All Exams >
ACT >
Biology for ACT >
All Questions
All questions of Genetics for ACT Exam
Which of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerase?
- a)Initiation
- b)Elongation
- c)Termination
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following steps in transcription is catalysed by RNA polymerase?
a)
Initiation
b)
Elongation
c)
Termination
d)
All of the above
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
RNA polymerase moves along the template strand, synthesising an mRNA molecule. In prokaryotes RNA polymerase is a holoenzyme consisting of a number of subunits, including a sigma factor (transcription factor) that recognises the promoter. In eukaryotes there are three RNA polymerases: I, II and III. The process includes a proofreading mechanism.
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16? - a)1
- b)4
- c)9
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a cross between a pure tall plant with green pod and a pure short plant with yellow pod. How many short plants are produced in F2 generation out of 16?
a)
1
b)
4
c)
9
d)
3

|
Vaibhav Kaushik answered |
Ratio is 9.3.3.1
where last 3.1 is drawf and green . drawf and yellow
4 answer
where last 3.1 is drawf and green . drawf and yellow
4 answer
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called?
- a)Lagging strand
- b)Coding strand
- c)Antisense strand
- d)Template strand
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called?
a)
Lagging strand
b)
Coding strand
c)
Antisense strand
d)
Template strand
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The strand of DNA that forms mRNA is called the template strand or the antisense strand. During transcription, the DNA molecule unwinds, and one of the strands (the template strand) is used as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule, which is called messenger RNA (mRNA). The other strand of DNA, which is not used as a template during transcription, is called the coding strand or the sense strand because it has the same sequence as the mRNA molecule (except for the presence of thymine instead of uracil).
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?- a)Mendel
- b)Morgan
- c)Watson
- d)Bateson
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Who is regarded as the father of genetics?
a)
Mendel
b)
Morgan
c)
Watson
d)
Bateson
|
|
Riyα answered |
Option {A}
Gregor Johann Mandel...
cz it's gave the idea of heredity...
XO type of sex determination is found in________.- a)Grasshopper
- b)Elephant
- c)Human beings
- d)Dog
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
XO type of sex determination is found in________.
a)
Grasshopper
b)
Elephant
c)
Human beings
d)
Dog
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
In grasshopper, sex determination is of XO type, in which the males have only one X-chromosome besides the autosomes whereas females have a pair of X-chromosomes.
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?- a)Resemblance
- b)Heredity
- c)Variation
- d)Inheritance
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called?
a)
Resemblance
b)
Heredity
c)
Variation
d)
Inheritance
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The innate tendency of offspring to resemble their parents is called heredity. The offspring resembles to parent due to same genetic combination inherited from parents.
Removal of the introns and joining of the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called- a)Capping
- b)Transformation
- c)Tailing
- d)Splicing
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Removal of the introns and joining of the exons in a defined order in a transcription unit is called
a)
Capping
b)
Transformation
c)
Tailing
d)
Splicing
|
|
Avantika Gupta answered |
Splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order in a transcription unit. This process takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and is mediated by a complex called the spliceosome.
Explanation:
• Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template. During transcription, the entire DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA, including both the introns and exons.
• Introns are non-coding sequences within a gene, while exons are the coding sequences that specify the amino acid sequence of a protein. Introns need to be removed from the RNA sequence before translation can occur.
• Splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order, resulting in a mature messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that can be translated into a protein.
• The splicing process is mediated by the spliceosome, a complex that consists of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and proteins. The snRNAs base-pair with the intron sequences, while the proteins catalyze the chemical reactions that remove the introns and join the exons.
• Splicing is essential for the proper expression of genes, as it allows for the creation of multiple protein variants from a single gene by alternative splicing. Mutations that affect splicing can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and genetic disorders.
In conclusion, splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order in a transcription unit, and it is essential for the proper expression of genes.
Explanation:
• Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template. During transcription, the entire DNA sequence is transcribed into RNA, including both the introns and exons.
• Introns are non-coding sequences within a gene, while exons are the coding sequences that specify the amino acid sequence of a protein. Introns need to be removed from the RNA sequence before translation can occur.
• Splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order, resulting in a mature messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that can be translated into a protein.
• The splicing process is mediated by the spliceosome, a complex that consists of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and proteins. The snRNAs base-pair with the intron sequences, while the proteins catalyze the chemical reactions that remove the introns and join the exons.
• Splicing is essential for the proper expression of genes, as it allows for the creation of multiple protein variants from a single gene by alternative splicing. Mutations that affect splicing can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and genetic disorders.
In conclusion, splicing is the process of removing introns and joining exons in a defined order in a transcription unit, and it is essential for the proper expression of genes.
Dihybrid cross proves the law of________.- a)Segregation
- b)Purity of gametes
- c)Law of independent assortment
- d)Dominance
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dihybrid cross proves the law of________.
a)
Segregation
b)
Purity of gametes
c)
Law of independent assortment
d)
Dominance

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Dihybrid cross proves the law of independent assortment. Mendel found that each pair of alleles segregates independently of the other pairs of alleles during gamete formation. This is known as Law of independent assortment. Dihybrid cross - cross between two parents that differ by two pairs of alleles (AABB X aabb). The formation of gametes is an application of this law.
Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?- a)Skin pigmentation in humans
- b)Sex-linkage in humans
- c)Pink flowers of Snapdragon
- d)The ABO blood groups in human
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?
a)
Skin pigmentation in humans
b)
Sex-linkage in humans
c)
Pink flowers of Snapdragon
d)
The ABO blood groups in human
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Co-dominance is the phenomenon that deviates from Mendel’s law of inheritance. Both the alleles appear in offspring instead of one as in Mendel’s experiment. ABO blood grouping in human being is example of co-dominance in which both IA and IB appear simultaneously to form AB blood type.
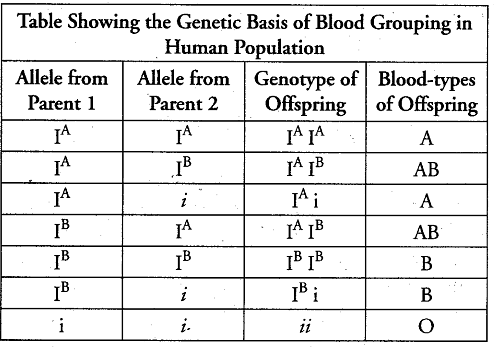
For ABO system of blood groups, allele IA produces N-acetylgalactosamine transferase enzyme which recognises H- antigen present in RBC membrane and adds N-acetylgalactosamine to sugar parts of H antigens to form A antigen.
The allele IB produces galactosyl transferase enzyme which recognized H antigen to form B antigens. Allele i does not produce any sugar or antigen.
IA and IB are completely dominant over i, in other words antigens A and B are produced. This is because of co-dominance. These antigens determine the type of blood group. Blood group A has antigens B have antigen, AB has both antigens while blood group. Blood group A have antigen A, group B have antigen B, AB has both antigens while blood group O do not carry any antigens.
Thus, six genotypes and four phenotypes are possible.
DNA contains nucleobases, sugar and phosphate. Removal of which among these from a DNA sample will not significantly affect the length of DNA?- a)Nucleobases
- b)Sugar
- c)Phosphate
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA contains nucleobases, sugar and phosphate. Removal of which among these from a DNA sample will not significantly affect the length of DNA?
a)
Nucleobases
b)
Sugar
c)
Phosphate
d)
None of the above

|
Kamlesh Bhivsane answered |
NUCLEOBASE(it is base pairing between nitrogen bases i.e A ,T,G,C) therefore it does not affect the length of DNA where as sugar phosphate bond is the back bone of DNA therefore they both affect the length of DNA
Protein synthesis occurs over- a)Cytoplasm
- b)Ribosomes
- c)Amino acids
- d)Mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Protein synthesis occurs over
a)
Cytoplasm
b)
Ribosomes
c)
Amino acids
d)
Mitochondria
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Ribosomes are site of protein synthesis and are known as protein factory
The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its- a)5′ end
- b)Anticodon site
- c)3′ end
- d)DHU loop
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The amino acid attaches to the tRNA at its
a)
5′ end
b)
Anticodon site
c)
3′ end
d)
DHU loop
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
TRNA with an attached amino acid is said to be "charged". The enzyme that attaches the amino acid to the 3'-OH is called an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (aaRS). There is a specific tRNA for each amino acid, 20 in all. Similarly, there is a specific aaRS for each tRNA.
In E. coli, the lac operon gets switched on when- a)Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
- b)RNA polymerase binds to the operator
- c)Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase
- d)Repressor binds to operator
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In E. coli, the lac operon gets switched on when
a)
Lactose is present and it binds to the repressor
b)
RNA polymerase binds to the operator
c)
Lactose is present and it binds to RNA polymerase
d)
Repressor binds to operator
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
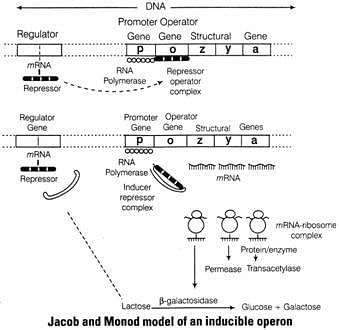
In case of lactose presence
(i) Lactose acts as an inducer which binds to the repressor and forms an inactive repressor.
(ii) The repressor fails to bind to the operator region.
(iii) The RNA polymerase binds to the operator and transcript lac mRNA.
(iv) lac mRNA is polycistronic, i.e., produces all three enzymes, β -galactosidase, permeaseand transacetylase.
(v) The lac operon is switched on.
In case of lactose absence
(i) When lactose is absent, i gene regulates and produces repressor mRNA which translate repression.
(ii) The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and as a resultprevents RNA polymerase to bind to the operon.
(iii) The operon is switched off.
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called- a)Enhancer
- b)Receptor
- c)Promoter
- d)Regulator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called
a)
Enhancer
b)
Receptor
c)
Promoter
d)
Regulator
|
|
Prashanth Chatterjee answered |
The site at which RNA polymerase binds during transcription is called the promoter. It is a specific region of DNA that is recognized by RNA polymerase, which then initiates the process of transcription. The promoter is located upstream of the transcriptional start site and contains specific DNA sequences that are recognized by RNA polymerase and other transcription factors.
The promoter plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression, as different promoters can activate or repress transcription depending on the cellular context. The strength of the promoter can also affect the rate of transcription, with stronger promoters resulting in higher levels of mRNA production.
There are different types of promoters, including constitutive promoters, which are active in all cells, and inducible promoters, which are activated in response to specific signals or conditions. The sequence and structure of the promoter can vary depending on the gene being transcribed and the organism in which it is expressed.
In summary, the promoter is a critical element in the process of transcription, serving as the site at which RNA polymerase binds and initiating the production of mRNA from DNA. It plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and can vary in strength and specificity depending on the cellular context and the gene being transcribed.
The promoter plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression, as different promoters can activate or repress transcription depending on the cellular context. The strength of the promoter can also affect the rate of transcription, with stronger promoters resulting in higher levels of mRNA production.
There are different types of promoters, including constitutive promoters, which are active in all cells, and inducible promoters, which are activated in response to specific signals or conditions. The sequence and structure of the promoter can vary depending on the gene being transcribed and the organism in which it is expressed.
In summary, the promoter is a critical element in the process of transcription, serving as the site at which RNA polymerase binds and initiating the production of mRNA from DNA. It plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and can vary in strength and specificity depending on the cellular context and the gene being transcribed.
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?- a)AABB
- b)AaBb
- c)AABb
- d)AaBB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
a)
AABB
b)
AaBb
c)
AABb
d)
AaBB
|
|
Om Desai answered |
If the genotype is AaBb the alleles that will be produced will be AB, Ab, aB, ab, since there are two diallelic characters in the genotypes the person must be heterozygous for both genes. AABB is homozygous. So, the correct answer is "AaBb".

The term ‘Genetics’ was proposed by- a)Johannsen
- b)Morgan
- c)Mendel
- d)Bateson
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The term ‘Genetics’ was proposed by
a)
Johannsen
b)
Morgan
c)
Mendel
d)
Bateson
|
|
Rahul Bansal answered |
Bateson co-discovered genetic linkage with Reginald Punnett and Edith Saunders, and he and Punnett founded the Journal of Genetics in 1910. Bateson also coined the term "epistasis" to describe the genetic interaction of two independent loci.
There is no DNA in- a)Hair root
- b)An enucleated ovum
- c)A mature spermatozoan
- d)Mature RBCs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
There is no DNA in
a)
Hair root
b)
An enucleated ovum
c)
A mature spermatozoan
d)
Mature RBCs
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In mature RBCs nucleus is absent and there is no DNA. Mature DNA do not divide to form new cells.
