All Exams >
Class 10 >
Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Federalism for Class 10 Exam
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Belgium and Spain has ‘holding together’ federation.
Reason : A big country divides power between constituent states and national government.
- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Belgium and Spain has ‘holding together’ federation.
Reason : A big country divides power between constituent states and national government.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The power of a large country is divided between constituent states and national government. The central government is more powerful than the states.
Which state of India enjoys a special status and has its own Constitution?- a)Bihar
- b)Uttar Pradesh
- c)Kerala
- d)Jammu and Kashmir
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which state of India enjoys a special status and has its own Constitution?
a)
Bihar
b)
Uttar Pradesh
c)
Kerala
d)
Jammu and Kashmir
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The independent States coming together on their own to form a bigger unit, so that by pooling sovereignty and retaining identity they can increase their security. This type of ‘coming together’ federations include the USA, Switzerland and Australia.
The head of the municipal corporation is called______.
- a)Mayor
- b)MLAs
- c)Sarpanchs
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The head of the municipal corporation is called______.
a)
Mayor
b)
MLAs
c)
Sarpanchs
d)
none of these
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
A mayor is the head of the Municipal Corporation. He is elected by the members of the Municipal Corporation. He is known as the first citizen of the city.
Which country has a two-party system?
- a)India
- b)Sri Lanka
- c)United Kingdom
- d)Nepal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which country has a two-party system?
a)
India
b)
Sri Lanka
c)
United Kingdom
d)
Nepal
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
The Constitution of India designates the official language of the Government of India as Hindi written in the Devanagari script, as well as English. There is no national language as declared by the Constitution of India.
Federations have been formed with the two kinds of- a)routes
- b)states
- c)people
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Federations have been formed with the two kinds of
a)
routes
b)
states
c)
people
d)
none of the above
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
First route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit this is known as coming together federation. The second route is where a large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the national government this is holding together federation.
Which form of power sharing is most commonly referred to as federalism?- a)Horizontal division of power
- b)Vertical division of power
- c)Division of power among various communities
- d)Sharing of power among political parties
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which form of power sharing is most commonly referred to as federalism?
a)
Horizontal division of power
b)
Vertical division of power
c)
Division of power among various communities
d)
Sharing of power among political parties
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
That vertical division of power among different levels of government is one of the major forms of power- sharing in modern democracies. In this chapter, we focus on this form of power-sharing. It is most commonly referred to as federalism.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding a unitary government?- a)There is either only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government
- b)The central government can pass on orders to the provincial government
- c)A state government is answerable to central government
- d)The powers of state governments are guaranteed by the Constitution
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect regarding a unitary government?
a)
There is either only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government
b)
The central government can pass on orders to the provincial government
c)
A state government is answerable to central government
d)
The powers of state governments are guaranteed by the Constitution
|
|
Rashi Dey answered |
In a unitary system, there is no list of distribution of powers in the constitution. All powers belong to the central government. 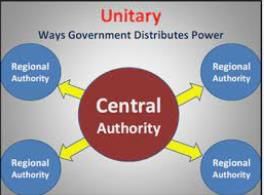

Under this system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government and state government is conservable to the central government.
You can go through the course to know everything about Indian Polity:
Which local govt works at district level ?- a)Panchayat samiti
- b)Village panchayat
- c)Zila Parishad
- d)None of the mention above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which local govt works at district level ?
a)
Panchayat samiti
b)
Village panchayat
c)
Zila Parishad
d)
None of the mention above
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Zilla Parishad is located at the apex of the Panchayat system at the district level. It consists of the Chairman of the Panchayat Samities as ex-officio Members, M.L.As, M.P.s of the area. Representatives of women, scheduled castes and tribes and backward class are co-opted as members.
Which of the following subjects is not included in the Union list?- a)Defence
- b)Foreign affairs
- c)Police
- d)Banking
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following subjects is not included in the Union list?
a)
Defence
b)
Foreign affairs
c)
Police
d)
Banking
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Union List includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency.
There are two kinds of routes through which federations have been formed. Which are they?- a)One route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit
- b)Second route is where a large country decides to divide its powers between the states and the national government
- c)Both the above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There are two kinds of routes through which federations have been formed. Which are they?
a)
One route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit
b)
Second route is where a large country decides to divide its powers between the states and the national government
c)
Both the above
d)
None of the above
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
First route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit. this is known as coming together federation. ex - USA, Australia, Switzerland.
The second route is where a large country decides to devide its power between the constituent states and the national government. this is holding together federation. ex - India, Belgium .
The second route is where a large country decides to devide its power between the constituent states and the national government. this is holding together federation. ex - India, Belgium .
What is the government at Block level called ?- a)Gram Sabha
- b)Gram Panchyat
- c)Panchayat Samiti
- d)Nayay Panchyat
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the government at Block level called ?
a)
Gram Sabha
b)
Gram Panchyat
c)
Panchayat Samiti
d)
Nayay Panchyat
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
A Panchayat Samiti (block panchayat) is a local government body at the tehsil level. This body works for the villages of the tehsil that together are called a "development block". The Panchayat Samiti is the link between the Gram Panchayat and the district administration.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which of the following is not one of the key features of federalism?
- A:
There are two or more levels of governments
- B:
Each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administation
- C:
The existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed
- D:
The Constitution can be unilaterally changed by any one level of government
The answer is D.
Which of the following is not one of the key features of federalism?
There are two or more levels of governments
Each tier has its own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administation
The existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed
The Constitution can be unilaterally changed by any one level of government

|
Surbhi Rane answered |
The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed byone level of government. Such changes require the consent of both the levels of government. Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government.
The Constitution of India originally provided for :- a)a two-tier system of government.
- b)a three-tier system of government.
- c)a single-tier system of government.
- d)a four-tier system of government.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Constitution of India originally provided for :
a)
a two-tier system of government.
b)
a three-tier system of government.
c)
a single-tier system of government.
d)
a four-tier system of government.
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
Three-Tier system means three levels of government. The Indian Constitution originally provided for a two-tier system of government.
1. The union government or the central government and
2. The state government.
But, later a third-tier of federalism was added in the form of Panchayats [Rural level] and Municipalities [Urban level]. Every level enjoys separate jurisdiction.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Zilla Parishad Chairperson is the political head of the zilla parishad.
Reason : Mayor is the head of municipal corporation.
- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : Zilla Parishad Chairperson is the political head of the zilla parishad.
Reason : Mayor is the head of municipal corporation.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Panchayat samitis of a district together form the zilla parishad. Zilla Parishad chairperson is the political head of the zilla parishad. Municipalities are set up in towns. Mayor is the head of municipal corporation. The reason does not however explain the assertion.
According to William Riker, what is the commonality found across many cases of federalism?- a)It is the result of a bargain among regional actors and a prospective national government that is driven by external threats
- b)It is the result of bargaining by foreign powers as they impose a political system on a territory
- c)It is a result of territorial bargaining by elite powers as they develop a national system in a region
- d)This is a trick question: Riker identifies no such commonality, declaring that “all cases are perfectly unique.”
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to William Riker, what is the commonality found across many cases of federalism?
a)
It is the result of a bargain among regional actors and a prospective national government that is driven by external threats
b)
It is the result of bargaining by foreign powers as they impose a political system on a territory
c)
It is a result of territorial bargaining by elite powers as they develop a national system in a region
d)
This is a trick question: Riker identifies no such commonality, declaring that “all cases are perfectly unique.”
|
|
Mohit Chakraborty answered |
A is the correct option.Riker's claim that federalism is always a result of a collective response to external or internal threats to dominant central and regional coalitions needs to be qualified to include economic and cultural threats.
When was the report of the States Reorganisation Commission implemented?- a)1956
- b)1958
- c)1960
- d)1965
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When was the report of the States Reorganisation Commission implemented?
a)
1956
b)
1958
c)
1960
d)
1965
|
|
Alok Verma answered |
The States Reorganisation Act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 remains the single most extensive change in state boundaries since the independence of India in 1947.
Which of the following statements is not correct about the federalism?- a)There are two or more levels of governments
- b)Different levels of govt, govern the same citizens but each level has its own jurisdiction in specific matters
- c)The jurisdiction of the respective levels or tiers of govt is specified in the constitution
- d)The fundamental provisions of the constitution can be unilaterally changed by the central govt
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct about the federalism?
a)
There are two or more levels of governments
b)
Different levels of govt, govern the same citizens but each level has its own jurisdiction in specific matters
c)
The jurisdiction of the respective levels or tiers of govt is specified in the constitution
d)
The fundamental provisions of the constitution can be unilaterally changed by the central govt
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
- There are two or more levels (or tiers) of government.
- The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of government are specified in the constitution. So the existence and authority of each tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of government. The highest court acts as an umpire if disputes arise between different levels of government in the exercise of their respective powers.
What is true regarding sources of revenue in a federal system?- a)States have no financial powers or independent sources of revenue.
- b)States are dependent for revenue or funds on the central government.
- c)Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
- d)States have no financial autonomy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true regarding sources of revenue in a federal system?
a)
States have no financial powers or independent sources of revenue.
b)
States are dependent for revenue or funds on the central government.
c)
Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
d)
States have no financial autonomy.
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The true statement is “Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy in a federal system.”
Here is the explanation of all the options:
• Financial Powers: States do have financial powers or independent sources of revenue. State government revenue comes from income, sales, and other taxes; charges and fees; and transfers from the federal government.
• Independent Sources of Revenue: States are not dependent for revenue or funds on the central government and have independent sources of revenue mentioned above.
• Distribution of Powers: The federal form of government provides for the distribution of powers between the Central and State Governments. To ensure financial autonomy the sources of revenue for both the central government and state governments are clearly specified in the constitution, which implies their main sources of income.
Hence, the Correct Answer is C
States do have financial autonomy and are not dependent for revenue or funds.
You can go through the course of Indian Economy and can cover all the important aspects of Indian Economy from UPSC point of view through it.
Which are the basic objectives of a federal system?- a)To safeguard and promote unity of the country
- b)To accommodate regional diversity
- c)To share powers among different communities
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which are the basic objectives of a federal system?
a)
To safeguard and promote unity of the country
b)
To accommodate regional diversity
c)
To share powers among different communities
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Anjana Khatri answered |
=> These two aspects are crucial for the institution and practice of federalism. The government at different levels should agree to some rules of power sharing.
=> They should also trust that each would abide by its part of agreement.
Hence, an ideal federal system has both aspects i.e., • Mutual trust and • Agreement to live together.
so option D is correct.
By what name local govt at urban area called?A) Municipality B) Municipal corporation C) Panchayat samiti- a)Only A is true
- b)Only B is true
- c)Both B and C are true
- d)Both A and B are true
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
By what name local govt at urban area called?
A) Municipality B) Municipal corporation C) Panchayat samiti
a)
Only A is true
b)
Only B is true
c)
Both B and C are true
d)
Both A and B are true
|
|
Bhavana Sen answered |
The urban area don't have local governments they have muncipality to manage the city in hindi nagar palika.
Which of the following is not a feature of federalism?- a)There are two or more levels of government
- b)Different tiers of government govern the same citizens
- c)Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified
- d)The central government can order the state government
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a feature of federalism?
a)
There are two or more levels of government
b)
Different tiers of government govern the same citizens
c)
Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified
d)
The central government can order the state government
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. The state government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
How many of the world’s 192 countries have federal political systems?- a)Only 50
- b)Only 80
- c)Only 25
- d)Only 100
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many of the world’s 192 countries have federal political systems?
a)
Only 50
b)
Only 80
c)
Only 25
d)
Only 100
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Though only 25 of the world’s 192 countries have federal political systems, their citizen’s make up 40 per cent of the world’s population.
Which is not true regarding changes in power-sharing arrangement between the centre and the states?- a)The Parliament cannot on its own change this arrangement.
- b)Any change to it has to be first passed by both the Houses with at least two-thirds majority.
- c)Then, it has to be ratified by the legislatures of at least half of the total states.
- d)The Parliament alone has the power to amend the provisions regarding power-sharing.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true regarding changes in power-sharing arrangement between the centre and the states?
a)
The Parliament cannot on its own change this arrangement.
b)
Any change to it has to be first passed by both the Houses with at least two-thirds majority.
c)
Then, it has to be ratified by the legislatures of at least half of the total states.
d)
The Parliament alone has the power to amend the provisions regarding power-sharing.
|
|
Aruna Singh answered |
What is the third tier of government known as?- a)Village Panchayats
- b)State government
- c)Local self-government
- d)Zila Parishad
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the third tier of government known as?
a)
Village Panchayats
b)
State government
c)
Local self-government
d)
Zila Parishad
|
|
Varun Kapoor answered |
There are 3 tiers of government that are provided by the Indian Constitution.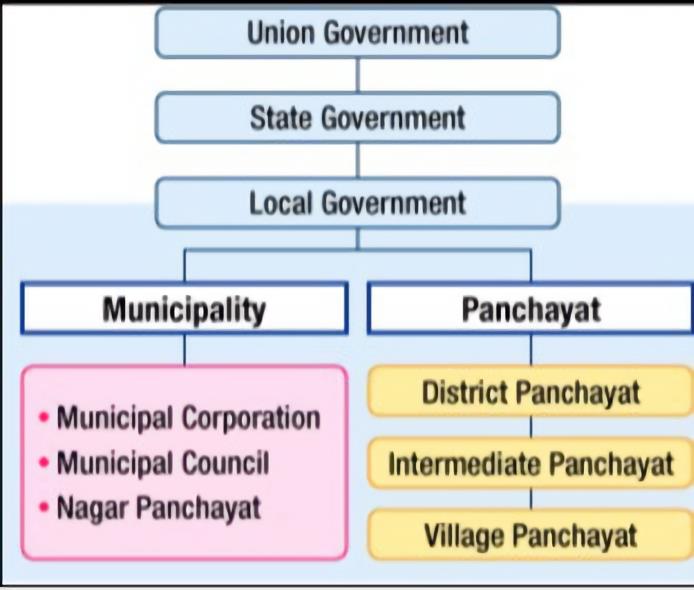
Local Government Includes Gram Panchayat at the village level, Panchayat Samiti at the block level, and Zila Parishad at the district level.
1. Union Government
2. State Government
3. Local Government
• Two Tiers (Union and State Government):
The Constitution originally provided for a two-tier system of government, the Union Government or what we call the Central Government, representing the Union of India and the State government.
Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in its own specific matters of legislation, taxation, and administration.
The Constitution originally provided for a two-tier system of government, the Union Government or what we call the Central Government, representing the Union of India and the State government.
Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in its own specific matters of legislation, taxation, and administration.
• Third Tier (Local Government):
Later, the third tier of federalism was also added within the form of Panchayats and Municipalities which is called the Local Government.
Later, the third tier of federalism was also added within the form of Panchayats and Municipalities which is called the Local Government.
Local Government Includes Gram Panchayat at the village level, Panchayat Samiti at the block level, and Zila Parishad at the district level.
• Jurisdictions of Levels
The jurisdictions of the respective levels of government are explained in the constitution.
Therefore the existence and authority of every tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
The jurisdictions of the respective levels of government are explained in the constitution.
Therefore the existence and authority of every tier of government is constitutionally guaranteed.
Hence, the Correct Answer is C
You can go through the course of Indian Polity:
and can cover all the important aspects of Indian Politics, Indian Government and much more from UPSC point of view through it.
Which of the following government has two or more levels ?- a)Federal Government
- b)Coalition Government
- c)Community Government
- d)Unitary Government
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following government has two or more levels ?
a)
Federal Government
b)
Coalition Government
c)
Community Government
d)
Unitary Government
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government.
On the subject of income tax- a)the union government has more powers than the state governments
- b)the state governments have more powers than the union government
- c)Both the union and the state governments have equal powers
- d)only the union government has powers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On the subject of income tax
a)
the union government has more powers than the state governments
b)
the state governments have more powers than the union government
c)
Both the union and the state governments have equal powers
d)
only the union government has powers
|
|
Shivam Goyal answered |
Union List includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. They are included in this list because we need a uniform policy on these matters throughout the country. The Union Government alone can make laws relating to the subjects mentioned in the Union List.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.Q. How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?- a)18
- b)20
- c)21
- d)22
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
Q. How many languages are included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution?
a)
18
b)
20
c)
21
d)
22
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The 22 languages in the Eighth Schedule are Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu.
Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?- a)State government - State List
- b)Central government - Union List
- c)Central and State governments - Concurrent List
- d)Local governments - Residuary powers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
a)
State government - State List
b)
Central government - Union List
c)
Central and State governments - Concurrent List
d)
Local governments - Residuary powers
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Schedule 7 of the Indian Constitution categorizes the legislative powers into Union List, State List and Concurrent List representing the powers conferred upon the Union, states and shared powers, respectively. The subjects not mentioned in any of the three lists are residuary powers. Parliament shall legislate upon the subjects in the residuary list.
Which among the following are examples of coming together federations?- a)Belgium, Switzerland and USA
- b)India, Belgium and USA
- c)USA, Switzerland and Sri Lanka
- d)Switzerland, USA and Australia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following are examples of coming together federations?
a)
Belgium, Switzerland and USA
b)
India, Belgium and USA
c)
USA, Switzerland and Sri Lanka
d)
Switzerland, USA and Australia
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
In this type of federalism, the states have an individual identity and have majority of control over their governance. USA, Switzerland and Australia are countries which combined different states together to form a country and hence an example for 'Coming Together' federation.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.Q. Which non- Hindi speaking State demanded that the use of English should continue after 1965?- a)Hyderabad
- b)Chennai
- c)Tamil Nadu
- d)Kerala
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
Q. Which non- Hindi speaking State demanded that the use of English should continue after 1965?
a)
Hyderabad
b)
Chennai
c)
Tamil Nadu
d)
Kerala
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
According to the Constitution, the use of English for the official purposes was to stop in 1965. However many non-Hindi speaking states demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu this movement took a militant form. The central government agreed to continue the use of English also with Hindi for official purposes.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.Q. Which of the following subjects comes under 'residuary' subjects?- a)Education
- b)Trade
- c)Banking
- d)Computer software
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
What about subjects that do not fall in any of the three lists? Or subjects like computer software that came up after the constitution was made? According to our Constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these 'residuary' subjects. We noted above that most federations that are formed by 'holding together' do not give equal power to its constituent units. Thus, all States in the Indian Union do not have identical powers. Some States enjoy a special status. Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here. Similar special provisions exist for some other States of India as well.
Q. Which of the following subjects comes under 'residuary' subjects?
a)
Education
b)
Trade
c)
Banking
d)
Computer software
|
|
Anirudh Goyal answered |
Understanding Residuary Subjects
The term 'residuary subjects' refers to topics or areas of legislation that are not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution or fall outside the three main lists: the Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent List. In India, the Union Government has the authority to legislate on these subjects.
Why Computer Software is a Residuary Subject
- The Constitution of India was enacted in 1950, long before the advent of advanced technologies such as computer software.
- As computer software did not exist at the time of the Constitution's framing, it does not fall under the predefined categories of subjects.
- Consequently, since it wasn't explicitly included in any of the lists, it is classified as a residuary subject, allowing the Union Government to create laws governing it.
Comparison with Other Subjects
- Education: This subject is covered under the Concurrent List, allowing both the Union and State Governments to legislate on educational matters.
- Trade: Trade is also included in the State List, meaning States have the authority to regulate trade within their territories.
- Banking: Banking falls under the Union List, empowering the central government to regulate banking institutions and their operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'D' (Computer software) because it is a subject that emerged after the Constitution was created and does not fit into the existing legislative categories outlined in the Constitution. This categorization allows the Union Government to legislate effectively on new and evolving subjects that arise over time.
The term 'residuary subjects' refers to topics or areas of legislation that are not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution or fall outside the three main lists: the Union List, the State List, and the Concurrent List. In India, the Union Government has the authority to legislate on these subjects.
Why Computer Software is a Residuary Subject
- The Constitution of India was enacted in 1950, long before the advent of advanced technologies such as computer software.
- As computer software did not exist at the time of the Constitution's framing, it does not fall under the predefined categories of subjects.
- Consequently, since it wasn't explicitly included in any of the lists, it is classified as a residuary subject, allowing the Union Government to create laws governing it.
Comparison with Other Subjects
- Education: This subject is covered under the Concurrent List, allowing both the Union and State Governments to legislate on educational matters.
- Trade: Trade is also included in the State List, meaning States have the authority to regulate trade within their territories.
- Banking: Banking falls under the Union List, empowering the central government to regulate banking institutions and their operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct answer is option 'D' (Computer software) because it is a subject that emerged after the Constitution was created and does not fit into the existing legislative categories outlined in the Constitution. This categorization allows the Union Government to legislate effectively on new and evolving subjects that arise over time.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.Q. Central and state governments are separately answerable to the _______.- a)people
- b)none
- c)each other
- d)president
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Q. Central and state governments are separately answerable to the _______.
a)
people
b)
none
c)
each other
d)
president
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
Under federal system, the Central government cannot order the State government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which ' it is not answerable to the Central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Which of the following is a unitary state?- a)France
- b)United States
- c)Venezuela
- d)Nigeria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a unitary state?
a)
France
b)
United States
c)
Venezuela
d)
Nigeria
|
|
Geetika Chavan answered |
A is the correct option.France is a unitary State organised on a decentralised basis under the 1958 Constitution. ... Decentralisation was further developed with the 2003 constitutional reform by which the status of the Regions was constitutionally recognised and France became a unitary and decentralised state.
Funds belonging to the Government of India are kept in- a)Consolidated Fund of India
- b)Public Accounts Fund of India
- c)Contingency Fund of India
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Funds belonging to the Government of India are kept in
a)
Consolidated Fund of India
b)
Public Accounts Fund of India
c)
Contingency Fund of India
d)
All of the above
|
|
Supriya singhania answered |
Overview of Government Funds in India
Funds belonging to the Government of India are primarily managed through different accounts, each serving specific purposes. Among these, the Consolidated Fund of India plays a crucial role.
Consolidated Fund of India
- The Consolidated Fund of India is the main account of the Government of India.
- It includes all revenues, loans, and money received by the government.
- All government expenditure is charged to this fund, making it the primary source for financing government activities.
Other Government Funds
While the Consolidated Fund is the principal account, there are two other important funds:
- Public Accounts Fund of India:
- This fund holds money that the government receives but does not belong to it.
- It includes transactions like provident funds, and money held for other departments and agencies.
- Contingency Fund of India:
- This fund is used for emergencies and unforeseen expenditures.
- The amount can be accessed by the President of India without legislative approval, but it must be replenished from the Consolidated Fund.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the Public Accounts Fund and Contingency Fund serve distinct purposes, the vast majority of government funds and expenditures are managed within the Consolidated Fund of India. Thus, the correct answer to the question is that the funds belonging to the Government of India are chiefly kept in the Consolidated Fund of India.
Funds belonging to the Government of India are primarily managed through different accounts, each serving specific purposes. Among these, the Consolidated Fund of India plays a crucial role.
Consolidated Fund of India
- The Consolidated Fund of India is the main account of the Government of India.
- It includes all revenues, loans, and money received by the government.
- All government expenditure is charged to this fund, making it the primary source for financing government activities.
Other Government Funds
While the Consolidated Fund is the principal account, there are two other important funds:
- Public Accounts Fund of India:
- This fund holds money that the government receives but does not belong to it.
- It includes transactions like provident funds, and money held for other departments and agencies.
- Contingency Fund of India:
- This fund is used for emergencies and unforeseen expenditures.
- The amount can be accessed by the President of India without legislative approval, but it must be replenished from the Consolidated Fund.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the Public Accounts Fund and Contingency Fund serve distinct purposes, the vast majority of government funds and expenditures are managed within the Consolidated Fund of India. Thus, the correct answer to the question is that the funds belonging to the Government of India are chiefly kept in the Consolidated Fund of India.
The first state in the Indian Union formed on the basis of linguistic differences is- a)Uttar Pradesh
- b)Andhra Pradesh
- c)Tamil Nadu
- d)Kerala
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The first state in the Indian Union formed on the basis of linguistic differences is
a)
Uttar Pradesh
b)
Andhra Pradesh
c)
Tamil Nadu
d)
Kerala
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
The first state in the Indian Union formed on the basis of linguistic differences is
Andhra Pradesh.
The distinguishing feature of a federal government is- a)The national government gives some powers to the provincial government.
- b)Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
- c)Governing or ruling power is divided between different levels of government.
- d)Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The distinguishing feature of a federal government is
a)
The national government gives some powers to the provincial government.
b)
Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
c)
Governing or ruling power is divided between different levels of government.
d)
Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
|
|
Rekha garg answered |
The distinguishing feature of a federal government is that governing or ruling power is divided between different levels of government. This means that there are multiple levels of government that share power and authority, with each level having its own set of responsibilities and areas of jurisdiction.
Here is a detailed explanation of this distinguishing feature:
Federalism and Power Distribution:
- In a federal government, power is shared between the central or national government and the provincial or state governments. This distribution of power is enshrined in the constitution and provides a framework for governance.
- The national government is responsible for handling national-level issues such as defense, foreign policy, and currency, while the provincial governments have authority over local matters like education, healthcare, and transportation.
- The division of power ensures that both levels of government have the autonomy and authority to make decisions within their respective jurisdictions, without interference from the other level.
Balance of Power:
- Federalism aims to strike a balance between the centralization of power in a unitary system and the fragmentation of power in a confederal system.
- By dividing power between the national and provincial governments, federalism ensures that no single level of government becomes too dominant or overbearing.
- This balance of power helps to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or institutions, promoting a system of checks and balances.
Cooperative Governance:
- In a federal system, the national and provincial governments work together to govern the country or region.
- While they have distinct areas of authority, they also collaborate and coordinate on matters of mutual concern, such as economic development, infrastructure projects, and disaster management.
- This cooperative governance allows for the pooling of resources and expertise, leading to more effective and efficient decision-making and policy implementation.
Flexibility and Local Autonomy:
- Federalism allows for flexibility and adaptation to regional diversity and local needs.
- The provincial governments have the freedom to address specific issues that are unique to their regions, taking into account the cultural, social, and economic differences that exist within the country.
- This local autonomy enables provinces to tailor policies and programs to better serve their populations, promoting a sense of ownership and participation in the democratic process.
In conclusion, the distinguishing feature of a federal government is the division of governing or ruling power between different levels of government. This feature promotes a balance of power, cooperative governance, flexibility, and local autonomy, ensuring the effective and inclusive governance of a country or region.
Here is a detailed explanation of this distinguishing feature:
Federalism and Power Distribution:
- In a federal government, power is shared between the central or national government and the provincial or state governments. This distribution of power is enshrined in the constitution and provides a framework for governance.
- The national government is responsible for handling national-level issues such as defense, foreign policy, and currency, while the provincial governments have authority over local matters like education, healthcare, and transportation.
- The division of power ensures that both levels of government have the autonomy and authority to make decisions within their respective jurisdictions, without interference from the other level.
Balance of Power:
- Federalism aims to strike a balance between the centralization of power in a unitary system and the fragmentation of power in a confederal system.
- By dividing power between the national and provincial governments, federalism ensures that no single level of government becomes too dominant or overbearing.
- This balance of power helps to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few individuals or institutions, promoting a system of checks and balances.
Cooperative Governance:
- In a federal system, the national and provincial governments work together to govern the country or region.
- While they have distinct areas of authority, they also collaborate and coordinate on matters of mutual concern, such as economic development, infrastructure projects, and disaster management.
- This cooperative governance allows for the pooling of resources and expertise, leading to more effective and efficient decision-making and policy implementation.
Flexibility and Local Autonomy:
- Federalism allows for flexibility and adaptation to regional diversity and local needs.
- The provincial governments have the freedom to address specific issues that are unique to their regions, taking into account the cultural, social, and economic differences that exist within the country.
- This local autonomy enables provinces to tailor policies and programs to better serve their populations, promoting a sense of ownership and participation in the democratic process.
In conclusion, the distinguishing feature of a federal government is the division of governing or ruling power between different levels of government. This feature promotes a balance of power, cooperative governance, flexibility, and local autonomy, ensuring the effective and inclusive governance of a country or region.
In which of the following states, Indians who are not residents of that state, are not allowed to buy the property of any form?- a)Arunachal Pradesh
- b)Jammu and Kashmir
- c)Mizoram
- d)Rajasthan
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following states, Indians who are not residents of that state, are not allowed to buy the property of any form?
a)
Arunachal Pradesh
b)
Jammu and Kashmir
c)
Mizoram
d)
Rajasthan
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Jammu and Kashmir have its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State without the approval of the State Assembly.
Match the following items given in Column A with those column B: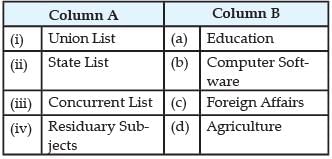
- a)(i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
- b)(i)-(a), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(b)
- c)(i)-(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
- d)(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following items given in Column A with those column B:

a)
(i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
b)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(b)
c)
(i)-(c), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(d)
d)
(i)-(a), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(b)
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
(i) Union List: Union List includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency. They are included in this list because we need a uniform policy on these matters throughout the country.
(ii) State List: In the Constitution, 'Agriculture' has been placed as Entry 14 in the State List along with several ancillary matters, while some agriculture-related items have been included in the Union List and the Concurrent List.
(iii) Concurrent list: The Indian constitution in its original enactment defined education as state subject. Under Article 42 of the constitution, an amendment was added in 1976 and education became a concurrent list subject which enables the central government to legislate it in the manner suited to it.
(iv) Residuary Subjects: Residuary Subjects are recognised as subjects that are not present in any of the lists stated in the constitution. The government of the Union has the powers to render law on Residuary Subjects. ,These subjects are e-commerce, Computer software and so on.
In a federal state- a)States are more powerful than the Centre
- b)The centre is more powerful than States
- c)A Presidential form of government functions.
- d)Constitution affects the division of powers between the Centre and States with safeguards against transgression of jurisdiction.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a federal state
a)
States are more powerful than the Centre
b)
The centre is more powerful than States
c)
A Presidential form of government functions.
d)
Constitution affects the division of powers between the Centre and States with safeguards against transgression of jurisdiction.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
A federal state is one where the power vests with the Center and state as per the constitutional arrangement and the exercise of those powers are limited by the constitution to be contained within the area of jurisdiction so defined.
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : India has a federal system.
Reason : Under a unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to central government.
- a)If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
- c)If assertion is true but reason is false.
- d)If both assertion and reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
Assertion : India has a federal system.
Reason : Under a unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to central government.
a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
d)
If both assertion and reason are false.
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Both Assertion and Reason are correct, but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion because the federal and unitary systems of government are two different systems.
India has adopted a federal structure of government wherein powers and governance are divided between the centre, state, and local levels. The federal system allows for a responsive government that addresses the issues of their respective jurisdictions so that every stratum of society gets an equal opportunity to voice its opinions. On the other hand, there is a unitary system of government wherein the central government is supreme, and there is no distribution of powers among different levels of government.
India has adopted a federal structure of government wherein powers and governance are divided between the centre, state, and local levels. The federal system allows for a responsive government that addresses the issues of their respective jurisdictions so that every stratum of society gets an equal opportunity to voice its opinions. On the other hand, there is a unitary system of government wherein the central government is supreme, and there is no distribution of powers among different levels of government.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.Q. Usually, a federation has _________ levels of government.- a)three
- b)four
- c)two
- d)five
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Q. Usually, a federation has _________ levels of government.
a)
three
b)
four
c)
two
d)
five
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.Q. How many languages are spoken in India?- a)More than 1200
- b)More than 1100
- c)More than 1400
- d)More than 1300
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
How many languages do we have in India? The answer depends on how one counts it. The latest information that we have is from the Census of India held in 2001. This census recorded more than 1500 distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues. These languages were grouped together under some major languages. For example, languages like Bhojpuri, Magadhi, Bundelkhandi, Chhattisgarhi, Rajasthani, Bhili and many others were grouped together under 'Hindi'. Even after this grouping, the Census found 114 major languages. Of these 22 languages are now included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution and are therefore, called 'Scheduled Languages'. Others are called 'non- Scheduled Languages'. In terms of languages, India is perhaps the most diverse country in the world.
Q. How many languages are spoken in India?
a)
More than 1200
b)
More than 1100
c)
More than 1400
d)
More than 1300
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Press Trust of India More than 19,500 languages or dialects are spoken in India as mother tongues, according to the latest analysis of a census released this week. There are 121 languages which are spoken by 10,000 or more people in India, which has a population of 121 crore, it said.
Find the incorrect option:Which of the following pair is incorrect?- a)State government – State List
- b)Central government – Union List
- c)Central and State – Concurrent List government List
- d)Local government – Residuary powers
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the incorrect option:
Which of the following pair is incorrect?
a)
State government – State List
b)
Central government – Union List
c)
Central and State – Concurrent List government List
d)
Local government – Residuary powers
|
|
Avinash Patel answered |
The Incorrect option is (d): Local government – Residuary powers
Correct answer is: Union government – Residuary powers.
Who makes laws on the subjects contained in the Concurrent List?- a)Union government
- b)State governmeants
- c)Both Union and state governments
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Who makes laws on the subjects contained in the Concurrent List?
a)
Union government
b)
State governmeants
c)
Both Union and state governments
d)
None of these
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Concurrent List includes subjects of common interest to both the Union Government as well as the State Governments, such as education, forest, trade unions, marriage, adoption and succession.
The idea of concurrent list in Indian constitution was borrowed from- a)England
- b)America
- c)Australia
- d)Russia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The idea of concurrent list in Indian constitution was borrowed from
a)
England
b)
America
c)
Australia
d)
Russia
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Idea of a concurrent list in Indian constitution was borrowed from Australia. There are 52 subjects in the concurrent list of VII schedule of Indian Constitution.
India is a federal state because its Constitution provides for- a)dual citizenship.
- b)Division of powers between the Union and the States.
- c)A written constitution.
- d)Election of members of Parliament by the people.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
India is a federal state because its Constitution provides for
a)
dual citizenship.
b)
Division of powers between the Union and the States.
c)
A written constitution.
d)
Election of members of Parliament by the people.
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
India has borrowed the concept of federalism from Canada. In this system, there is a clear division of powers between the union and states.
Choose the incorrect statement.- a)Usually a federation has two levels of governments
- b)Both the levels of governments enjoy theirs powers independent of one another
- c)In a federal system, a state government has powers of its own
- d)In a federal system, the state government is answerable to the central government
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the incorrect statement.
a)
Usually a federation has two levels of governments
b)
Both the levels of governments enjoy theirs powers independent of one another
c)
In a federal system, a state government has powers of its own
d)
In a federal system, the state government is answerable to the central government
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
Explanation:
- A state government is the government of a country subdivision in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, or be subject to the direct control of the federal government. This relationship may be defined by a constitution.
- The reference to "state" denotes country subdivisions which are officially or widely known as "states", and should not be confused with a "sovereign state". Provinces are usually divisions of unitary states. Their governments, which are also provincial governments, are not the subject of this article.
- The United States and Australia are the main examples of federal systems in which the term "state" is used for the subnational components of the federation. In addition, the Canadian provinces fulfil a similar role. The term for subnational units in non-English-speaking federal countries may also often be translated as "state", e.g. States of Germany
You can study Short Answer Questions of chapter Federalism through the document:
Of the following which one is correct about a federation?- a)Federation is the domination of the centre of the states.
- b)Federation is dependent on the centre on the states.
- c)The centre and the states interfere in the matters of each other.
- d)Federation is an association of states that forms a new one, and all the units and centre derive power from the Constitution.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the following which one is correct about a federation?
a)
Federation is the domination of the centre of the states.
b)
Federation is dependent on the centre on the states.
c)
The centre and the states interfere in the matters of each other.
d)
Federation is an association of states that forms a new one, and all the units and centre derive power from the Constitution.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The distinguishing feature of a federal government is division of powers between different levels of government.
India is federal because the powers of the union and state governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.Q. What was the first and major test for democratic Politics in our country?- a)The creation of linguistic states
- b)The creation of the language policy
- c)The creation of new federal states
- d)The creation of new federal territories
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
A second test for Indian federation is the language policy. Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians. Therefore, there were many safeguards to protect other languages. Besides Hindi, there are 21 other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution. A candidate in an examination conducted for the Central Government positions may opt to take the examination in any of these languages. States too have their own official languages. Much of the government work takes place in the official language of the concerned State. Unlike Sri Lanka, the leaders of our country adopted a very cautious attitude in spreading the use of Hindi. According to the Constitution, the use of English for official purposes was stopped in 1965. However, many non- Hindi speaking States demanded that the use of English should continue. In Tamil Nadu, this movement took a violent form. The Central Government responded by agreeing to continue the use of English along with Hindi for official purposes. Many critics think that this solution favoured the English-speaking elites. Promotion of Hindi continues to be the official policy of the Government of India. Promotion does not mean that the Central Government can impose Hindi on States where people speak a different language. The flexibility shown by Indian political leaders helped our country avoid the kind of situation that Sri Lanka finds itself in.
Q. What was the first and major test for democratic Politics in our country?
a)
The creation of linguistic states
b)
The creation of the language policy
c)
The creation of new federal states
d)
The creation of new federal territories
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The creation of Linguistic States was the first and a major test for democratic politics in our country. In 1947, the boundaries of several old States of India were changed in order to create new States. This was done to ensure that people who spoke the same language lived in the same State. Some States were created not on the basis of language but to recognise differences based on culture, ethnicity or geography.
These include States like Nagaland, Uttarakhand and Jharkhand. When the demand for the formation of States on the basis of language was raised, some national leaders feared that it would lead to the disintegration of the country. The Central Government resisted linguistic States for some time. But the experience has shown that the formation of linguistic States has actually made the country, more united. It has also made administration easier.
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.Q. Under which of the following systems, the central government can pass on orders to the provincial government?- a)Federal system
- b)Monarchy
- c)Unitary system
- d)Dictatorship
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given extract and answer the questions that follows:
Federalism is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country. Usually, a federation has two levels of government. One is the government for the entire country that is usually responsible for a few subjects of common national interest. The others are governments at the level of provinces or states that look after much of the day-to-day administering of their state. Both these levels of governments enjoy their power independent of the other. In this sense, federations are contrasted with unitary governments. Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government. But in a federal system, the central government cannot order the state government to do something. State government has powers of its own for which it is not answerable to the central government. Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
Q. Under which of the following systems, the central government can pass on orders to the provincial government?
a)
Federal system
b)
Monarchy
c)
Unitary system
d)
Dictatorship
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government.
Chapter doubts & questions for Federalism - Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Federalism - Online MCQ Tests for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Related Class 10 Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily













