All Exams >
UPSC >
Lucent For GK >
All Questions
All questions of Agriculture for UPSC CSE Exam
In an area with an annual rainfall of more than 200 cm and sloping hills which crop will be ideal?- a) Jute
- b) Cotton
- c) Maize
- d) Tea
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an area with an annual rainfall of more than 200 cm and sloping hills which crop will be ideal?
a)
Jute
b)
Cotton
c)
Maize
d)
Tea
|
|
Karishma Karishma answered |
Yes, tea is rainfall of more than 200 cm and sloping hills tea crop will be ideal
Parts of Himachal Pradesh had evolved a local system of canal irrigation over four hundred years ago. It is called— - a) Kulhs
- b) Baori
- c) Jhalara
- d) Khadin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Parts of Himachal Pradesh had evolved a local system of canal irrigation over four hundred years ago. It is called—
a)
Kulhs
b)
Baori
c)
Jhalara
d)
Khadin
|
|
Deepa Iyer answered |
Kuhls are a traditional irrigation system in Himachal Pradesh. They are surface channels diverting water from natural flowing streams (khuds). A typical community Kuhl services 6 to 30 farmers, irrigating an area of about 20 ha.
Which of the following are not examples of shifting cultivation? Select the correct answer from the codes given below:1. Ladang2. Jhum3. Pondu4. FazendaCodes:- a) 1 and 4
- b) 3 and 4
- c) 1, 2, and 3
- d) 2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are not examples of shifting cultivation? Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
1. Ladang
2. Jhum
3. Pondu
4. Fazenda
Codes:
a)
1 and 4
b)
3 and 4
c)
1, 2, and 3
d)
2 and 4

|
Humc-01 Aditee answered |
Lading and jump are two different names of shifting cultivation also known as slash and burn agriculture
Which of the following crops are grown mostly under subsistence farming? - a) Millets and Rice
- b) Cotton and Tobacco
- c) Tea and Coffee
- d) Vegetables and Fruits
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following crops are grown mostly under subsistence farming?
a)
Millets and Rice
b)
Cotton and Tobacco
c)
Tea and Coffee
d)
Vegetables and Fruits
|
|
Prerna Rane answered |
Subsistence farming and the crops grown:
Subsistence farming is a type of farming where the farmer grows crops primarily for the consumption of their own family or community, rather than for commercial purposes. It is characterized by small-scale agricultural practices, minimal use of modern technology, and limited surplus production. In subsistence farming, the main goal is to produce enough food to meet the immediate needs of the household.
The crops grown mostly under subsistence farming:
Among the given options, the crops that are grown mostly under subsistence farming are Millets and Rice. Let's understand why these are the preferred crops for subsistence farming:
1. Millets:
- Millets are small-seeded grains that are highly suitable for subsistence farming due to their resilience and adaptability to diverse climatic conditions. They can be grown in areas with low rainfall and poor soil fertility.
- Millets such as pearl millet, foxtail millet, and finger millet are staple food crops in many parts of India and Africa, where subsistence farming is prevalent.
- These crops require minimal inputs in terms of irrigation, fertilizers, and pesticides, making them cost-effective for small-scale farmers.
- Millets are highly nutritious and provide essential nutrients like carbohydrates, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an important food source for subsistence farmers.
2. Rice:
- Rice is a major staple crop in many parts of Asia, particularly in countries like India, China, and Indonesia. It is also a primary crop for subsistence farming in these regions.
- Rice cultivation requires a significant amount of water, making it suitable for areas with abundant rainfall or access to irrigation facilities.
- It is a high-calorie food crop and provides a good source of carbohydrates, which is crucial for subsistence farmers who rely on their own produce for sustenance.
- Rice can be stored for a longer duration, allowing subsistence farmers to have a steady food supply throughout the year.
In conclusion:
Millets and rice are the crops that are predominantly grown under subsistence farming. These crops are well-suited for small-scale farmers due to their resilience, adaptability, nutritional value, and relatively low input requirements. They play a vital role in ensuring food security and sustenance for subsistence farming communities.
Subsistence farming is a type of farming where the farmer grows crops primarily for the consumption of their own family or community, rather than for commercial purposes. It is characterized by small-scale agricultural practices, minimal use of modern technology, and limited surplus production. In subsistence farming, the main goal is to produce enough food to meet the immediate needs of the household.
The crops grown mostly under subsistence farming:
Among the given options, the crops that are grown mostly under subsistence farming are Millets and Rice. Let's understand why these are the preferred crops for subsistence farming:
1. Millets:
- Millets are small-seeded grains that are highly suitable for subsistence farming due to their resilience and adaptability to diverse climatic conditions. They can be grown in areas with low rainfall and poor soil fertility.
- Millets such as pearl millet, foxtail millet, and finger millet are staple food crops in many parts of India and Africa, where subsistence farming is prevalent.
- These crops require minimal inputs in terms of irrigation, fertilizers, and pesticides, making them cost-effective for small-scale farmers.
- Millets are highly nutritious and provide essential nutrients like carbohydrates, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an important food source for subsistence farmers.
2. Rice:
- Rice is a major staple crop in many parts of Asia, particularly in countries like India, China, and Indonesia. It is also a primary crop for subsistence farming in these regions.
- Rice cultivation requires a significant amount of water, making it suitable for areas with abundant rainfall or access to irrigation facilities.
- It is a high-calorie food crop and provides a good source of carbohydrates, which is crucial for subsistence farmers who rely on their own produce for sustenance.
- Rice can be stored for a longer duration, allowing subsistence farmers to have a steady food supply throughout the year.
In conclusion:
Millets and rice are the crops that are predominantly grown under subsistence farming. These crops are well-suited for small-scale farmers due to their resilience, adaptability, nutritional value, and relatively low input requirements. They play a vital role in ensuring food security and sustenance for subsistence farming communities.
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer by using the codes Assertion (A): Assam is the largest producer of tea in India.Reason (R): Cheap tribal labour is available in abundance in AssamCodes:- a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c) A is true, but R is false.
- d) A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer by using the codes
Assertion (A): Assam is the largest producer of tea in India.
Reason (R): Cheap tribal labour is available in abundance in Assam
Codes:
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Arnab Saha answered |
Assertion (A): Assam is the largest producer of tea in India.
- Assam is indeed the largest tea-producing state in India, contributing a significant portion of the country's total tea production.
- The state's climatic conditions, including its fertile soil and abundant rainfall, create an ideal environment for tea cultivation.
Reason (R): Cheap tribal labour is available in abundance in Assam.
- The availability of labor, including tribal communities, has historically played a role in the tea industry.
- However, attributing Assam's tea production solely to the availability of cheap labor oversimplifies the situation. Other factors, such as geographical advantages, investment in tea plantations, and established infrastructure, also contribute significantly to Assam's tea production.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option B):
- Both statements A and R are true.
- While the reason (R) mentions cheap tribal labor, it does not fully explain why Assam is the largest producer of tea. The region's climate, soil quality, and historical investment in tea cultivation are equally, if not more, important factors.
- Thus, while R is true, it is not the correct explanation for A, leading to the conclusion that option B is correct.
Conclusion:
- The correct answer is option B: Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- This highlights the multifaceted nature of agricultural production, where various elements contribute to a state's prominence in a specific industry.
- Assam is indeed the largest tea-producing state in India, contributing a significant portion of the country's total tea production.
- The state's climatic conditions, including its fertile soil and abundant rainfall, create an ideal environment for tea cultivation.
Reason (R): Cheap tribal labour is available in abundance in Assam.
- The availability of labor, including tribal communities, has historically played a role in the tea industry.
- However, attributing Assam's tea production solely to the availability of cheap labor oversimplifies the situation. Other factors, such as geographical advantages, investment in tea plantations, and established infrastructure, also contribute significantly to Assam's tea production.
Explanation of the Correct Answer (Option B):
- Both statements A and R are true.
- While the reason (R) mentions cheap tribal labor, it does not fully explain why Assam is the largest producer of tea. The region's climate, soil quality, and historical investment in tea cultivation are equally, if not more, important factors.
- Thus, while R is true, it is not the correct explanation for A, leading to the conclusion that option B is correct.
Conclusion:
- The correct answer is option B: Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- This highlights the multifaceted nature of agricultural production, where various elements contribute to a state's prominence in a specific industry.
Which of the following are responsible for the decrease of per capita holding of cultivated land in India?1. Low per capita income.2. Rapid rate of increase of population3. Practice of dividing land equally among the heirs.4. Use of traditional techniques of ploughing.Select the correct answer using the codes given below:- a) 1 and 2
- b) 2 and 3
- c) 1 and 4
- d) 2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are responsible for the decrease of per capita holding of cultivated land in India?
1. Low per capita income.
2. Rapid rate of increase of population
3. Practice of dividing land equally among the heirs.
4. Use of traditional techniques of ploughing.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 and 3
c)
1 and 4
d)
2, 3 and 4
|
|
Devansh Yadav answered |
Explanation:
The decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land in India is influenced by various factors. Let's analyze each option to understand their impact.
1. Low per capita income:
Low per capita income implies that individuals have limited financial resources. This restricts their ability to purchase or lease additional land for cultivation. As a result, the per capita holding of cultivated land decreases. Therefore, option 1 is a valid reason for the decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land.
2. Rapid rate of increase of population:
The rapid increase in population leads to a higher demand for food and other agricultural products. To meet this demand, farmers need to increase their agricultural output. However, due to the limited availability of land, the per capita holding of cultivated land decreases as more people rely on the existing land for their livelihood. Hence, option 2 is also a valid reason.
3. Practice of dividing land equally among the heirs:
The practice of dividing land equally among the heirs, also known as fragmentation of land, is a common practice in India. When land is divided among multiple heirs, the size of individual land holdings decreases. This division continues with each subsequent generation, resulting in smaller land holdings. Consequently, the per capita holding of cultivated land decreases. Therefore, option 3 is a valid reason.
4. Use of traditional techniques of ploughing:
The use of traditional techniques of plowing in agriculture can limit the productivity of the land. Traditional methods may not be as efficient as modern techniques, resulting in lower crop yields. This may lead to the need for more land to compensate for the lower productivity. However, the option does not directly contribute to the decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land. Therefore, option 4 is not a valid reason.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, options 2 and 3 are responsible for the decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land in India. The rapid rate of increase of population and the practice of dividing land equally among the heirs lead to a decrease in the size of individual land holdings, thereby reducing the per capita holding of cultivated land.
The decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land in India is influenced by various factors. Let's analyze each option to understand their impact.
1. Low per capita income:
Low per capita income implies that individuals have limited financial resources. This restricts their ability to purchase or lease additional land for cultivation. As a result, the per capita holding of cultivated land decreases. Therefore, option 1 is a valid reason for the decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land.
2. Rapid rate of increase of population:
The rapid increase in population leads to a higher demand for food and other agricultural products. To meet this demand, farmers need to increase their agricultural output. However, due to the limited availability of land, the per capita holding of cultivated land decreases as more people rely on the existing land for their livelihood. Hence, option 2 is also a valid reason.
3. Practice of dividing land equally among the heirs:
The practice of dividing land equally among the heirs, also known as fragmentation of land, is a common practice in India. When land is divided among multiple heirs, the size of individual land holdings decreases. This division continues with each subsequent generation, resulting in smaller land holdings. Consequently, the per capita holding of cultivated land decreases. Therefore, option 3 is a valid reason.
4. Use of traditional techniques of ploughing:
The use of traditional techniques of plowing in agriculture can limit the productivity of the land. Traditional methods may not be as efficient as modern techniques, resulting in lower crop yields. This may lead to the need for more land to compensate for the lower productivity. However, the option does not directly contribute to the decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land. Therefore, option 4 is not a valid reason.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, options 2 and 3 are responsible for the decrease in per capita holding of cultivated land in India. The rapid rate of increase of population and the practice of dividing land equally among the heirs lead to a decrease in the size of individual land holdings, thereby reducing the per capita holding of cultivated land.
Double cropping is a common practice in areas having1. a lot of rainfall.2. good irrigation facilities.3. a long growing period.4. alluvial soils.Codes: - a) 2, 3 and 4
- b) 1, 2 and 4
- c) 1, 2 and 3
- d) 1, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Double cropping is a common practice in areas having
1. a lot of rainfall.
2. good irrigation facilities.
3. a long growing period.
4. alluvial soils.
Codes:
a)
2, 3 and 4
b)
1, 2 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 3
d)
1, 3 and 4
|
|
Ritika Choudhury answered |
- In agriculture, multiple cropping is the practice of growing two or more crops in the same piece of land during a single growing season. It is a form of polyculture. It can take the form of double-cropping, in which a second crop is planted after the first has been harvested, or relay cropping, in which the second crop is started amidst the first crop before it has been harvested.
- A related practice, companion planting, is sometimes used in gardening and intensive cultivation of vegetables and fruits. One example of multi-cropping is tomatoes + onions + marigold; the marigolds repel some tomato pests.
Which of the following statements are correct? 1. Assam produces nearly 80% of jute in India.2. Jute grows well on loamy soil.3. Hot and humid conditions are ideal for growing jute.4. Jute is commonly cultivated with wheat in rotation.Select the correct answer using the code given below:- a) 1, 2 and 3
- b) 2, 3 and 4
- c) 2 and 3 only
- d) 1 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements are correct?
1. Assam produces nearly 80% of jute in India.
2. Jute grows well on loamy soil.
3. Hot and humid conditions are ideal for growing jute.
4. Jute is commonly cultivated with wheat in rotation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1 and 4 only
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
- In India, Jute (corchorus spp) is produced in West Bengal (Ist rank}, Bihar and Assam mainly. Jute grows well in loamy soils under hot and humid conditions-as ideal climatic condition.
- Generally, Maize/Moong/Urd (spring season)- Jute-Rice crop rotation is followed, while Jute rice-wheat rotation is followed on less amount.
Which of the following methods is/are suitable for soil conservation in the hilly region?1. Terracing and contour bunding2. Shifting cultivation3. Contour ploughingSelect the correct answer using the codes given below :- a) 1 and 3
- b) Only 2
- c) Only 3
- d) All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following methods is/are suitable for soil conservation in the hilly region?
1. Terracing and contour bunding
2. Shifting cultivation
3. Contour ploughing
Select the correct answer using the codes given below :
a)
1 and 3
b)
Only 2
c)
Only 3
d)
All of these
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
Level terrace or contour bunding involves the construction of bind passing through the points having same elevation ploughing and/or planting across a slope following its elevation contour lines.
Consider the following statements1. Rural forestry aims to raise the trees on community land and privately owned land.2. Farm forestry encourages individual farmers to plant trees ontheir farmland to meet the domestic needs of the family.Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?- a) Only 1
- b) Only 2
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements
1. Rural forestry aims to raise the trees on community land and privately owned land.
2. Farm forestry encourages individual farmers to plant trees on
their farmland to meet the domestic needs of the family.
Which of the statement(s) given above is/are correct?
a)
Only 1
b)
Only 2
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
- Rural forestry (also known as community forestry) aims to raise the trees on community land and privately owned land as in farm forestry.
- Farm forestry encouraged individual farmers to plant trees on their farmland to meet the domestic needs of the family. All these schemes are taken up under the social forestry programme.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct codes given below:1. Jhum cultivation is adopted in the North-Eastern State of India.2. Jhum cultivation is a process of afforestation.- a) 1 only
- b) 2 only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and choose the correct codes given below:
1. Jhum cultivation is adopted in the North-Eastern State of India.
2. Jhum cultivation is a process of afforestation.
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Diya Singh answered |
Jhum cultivation in the North-Eastern State of India
Jhum cultivation, also known as slash-and-burn agriculture or shifting cultivation, is a traditional method of farming practiced in the North-Eastern states of India. It involves clearing a patch of forest land, burning the vegetation, and then cultivating crops on the fertile ash-enriched soil. This process is repeated in a cyclical manner as the soil fertility diminishes, and new patches of land are cleared for cultivation.
Statement 1: Jhum cultivation is adopted in the North-Eastern State of India.
The first statement is correct. Jhum cultivation is primarily practiced in the North-Eastern states of India, including states like Assam, Nagaland, Mizoram, Manipur, Meghalaya, and Arunachal Pradesh. These states have hilly terrains with dense forests, and the indigenous communities living in these regions have traditionally relied on jhum cultivation for their sustenance.
Statement 2: Jhum cultivation is a process of afforestation.
The second statement is incorrect. Jhum cultivation is not a process of afforestation but rather a method of shifting cultivation. It involves the temporary clearance of forest land for agricultural purposes. The cycle of jhum cultivation includes both the clearing of forest land and the regrowth of vegetation after cultivation is complete. However, due to the rapid population growth and increased agricultural activities, the cycle of jhum cultivation has been shortened in recent years, leading to deforestation and soil degradation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the correct codes for the given statements are:
a) 1 only
Statement 1 is correct as jhum cultivation is indeed practiced in the North-Eastern states of India. However, statement 2 is incorrect as jhum cultivation is not a process of afforestation, but rather a form of shifting cultivation that involves temporary forest clearance for agriculture.
Jhum cultivation, also known as slash-and-burn agriculture or shifting cultivation, is a traditional method of farming practiced in the North-Eastern states of India. It involves clearing a patch of forest land, burning the vegetation, and then cultivating crops on the fertile ash-enriched soil. This process is repeated in a cyclical manner as the soil fertility diminishes, and new patches of land are cleared for cultivation.
Statement 1: Jhum cultivation is adopted in the North-Eastern State of India.
The first statement is correct. Jhum cultivation is primarily practiced in the North-Eastern states of India, including states like Assam, Nagaland, Mizoram, Manipur, Meghalaya, and Arunachal Pradesh. These states have hilly terrains with dense forests, and the indigenous communities living in these regions have traditionally relied on jhum cultivation for their sustenance.
Statement 2: Jhum cultivation is a process of afforestation.
The second statement is incorrect. Jhum cultivation is not a process of afforestation but rather a method of shifting cultivation. It involves the temporary clearance of forest land for agricultural purposes. The cycle of jhum cultivation includes both the clearing of forest land and the regrowth of vegetation after cultivation is complete. However, due to the rapid population growth and increased agricultural activities, the cycle of jhum cultivation has been shortened in recent years, leading to deforestation and soil degradation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the correct codes for the given statements are:
a) 1 only
Statement 1 is correct as jhum cultivation is indeed practiced in the North-Eastern states of India. However, statement 2 is incorrect as jhum cultivation is not a process of afforestation, but rather a form of shifting cultivation that involves temporary forest clearance for agriculture.
Which crop is afflicted by the disease called red rot? - a) Rice
- b) Wheat
- c) Bajra
- d) Sugarcane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which crop is afflicted by the disease called red rot?
a)
Rice
b)
Wheat
c)
Bajra
d)
Sugarcane
|
|
Deepak Dasgupta answered |
Understanding Red Rot Disease
Red rot is a significant disease that primarily affects sugarcane, leading to severe economic losses in sugar production. This disease is caused by the fungus *Colletotrichum falcatum*, which infects the plant and causes various detrimental effects.
Symptoms of Red Rot
- The most notable symptom of red rot is the presence of red streaks or patches on the stem of the sugarcane.
- The affected areas can become soft and mushy, eventually leading to the rotting of the cane.
- In severe cases, the entire plant can collapse, resulting in a complete loss of yield.
Impact on Sugarcane Production
- Red rot can significantly reduce the sucrose content in sugarcane, affecting the quality of sugar produced.
- Infested crops often require more inputs for management, increasing the overall cost for farmers.
- The disease can spread rapidly, especially in humid conditions, making it crucial for farmers to implement effective management practices.
Management Strategies
- Crop rotation and the use of resistant sugarcane varieties are effective methods to combat red rot.
- Proper sanitation practices, like removing infected plant debris, can help limit the spread of the disease.
- Regular monitoring and timely fungicide application may also be necessary to control outbreaks.
In conclusion, red rot is a serious threat to sugarcane, and understanding its symptoms, impact, and management strategies is essential for farmers to mitigate losses and ensure sustainable production.
Red rot is a significant disease that primarily affects sugarcane, leading to severe economic losses in sugar production. This disease is caused by the fungus *Colletotrichum falcatum*, which infects the plant and causes various detrimental effects.
Symptoms of Red Rot
- The most notable symptom of red rot is the presence of red streaks or patches on the stem of the sugarcane.
- The affected areas can become soft and mushy, eventually leading to the rotting of the cane.
- In severe cases, the entire plant can collapse, resulting in a complete loss of yield.
Impact on Sugarcane Production
- Red rot can significantly reduce the sucrose content in sugarcane, affecting the quality of sugar produced.
- Infested crops often require more inputs for management, increasing the overall cost for farmers.
- The disease can spread rapidly, especially in humid conditions, making it crucial for farmers to implement effective management practices.
Management Strategies
- Crop rotation and the use of resistant sugarcane varieties are effective methods to combat red rot.
- Proper sanitation practices, like removing infected plant debris, can help limit the spread of the disease.
- Regular monitoring and timely fungicide application may also be necessary to control outbreaks.
In conclusion, red rot is a serious threat to sugarcane, and understanding its symptoms, impact, and management strategies is essential for farmers to mitigate losses and ensure sustainable production.
What is the chief cause of low yields of crops in India?1. Small size of holdings2. Traditional methods of farming3. less farmers4. Low level of farm mechanizationCodes:- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)1, 2 and 4
- c)2, 3 and 4
- d)1, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the chief cause of low yields of crops in India?
1. Small size of holdings
2. Traditional methods of farming
3. less farmers
4. Low level of farm mechanization
Codes:
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
1, 2 and 4
c)
2, 3 and 4
d)
1, 3 and 4
|
|
Ojasvi Mehta answered |
The low productivity in India is a result of the following factors:
- The average size of land holdings is very small (less than 2 hectares) and is subject to fragmentation due to land ceiling acts, and in some cases, family disputes
- Adoption of modern agricultural practices and use of technology is inadequate
- India has inadequate infrastructure and services.
- Illiteracy, general socio-economic backwardness, slow progress in implementing land reforms and inadequate or inefficient finance and marketing services.
- Inconsistent government policy.
- Irrigation facilities are inadequate,
Which soil needs little irrigation as it retains soil moisture?- a) Alluvial soil
- b) Black soil
- c) Red soil
- d) Laterite soil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which soil needs little irrigation as it retains soil moisture?
a)
Alluvial soil
b)
Black soil
c)
Red soil
d)
Laterite soil
|
|
Anagha Rane answered |
Black soil retains soil moisture and requires little irrigation
Black soil, also known as regur soil or black cotton soil, is a type of soil that is found in several parts of India. It is known for its high fertility and ability to retain soil moisture, making it suitable for agriculture. Here are the reasons why black soil needs little irrigation:
1. Composition and Structure:
- Black soil is composed of fine-grained clayey material, which has the ability to hold water.
- It has a good crumb structure, which allows water to penetrate and be retained in the soil.
2. High Water Holding Capacity:
- Black soil has a high water holding capacity due to its clay content.
- The clay particles in the soil have a large surface area, which allows them to hold onto water molecules.
- This means that black soil can retain moisture for a longer period, reducing the need for frequent irrigation.
3. Slow Drainage:
- Black soil has a slow drainage rate due to its compact nature and high clay content.
- The compactness of the soil restricts the movement of water, allowing it to be retained in the soil for a longer time.
- This slow drainage helps in conserving soil moisture and reducing the need for irrigation.
4. Drought Resistance:
- Black soil is known for its drought resistance properties.
- It can withstand dry periods without losing its fertility or moisture content.
- This resilience to drought conditions further reduces the need for irrigation.
Conclusion:
Black soil, with its composition, structure, high water holding capacity, slow drainage, and drought resistance properties, has the ability to retain soil moisture for a longer time. This reduces the need for frequent irrigation, making it a suitable soil for agriculture in areas with limited water availability.
Black soil, also known as regur soil or black cotton soil, is a type of soil that is found in several parts of India. It is known for its high fertility and ability to retain soil moisture, making it suitable for agriculture. Here are the reasons why black soil needs little irrigation:
1. Composition and Structure:
- Black soil is composed of fine-grained clayey material, which has the ability to hold water.
- It has a good crumb structure, which allows water to penetrate and be retained in the soil.
2. High Water Holding Capacity:
- Black soil has a high water holding capacity due to its clay content.
- The clay particles in the soil have a large surface area, which allows them to hold onto water molecules.
- This means that black soil can retain moisture for a longer period, reducing the need for frequent irrigation.
3. Slow Drainage:
- Black soil has a slow drainage rate due to its compact nature and high clay content.
- The compactness of the soil restricts the movement of water, allowing it to be retained in the soil for a longer time.
- This slow drainage helps in conserving soil moisture and reducing the need for irrigation.
4. Drought Resistance:
- Black soil is known for its drought resistance properties.
- It can withstand dry periods without losing its fertility or moisture content.
- This resilience to drought conditions further reduces the need for irrigation.
Conclusion:
Black soil, with its composition, structure, high water holding capacity, slow drainage, and drought resistance properties, has the ability to retain soil moisture for a longer time. This reduces the need for frequent irrigation, making it a suitable soil for agriculture in areas with limited water availability.
Farmers are requested to mix lime with soil while farming their fields. This is because
- a)lime is very helpful in maintaining the water content in the soil
- b)lime decreases the acidity of the soil
- c)lime decreases the basicity of soil
- d)the high concentration of lime is necessary for the plant growth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Farmers are requested to mix lime with soil while farming their fields. This is because
a)
lime is very helpful in maintaining the water content in the soil
b)
lime decreases the acidity of the soil
c)
lime decreases the basicity of soil
d)
the high concentration of lime is necessary for the plant growth
|
|
Jaideep Verma answered |
Explanation:
Introduction:
Lime is commonly used in farming practices to improve the quality of soil. It is a type of soil amendment that helps in altering the pH level of the soil. The pH level of the soil plays a crucial role in determining its fertility and the availability of nutrients to plants.
Acidity and Basicity of Soil:
Soil can be acidic, neutral, or alkaline (basic) based on its pH level. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH level below 7 indicates acidity, while a pH level above 7 indicates alkalinity.
Importance of pH level in soil:
The pH level of the soil affects the solubility and availability of nutrients for plant growth. Different plants have different pH requirements for optimal growth. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH level (around 6 to 7), as this range allows for better nutrient availability.
Effect of acidity on soil:
Acidic soil can have a detrimental effect on plant growth. It reduces the availability of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Additionally, it can lead to the accumulation of toxic elements like aluminum and manganese, which can harm plant roots. Acidic soil also affects microbial activity, reducing the breakdown of organic matter and nutrient cycling.
Role of lime in soil:
Lime is commonly used to neutralize acidic soils. When lime is added to the soil, it reacts with the acidic components, such as hydrogen ions (H+), and raises the pH level. This process is known as liming or soil sweetening.
Benefits of adding lime to soil:
Adding lime to soil offers several benefits:
1. Decreases soil acidity: Lime helps in raising the pH level of acidic soil, making it more neutral or slightly alkaline. This makes the soil more suitable for plant growth and improves nutrient availability.
2. Enhances nutrient availability: By neutralizing acidity, lime helps in unlocking nutrients in the soil, making them more available for plant uptake. This promotes better nutrient absorption and overall plant health.
3. Improves soil structure: Lime aids in the formation of stable soil aggregates, improving soil structure and reducing compaction. This allows for better water infiltration and root penetration.
4. Enhances microbial activity: Lime provides a favorable environment for beneficial soil microorganisms, which play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition.
5. Prevents nutrient deficiencies: Lime application can prevent nutrient deficiencies by ensuring that essential nutrients are readily available to plants.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, farmers are requested to mix lime with soil while farming their fields primarily because it decreases the acidity of the soil. By raising the pH level, lime improves nutrient availability, enhances soil structure, and promotes overall plant health.
Introduction:
Lime is commonly used in farming practices to improve the quality of soil. It is a type of soil amendment that helps in altering the pH level of the soil. The pH level of the soil plays a crucial role in determining its fertility and the availability of nutrients to plants.
Acidity and Basicity of Soil:
Soil can be acidic, neutral, or alkaline (basic) based on its pH level. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. A pH level below 7 indicates acidity, while a pH level above 7 indicates alkalinity.
Importance of pH level in soil:
The pH level of the soil affects the solubility and availability of nutrients for plant growth. Different plants have different pH requirements for optimal growth. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH level (around 6 to 7), as this range allows for better nutrient availability.
Effect of acidity on soil:
Acidic soil can have a detrimental effect on plant growth. It reduces the availability of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Additionally, it can lead to the accumulation of toxic elements like aluminum and manganese, which can harm plant roots. Acidic soil also affects microbial activity, reducing the breakdown of organic matter and nutrient cycling.
Role of lime in soil:
Lime is commonly used to neutralize acidic soils. When lime is added to the soil, it reacts with the acidic components, such as hydrogen ions (H+), and raises the pH level. This process is known as liming or soil sweetening.
Benefits of adding lime to soil:
Adding lime to soil offers several benefits:
1. Decreases soil acidity: Lime helps in raising the pH level of acidic soil, making it more neutral or slightly alkaline. This makes the soil more suitable for plant growth and improves nutrient availability.
2. Enhances nutrient availability: By neutralizing acidity, lime helps in unlocking nutrients in the soil, making them more available for plant uptake. This promotes better nutrient absorption and overall plant health.
3. Improves soil structure: Lime aids in the formation of stable soil aggregates, improving soil structure and reducing compaction. This allows for better water infiltration and root penetration.
4. Enhances microbial activity: Lime provides a favorable environment for beneficial soil microorganisms, which play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition.
5. Prevents nutrient deficiencies: Lime application can prevent nutrient deficiencies by ensuring that essential nutrients are readily available to plants.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, farmers are requested to mix lime with soil while farming their fields primarily because it decreases the acidity of the soil. By raising the pH level, lime improves nutrient availability, enhances soil structure, and promotes overall plant health.
Dapog method of rice nursery was developed in - a) China
- b) Indonesia
- c) Japan
- d) Philippines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dapog method of rice nursery was developed in
a)
China
b)
Indonesia
c)
Japan
d)
Philippines
|
|
Anmol Kumar answered |
The correct answer is option 'D' - Philippines.
The Dapog method of rice nursery is a technique that was developed in the Philippines. It is a traditional method of raising rice seedlings in a nursery before transplanting them to the main field. This method has been widely used by Filipino farmers for many years and has proven to be effective in increasing rice productivity.
Here is an explanation of the Dapog method of rice nursery in detail:
1. Definition and Purpose:
- The Dapog method involves the use of small seedbeds or nurseries to grow rice seedlings before they are transplanted to the main field.
- The purpose of this method is to ensure the healthy growth of seedlings, improve their survival rate, and achieve higher yields in the main field.
2. Preparation of the Nursery:
- A suitable area of land is selected for the nursery, usually near a water source for irrigation.
- The land is plowed and leveled to create a smooth seedbed.
- The size of the nursery can vary depending on the number of seedlings needed.
- The nursery is divided into small plots or dapogs, usually measuring around 1.5 meters by 1.5 meters.
3. Seed Preparation and Sowing:
- High-quality rice seeds are selected and soaked in water for about 24 hours.
- The soaked seeds are then spread evenly on a clean cloth or mat to allow them to dry for a few hours.
- The dried seeds are sown in the prepared dapogs, with a recommended spacing of 2-3 seeds per hole.
- The depth of sowing is around 1-2 centimeters.
4. Water Management:
- After sowing, the nursery is irrigated with water to keep the soil moist.
- Excessive water should be avoided to prevent seed rot or fungal diseases.
- The water level is maintained at around 2-3 centimeters throughout the nursery.
5. Care and Maintenance:
- Weeding is an important aspect of the Dapog method. Weeds compete with rice seedlings for nutrients and sunlight, so regular weeding is necessary.
- Pests and diseases should be monitored and appropriate measures taken to control them.
- Fertilizers can be applied to the nursery if necessary, following recommended guidelines.
6. Transplanting:
- After about 25-30 days, when the seedlings have grown to a suitable size (around 10-15 centimeters), they are ready for transplanting.
- The seedlings are carefully uprooted from the nursery and transplanted to the main field.
Overall, the Dapog method of rice nursery is an effective technique for raising healthy rice seedlings before transplanting them to the main field. It helps to ensure better crop establishment and higher yields, contributing to improved rice production in the Philippines.
The Dapog method of rice nursery is a technique that was developed in the Philippines. It is a traditional method of raising rice seedlings in a nursery before transplanting them to the main field. This method has been widely used by Filipino farmers for many years and has proven to be effective in increasing rice productivity.
Here is an explanation of the Dapog method of rice nursery in detail:
1. Definition and Purpose:
- The Dapog method involves the use of small seedbeds or nurseries to grow rice seedlings before they are transplanted to the main field.
- The purpose of this method is to ensure the healthy growth of seedlings, improve their survival rate, and achieve higher yields in the main field.
2. Preparation of the Nursery:
- A suitable area of land is selected for the nursery, usually near a water source for irrigation.
- The land is plowed and leveled to create a smooth seedbed.
- The size of the nursery can vary depending on the number of seedlings needed.
- The nursery is divided into small plots or dapogs, usually measuring around 1.5 meters by 1.5 meters.
3. Seed Preparation and Sowing:
- High-quality rice seeds are selected and soaked in water for about 24 hours.
- The soaked seeds are then spread evenly on a clean cloth or mat to allow them to dry for a few hours.
- The dried seeds are sown in the prepared dapogs, with a recommended spacing of 2-3 seeds per hole.
- The depth of sowing is around 1-2 centimeters.
4. Water Management:
- After sowing, the nursery is irrigated with water to keep the soil moist.
- Excessive water should be avoided to prevent seed rot or fungal diseases.
- The water level is maintained at around 2-3 centimeters throughout the nursery.
5. Care and Maintenance:
- Weeding is an important aspect of the Dapog method. Weeds compete with rice seedlings for nutrients and sunlight, so regular weeding is necessary.
- Pests and diseases should be monitored and appropriate measures taken to control them.
- Fertilizers can be applied to the nursery if necessary, following recommended guidelines.
6. Transplanting:
- After about 25-30 days, when the seedlings have grown to a suitable size (around 10-15 centimeters), they are ready for transplanting.
- The seedlings are carefully uprooted from the nursery and transplanted to the main field.
Overall, the Dapog method of rice nursery is an effective technique for raising healthy rice seedlings before transplanting them to the main field. It helps to ensure better crop establishment and higher yields, contributing to improved rice production in the Philippines.
Consider the following statements:1. In India, natural rubber is produced in southern India only.2. Among the coffee-growing states of India, the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee is in Kerala.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a) 1 only
- b) 2 only
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. In India, natural rubber is produced in southern India only.
2. Among the coffee-growing states of India, the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2
|
|
Aman Joshi answered |
Statement 1: In India, natural rubber is produced in southern India only.
Statement 2: Among the coffee-growing states of India, the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee is in Kerala.
To determine the correctness of the given statements, let's evaluate each one separately:
Statement 1: In India, natural rubber is produced in southern India only.
This statement is incorrect. While it is true that southern India is a major producer of natural rubber, it is not the only region where rubber is produced in India. Natural rubber is also produced in northeastern states like Assam, Tripura, and Meghalaya. In fact, Kerala, which is located in southern India, is the largest producer of natural rubber in the country. Therefore, statement 1 is false.
Statement 2: Among the coffee-growing states of India, the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee is in Kerala.
This statement is correct. Kerala is one of the major coffee-growing states in India, along with Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. However, Kerala has the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee among these states. This is primarily due to the small landholdings of coffee plantations in Kerala, which often results in inefficient farming practices and lower productivity. Therefore, statement 2 is true.
In conclusion, among the given statements, statement 2 is correct while statement 1 is incorrect. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - 1 only.
Statement 2: Among the coffee-growing states of India, the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee is in Kerala.
To determine the correctness of the given statements, let's evaluate each one separately:
Statement 1: In India, natural rubber is produced in southern India only.
This statement is incorrect. While it is true that southern India is a major producer of natural rubber, it is not the only region where rubber is produced in India. Natural rubber is also produced in northeastern states like Assam, Tripura, and Meghalaya. In fact, Kerala, which is located in southern India, is the largest producer of natural rubber in the country. Therefore, statement 1 is false.
Statement 2: Among the coffee-growing states of India, the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee is in Kerala.
This statement is correct. Kerala is one of the major coffee-growing states in India, along with Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. However, Kerala has the lowest average yield per hectare of plucked coffee among these states. This is primarily due to the small landholdings of coffee plantations in Kerala, which often results in inefficient farming practices and lower productivity. Therefore, statement 2 is true.
In conclusion, among the given statements, statement 2 is correct while statement 1 is incorrect. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - 1 only.
Calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN) is a popular nitrogen fertilizer because it is- a) slow supplier of nitrogen.
- b) having more percentage of nitrogen in it.
- c) fixing the nitrogen in the soil.
- d) capable of making the soil acidic.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calcium ammonium nitrate (CAN) is a popular nitrogen fertilizer because it is
a)
slow supplier of nitrogen.
b)
having more percentage of nitrogen in it.
c)
fixing the nitrogen in the soil.
d)
capable of making the soil acidic.
|
|
Anagha Iyer answered |
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN): A Slow Supplier of Nitrogen
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) is a popular nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture. It is widely used because it acts as a slow supplier of nitrogen to the plants. Let's explore the reasons why CAN is considered a slow supplier of nitrogen.
1. Composition of CAN:
- CAN is composed of two key nutrients: calcium and ammonium nitrate.
- Calcium (Ca) is an essential macronutrient required for the growth and development of plants. It plays a vital role in cell wall structure, enzyme activation, and nutrient uptake.
- Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) is a compound that contains both ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) ions. These ions are the main sources of nitrogen for plants.
2. Slow-Release Property:
- One of the main characteristics of CAN is its slow-release property. It gradually releases nitrogen over an extended period, providing a consistent supply of nutrients to the plants.
- This slow-release property is beneficial because it prevents the plants from experiencing a sudden surge of nitrogen, which can lead to rapid growth, weak stems, and susceptibility to diseases.
- The slow-release of nitrogen from CAN ensures a steady and balanced uptake of nutrients by the plants, promoting healthier and more sustainable growth.
3. Advantages of Slow-Release Nitrogen:
- Slow-release nitrogen fertilizers, like CAN, have several advantages over fast-release fertilizers:
- Reduced nutrient losses: Slow-release nitrogen minimizes the risk of nutrient leaching and volatilization, ensuring better nutrient uptake by plants and reducing environmental pollution.
- Long-lasting effect: The slow-release of nitrogen from CAN extends its effectiveness over a longer period, reducing the frequency of fertilizer application.
- Improved plant health: The gradual supply of nitrogen supports balanced growth, stronger root development, and increased resistance to pests and diseases.
In conclusion, Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) is a popular nitrogen fertilizer because of its slow-release property. It provides a steady and balanced supply of nitrogen to the plants, promoting healthier growth and minimizing nutrient losses.
Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) is a popular nitrogen fertilizer used in agriculture. It is widely used because it acts as a slow supplier of nitrogen to the plants. Let's explore the reasons why CAN is considered a slow supplier of nitrogen.
1. Composition of CAN:
- CAN is composed of two key nutrients: calcium and ammonium nitrate.
- Calcium (Ca) is an essential macronutrient required for the growth and development of plants. It plays a vital role in cell wall structure, enzyme activation, and nutrient uptake.
- Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) is a compound that contains both ammonium (NH4+) and nitrate (NO3-) ions. These ions are the main sources of nitrogen for plants.
2. Slow-Release Property:
- One of the main characteristics of CAN is its slow-release property. It gradually releases nitrogen over an extended period, providing a consistent supply of nutrients to the plants.
- This slow-release property is beneficial because it prevents the plants from experiencing a sudden surge of nitrogen, which can lead to rapid growth, weak stems, and susceptibility to diseases.
- The slow-release of nitrogen from CAN ensures a steady and balanced uptake of nutrients by the plants, promoting healthier and more sustainable growth.
3. Advantages of Slow-Release Nitrogen:
- Slow-release nitrogen fertilizers, like CAN, have several advantages over fast-release fertilizers:
- Reduced nutrient losses: Slow-release nitrogen minimizes the risk of nutrient leaching and volatilization, ensuring better nutrient uptake by plants and reducing environmental pollution.
- Long-lasting effect: The slow-release of nitrogen from CAN extends its effectiveness over a longer period, reducing the frequency of fertilizer application.
- Improved plant health: The gradual supply of nitrogen supports balanced growth, stronger root development, and increased resistance to pests and diseases.
In conclusion, Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN) is a popular nitrogen fertilizer because of its slow-release property. It provides a steady and balanced supply of nitrogen to the plants, promoting healthier growth and minimizing nutrient losses.
What are the conditions favourable for tea cultivation?
1. Warm temperature
2. High rainfall
3. High altitude
4. Sloping land
- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1, 2 and 4
- d)All the four
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the conditions favourable for tea cultivation?
1. Warm temperature
2. High rainfall
3. High altitude
4. Sloping land
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 4
d)
All the four
|
|
Meera Kapoor answered |
India is the largest producer and exporter of tea in the world. The ideal climatic conditions for the production and growing of tea are as follows:
-
Temperature: 21°C to 29°C is ideal for the production of tea. High temperature is required in summer. The lowest temperature for the growth of tea is 16°C.
-
Rainfall: 150-250 cm of rainfall is required for tea cultivation.
-
Soil: Tea shrubs require fertile mountain soil mixed with lime and iron. The soil should be rich in humus.
-
Land: Tea cultivation needs well-drained land. Stagnation of water is not good for tea plants. Heavy rainfall but no stagnancy of water, such mountain slopes are good for tea cultivation.
Leaves of which of the following plants are not used for the rearing of silkworms?
- a)Mulberry
- b)Castor
- c)Oak
- d)Teak
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Leaves of which of the following plants are not used for the rearing of silkworms?
a)
Mulberry
b)
Castor
c)
Oak
d)
Teak
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
Castor plants are not used for rearing silkworms. Castor oil has many uses in medicine and other applications.
The agricultural production in different parts of India is very much affected by varying intensities of floods and droughts. Which one of the following measures would not be sustainable in this respect? (a) Provision for extensive irrigation facilities(b) Change in the crop calendar(c) Avoidance of flood and drought-prone areas for agriculture(d) Emphasis on the selection of crops best suited to flood and drought conditionsCorrect answer is 'c'. Can you explain this answer?
The agricultural production in different parts of India is very much affected by varying intensities of floods and droughts. Which one of the following measures would not be sustainable in this respect?
(a) Provision for extensive irrigation facilities
(b) Change in the crop calendar
(c) Avoidance of flood and drought-prone areas for agriculture
(d) Emphasis on the selection of crops best suited to flood and drought conditions
|
|
Sanjay Rana answered |
Avoidance of flood and drought-prone areas for agriculture would not be sustainable in this respect.
Which one of the following statements is not correct regarding tank irrigation in peninsular India? - a) Percolation of rainwater is less due to hard rock.
- b) Most of the rivers are seasonal and dry up in the summer season.
- c) Underground water level is higher
- d) Rainwater can be easily stored by constructing tanks.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is not correct regarding tank irrigation in peninsular India?
a)
Percolation of rainwater is less due to hard rock.
b)
Most of the rivers are seasonal and dry up in the summer season.
c)
Underground water level is higher
d)
Rainwater can be easily stored by constructing tanks.
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
The underground water level is less in the peninsular region of India and high in the North region of India.
Which among the following monoculture crops provide(s) immediate cash to the farmers?1. Tea in Assam2. Rubber in Africa3. Sugarcane in Malaysia4. Coffee in Brazil- a)Only 1
- b)2 and 3
- c)1 and 4
- d)3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following monoculture crops provide(s) immediate cash to the farmers?
1. Tea in Assam
2. Rubber in Africa
3. Sugarcane in Malaysia
4. Coffee in Brazil
a)
Only 1
b)
2 and 3
c)
1 and 4
d)
3 and 4
|
|
Eesha Bhat answered |
Tea in Assam and Coffee in Brazil are mono-culture crops provides immediate cash to the farmers.
The chief characteristics of shifting cultivation are1. High dependence on manual labour2. Low level of technology3. Utilization of poor soils through fallowing4. Use of chemical fertilizersCodes: - a) 1, 2 and 4
- b) 2, 3 and 4
- c) 1, 3 and 4
- d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The chief characteristics of shifting cultivation are
1. High dependence on manual labour
2. Low level of technology
3. Utilization of poor soils through fallowing
4. Use of chemical fertilizers
Codes:
a)
1, 2 and 4
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1, 3 and 4
d)
1, 2 and 3
|
|
Puja Roy answered |
Shifting cultivation, also known as slash-and-burn agriculture, is a traditional agricultural practice that involves clearing a plot of land, burning the vegetation, and then planting crops. After a few years of cultivation, the land is left to fallow and regenerate before being used again. The chief characteristics of shifting cultivation are:
1. High dependence on manual labour
Shifting cultivation is highly labour-intensive, as it involves clearing the land by hand and planting crops without the aid of machines. The entire process, from clearing the land to harvesting the crops, is performed manually by the farmers and their families.
2. Low level of technology
Shifting cultivation is a low-tech agricultural practice, as it does not require modern machinery or advanced farming techniques. Farmers rely on their traditional knowledge and skills to cultivate the land and produce crops.
3. Utilization of poor soils through fallowing
Shifting cultivation is often practiced on poor soils that are unsuitable for continuous cropping. By using fallow periods, farmers allow the soil to recover and regenerate, which helps to maintain soil fertility and prevent soil erosion.
4. Use of chemical fertilizers
Shifting cultivation does not involve the use of chemical fertilizers, as farmers rely on natural soil fertility and the nutrients provided by the vegetation that is burned and incorporated into the soil. However, some farmers may use small amounts of chemical fertilizers to enhance crop yields.
In conclusion, shifting cultivation is a traditional agricultural practice that is characterized by high labour intensity, low levels of technology, the utilization of poor soils through fallowing, and minimal use of chemical fertilizers. Although it has been criticized for its environmental impact, shifting cultivation remains an important source of livelihood for many rural communities in developing countries.
1. High dependence on manual labour
Shifting cultivation is highly labour-intensive, as it involves clearing the land by hand and planting crops without the aid of machines. The entire process, from clearing the land to harvesting the crops, is performed manually by the farmers and their families.
2. Low level of technology
Shifting cultivation is a low-tech agricultural practice, as it does not require modern machinery or advanced farming techniques. Farmers rely on their traditional knowledge and skills to cultivate the land and produce crops.
3. Utilization of poor soils through fallowing
Shifting cultivation is often practiced on poor soils that are unsuitable for continuous cropping. By using fallow periods, farmers allow the soil to recover and regenerate, which helps to maintain soil fertility and prevent soil erosion.
4. Use of chemical fertilizers
Shifting cultivation does not involve the use of chemical fertilizers, as farmers rely on natural soil fertility and the nutrients provided by the vegetation that is burned and incorporated into the soil. However, some farmers may use small amounts of chemical fertilizers to enhance crop yields.
In conclusion, shifting cultivation is a traditional agricultural practice that is characterized by high labour intensity, low levels of technology, the utilization of poor soils through fallowing, and minimal use of chemical fertilizers. Although it has been criticized for its environmental impact, shifting cultivation remains an important source of livelihood for many rural communities in developing countries.
What is mixed farming? - a) Growing of several crops in a planned way
- b) Growing rabi as well as Kharif crops
- c) Growing several crops and also rearing animals
- d) Growing of fruits as well as vegetables
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is mixed farming?
a)
Growing of several crops in a planned way
b)
Growing rabi as well as Kharif crops
c)
Growing several crops and also rearing animals
d)
Growing of fruits as well as vegetables
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Mixed farming is an agrarian system that mixes arable farming with the raising of livestock. When on a farm along with crop production, some other agriculture-based practice like poultry, dairy farming or beekeeping etc. is adopted then this is known as mixed farming.
Which is not a food crop from the following? - a)Rice
- b)Tea
- c)Maize
- d)Barley
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not a food crop from the following?
a)
Rice
b)
Tea
c)
Maize
d)
Barley
|
|
Aarav Saini answered |
Food Crops
Rice
Rice is a staple food crop that is widely consumed worldwide, especially in Asia. It is a primary source of carbohydrates for a large portion of the global population.
Maize
Maize, also known as corn, is another important food crop that is widely cultivated for its edible kernels. It is used in a variety of food products and animal feed.
Barley
Barley is a cereal grain that is primarily used for animal feed, malting, and in the production of certain alcoholic beverages. While barley can be consumed by humans in the form of barley flour or pearl barley, it is not as commonly consumed as rice or maize.
Tea
Tea is not a food crop in the traditional sense. It is a beverage that is made from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant. While tea is widely consumed around the world, it is not considered a staple food crop like rice, maize, or barley.
A state in India has the following characteristics:1. The northern part is arid and semiarid.2. Its central part produces cotton.3. Cultivation of cash crops is predominant over food crops.Which one of the following states has all of the above characteristics?- a) Andhra Pradesh
- b) Gujarat
- c) Karnataka
- d) Tamil Nadu
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A state in India has the following characteristics:
1. The northern part is arid and semiarid.
2. Its central part produces cotton.
3. Cultivation of cash crops is predominant over food crops.
Which one of the following states has all of the above characteristics?
a)
Andhra Pradesh
b)
Gujarat
c)
Karnataka
d)
Tamil Nadu
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
The total geographical area of Gujarat is 19,602,400 hectares, of which crops take up 10,630,700 hectares. The three main sources of growth in Gujarat’s agriculture are from cotton production, the rapid growth of high- value foods such as livestock, fruits and vegetables, and wheat.
Match the Crops with the Soil required by them and accordingly select the correct alternative: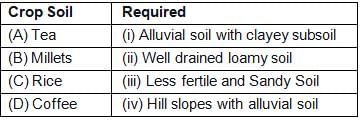
- a)A - iv, B - iii, C - i, D - ii
- b)A - ii, B - iii, C - iv, D - i
- c)A - ii, B - iv, C - i, D - iii
- d)A - iv, B - ii, C - i, D - iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the Crops with the Soil required by them and accordingly select the correct alternative:

a)
A - iv, B - iii, C - i, D - ii
b)
A - ii, B - iii, C - iv, D - i
c)
A - ii, B - iv, C - i, D - iii
d)
A - iv, B - ii, C - i, D - iii
|
|
Ravi Sharma answered |
Tea – Hill slopes with alluvial soil
Millets – Less fertile and sandy soil
Rice – Alluvial soil with clayey subsoil
Coffee – well-drained loamy soil
Which one of the following agriculture practices is eco -friendly? - a) Cultivation of high yielding varieties
- b) Growing plants in glass houses
- c) Shifting cultivation
- d) Organic farming
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following agriculture practices is eco -friendly?
a)
Cultivation of high yielding varieties
b)
Growing plants in glass houses
c)
Shifting cultivation
d)
Organic farming
|
|
Anagha Iyer answered |
Organic farming is an eco-friendly agriculture practice that promotes the sustainable use of natural resources and the preservation of the environment. It involves avoiding the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and instead focuses on using natural methods to enhance soil fertility, control pests and diseases, and promote biodiversity.
Advantages of Organic Farming:
1. Environmental Benefits: Organic farming practices prioritize the conservation and protection of soil, water, and air quality. By avoiding the use of synthetic inputs, organic farmers prevent the contamination of groundwater and reduce the release of harmful chemicals into the environment. They also promote the use of renewable resources and minimize the carbon footprint associated with agriculture.
2. Improved Soil Health: Organic farming relies on practices such as crop rotation, composting, and the use of organic manures to enhance soil fertility. These practices promote the development of a healthy soil ecosystem, with increased microbial activity, improved nutrient availability, and better water retention. Organic soils also have higher organic matter content, which helps in carbon sequestration and mitigating climate change.
3. Biodiversity Conservation: Organic farming encourages the conservation of natural habitats, which in turn supports a diverse range of plant and animal species. Organic farms often have higher levels of biodiversity, including beneficial insects, birds, and pollinators, due to the absence of chemical pesticides and the presence of diverse crop rotations and hedgerows.
4. Health Benefits: Organic farming aims to produce food that is free from synthetic chemicals, hormones, antibiotics, and GMOs. Organic produce is considered to be healthier as it has higher levels of beneficial nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It also reduces the risk of exposure to pesticide residues, which can have negative effects on human health.
5. Sustainable and Economic Viability: Organic farming promotes the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems by reducing dependence on external inputs and improving the resilience of farming communities. Organic farmers often adopt practices that enhance resource efficiency, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
In conclusion, organic farming is an eco-friendly agriculture practice that promotes environmental sustainability, soil health, biodiversity conservation, and human health. It is a holistic approach to farming that emphasizes the use of natural resources and the protection of the environment, making it the most suitable option among the given choices.
Advantages of Organic Farming:
1. Environmental Benefits: Organic farming practices prioritize the conservation and protection of soil, water, and air quality. By avoiding the use of synthetic inputs, organic farmers prevent the contamination of groundwater and reduce the release of harmful chemicals into the environment. They also promote the use of renewable resources and minimize the carbon footprint associated with agriculture.
2. Improved Soil Health: Organic farming relies on practices such as crop rotation, composting, and the use of organic manures to enhance soil fertility. These practices promote the development of a healthy soil ecosystem, with increased microbial activity, improved nutrient availability, and better water retention. Organic soils also have higher organic matter content, which helps in carbon sequestration and mitigating climate change.
3. Biodiversity Conservation: Organic farming encourages the conservation of natural habitats, which in turn supports a diverse range of plant and animal species. Organic farms often have higher levels of biodiversity, including beneficial insects, birds, and pollinators, due to the absence of chemical pesticides and the presence of diverse crop rotations and hedgerows.
4. Health Benefits: Organic farming aims to produce food that is free from synthetic chemicals, hormones, antibiotics, and GMOs. Organic produce is considered to be healthier as it has higher levels of beneficial nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It also reduces the risk of exposure to pesticide residues, which can have negative effects on human health.
5. Sustainable and Economic Viability: Organic farming promotes the long-term sustainability of agricultural systems by reducing dependence on external inputs and improving the resilience of farming communities. Organic farmers often adopt practices that enhance resource efficiency, reduce waste, and increase profitability.
In conclusion, organic farming is an eco-friendly agriculture practice that promotes environmental sustainability, soil health, biodiversity conservation, and human health. It is a holistic approach to farming that emphasizes the use of natural resources and the protection of the environment, making it the most suitable option among the given choices.
Among the following states, which one has the most suitable climatic conditions for the cultivation of a large variety of orchids with a minimum cost of production and can develop an export-oriented industry in this field?- a) Goa
- b) U.P.
- c) M.P
- d) Arunachal Pradesh
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following states, which one has the most suitable climatic conditions for the cultivation of a large variety of orchids with a minimum cost of production and can develop an export-oriented industry in this field?
a)
Goa
b)
U.P.
c)
M.P
d)
Arunachal Pradesh

|
Anshul Verma answered |
Climatic Suitability for Orchids
Arunachal Pradesh is recognized for its favorable climatic conditions that are ideal for orchid cultivation. Here’s why it stands out:
1. Diverse Climate
- Arunachal Pradesh has a varied climate ranging from subtropical in the valleys to temperate and alpine in the higher altitudes.
- This climatic diversity supports a wide range of orchid species, which thrive in different temperature and humidity levels.
2. Rich Biodiversity
- The state is part of the Eastern Himalayas, a biodiversity hotspot.
- It is home to numerous native orchid species, making it an optimal location for both cultivation and conservation.
3. Favorable Soil Conditions
- The soil in Arunachal Pradesh is generally rich in organic matter and nutrients, crucial for healthy orchid growth.
- Well-drained soils, typical in hilly terrains, help prevent root rot, enhancing production efficiency.
4. Low Production Costs
- The local climate allows for year-round cultivation, reducing the need for artificial climate control, which can be expensive.
- Availability of local resources and labor can also lower production costs significantly.
5. Export Potential
- With proper agricultural practices and quality control, the state can develop an export-oriented industry for orchids.
- The global demand for exotic orchids presents a significant opportunity for economic growth.
In summary, Arunachal Pradesh's climatic advantages, rich biodiversity, and favorable soil conditions make it the most suitable state among the options for cultivating a variety of orchids economically and sustainably.
Arunachal Pradesh is recognized for its favorable climatic conditions that are ideal for orchid cultivation. Here’s why it stands out:
1. Diverse Climate
- Arunachal Pradesh has a varied climate ranging from subtropical in the valleys to temperate and alpine in the higher altitudes.
- This climatic diversity supports a wide range of orchid species, which thrive in different temperature and humidity levels.
2. Rich Biodiversity
- The state is part of the Eastern Himalayas, a biodiversity hotspot.
- It is home to numerous native orchid species, making it an optimal location for both cultivation and conservation.
3. Favorable Soil Conditions
- The soil in Arunachal Pradesh is generally rich in organic matter and nutrients, crucial for healthy orchid growth.
- Well-drained soils, typical in hilly terrains, help prevent root rot, enhancing production efficiency.
4. Low Production Costs
- The local climate allows for year-round cultivation, reducing the need for artificial climate control, which can be expensive.
- Availability of local resources and labor can also lower production costs significantly.
5. Export Potential
- With proper agricultural practices and quality control, the state can develop an export-oriented industry for orchids.
- The global demand for exotic orchids presents a significant opportunity for economic growth.
In summary, Arunachal Pradesh's climatic advantages, rich biodiversity, and favorable soil conditions make it the most suitable state among the options for cultivating a variety of orchids economically and sustainably.
Monoculture is a distinct characteristic of - a) Commercial grain farming
- b) Shifting cultivation
- c) Subsistence farming
- d) Organic farming
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Monoculture is a distinct characteristic of
a)
Commercial grain farming
b)
Shifting cultivation
c)
Subsistence farming
d)
Organic farming
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
Monoculture is a distinct characteristic of commercial grain farming. Monoculture is the agricultural practise of producing or growing a single crop or plant species over a wide area and for a large number of consecutive years.
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns:
- a)A (i), B (ii), C (iii), D (iv)
- b)A (iii), B (iv), C (i), D (ii)
- c)A (ii), B (i), C (iv), D (iii)
- d)A (i), B (iii), C (iv), D (ii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer using the code given below the columns:

a)
A (i), B (ii), C (iii), D (iv)
b)
A (iii), B (iv), C (i), D (ii)
c)
A (ii), B (i), C (iv), D (iii)
d)
A (i), B (iii), C (iv), D (ii)
|
|
Ravi Sharma answered |
Rice is produced under 15 - 25̊ C, Tea is produced under 30 – 40 ̊ C, Cotton is produced under 25 ̊ C while coffee is produced under 20 ̊ C.
The shaded area in the map given below is the major producer of which one of the following?
- a)Wheat
- b)Groundnut
- c)Cotton
- d)Mustard
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The shaded area in the map given below is the major producer of which one of the following?

a)
Wheat
b)
Groundnut
c)
Cotton
d)
Mustard
|
|
Ananya Deshmukh answered |
The shaded area on the map is major cotton producer states in India. Cotton-producing states in India are Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, etc.
Chapter doubts & questions for Agriculture - Lucent For GK 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Agriculture - Lucent For GK in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