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into______.- a)Male
- b)Female
- c)Sterile
- d)Any of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In human beings, if ovum fertilizes with a sperm carrying X-chromosome the zygote develops into______.
a)
Male
b)
Female
c)
Sterile
d)
Any of the above

|
Smruti Sucharita answered |
In human male progeny contains XY chromosome
female progeny contains XX chromosome
female progeny contains XX chromosome
In DNA replication, the leading strand replicates in the
- a)5′ → 3′ direction discontinuously
- b)5’→ 3′ direction continuously
- c)3′ → 5′ direction discontinuously
- d)3’→ 5′ direction continuously
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In DNA replication, the leading strand replicates in the
a)
5′ → 3′ direction discontinuously
b)
5’→ 3′ direction continuously
c)
3′ → 5′ direction discontinuously
d)
3’→ 5′ direction continuously
|
|
Anjana Sharma answered |
The replication occurs in three steps in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. These are include-
• Initiation
• Elongation
• Termination
The elongation steps involve the synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
The helicase and Dna B unzips the double-stranded DNA for replication, making a forked structure. The primase then performs the task of generating short strands of RNA that bind to the single-stranded DNA to initiate DNA synthesis with the help of DNA polymerase. This enzyme can work only in the 5′5′ to 3′3′ direction, the replication of the leading strand is done continuously whereas lagging-strand replication is discontinuous, with short Okazaki fragments being formed and later linked together.
So, the leading strand is the one that replicates in the 5′→3' direction continuously.
• Initiation
• Elongation
• Termination
The elongation steps involve the synthesis of leading and lagging strands.
The helicase and Dna B unzips the double-stranded DNA for replication, making a forked structure. The primase then performs the task of generating short strands of RNA that bind to the single-stranded DNA to initiate DNA synthesis with the help of DNA polymerase. This enzyme can work only in the 5′5′ to 3′3′ direction, the replication of the leading strand is done continuously whereas lagging-strand replication is discontinuous, with short Okazaki fragments being formed and later linked together.
So, the leading strand is the one that replicates in the 5′→3' direction continuously.
Repressor proteins are coded for by ______ genes.- a)Promoter
- b)Structural
- c)Regulator
- d)Operator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Repressor proteins are coded for by ______ genes.
a)
Promoter
b)
Structural
c)
Regulator
d)
Operator
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Regulator genes codes for repressor proteins during translation of DNA into protein via mRNA.
Out of 64 codons, the number of codons with GGG is- a)4
- b)1
- c)2
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Out of 64 codons, the number of codons with GGG is
a)
4
b)
1
c)
2
d)
6
|
|
Sankar Banerjee answered |
GGG code is present only 1 tym nd the amino acid produced by GGG is glycine.
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as? - a)Phenotype
- b)Morphology
- c)Ecotype
- d)Genotype
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The physical expression or appearance of a character is called as?
a)
Phenotype
b)
Morphology
c)
Ecotype
d)
Genotype

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The physical appearance of a character is called as phenotype. The genetic make of individual is called genotype. Tallness, round, wrinkled, yellow etc. are physical appearance.
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome________.- a)Hardly any cross-overs are produced
- b)The percentage of crossing over between them is very high
- c)No crossing over can take place
- d)Only double cross-over can occur between them
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When two genes are situated very close to one another on a chromosome________.
a)
Hardly any cross-overs are produced
b)
The percentage of crossing over between them is very high
c)
No crossing over can take place
d)
Only double cross-over can occur between them
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
- When two genes are situated very close to one another on chromosome, hardly any cross-over are produced.
- Such genes are called linkage and do not separate from each other during gamete formation.
The portion of DNA which contains information for an entire polypeptide is called- a)Operon
- b)Recon
- c)Muton
- d)Cistron
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The portion of DNA which contains information for an entire polypeptide is called
a)
Operon
b)
Recon
c)
Muton
d)
Cistron
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Cistron is a nucleotide sequence responsible for the synthesis of a polypeptide sequence of a functional protein.
The word cistron is used to emphasize that genes exhibit a specific behavior in a cis-trans test, distinct positions (or loci) within a genome are cistronic.
Sex determination in human being is______.- a)XY type
- b)XX type
- c)XXY type
- d)YY type
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sex determination in human being is______.
a)
XY type
b)
XX type
c)
XXY type
d)
YY type
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
- In humans, the males are heterogametic as they have XY sex chromosomes, so they make 50% sperms with X chromosome and 50% sperms with Y chromosome. Females are homogametic. All gametes made by them have X chromosomes. So, humans show XX-XY type of sex determination.

Hence, the correct option is A.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 87 of topic “5.6 SEX DETERMINATION” of chapter 5.
NCERT Reference: Page no. 87 of topic “5.6 SEX DETERMINATION” of chapter 5.
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed to produce offspring. Offspring were self-crossed. Find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf.- a)3:1
- b)1:1
- c)2:1
- d)1:2:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed to produce offspring. Offspring were self-crossed. Find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf.
a)
3:1
b)
1:1
c)
2:1
d)
1:2:1
|
|
Rajesh Chatterjee answered |
As true tall breeding and true dwarf breeding is seen only a single time in F2 generation, and the remaining are hybtid tall...so the ratio becomes 1:2:2:1.But 1:1 is the ratio for only true tall breeding nd true dwarf breeding in F2 generation.
The coding segment of DNA isa)Mutonb)Repliconc)Intrond)CodonCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Exon: The coding sequences or expressed sequences are defined as exon. Exons are said to be those sequences that appear in mature or processed RNA.
Identify the purine base of nucleic acids in the following- a)Cytosine
- b)Thymine
- c)Uracil
- d)Adenine
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the purine base of nucleic acids in the following
a)
Cytosine
b)
Thymine
c)
Uracil
d)
Adenine

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
Purines have two rings in their structure, but pyrimidine bases have only one ring.Adenine has two rings in its structure.
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower bearing snapdragon plants results into pink coloured flower.Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results into pink coloured flower.- a)Both assertion and reason are correct
- b)Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
- c)Both assertion and reason are incorrect
- d)Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: The cross between red and white flower bearing snapdragon plants results into pink coloured flower.
Reason: Incomplete dominance of red and white flower results into pink coloured flower.
a)
Both assertion and reason are correct
b)
Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect
c)
Both assertion and reason are incorrect
d)
Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
- In Snapdragon flower, cross between true-breeding white and red coloured flower produce pink coloured flower in the F1 generation.
- This happens due to the incomplete dominance of alleles over the other.
XY chromosome that determine the sex in human beings are:
- a)Homomorphic
- b)Heterologous
- c)Both A and B
- d)Heteromorphic
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
XY chromosome that determine the sex in human beings are:
a)
Homomorphic
b)
Heterologous
c)
Both A and B
d)
Heteromorphic
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Sex chromosomes of human beings are heteromorphic as they are of different size. Y chromosome is smaller than X chromosome in size.
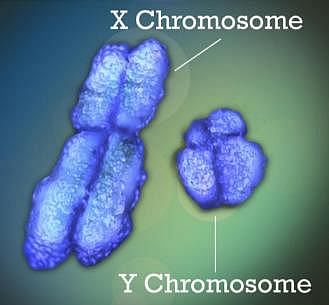
Hence, the correct option is D.
NCERT Reference: Topic- SEX DETERMINATION of chapter "Principles of Inheritance and Variation" of NCERT.
NCERT Reference: Topic- SEX DETERMINATION of chapter "Principles of Inheritance and Variation" of NCERT.
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?- a)3 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
- b)4 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
- c)3 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
- d)4 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
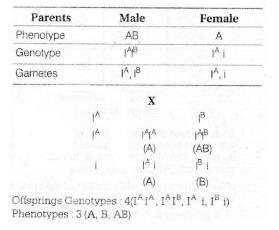
The genotypes of a husband and wife are IA IB and IAi. Among the blood types of their children how many different genotypes and phenotypes are possible?
a)
3 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
b)
4 Genotypes; 3 Phenotypes
c)
3 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes
d)
4 Genotypes; 4 Phenotypes

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
A cross between two individuals, one with AB blood group and other with A blood group will produce four genotypes and three phenotypes.

In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plants, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?- a)9:1
- b)3:1
- c)50:50
- d)1:3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green, If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with a green seeded plants, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in F1 generation?
a)
9:1
b)
3:1
c)
50:50
d)
1:3

|
Mehul Iyer answered |
If a heterozygous yellow seeded plant is crossed with green seeded plants, the ratio of yellow and green seeded plants are 50:50 or 1:1 similar to test cross.
Which of the following are not the components of RNA?- a)Thymine
- b)Adenine
- c)Guanine
- d)Cytosine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are not the components of RNA?
a)
Thymine
b)
Adenine
c)
Guanine
d)
Cytosine

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
Thymine is present in DNA but not in RNA.
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was______.- a)Lathyrusodaratus
- b)Oryza sativa
- c)Pisumsativum
- d)Mirabilis jalappa
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Material used for conducting experiments on genetic traits by Mendel was______.
a)
Lathyrusodaratus
b)
Oryza sativa
c)
Pisumsativum
d)
Mirabilis jalappa
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option c is correct.. mendel conducted experiment's on pisumsativum (garden pea)...mirabilus jalapa is also called 4'o clock plant, oryza sativa (rice)...
The gene which controls many characters is called- a)Pleiotropic gene
- b)Co-dominant gene
- c)Multiple gene
- d)Polygene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The gene which controls many characters is called
a)
Pleiotropic gene
b)
Co-dominant gene
c)
Multiple gene
d)
Polygene
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A single gene may have two or more phenotypic expressions. The multiple phenotypic effect of a single gene is called pleiotropism. Hence the gene associated with this phenomenon is called Pleiotropic gene.
Why are UGA, UAG and UAA called termination codons?- a)They terminate anticodons
- b)They are presenting at the beginning of mRNA
- c)They indicate initiation of translation
- d)They do not specify any amino acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why are UGA, UAG and UAA called termination codons?
a)
They terminate anticodons
b)
They are presenting at the beginning of mRNA
c)
They indicate initiation of translation
d)
They do not specify any amino acid
|
|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Since The stop codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA. They encode no amino acid. The ribosome pauses and falls off the mRNA.
Which particular process was used by Meselson and Stahl in order to study the semi-conservative replication of DNA?
- a)Density gradient centrifugation
- b)Chromatography
- c)Centrifugation
- d)Buoyant density centrifugation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which particular process was used by Meselson and Stahl in order to study the semi-conservative replication of DNA?
a)
Density gradient centrifugation
b)
Chromatography
c)
Centrifugation
d)
Buoyant density centrifugation
|
|
Sahil Basu answered |
Density Gradient Centrifugation
Meselson and Franklin used density gradient centrifugation to study the semi-conservative replication of DNA. This technique is based on the principle that molecules of different densities will settle at different positions in a gradient when subjected to centrifugal force.
Steps Involved in the Process
1. Growing bacteria in a medium containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen
The experiment involved growing E. coli bacteria in a medium containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15N, for many generations. This resulted in all the bacterial DNA being labeled with 15N.
2. Transferring bacteria to a medium containing a lighter isotope of nitrogen
Next, the bacteria were transferred to a medium containing a lighter isotope of nitrogen, 14N, and allowed to grow for one generation.
3. Isolation of DNA
The bacterial cells were then harvested and their DNA was extracted.
4. Density gradient centrifugation
The DNA samples were subjected to density gradient centrifugation, which involved placing the DNA in a tube containing a gradient of cesium chloride. The tube was then spun at high speeds in a centrifuge, causing the DNA molecules to migrate to the position in the gradient that corresponded to their buoyant density.
5. Observations
The resulting DNA bands were observed under ultraviolet light. If DNA replication was conservative, the DNA band would have been a single band of intermediate density, whereas if it was semi-conservative, two bands would have been observed, one of intermediate density and one of lighter density.
6. Conclusion
Meselson and Franklin observed that the DNA bands were indeed two distinct bands, one of intermediate density and one of lighter density. This provided evidence for the semi-conservative replication of DNA.
Conclusion
Density gradient centrifugation was a crucial technique used by Meselson and Franklin to study the semi-conservative replication of DNA. This technique allowed them to separate the newly synthesized DNA from the parental DNA and provided evidence for the semi-conservative mode of DNA replication.
Meselson and Franklin used density gradient centrifugation to study the semi-conservative replication of DNA. This technique is based on the principle that molecules of different densities will settle at different positions in a gradient when subjected to centrifugal force.
Steps Involved in the Process
1. Growing bacteria in a medium containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen
The experiment involved growing E. coli bacteria in a medium containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15N, for many generations. This resulted in all the bacterial DNA being labeled with 15N.
2. Transferring bacteria to a medium containing a lighter isotope of nitrogen
Next, the bacteria were transferred to a medium containing a lighter isotope of nitrogen, 14N, and allowed to grow for one generation.
3. Isolation of DNA
The bacterial cells were then harvested and their DNA was extracted.
4. Density gradient centrifugation
The DNA samples were subjected to density gradient centrifugation, which involved placing the DNA in a tube containing a gradient of cesium chloride. The tube was then spun at high speeds in a centrifuge, causing the DNA molecules to migrate to the position in the gradient that corresponded to their buoyant density.
5. Observations
The resulting DNA bands were observed under ultraviolet light. If DNA replication was conservative, the DNA band would have been a single band of intermediate density, whereas if it was semi-conservative, two bands would have been observed, one of intermediate density and one of lighter density.
6. Conclusion
Meselson and Franklin observed that the DNA bands were indeed two distinct bands, one of intermediate density and one of lighter density. This provided evidence for the semi-conservative replication of DNA.
Conclusion
Density gradient centrifugation was a crucial technique used by Meselson and Franklin to study the semi-conservative replication of DNA. This technique allowed them to separate the newly synthesized DNA from the parental DNA and provided evidence for the semi-conservative mode of DNA replication.
According to Chargaff’s rule, which one is correct?- a)[A] + [T] = [G] + [C]
- b)[A] + [C] = [G] + [T]
- c)[A] + [G] = [T] + [C]
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Chargaff’s rule, which one is correct?
a)
[A] + [T] = [G] + [C]
b)
[A] + [C] = [G] + [T]
c)
[A] + [G] = [T] + [C]
d)
All of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
According to Chargaff’s rule in all cellular DNA, regardless of the species, number of adenosine residues is equal to the number of thymidine residues which means that A = T and the number of guanosine residues is equal to the number of cytidine residues; G = C . Hence, that the sum of the purine residues equals the sum of the pyrimidine residues; i.e., A + G = T + C.
Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that a genetic code is a triplet?- a)Nirenberg and Matthaei
- b)Hershey and Chase
- c)Beadle and Tatum
- d)Morgan and Sturtevant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that a genetic code is a triplet?
a)
Nirenberg and Matthaei
b)
Hershey and Chase
c)
Beadle and Tatum
d)
Morgan and Sturtevant
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The existence of a triplet code was simply an assumption till 1961 when Nirenberg and Methaei proved its existence by experiment. They were able to synthesise artificial mRNA, which contained only one nitrogenous base, ie, uracil. This synthetic poly-U sequence was then placed in a cell-free system containing protein synthesizing enzymes (extracted from bacterium E. coil) and 20 amino acids together with necessary ATP. During the process, a small polypeptide molecule was produced, which was formed by the linking of phenylalanine. This issuggested that UUU is code for phenylalanine. Nirenberg got Nobel Prize for his contributions.
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?- a)Haemophilia
- b)Turner’s syndrome
- c)Cystic fibrosis
- d)Colour blindness
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?
a)
Haemophilia
b)
Turner’s syndrome
c)
Cystic fibrosis
d)
Colour blindness
|
|
Devanshi Mehta answered |
All humans have 46 chromosomes, which determine who and what we are genetically. Boys have an X and Y chromosome. Girls have 2 X chromosomes. Turner Syndrome is a chromosomal disorder in girls in which part or all of one of the X-chromosomes is missing.
This loss of genetic material causes 2 primary features: namely, short stature and underdeveloped ovaries causing delayed or absent puberty. It is usually diagnosed when a girl is noted to be very short and a chromosome blood test is obtained. It should also be suspected if a girl has not developed breasts by 13-14 years of age or had her menstrual period by 15-16 years of age. Effective hormonal treatment is available for both the short stature and to stimulate normal pubertal changes.
This loss of genetic material causes 2 primary features: namely, short stature and underdeveloped ovaries causing delayed or absent puberty. It is usually diagnosed when a girl is noted to be very short and a chromosome blood test is obtained. It should also be suspected if a girl has not developed breasts by 13-14 years of age or had her menstrual period by 15-16 years of age. Effective hormonal treatment is available for both the short stature and to stimulate normal pubertal changes.
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?- a)Back cross
- b)F1 cross
- c)Test cross
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called?
a)
Back cross
b)
F1 cross
c)
Test cross
d)
All of these
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
The crossing of F1 to any one of the parents is called back cross. It is used to check the purity of individual. When F1 is crossed with recessive parent, it is called test cross.
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon; hence, the code is- a)Unambiguous
- b)Universal
- c)Degenerate
- d)Initiator
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon; hence, the code is
a)
Unambiguous
b)
Universal
c)
Degenerate
d)
Initiator
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The genetic code is degenerate: Some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon, inasmuch as there are 64 possible base triplets and only 20 amino acids. In fact, 61 of the 64 possible triplets specify particular amino acids and 3 triplets (called stop codons) designate the termination of translation. Thus, for most amino acids, there is more than one code word.
F2 generation is obtained by______.- a)Crossing of F1 and F2
- b)Selfing of F1
- c)Selfing of F2
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
F2 generation is obtained by______.
a)
Crossing of F1 and F2
b)
Selfing of F1
c)
Selfing of F2
d)
None of these
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
F2 generation is obtained by selfing of F1 progeny..where F1 generation is obtained by crossing two parents..option B
DNA is made of two chains that twist about one another in the shape of a _______.- a)Broken ladder
- b)Straight ladder
- c)Straight spiral
- d)Double helix
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA is made of two chains that twist about one another in the shape of a _______.
a)
Broken ladder
b)
Straight ladder
c)
Straight spiral
d)
Double helix
|
|
Ananya Duney answered |
They are twist in a right handed double helical way therefore it's called double helix DNA which was given by Watson and crick
"hope it'll help"
"hope it'll help"
Codon is made up of- a)Single nucleotide
- b)Four nucleotides
- c)three nucleotides
- d)two nucleotides
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Codon is made up of
a)
Single nucleotide
b)
Four nucleotides
c)
three nucleotides
d)
two nucleotides
|
|
Gopikas S answered |
Codons are found in mRNA.A sequence of three nucleotides in messenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid. A codon is a sequence of three adjacent nucleotides constituting the genetic code that determines the insertion of a specific amino acid in a polypeptide chain during protein synthesis or the signal to stop protein synthesis. A codon is defined by the initial nucleotide from which translation starts.
Which of the following is true about phosphodiester linkage?- a)5’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
- b)3’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 5’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
- c)5’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 5’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
- d)3’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true about phosphodiester linkage?
a)
5’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
b)
3’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 5’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
c)
5’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 5’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide
d)
3’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
5’-phosphate group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3’-hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide.
Which chromosome of human genome contains least number of genes?- a)Chromosome 12
- b)Chromosome X
- c)Chromosome Y
- d)Chromosome 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which chromosome of human genome contains least number of genes?
a)
Chromosome 12
b)
Chromosome X
c)
Chromosome Y
d)
Chromosome 1
|
|
Muraad answered |
Chromosome 1 contains a maximum of 2968 genes and chromosome y contains the minimum 231 genes.
DNA has genetic properties was revealed for the first time by- a)Chargaff
- b)Griffith
- c)Avery
- d)Wilkins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA has genetic properties was revealed for the first time by
a)
Chargaff
b)
Griffith
c)
Avery
d)
Wilkins
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
The discovery that DNA has genetic properties was first revealed by Oswald Avery and his team of scientists in 1944. Avery was a molecular biologist who worked at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research in New York City.
Experiment
Avery and his team conducted a series of experiments to determine whether DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation of bacteria. They used two strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae, one that was virulent (able to cause disease) and one that was non-virulent. The virulent strain had a capsule made of a complex sugar that protected it from the immune system, while the non-virulent strain lacked this capsule and was easily destroyed by the immune system.
Results
Avery and his team extracted various biochemical components from the virulent strain of bacteria, including proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA. They then mixed each of these components with the non-virulent strain to see if they could induce transformation. Only the DNA extract was able to transform the non-virulent strain into a virulent one, proving that DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation.
Conclusion
Avery's discovery was groundbreaking because it showed that DNA, which was previously thought to be a simple molecule with no biological significance, was in fact the carrier of genetic information. This discovery paved the way for the development of the field of molecular biology and our current understanding of genetics.
Experiment
Avery and his team conducted a series of experiments to determine whether DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation of bacteria. They used two strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae, one that was virulent (able to cause disease) and one that was non-virulent. The virulent strain had a capsule made of a complex sugar that protected it from the immune system, while the non-virulent strain lacked this capsule and was easily destroyed by the immune system.
Results
Avery and his team extracted various biochemical components from the virulent strain of bacteria, including proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA. They then mixed each of these components with the non-virulent strain to see if they could induce transformation. Only the DNA extract was able to transform the non-virulent strain into a virulent one, proving that DNA was the genetic material responsible for the transformation.
Conclusion
Avery's discovery was groundbreaking because it showed that DNA, which was previously thought to be a simple molecule with no biological significance, was in fact the carrier of genetic information. This discovery paved the way for the development of the field of molecular biology and our current understanding of genetics.
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?- a)Insects
- b)Human beings
- c)Lizards
- d)Birds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which organism’s male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes?
a)
Insects
b)
Human beings
c)
Lizards
d)
Birds
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
In birds male contain a pair of Z chromosome as sex chromosome besides autosomes while female contain one Z and one W chromosome.
Chapter doubts & questions for Genetics - Biology for ACT 2025 is part of ACT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the ACT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for ACT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Genetics - Biology for ACT in English & Hindi are available as part of ACT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for ACT Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for ACT
208 videos|226 docs|136 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup