumamminepentachloridoplatinate (IV)
- b)[Ag(CN)2]- = dicyanidoargentate(l) ion
- c)K3[Cr(C2O4)3] = tripotassium trioxalatochromate(lll)
- d)Na2[Ni(EDTA)] = sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetatonickel(ll)
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following complexes have correct name?
a)
K [Pt(NH3)CI5] = potassiumamminepentachloridoplatinate (IV)
b)
[Ag(CN)2]- = dicyanidoargentate(l) ion
c)
K3[Cr(C2O4)3] = tripotassium trioxalatochromate(lll)
d)
Na2[Ni(EDTA)] = sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetatonickel(ll)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
Complexes K[Pt(NH3)Cl5] and [Ag(CN)2]- have been given their respective IUPAC names.
The IUPAC name of the complex [(CO)5Mn - Mn(CO)5] is- a)bis (pentacarbonyl dimanganese)
- b)bis (pentacarbonyldimanganate(ll)
- c)decacarbonyldimanganate (0).
- d)bis (pentacarbonyldimanganese(O)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the complex [(CO)5Mn - Mn(CO)5] is
a)
bis (pentacarbonyl dimanganese)
b)
bis (pentacarbonyldimanganate(ll)
c)
decacarbonyldimanganate (0).
d)
bis (pentacarbonyldimanganese(O)
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Decacarbonyldimanganese (0), Mn2(CO)10, is made up of two square pyramidal Mn(CO)5 units joined by a Mn-Mn bond.
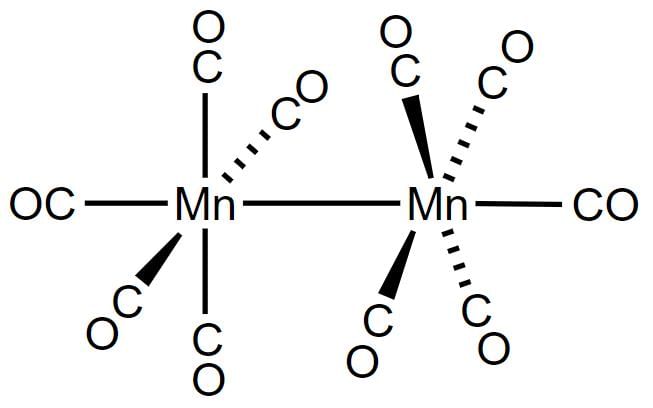
The spin only magnetic moment value (in Bohr magneton units) of Cr(CO)6 is- a)0
- b)2.84
- c)4.90
- d)5.92
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The spin only magnetic moment value (in Bohr magneton units) of Cr(CO)6 is
a)
0
b)
2.84
c)
4.90
d)
5.92
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The electron configuration is [Ar]3d^5 4s^1.We have to accomodate the 6 Ligands and the fact that CO is a strong ligand.
This results in d^2sp^3 hybridization. Therefore, there are no unpaired electrons in Cr(CO)6. Hence n=0
And the spin only magnetic moment is also 0.
The effective atomic number of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is- a)36
- b)24
- c)34
- d)26
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The effective atomic number of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is
a)
36
b)
24
c)
34
d)
26

|
Anupama Nair answered |
EAN= atomic no of Fe - oxidation state + no of e donated by ligand... Oxidation state of Fe is 0 since CO is neutral ligand... Two donor atoms hence no of e = 2×5=10.... EAN= 26-0+10=36
The formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is- a)[Co(NH3)6]CISO4
- b)[Co(NH3)6CI]SO4
- c)[Co(NH3)6CISO4]
- d)None of these
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is
a)
[Co(NH3)6]CISO4
b)
[Co(NH3)6CI]SO4
c)
[Co(NH3)6CISO4]
d)
None of these
|
|
Anshika Menon answered |
Formula of Complex Hexamminecobalt (III) Chloride Sulphate
The correct answer is 'A' which represents the formula [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. Let's break down the answer into the following headings:
I. Understanding the Formula
II. Explanation of the Formula
III. Conclusion
I. Understanding the Formula
Before we dive into the formula, let's understand some key terms:
- Complex: A molecule or ion formed by the combination of a metal ion with a ligand (a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the metal ion)
- Hexamminecobalt (III) chloride: A complex formed by the combination of cobalt (III) ion with six ammonia molecules and one chloride ion
- Sulphate: A compound containing the sulphate ion (SO4 2-)
II. Explanation of the Formula
The given complex contains cobalt (III) ion, six ammonia molecules (NH3), one chloride ion (Cl-), and one sulphate ion (SO4 2-). The cobalt (III) ion is coordinated by six ammonia molecules forming an octahedral complex. The chloride ion and sulphate ion occupy the remaining two positions of the octahedral complex. Therefore, the formula of the complex is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4.
III. Conclusion
In conclusion, the formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. The complex contains cobalt (III) ion coordinated by six ammonia molecules, one chloride ion, and one sulphate ion.
The correct answer is 'A' which represents the formula [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. Let's break down the answer into the following headings:
I. Understanding the Formula
II. Explanation of the Formula
III. Conclusion
I. Understanding the Formula
Before we dive into the formula, let's understand some key terms:
- Complex: A molecule or ion formed by the combination of a metal ion with a ligand (a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the metal ion)
- Hexamminecobalt (III) chloride: A complex formed by the combination of cobalt (III) ion with six ammonia molecules and one chloride ion
- Sulphate: A compound containing the sulphate ion (SO4 2-)
II. Explanation of the Formula
The given complex contains cobalt (III) ion, six ammonia molecules (NH3), one chloride ion (Cl-), and one sulphate ion (SO4 2-). The cobalt (III) ion is coordinated by six ammonia molecules forming an octahedral complex. The chloride ion and sulphate ion occupy the remaining two positions of the octahedral complex. Therefore, the formula of the complex is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4.
III. Conclusion
In conclusion, the formula of the complex hexamminecobalt (III) chloride sulphate is [Co(NH3)6]ClSO4. The complex contains cobalt (III) ion coordinated by six ammonia molecules, one chloride ion, and one sulphate ion.
Which of the following statements is/are correct?- a)[Co(en)2NO2Cl] Br is cationic complex
- b)[Co(en)3]CI3 produces 3 ions in solution
- c)[Fe(CO)5] is neutral complex
- d)[Cu(NH3)4]SO4 is deep blue colour
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
a)
[Co(en)2NO2Cl] Br is cationic complex
b)
[Co(en)3]CI3 produces 3 ions in solution
c)
[Fe(CO)5] is neutral complex
d)
[Cu(NH3)4]SO4 is deep blue colour
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
[Co(en)3]CI3 produces 4 ions in solution as follows :
[Co(en)3] CI3→ [Co(en)3]3+ + 3CI-
[Co(en)3] CI3→ [Co(en)3]3+ + 3CI-
- is correct as charge on the complex ion will be +1
- is incorrect as the complex will form 4 ions in solution
- is correct as there is no charge on the complex
- is also correct as cu+2 has blue color in solution
Hence A, C and D are correct.
Which one of the following is expected to exhibit optical isomerism? (en = eth ylen ediamine) [2 00 5]- a)cis [Pt(NH3)2 Cl2]
- b)trans [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
- c)cis [Co(en)2Cl2]
- d)trans [Co(en)2Cl2]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is expected to exhibit optical isomerism? (en = eth ylen ediamine) [2 00 5]
a)
cis [Pt(NH3)2 Cl2]
b)
trans [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
c)
cis [Co(en)2Cl2]
d)
trans [Co(en)2Cl2]

|
Shivani Rane answered |
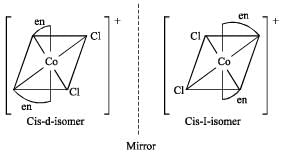
Transform of [M(AA)2 a2]n± does not shows optical isomerism.
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is - a)Platinum diamminechloronitrite
- b)Chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II)
- c)Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
- d)Diamminechloronitrito-N-plantinate (II)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)] is
a)
Platinum diamminechloronitrite
b)
Chloronitrito-N-ammineplatinum (II)
c)
Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
d)
Diamminechloronitrito-N-plantinate (II)
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Ans: c
Explanation:Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)
m − 2 = 0
m = +2
(NH3)2 ⇒ Diammine
Cl ⇒ Chlorido
NO2 ⇒ Nitrito-N.
So, IUPAC NAME: diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum(II)
The hybrisation of Co in [Co(H2O)6]3+ is :
- a)d2sp3
- b)dsp2
- c)dsp3
- d)spd3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The hybrisation of Co in [Co(H2O)6]3+ is :
a)
d2sp3
b)
dsp2
c)
dsp3
d)
spd3
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
In this complex compound the total charge is +3 as H2O is a neutral compound so the oxidation state of cobalt is +3 and the electronic configuration of Co is 3d7 4s2. So, Co(+3)=4d6 and H2O is a weak ligand so there is no pairing of electron. So,4s 4p3 and 4d2 orbital make hybrid orbital to have a hybridization of d2sp3.
A freshly prepared aqueous solution of Pd(NH3)2CI2 does not conduct electricity, it suggests that- a)the structure of the compound involves covalent bonding only
- b)the chlorine atoms must be in coordination sphere
- c)the van't Hoff factor of the compound would be unity
- d)on adding excess aqueous AgNO3 to 0.1 L of 0.1 M solution of the compound, 0.02 mole of AgCI would be obtained
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
A freshly prepared aqueous solution of Pd(NH3)2CI2 does not conduct electricity, it suggests that
a)
the structure of the compound involves covalent bonding only
b)
the chlorine atoms must be in coordination sphere
c)
the van't Hoff factor of the compound would be unity
d)
on adding excess aqueous AgNO3 to 0.1 L of 0.1 M solution of the compound, 0.02 mole of AgCI would be obtained

|
Sankar Chakraborty answered |
In the aqueous solution of Pd(NH3)2CI2, the atoms of chlorine I are in coordination sphere and the van't Hoff factor of the ] compound are unite.
Complex compounds are addition compounds formed by the stoichiometric combination of two or more simple salts but do not decompose into constituent ions completely. The first such complex prepared by Tassaert is hexamine cobalt (III) chloride. Later many such compounds were prepared and their properties were studied. The chloramines complexes of cobalt (III) chromium (III) not only exhibit a spectrum of colours but also differ in the reactivity of their chlorides. Moreover, greater the number of ions produced by a complex in solution, greater is the electrical conductivity. This type of information was obtained for several series of complexes.Q. The number of ions per mole of the complex CoCI3 . 5NH3 in aqueous solution will be- a)3
- b)9
- c)2
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Complex compounds are addition compounds formed by the stoichiometric combination of two or more simple salts but do not decompose into constituent ions completely. The first such complex prepared by Tassaert is hexamine cobalt (III) chloride. Later many such compounds were prepared and their properties were studied. The chloramines complexes of cobalt (III) chromium (III) not only exhibit a spectrum of colours but also differ in the reactivity of their chlorides. Moreover, greater the number of ions produced by a complex in solution, greater is the electrical conductivity. This type of information was obtained for several series of complexes.
Q.
The number of ions per mole of the complex CoCI3 . 5NH3 in aqueous solution will be
a)
3
b)
9
c)
2
d)
4
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
[Co(NH3)5CI]CI2→[Co(NH3)5CI]2++ 2Cl-
Hence, 3 ions are present for one mole of the complex in the solution.
Hence, 3 ions are present for one mole of the complex in the solution.
23. One projectile moving with velocity v in space get burst into 2 parts of masses in the ratio of 1 : 2. The smaller part becomes stationary, velocity of other part is : - a)uv
- b)3v/2
- c)4v/3
- d)2v/3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
23. One projectile moving with velocity v in space get burst into 2 parts of masses in the ratio of 1 : 2. The smaller part becomes stationary, velocity of other part is :
a)
uv
b)
3v/2
c)
4v/3
d)
2v/3
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Let the mass =m
Apply law of momentum conservation
mv = m/4*0 + 2mv1/3
v = 2v1/3
v1 = 3v/2
Apply law of momentum conservation
mv = m/4*0 + 2mv1/3
v = 2v1/3
v1 = 3v/2
The IUPAC name of the compound [Cr(NH3)5(NCS)][ZnCI4] is- a)pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
- b)pentaammine thiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
- c)pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV)
- d)pentammine thiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of the compound [Cr(NH3)5(NCS)][ZnCI4] is
a)
pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
b)
pentaammine thiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II)
c)
pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV)
d)
pentammine thiocyanatochromium (0) tetrachlorozincate (IV

|
Avantika Joshi answered |
The lUPAC name of [Cr(NH3)5(NCS)][ZnCI4] is pentammine isothiocyanatochromium (III) tetrachlorozincate (II).
Which of the following complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light ? [2010]- a)Ni(CN)42
- b)Cr(NH3)6 3
- c)2Fe(H2 O)6
- d)Ni(H2O)62
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complex ion is not expected to absorb visible light ? [2010]
a)
Ni(CN)42
b)
Cr(NH3)6 3
c)
2Fe(H2 O)6
d)
Ni(H2O)62

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
Absorption of visual light is associated with an energy difference between two orbitals — one occupied, one unoccupied — and electrons must be able to be excited from one to the other.
In coordination complexes, these excitations typically happen within the metal’s d subshell, so it is usually sufficient to examine that and approximately determine which excitations are possible. The main selection rules are:
the spin rule. The electron must be excitable without a spin-flip
the Laporte rule. Basically, d to d transitions are forbidden in octahedral complexes
The spin rule is very strongly observed. The color of manganese(II) whose transition is spin-forbidden is extremely faint. The Laporte rule only holds true as long as the complex is inversion-symmetric, so any asymmetric vibration is enough to make it void; thus, Laporte-forbidden transitions are typically still visible but somewhat faint.
Let’s examine the complexes:
[Ni(CN)4]2−This is expected to be square planar and d8. The energy difference between the two highest orbitals — dxy and dx2−y2 — is expected to be high. The former is expected to be fully populated, the latter to be unpopulated.
[Cr(NH3)6]3+ This is a d3 system. It is expected to be octahedral with a standard difference between the lower and higher energy levels.
[Fe(H2O)6]2+This is a d6 octahedral system. There is no reason to assume a low spin state. The energy difference is expected to be slightly less than in the previous case.
[Ni(H2O)6]2+ this is expected to be a high-spin d8system and octahedral. The same expectation regarding energy levels as on the previous case applies.
We realize that the of our complexes are average high spin octahedral complexes. For these, visible light absorption is always expected. Only one case is different. In that different case, the HOMO-LUMO difference is large. While we can still expect absorption, it seems most reasonable to assign this absorption band an ultraviolet wavelength.
Thus, [Ni(CN)4]2− is the answer.
The complex potassium dicyanodioxalatonickelate (II) in solution produce....... ions.
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
The complex potassium dicyanodioxalatonickelate (II) in solution produce....... ions.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The structure of potassium dicyanodio xalatonickelate (II) is
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2].
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2] → 4K+ + [Ni(CN)2(ox)2]-
This produce 5 ions in solution.
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2].
K4[Ni(CN)2(ox)2] → 4K+ + [Ni(CN)2(ox)2]-
This produce 5 ions in solution.
What is the IUPAC name of compound NaBH4?- a)Sodium boronhydride
- b)Sodium tetrahydridoboron (III)
- c)Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III)
- d)Sodium tetrahydridoborate (I)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the IUPAC name of compound NaBH4?
a)
Sodium boronhydride
b)
Sodium tetrahydridoboron (III)
c)
Sodium tetrahydridoborate (III)
d)
Sodium tetrahydridoborate (I)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Common name of NaBH4 is sodium borohydride
IUPAC name of NaBH4is sodium tetrahydridoborate{III}
In the complex PtCl4.3NH3 the number of ionisable chlorines is- a)1
- b)3
- c)2
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex PtCl4.3NH3 the number of ionisable chlorines is
a)
1
b)
3
c)
2
d)
0

|
Srishti Kaur answered |
Pt has coordination number of 4 so 3 chlorine will come outside the coordination sphere.
Number of EDTA molecules required to form an octahedral complex.
Correct answer is '1'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of EDTA molecules required to form an octahedral complex.
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
One EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) molecule is required to make an octahedral complex with Ca^2+ ion
When AgNO3 solution is added in excess to 1 M solution of CoCI3 . xNH3, one mole of AgCI is formed. The value of x is
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
When AgNO3 solution is added in excess to 1 M solution of CoCI3 . xNH3, one mole of AgCI is formed. The value of x is
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
AgNO3 solution is added in excess of 1 M solution of CoCI3 . xNH3.
CoCl3.xNH3+AgNO3→AgCl (1mole)
CoCl3.xNH3+AgNO3→AgCl (1mole)
This precipitation of 1 mol of AgCl by this reaction shows that there is only one Cl outside the coordination sphere, which is not as a ligand ( as ligands are not ionisable).
Hence, the compound must be as follows:(showing the coordination sphere) [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl, as this is the octahedral complex, where it is clear that there are only 2 Cl as ligand and other ligands are NH3.
So, 6−2 = 4 NH3 ligands.
A cobaltamine has the formula CoCI3 . xNH3. This when reacted with AgNO3 solution, one third of the chloride is precipitated. It can have the structure- a)[Co(NH3)6]CI3
- b)[Co(NH3)5]CI2
- c)[Co(NH3)4CI2]CI
- d)[Co(NH3)5H2O]CI3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cobaltamine has the formula CoCI3 . xNH3. This when reacted with AgNO3 solution, one third of the chloride is precipitated. It can have the structure
a)
[Co(NH3)6]CI3
b)
[Co(NH3)5]CI2
c)
[Co(NH3)4CI2]CI
d)
[Co(NH3)5H2O]CI3
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Total chlorine molecules are 3 and one third means one chlorine molecule precipitates. So, one chlorine has to be outside the coordination sphere and that is in option C.
The number of ligands which have strong crystal field splitting thanH2O among SCN-, NCS-, EDTA4- , 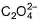 ,
, 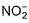 , Br-, PPh3, F-
, Br-, PPh3, F-
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of ligands which have strong crystal field splitting than
H2O among SCN-, NCS-, EDTA4- , 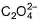 ,
, 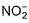 , Br-, PPh3, F-
, Br-, PPh3, F-

|
Learners Habitat answered |
NCS- edta4- , 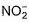 and PPh3 are strong field ligand than H2O.
and PPh3 are strong field ligand than H2O.
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
An example of double salt is/a
- a)hypo
- b)bleaching powder
- c)common alum
- d)carnallite
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
An example of double salt is/a
a)
hypo
b)
bleaching powder
c)
common alum
d)
carnallite

|
Aravind Mehra answered |
Common alum is K2SO4.AI2(SO4)3.24H2O and carnallite is KCl.MgCl2.6H2O.
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is a- a)Double salt
- b)Mixed salt
- c)Basic salt
- d)Complex salt
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is a
a)
Double salt
b)
Mixed salt
c)
Basic salt
d)
Complex salt

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is double salt
From the stability constant (hypothetical values), given below, predict which is the strongest ligand:- a)Cu2+ + 4NH3
 [Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011
[Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011 - b)Cu2+ + 4CN-
 [Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027
[Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027 - c)Cu2+ + 2en
 [Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015
[Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015 - d)Cu2+ + 4H2O
 [Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108
[Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From the stability constant (hypothetical values), given below, predict which is the strongest ligand:
a)
Cu2+ + 4NH3  [Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011
[Cu(NH3)4]2+, K = 4.5 × 1011
b)
Cu2+ + 4CN-  [Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027
[Cu(CN)4]2- , K = 2.0 × 1027
c)
Cu2+ + 2en  [Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015
[Cu(en)2]2+, K = 3.0 × 1015
d)
Cu2+ + 4H2O  [Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108
[Cu(H2O)4]2+, K = 9.5 × 108

|
Raghav Yadav answered |
Higher the value of K higher will be strength of ligand & more will be thermodynamic stability of complex produced.
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand is- a)acetylacetonate (acac)
- b)propylene diamine (pn)
- c)ethylene diamine (en)
- d)bipyridyl (bip
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand is
a)
acetylacetonate (acac)
b)
propylene diamine (pn)
c)
ethylene diamine (en)
d)
bipyridyl (bip

|
Ishani Yadav answered |
CH3COCH2COCH3
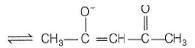
It can ligate through two oxygen atoms.
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Primary and secondary valency of Pt in [Pt(en)2CI2] are- a)+ 4 and - 4
- b)+ 4 and 6
- c)+ 6 and 4
- d)+ 2 and 6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Primary and secondary valency of Pt in [Pt(en)2CI2] are
a)
+ 4 and - 4
b)
+ 4 and 6
c)
+ 6 and 4
d)
+ 2 and 6
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
The primary valence is its oxidation number, which is +2 in this case (en is uncharged, and the Cl ligands carry a -1 charge each, so Pt must be +2 to balance).
Secondary valence is coordination number. The en ligand is bidentate, and Cl is monodentate, so you have 2(2) + 2(1) = 6, so the Pt has a coordination number of 6.
In the formation of complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as- a)Bronsted acid
- b)Lewis base
- c)Lewis acid
- d)Bronsted base
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the formation of complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as
a)
Bronsted acid
b)
Lewis base
c)
Lewis acid
d)
Bronsted base

|
Rocky Handsome answered |
Solution:
It is a Lewis acid as it accepts pair of electrons from the ligand while forming coordination bond.
.. . ( .__.)
Which one of the following is an outer orbital complex and exhibits paramagnetic behaviour ? [2012]- a)[Ni(NH3)6]2+
- b)[Zn(NH3)6)]2+
- c)[Cr(NH3)6]3+
- d)[CO(NH3)6]3+
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is an outer orbital complex and exhibits paramagnetic behaviour ? [2012]
a)
[Ni(NH3)6]2+
b)
[Zn(NH3)6)]2+
c)
[Cr(NH3)6]3+
d)
[CO(NH3)6]3+

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
[Ni(NH3)6]2+
Ni2+ = 3d8, according to 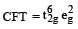 therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.
therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.
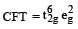 therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.
therefore, hybridisation is sp3d2 & complex is paramagnetic.Which is the diamagnetic?
- a)[CoF6]3-
- b)[Ni(CN)4]2-
- c)[NiCI3]2-
- d)[Fe(CN)6]3-
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the diamagnetic?
a)
[CoF6]3-
b)
[Ni(CN)4]2-
c)
[NiCI3]2-
d)
[Fe(CN)6]3-
|
|
Niti Mishra answered |
Explanation:
Diamagnetic substances are those which do not have any unpaired electrons and are not attracted by a magnetic field. On the other hand, paramagnetic substances have unpaired electrons and are attracted by a magnetic field.
Let's examine the given options to determine which one is diamagnetic.
[CoF6]3-
Cobalt has 27 electrons. In this complex, cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state. The six fluoride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the cobalt ion. The complex has a total of 33 electrons, and there are three unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the cobalt ion. Therefore, [CoF6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
[Ni(CN)4]2-
Nickel has 28 electrons. In this complex, nickel is in the +2 oxidation state. The four cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 34 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [Ni(CN)4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[NiCl4]2-
Similar to the above complex, nickel has 28 electrons and is in the +2 oxidation state. The four chloride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [NiCl4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[Fe(CN)6]3-
Iron has 26 electrons. In this complex, iron is in the +3 oxidation state. The six cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the iron ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and there are five unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the iron ion. Therefore, [Fe(CN)6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
Therefore, the diamagnetic complex among the given options is [Ni(CN)4]2-.
Diamagnetic substances are those which do not have any unpaired electrons and are not attracted by a magnetic field. On the other hand, paramagnetic substances have unpaired electrons and are attracted by a magnetic field.
Let's examine the given options to determine which one is diamagnetic.
[CoF6]3-
Cobalt has 27 electrons. In this complex, cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state. The six fluoride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the cobalt ion. The complex has a total of 33 electrons, and there are three unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the cobalt ion. Therefore, [CoF6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
[Ni(CN)4]2-
Nickel has 28 electrons. In this complex, nickel is in the +2 oxidation state. The four cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 34 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [Ni(CN)4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[NiCl4]2-
Similar to the above complex, nickel has 28 electrons and is in the +2 oxidation state. The four chloride ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the nickel ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and all the electrons are paired. Therefore, [NiCl4]2- is a diamagnetic complex.
[Fe(CN)6]3-
Iron has 26 electrons. In this complex, iron is in the +3 oxidation state. The six cyanide ions act as ligands and each donate one pair of electrons to the iron ion. The complex has a total of 32 electrons, and there are five unpaired electrons in the d-orbitals of the iron ion. Therefore, [Fe(CN)6]3- is a paramagnetic complex.
Therefore, the diamagnetic complex among the given options is [Ni(CN)4]2-.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. According to IUPAC nomenclature, sodium nitroprusside is named as
- a)sodium nitroferricyanide
- b)sodium nitroferrocyanide
- c)sodium pentacyanonitrosyliumferrate (II)
- d)sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q. According to IUPAC nomenclature, sodium nitroprusside is named as
a)
sodium nitroferricyanide
b)
sodium nitroferrocyanide
c)
sodium pentacyanonitrosyliumferrate (II)
d)
sodium pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III)
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
IUPAC name of sodium nitroprusside Na2[Fe(CN)5NO] is sodium pentacyanonitrosyl ferrate (III) because in it NO is neutral ligand and the oxidation number of Fe is +3. Which is calculated as Na2[Fe(CN)5NO]
2 × (+1) + x +5×(−1)+1×0 = 0
2 + x - 5 = 0
x - 3 = 0
x = + 3
2 × (+1) + x +5×(−1)+1×0 = 0
2 + x - 5 = 0
x - 3 = 0
x = + 3
The d electron configurations of Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Ni2+ are 3d4, 3d5, 3d6 and 3d8 respectively. Which one of the following aqua complexes will exhibit the minimum paramagnetic behaviour? [2007] (At. No. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Ni = 28)- a)[Fe(H2O)6]2+
- b)[Ni(H2O)6]2+
- c)[Cr(H2O)6]2+
- d)[Mn(H2O)6]2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The d electron configurations of Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+ and Ni2+ are 3d4, 3d5, 3d6 and 3d8 respectively. Which one of the following aqua complexes will exhibit the minimum paramagnetic behaviour? [2007] (At. No. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Ni = 28)
a)
[Fe(H2O)6]2+
b)
[Ni(H2O)6]2+
c)
[Cr(H2O)6]2+
d)
[Mn(H2O)6]2+
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Lesser is the number of unpaired electrons smaller will be the paramagnetic behaviour.
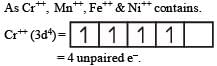


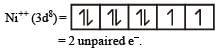
As Ni++ has minimum no. of unpaired e– thus this is least paramagnetic.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:sp3-hybridisation is found in
- A:
[ZnCI4]2-
- B:
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
- C:
[CuCI4]2-
- D:
[Ni(CO)4]
The answer is A,C,D.
sp3-hybridisation is found in
[ZnCI4]2-
[Cu(NH3)4]2+
[CuCI4]2-
[Ni(CO)4]
|
|
Dipika Rane answered |
Explanation:
SP3 hybridization is a type of hybridization where one s orbital and three p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral shape around the central atom.
The given options are:
a) [ZnCl4]2-
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2
c) [CuCl4]2-
d) [Ni(CO)4]
a) [ZnCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central zinc atom is sp3 hybridized. The zinc ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s0. The hybridization of the zinc ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is dsp2 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital, two 4p orbitals, and one 3d orbital to form five dsp2 hybrid orbitals.
c) [CuCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is sp3 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
d) [Ni(CO)4]: In this complex ion, the central nickel atom is sp3 hybridized. The nickel ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d84s2. The hybridization of the nickel ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Conclusion:
Thus, the correct options are A, C, and D, as all these complex ions have a central atom that is sp3 hybridized. The complex ion in option B has a central copper atom that is dsp2 hybridized.
SP3 hybridization is a type of hybridization where one s orbital and three p orbitals of the same shell of an atom mix to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral shape around the central atom.
The given options are:
a) [ZnCl4]2-
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2
c) [CuCl4]2-
d) [Ni(CO)4]
a) [ZnCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central zinc atom is sp3 hybridized. The zinc ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s0. The hybridization of the zinc ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
b) [Cu(NH3)4]2: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is dsp2 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital, two 4p orbitals, and one 3d orbital to form five dsp2 hybrid orbitals.
c) [CuCl4]2-: In this complex ion, the central copper atom is sp3 hybridized. The copper ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d104s1. The hybridization of the copper ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
d) [Ni(CO)4]: In this complex ion, the central nickel atom is sp3 hybridized. The nickel ion has an electronic configuration of [Ar]3d84s2. The hybridization of the nickel ion takes place by mixing one 4s orbital and three 4p orbitals to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Conclusion:
Thus, the correct options are A, C, and D, as all these complex ions have a central atom that is sp3 hybridized. The complex ion in option B has a central copper atom that is dsp2 hybridized.
Statement TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 24 and 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.Q. Statement I : Oxidation state of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is zero.
Statement II : EAN of Fe in this complex is 36.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 24 and 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : Oxidation state of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is zero.
Statement II : EAN of Fe in this complex is 36.
Statement II : EAN of Fe in this complex is 36.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Shail Chakraborty answered |
Statement I is true because CO is a neutral ligand, Statement II is true because
EAN of Fe
= Atomic number of Fe + Electrons gained by coordination
= 26 + 2 x 5 = 36
But Statement II is not the correct explanation. Correct explanation is that oxidation state of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is zero because CO is a neutral ligand.
EAN of Fe
= Atomic number of Fe + Electrons gained by coordination
= 26 + 2 x 5 = 36
But Statement II is not the correct explanation. Correct explanation is that oxidation state of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is zero because CO is a neutral ligand.
29. A body of mass m1 is moving with velocity u. It collides with another stationary body of mass m2. They get embedded. At the point of collision, the velocity of the system :- a)increases
- b)decreases but does not become zero
- c)remains same
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
29. A body of mass m1 is moving with velocity u. It collides with another stationary body of mass m2. They get embedded. At the point of collision, the velocity of the system :
a)
increases
b)
decreases but does not become zero
c)
remains same
d)
zero
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answer is Option B
Just before the collision the velocity of the center of mass will be
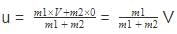
after the collision if the system moves with velocity V0 then on conserving the momentum
we will get m1V + 0=(m1 + m2)V0
or V0 =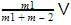 we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.
we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.
Just before the collision the velocity of the center of mass will be
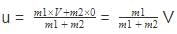
after the collision if the system moves with velocity V0 then on conserving the momentum
we will get m1V + 0=(m1 + m2)V0
or V0 =
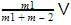 we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.
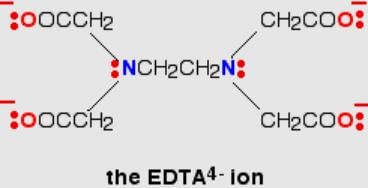
we can notice that both V0 and u are the same, due to absence of external force on the system.One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. Ethylenediamminetetraacetate ion is a polydentate ligand and negatively charged. The magnitude of negative charge is
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20-24) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Ethylenediamminetetraacetate ion is a polydentate ligand and negatively charged. The magnitude of negative charge is
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The correct answer is 4.

The volume (in mL) of 0.1 M AgNO3 required for complex precipitation of chloride ions present in 30 mL of 0.01 M solution of [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2, as silver chloride is close to- a)3
- b)4
- c)5
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume (in mL) of 0.1 M AgNO3 required for complex precipitation of chloride ions present in 30 mL of 0.01 M solution of [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2, as silver chloride is close to
a)
3
b)
4
c)
5
d)
6

|
Sanchita Reddy answered |
The chemical reaction between them is...[Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2 + {2}AgNO3 ——> {2}AgCl(↓) + [Cr(H2O)5Cl]^2+ + {2}NO3-moles of coordinate compound given = molarity x volume(in litre)mole = 0.01 x (30/1000) = (3/10000)for one mole coordinate compound.. we need 2 mole AgNO3....i.e.,1mole complex ===> 2 mole AgNO3(3/10000) mole ==> (2x3/10000) mole AgNO3molarity = moles/volume (in litre)volume(in litre) = mole / molarityV= (6/10000)/0.1 = (0.6) Litrehence volume required = 0.6litre = 6ml
Chapter doubts & questions for Coordination Compounds - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Coordination Compounds - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup