All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Properties of Organic Compounds for EmSAT Achieve Exam
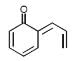
Correct IUPAC name of the following compound is :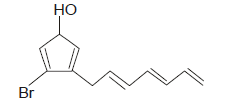
- a)3-(Hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)-4 bromo cyclopenta-2, 4, -dien-1-ol
- b)7-(2-Bromo-4-hydroxy cyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
- c)7-(5-Bromo-3-hydroxycyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
- d)3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct IUPAC name of the following compound is :
a)
3-(Hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)-4 bromo cyclopenta-2, 4, -dien-1-ol
b)
7-(2-Bromo-4-hydroxy cyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
c)
7-(5-Bromo-3-hydroxycyclopenta-1,4-dienyl)hepta-1,3,5-triene
d)
3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option D
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
according to the rule of nearly attached halogen count first.so we count the the chain where bromo is near
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
3-Bromo-4-(hepta-2,4,6-trienyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-oll
according to the rule of nearly attached halogen count first.so we count the the chain where bromo is near
The correct IUPAC name of the folllowing compound is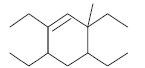
- a)5,6-Diethyl-8-methyl dec-6-ene
- b)5,7-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
- c)5,6-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
- d)2,4,5-Triethylnon-3-ene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of the folllowing compound is
a)
5,6-Diethyl-8-methyl dec-6-ene
b)
5,7-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
c)
5,6-Diethyl-3-methyl dec-4-ene
d)
2,4,5-Triethylnon-3-ene

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
The IUPAC name of the given compound is 5, 6 - diethyl -2- methyldec - 4 - ene.
The parent hydrocarbon contains 10 carbon atoms and a double bond.
It is called dec-4-ene.
One methyl group is present on second carbon atom and two ethyl groups are present on fifth and sixth carbon atoms.
The parent hydrocarbon contains 10 carbon atoms and a double bond.
It is called dec-4-ene.
One methyl group is present on second carbon atom and two ethyl groups are present on fifth and sixth carbon atoms.
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar - a)The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
- b)In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
- c)In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
- d)The most stable conformer is non-polar
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
Which is true about conformers of 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane?
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a) The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b) In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c) In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d) The most stable conformer is non-polar
a)
The most stable conformer has dihedral angle of 60° between all adjacent chlorine atoms
b)
In the least stable conformer, two Cl-atoms are eclipsing one another while other two Cl-atoms are eclipsed to hydrogen atoms
c)
In the most stable conformer, dihedral angle between hydrogen atoms is 60°
d)
The most stable conformer is non-polar
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The correct answer is option D
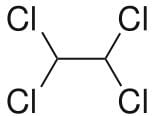
This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°

This molecule is non-polar two Cl atoms in one carbon atom cancel the polarity other two Cl atoms on the next carbon.
Also all the Cl atoms are at max distance from each other so max. Stability due to less repulsion between Cl atoms. Dihedral angle between H and Cl is 60°
Pick the odd one out:- a)Napthalene
- b)Sodium chloride
- c)Ammonium chloride
- d)Camphor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pick the odd one out:
a)
Napthalene
b)
Sodium chloride
c)
Ammonium chloride
d)
Camphor

|
Sameer Jain answered |
Explanation:
The odd one out among the given options is Sodium chloride. Here's why:
Napthalene:
- Napthalene is a white, crystalline solid that is commonly found in mothballs.
- It is composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a specific structure.
- It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like benzene and toluene.
- Napthalene is used in various applications such as in the production of dyes, plastics, and synthetic resins.
Ammonium chloride:
- Ammonium chloride is a white, crystalline salt that consists of ammonium ions (NH4+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
- It is highly soluble in water and forms an acidic solution.
- Ammonium chloride is commonly used in fertilizers, as a flux in soldering, and in the preparation of dry cells.
Camphor:
- Camphor is a white, waxy solid derived from the wood of the camphor tree.
- It has a strong, distinctive odor and sublimes at room temperature (changes directly from a solid to a gas).
- Camphor is soluble in organic solvents but only sparingly soluble in water.
- It is used in various applications such as in the production of medicines, as an insect repellent, and in religious ceremonies.
Sodium chloride:
- Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is a white, crystalline solid.
- It is composed of sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
- Sodium chloride is highly soluble in water and forms a neutral solution.
- It is widely used as a seasoning in food, in the production of chemicals, and in various industrial processes.
Conclusion:
The odd one out among the given options is Sodium chloride because it is the only compound that is primarily used as a seasoning in food and does not have the properties of a hydrocarbon or an ionic salt.
The odd one out among the given options is Sodium chloride. Here's why:
Napthalene:
- Napthalene is a white, crystalline solid that is commonly found in mothballs.
- It is composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a specific structure.
- It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like benzene and toluene.
- Napthalene is used in various applications such as in the production of dyes, plastics, and synthetic resins.
Ammonium chloride:
- Ammonium chloride is a white, crystalline salt that consists of ammonium ions (NH4+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
- It is highly soluble in water and forms an acidic solution.
- Ammonium chloride is commonly used in fertilizers, as a flux in soldering, and in the preparation of dry cells.
Camphor:
- Camphor is a white, waxy solid derived from the wood of the camphor tree.
- It has a strong, distinctive odor and sublimes at room temperature (changes directly from a solid to a gas).
- Camphor is soluble in organic solvents but only sparingly soluble in water.
- It is used in various applications such as in the production of medicines, as an insect repellent, and in religious ceremonies.
Sodium chloride:
- Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is a white, crystalline solid.
- It is composed of sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
- Sodium chloride is highly soluble in water and forms a neutral solution.
- It is widely used as a seasoning in food, in the production of chemicals, and in various industrial processes.
Conclusion:
The odd one out among the given options is Sodium chloride because it is the only compound that is primarily used as a seasoning in food and does not have the properties of a hydrocarbon or an ionic salt.
Identify the pair of enantiomers amongst the given pairs:- a)
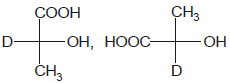
- b)
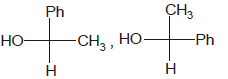
- c)
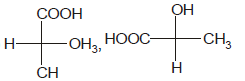
- d)
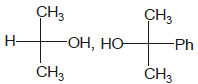
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the pair of enantiomers amongst the given pairs:
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
The 1st option has R configuration and 2nd has S configuration hence they are non super imposable mirror images of each other and are enantiomers.
The 1st option has R configuration and 2nd has S configuration hence they are non super imposable mirror images of each other and are enantiomers.
Nitration of benzene is:- a)Free radical substitution reaction
- b)Nucleophilic addition reaction
- c)Nucleophilic substitution reaction
- d)Electrophilic substitution reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Nitration of benzene is:
a)
Free radical substitution reaction
b)
Nucleophilic addition reaction
c)
Nucleophilic substitution reaction
d)
Electrophilic substitution reaction
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Nitration and sulfonation of benzene are two examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution. The nitronium ion (NO2+) and sulfur trioxide (SO3) are the electrophiles and individually react with benzene to give nitrobenzene and benzenesulfonic acid respectively.
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by:- a)Distillation
- b)Chromatography
- c)Crystallisation
- d)Sublimation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by:
a)
Distillation
b)
Chromatography
c)
Crystallisation
d)
Sublimation
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Impure sample of Naphthalene can be purified by Sublimation.
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)- a)Naphthalene
- b)Aniline
- c)Pyridine
- d)Tropolone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an aromatic compound(in specific)
a)
Naphthalene
b)
Aniline
c)
Pyridine
d)
Tropolone

|
Sai Mishra answered |
Pyridine is heterocyclic aromatic compound. Whereas naphthalene and aniline are benzenoid aromatic compounds and tropolone is a non-benzenoid aromatic compound.
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
- a)alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
- b)Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
- c)Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
- d)Open chain compounds and closed compounds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds are broadly classified as
a)
alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
b)
Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
c)
Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
d)
Open chain compounds and closed compounds

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
The correct answer is option D
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Organic compounds are broadly classified into open chain and closed chain compounds. Explanation: open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?- a)Theoretically infinite conformers exist
- b)Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
- c)Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
- d)By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true regarding conformers of ethane?
a)
Theoretically infinite conformers exist
b)
Staggered conformer has lower torsional strain than eclipsed one
c)
Increasing temperature increases the percentage of eclipsed conformer
d)
By precise experimental setup, staggered conformer can be separated out of system
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Although conformers differ in potential energy and stability, the difference is so small that it does not allow their practical separation.
Process of separation of mixtures into their components and to purify the compounds by using adsorption is known as:- a)Sublimation
- b)Differential extraction
- c)Distillation
- d)Chromatography
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Process of separation of mixtures into their components and to purify the compounds by using adsorption is known as:
a)
Sublimation
b)
Differential extraction
c)
Distillation
d)
Chromatography
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is Option D.
Chromatography is an important separation technique used to separate constituent particles of a mixture of substances, to purify the compounds and check the purity of organic compounds. In this technique on a stationary phase (solid or a liquid) a mixture of substances is applied. The mixture of gas or the pure solvent is allowed to move slowly on the stationary phase. Due to which the components of the mixture start separating from one another.
Chromatography is an important separation technique used to separate constituent particles of a mixture of substances, to purify the compounds and check the purity of organic compounds. In this technique on a stationary phase (solid or a liquid) a mixture of substances is applied. The mixture of gas or the pure solvent is allowed to move slowly on the stationary phase. Due to which the components of the mixture start separating from one another.
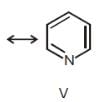
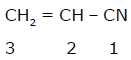 C1 - C2 bond of this molecules is formed by:
C1 - C2 bond of this molecules is formed by:- a)sp3-sp2 overlap
- b)sp2-sp3 overlap
- c)sp2-sp overlap
- d)sp2-sp2 overlap
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
C1 - C2 bond of this molecules is formed by:
a)
sp3-sp2 overlap
b)
sp2-sp3 overlap
c)
sp2-sp overlap
d)
sp2-sp2 overlap

|
Rohith.v answered |
In C1 carbon had thripal bond so it is sp hybridised in C2 carbon had one double bond so it is sp2 hybridization
Aliphatic compound is the other name for- a)Acyclic compounds
- b)Alicyclic compounds
- c)Ring compounds
- d)Closed chain compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Aliphatic compound is the other name for
a)
Acyclic compounds
b)
Alicyclic compounds
c)
Ring compounds
d)
Closed chain compounds

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Open chain compounds or acyclic compounds are otherwise called as aliphatic compounds.
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group? - a)Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
- b)Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
- c)Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
- d)Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following correctly ranks the cycloalkanes in order of increasing ring strain per methylene group?
a)
Cyclopropane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclohexane
b)
Cyclohexane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopropane
c)
Cyclohexane < Cyclobutane < Cyclopentane < Cyclopropane
d)
Cyclopropane < Cyclopentane < Cyclobutane < Cyclohexane
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
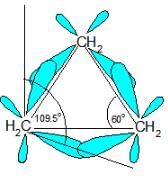
The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.

The C-C-C bond angles in cyclopropane (60o) and cyclobutane (90o) are much different than the ideal bond angle of 109.5o.This bond angle causes cyclopropane and cyclobutane to have a high ring strain. However, molecules, such as cyclohexane and cyclopentane, would have a much lower ring strain because the bond angle between the carbons is much closer to 109.5o.
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?- a)Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
- b)Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
- c)Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
- d)Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which,of the following correctly lists the conformations of cyclohexane in order of increasing potential energies?
a)
Chair < Boat < Twist boat < Half-chair
b)
Half-chair < Boat < Twist boat < Chair
c)
Chair < Twist boat < Half-chair < Boat
d)
Chair < Twist boat < Boat < Half-chair
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Correct answer is option D
Chair >Twist boat > Boat > Half-chair
above is the stability order of
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
the conformed.
Stability is inversely proportional to potential energy.
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group- a)Isocyanide
- b)Isocyano
- c)Carboxyl
- d)Carbonyl
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Organic compounds can be classified even based upon the function groups. Identify the one which is not a functional group
a)
Isocyanide
b)
Isocyano
c)
Carboxyl
d)
Carbonyl

|
Mansi Mukherjee answered |
Isocyanide is a compound and it is not a functional group.
This apparatus provides many surfaces for heat exchange between the ascending vapours and the descending condensed liquid.
- a)Round bottom flask
- b)Pipette
- c)Burette
- d)Fractionating column
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
This apparatus provides many surfaces for heat exchange between the ascending vapours and the descending condensed liquid.
a)
Round bottom flask
b)
Pipette
c)
Burette
d)
Fractionating column
|
|
Anand Kapoor answered |
**Explanation:**
The correct answer is option D, the fractionating column. Let's break down the explanation:
**1. Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus mentioned in the question is designed to facilitate heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid. Heat exchange is an essential process that occurs in various applications, such as distillation, where it helps in separating mixtures based on differences in boiling points.
**2. Surfaces for Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus should provide multiple surfaces or stages where heat exchange can occur. This means that the ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid should come into close contact with each other, allowing thermal energy transfer.
**3. Round Bottom Flask, Pipette, and Burette:**
The options A (round bottom flask), B (pipette), and C (burette) do not meet the criteria for providing multiple surfaces for heat exchange. Let's briefly explain why:
- **Round Bottom Flask (Option A):** A round bottom flask is a commonly used laboratory glassware that is primarily used for holding liquids and conducting chemical reactions. It does not provide multiple surfaces for heat exchange as required in the question.
- **Pipette (Option B):** A pipette is a laboratory tool used for accurately measuring and transferring small volumes of liquids. It is not designed for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
- **Burette (Option C):** A burette is a long, graduated glass tube with a stopcock at the bottom. It is commonly used in titrations for precise volume measurements but does not provide the required surfaces for heat exchange.
**4. Fractionating Column (Option D):**
The fractionating column is a specially designed apparatus used in distillation processes to achieve separation of liquid mixtures based on differences in boiling points. It consists of multiple stages or trays, providing numerous surfaces for heat exchange.
- **Heat Exchange in the Fractionating Column:** As the vapor rises through the fractionating column, it comes into contact with the descending condensed liquid. Heat is exchanged between the ascending vapors and the descending liquid, allowing the separation of components with different boiling points.
- **Multiple Surfaces for Heat Exchange:** The fractionating column contains several trays or stages, each acting as a surface for heat exchange. The vapors and condensed liquid interact on these trays, promoting efficient heat transfer between the two phases.
Therefore, the fractionating column is the apparatus that best fits the description provided in the question, offering multiple surfaces for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
The correct answer is option D, the fractionating column. Let's break down the explanation:
**1. Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus mentioned in the question is designed to facilitate heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid. Heat exchange is an essential process that occurs in various applications, such as distillation, where it helps in separating mixtures based on differences in boiling points.
**2. Surfaces for Heat Exchange:**
The apparatus should provide multiple surfaces or stages where heat exchange can occur. This means that the ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid should come into close contact with each other, allowing thermal energy transfer.
**3. Round Bottom Flask, Pipette, and Burette:**
The options A (round bottom flask), B (pipette), and C (burette) do not meet the criteria for providing multiple surfaces for heat exchange. Let's briefly explain why:
- **Round Bottom Flask (Option A):** A round bottom flask is a commonly used laboratory glassware that is primarily used for holding liquids and conducting chemical reactions. It does not provide multiple surfaces for heat exchange as required in the question.
- **Pipette (Option B):** A pipette is a laboratory tool used for accurately measuring and transferring small volumes of liquids. It is not designed for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
- **Burette (Option C):** A burette is a long, graduated glass tube with a stopcock at the bottom. It is commonly used in titrations for precise volume measurements but does not provide the required surfaces for heat exchange.
**4. Fractionating Column (Option D):**
The fractionating column is a specially designed apparatus used in distillation processes to achieve separation of liquid mixtures based on differences in boiling points. It consists of multiple stages or trays, providing numerous surfaces for heat exchange.
- **Heat Exchange in the Fractionating Column:** As the vapor rises through the fractionating column, it comes into contact with the descending condensed liquid. Heat is exchanged between the ascending vapors and the descending liquid, allowing the separation of components with different boiling points.
- **Multiple Surfaces for Heat Exchange:** The fractionating column contains several trays or stages, each acting as a surface for heat exchange. The vapors and condensed liquid interact on these trays, promoting efficient heat transfer between the two phases.
Therefore, the fractionating column is the apparatus that best fits the description provided in the question, offering multiple surfaces for heat exchange between ascending vapors and descending condensed liquid.
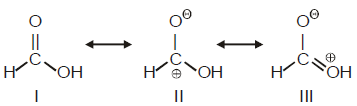 Among these canonical structures, the correct order of stability is
Among these canonical structures, the correct order of stability is- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I
- c)I > III > II
- d)II > I > III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among these canonical structures, the correct order of stability is
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I
c)
I > III > II
d)
II > I > III

|
Armaan Sharma answered |
In structure no 1 no charge is present.in third one positive charge is on "OH" which sjows negative I effect and also "O" atom is more electronegative than C so 3rd is more stable than 2
Rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is:- a)Br2> I2>F2>Cl2
- b)Cl2> Br2> I2>F2
- c)F2>Cl2> Br2> I2
- d)Cl2> Br2>F2> I2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Rate of reaction of alkanes with halogens is:
a)
Br2> I2>F2>Cl2
b)
Cl2> Br2> I2>F2
c)
F2>Cl2> Br2> I2
d)
Cl2> Br2>F2> I2
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answer is option C
The reactivity of the halogens decreases in the following order: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
fluorine is so explosively reactive it is difficult to control, and iodine is generally unreactive. Chlorination and bromination are normally exothermic.
The reactivity of the halogens decreases in the following order: F2>Cl2>Br2>I2
fluorine is so explosively reactive it is difficult to control, and iodine is generally unreactive. Chlorination and bromination are normally exothermic.
Addition of dihydrogen to propyne forms:- a)Ethanal
- b)Carbocation
- c)Propene
- d)carbanion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Addition of dihydrogen to propyne forms:
a)
Ethanal
b)
Carbocation
c)
Propene
d)
carbanion
|
|
Ashish Roy answered |
The addition of dihydrogen to propyne is a type of hydrogenation reaction, where the double bond in propyne is broken and replaced with two hydrogen atoms. This leads to the formation of a new compound, propene.
Explanation:
Propyne has the chemical formula C3H4, containing a triple bond between the second and third carbon atoms. When dihydrogen (H2) is added to propyne, it reacts with the triple bond and leads to the formation of a new compound, propene (C3H6). The reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
C3H4 + H2 → C3H6
This reaction is an example of an addition reaction, where the reactants combine to form a single product. The addition of dihydrogen to propyne breaks the triple bond between the carbon atoms and forms a single bond between them. The remaining carbon-carbon double bond in propene is more stable than the triple bond in propyne, making it a more favorable product.
Option (C) is the correct answer, as propene is the product formed when dihydrogen is added to propyne.
In summary, the addition of dihydrogen to propyne leads to the formation of propene, where the triple bond in propyne is broken and replaced with a carbon-carbon double bond.
Explanation:
Propyne has the chemical formula C3H4, containing a triple bond between the second and third carbon atoms. When dihydrogen (H2) is added to propyne, it reacts with the triple bond and leads to the formation of a new compound, propene (C3H6). The reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
C3H4 + H2 → C3H6
This reaction is an example of an addition reaction, where the reactants combine to form a single product. The addition of dihydrogen to propyne breaks the triple bond between the carbon atoms and forms a single bond between them. The remaining carbon-carbon double bond in propene is more stable than the triple bond in propyne, making it a more favorable product.
Option (C) is the correct answer, as propene is the product formed when dihydrogen is added to propyne.
In summary, the addition of dihydrogen to propyne leads to the formation of propene, where the triple bond in propyne is broken and replaced with a carbon-carbon double bond.
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?- a)Alcohols
- b)Aldehydes
- c)Alkyl halides
- d)Cyanides
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible?
a)
Alcohols
b)
Aldehydes
c)
Alkyl halides
d)
Cyanides

|
Naina Menon answered |
Alkyl halides do not show functional isomerism. Alcohols and ethers, aldehydes and ketones, cyanides and isocyanides are functional isomers.
IUPAC name of compound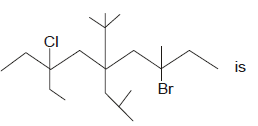
- a)3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-3-methylnonane
- b)3-Bromo7-chloro-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-7-ethyl-3methyl-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
- c)3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-3-,methyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
- d)3-Bromo-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-7-chloro-7ethyl-5--3-methylnonane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
IUPAC name of compound
a)
3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-3-methylnonane
b)
3-Bromo7-chloro-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-7-ethyl-3methyl-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
c)
3-Bromo7-chloro-7ethyl-3-,methyl-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)nonane
d)
3-Bromo-5-(1,1-dimethyethyl)-5-(2-methylpropyl)-7-chloro-7ethyl-5--3-methylnonane

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The correct answer is option B
First of all, we should number the carbon atoms from right to left for the above molecule. According to IUPAC rule, we have to name the functional groups alphabetically. Hence, bromine which is attached to 3rd carbon is named as 3-bromo, chlorine which is attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-chloro and ethyl group which is also attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-ethyl. 5-(1,1-dimethyethyl) indicates that, 2 methyl groups are attached to the 1st carbon of ethyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. 5-(2-methylpropyl) indicates that, a methyl group is attached to the 2nd carbon of propyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. Finally, since the molecule has nine atoms and it is an alkane, the word nonane is added to the IUPAC name.
First of all, we should number the carbon atoms from right to left for the above molecule. According to IUPAC rule, we have to name the functional groups alphabetically. Hence, bromine which is attached to 3rd carbon is named as 3-bromo, chlorine which is attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-chloro and ethyl group which is also attached to 7th carbon is named as 7-ethyl. 5-(1,1-dimethyethyl) indicates that, 2 methyl groups are attached to the 1st carbon of ethyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. 5-(2-methylpropyl) indicates that, a methyl group is attached to the 2nd carbon of propyl group which is attached to the 5th carbon of the given molecule. Finally, since the molecule has nine atoms and it is an alkane, the word nonane is added to the IUPAC name.
Identify the odd one among the following- a)Indene
- b)Anthracene
- c)o,m,p-xylene
- d)Azulene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the odd one among the following
a)
Indene
b)
Anthracene
c)
o,m,p-xylene
d)
Azulene

|
Saumya Ahuja answered |
Azulene is a non- benzenoid compound. Whereas, Indene, anthracene, and o,m,p-Xylene are examples of benzenoid aromatic compounds.
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ?- a)Cl3CCOOH
- b)ClCH2 COOH
- c)Cl2CH COOH
- d)CH3 COOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is the strongest acid ?
a)
Cl3CCOOH
b)
ClCH2 COOH
c)
Cl2CH COOH
d)
CH3 COOH

|
Subhashini Nimashakavi answered |
Because cl3c reacts string than all
Which of the following statements is not correct?- a)A compound whose molecule has D configuration will always be dextrorotatory
- b)A compound whose molecule has D configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory
- c)A compound whose molecule has R configuration may be dexrotatory or levorotatory
- d)A compound whose molecule has L configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct?
a)
A compound whose molecule has D configuration will always be dextrorotatory
b)
A compound whose molecule has D configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory
c)
A compound whose molecule has R configuration may be dexrotatory or levorotatory
d)
A compound whose molecule has L configuration may be dextrorotatory or levorotatory

|
Avantika Saha answered |
The configuration in a compound is independent of its physical properties (optical activity)
How manyh assymmetric carbon atoms are present in
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene- a)2,1,1
- b)1,1,1
- c)2,0.2
- d)2,0,1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How manyh assymmetric carbon atoms are present in
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene
a)
2,1,1
b)
1,1,1
c)
2,0.2
d)
2,0,1
|
|
Aarya Khanna answered |
Asymmetric carbon atoms are those carbon atoms which are attached to four different groups or atoms. These carbon atoms are also known as chiral centers.
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane:
- Cyclohexane has no asymmetric carbon atoms.
- When two methyl groups are attached to cyclohexane, it becomes 2,3-dimethyl cyclohexane.
- The carbon at position 2 is attached to two methyl groups and two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, it is not an asymmetric carbon atom.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one methyl group, and one cyclohexane ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane.
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene:
- Cyclopentene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclopentene at position 3, it becomes 3-methyl cyclopentene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclopentene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methyl cyclopentene.
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene:
- Cyclohexene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclohexene at position 3, it becomes 3-methylcyclohexene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclohexene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methylcyclohexene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (2,1,1) as there are 2 asymmetric carbon atoms in total, with 1 in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane, 1 in 3-methyl cyclopentene, and 1 in 3-methylcyclohexene.
(i) 2-Dimethyl cyclohexane:
- Cyclohexane has no asymmetric carbon atoms.
- When two methyl groups are attached to cyclohexane, it becomes 2,3-dimethyl cyclohexane.
- The carbon at position 2 is attached to two methyl groups and two hydrogen atoms. Therefore, it is not an asymmetric carbon atom.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one methyl group, and one cyclohexane ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane.
(ii) 3-Methyl cyclopentene:
- Cyclopentene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclopentene at position 3, it becomes 3-methyl cyclopentene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclopentene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methyl cyclopentene.
(iii) 3-Methylcyclohexene:
- Cyclohexene has one asymmetric carbon atom.
- When a methyl group is attached to cyclohexene at position 3, it becomes 3-methylcyclohexene.
- The carbon at position 3 is attached to one methyl group, one hydrogen atom, one double bond with carbon, and one cyclohexene ring. Therefore, it is an asymmetric carbon atom.
- Hence, there is one asymmetric carbon atom in 3-methylcyclohexene.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (2,1,1) as there are 2 asymmetric carbon atoms in total, with 1 in 2-dimethyl cyclohexane, 1 in 3-methyl cyclopentene, and 1 in 3-methylcyclohexene.
 Among these compounds, the correct order of resonance energy is
Among these compounds, the correct order of resonance energy is- a)I > II > III
- b)III > II > I
- c)II > III > I
- d)II > I > III
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among these compounds, the correct order of resonance energy is
a)
I > II > III
b)
III > II > I
c)
II > III > I
d)
II > I > III
|
|
Shiva Reddy answered |
Resonance energy is directly proportional to stability
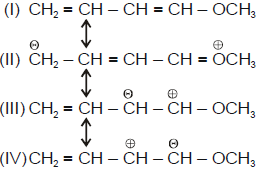 Amongt these canonical structures which one is least stable ?
Amongt these canonical structures which one is least stable ?- a)I
- b)II
- c)III
- d)IV
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Amongt these canonical structures which one is least stable ?
a)
I
b)
II
c)
III
d)
IV
|
|
Jyoti Aiims Aspirant answered |
Rules of checking out canonical stability1 neutral structure will be more stable2 resonating structure having all atom complete octet3 more the number of covalent bond more will be the stability 4 less formal charge more stable5 more electronegative atom have negTive charge and more electropositive atom positive charge6 if identical charge are in adjacent atom leasts stableACC TO QUESTION1 --- is neutrali2---- have complete octet of all atom3---- backbonding in positive charge via lone pair of och3which stabilize positive charge4---- repulsion between negative charge and lone pair least stableTHESE RULES MUST BE FOLLOW IN THE SEQUENCE AS THEY ARE WRITTEN
For phenol which ofthe following resonating structure is the most stable ?- a)
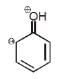
- b)
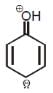
- c)
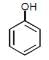
- d)All have equal stability
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For phenol which ofthe following resonating structure is the most stable ?
a)

b)

c)

d)
All have equal stability

|
Naina Menon answered |
The phenol molecule is highly acidic because it has a partial positive charge on the oxygen atom due to resonance, and the anion that is formed by loss of a hydrogen ion is also resonance stabilized.
SO OPTION C IS CORRECT.
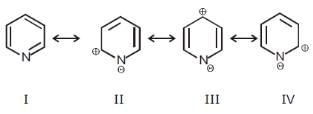
 Among these canonical structures of pyridiine, the correct order of stability is
Among these canonical structures of pyridiine, the correct order of stability is- a)(I = V) > (II = IV) > III
- b)(II = IV) > (I = V) > III
- c)(I = V) > III > (II = IV)
- d)III > (II = IV) > (I = V)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?


Among these canonical structures of pyridiine, the correct order of stability is
a)
(I = V) > (II = IV) > III
b)
(II = IV) > (I = V) > III
c)
(I = V) > III > (II = IV)
d)
III > (II = IV) > (I = V)

|
Parteek Pandit answered |
Correction option is A
because neutral species are more stable than polarised species
and when opposite charges are separated by less distance then the structure is more stable than that of the molecule in which opposite charges are separated by more distance
because neutral species are more stable than polarised species
and when opposite charges are separated by less distance then the structure is more stable than that of the molecule in which opposite charges are separated by more distance
The correct statement regarding cyclopropane is/are- a)It has the highest angle strain among cycloalkanes
- b)It has smaller heat of hydrogenation per mole of —CH2— than cyclohexane
- c)It has large torsional strain due to all eclipsed C—H bonds on adjacent carbons
- d)Conformations in cyclopropane is due to flipping of bonds
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement regarding cyclopropane is/are
a)
It has the highest angle strain among cycloalkanes
b)
It has smaller heat of hydrogenation per mole of —CH2— than cyclohexane
c)
It has large torsional strain due to all eclipsed C—H bonds on adjacent carbons
d)
Conformations in cyclopropane is due to flipping of bonds
|
|
Puja Pillai answered |
The correct answers are Options A and C.
In cyclopropane the angle strain is maximum. Hence, it is a highly strained molecule and consequently most unstable.In cyclopropane, the adjacent CH2 groups are also eclipsed. Unlike in ethane, this strain cannot be relieved through rotation (the ring is too rigid). In other words, the CH2 groups are locked in the eclipsed conformation, which results in torsional strain – much like a propeller that has been wound up but held in position.
In cyclopropane the angle strain is maximum. Hence, it is a highly strained molecule and consequently most unstable.In cyclopropane, the adjacent CH2 groups are also eclipsed. Unlike in ethane, this strain cannot be relieved through rotation (the ring is too rigid). In other words, the CH2 groups are locked in the eclipsed conformation, which results in torsional strain – much like a propeller that has been wound up but held in position.
Find the odd one among the following:- a)Alicyclic compounds
- b)Heterogeneous compounds
- c)Branched chain compounds
- d)Aromatic compounds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the odd one among the following:
a)
Alicyclic compounds
b)
Heterogeneous compounds
c)
Branched chain compounds
d)
Aromatic compounds

|
Shruti Ahuja answered |
Branched chain compound is a classification of open-chain compounds. Whereas, alicyclic, aromatic and heterogeneous compounds are sub-classifications of cyclic compounds.
The correct statement concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol is/are- a)Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer
- b)There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer
- c)The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer
- d) Dissolving, in water lower the percentage of most stable conformer
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol is/are
a)
Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer
b)
There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer
c)
The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer
d)
Dissolving, in water lower the percentage of most stable conformer
|
|
Naveen Chavan answered |
Conformers of 2-Fluoroethanol:
Conformers are different arrangements of atoms that can be achieved by rotating around single bonds. For 2-fluoroethanol, there are three different conformers possible:
1) Anti-conformer
2) Gauche-conformer
3) Syn-conformer
Statement Analysis:
a) Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable conformer of 2-fluoroethanol is the gauche-conformer.
b) There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer - This statement is correct. In the most stable gauche-conformer, there is intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl (-OH) group and the fluorine atom.
c) The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable gauche-conformer has the least steric strain among all three conformers.
d) Dissolving in water lowers the percentage of the most stable conformer - This statement is correct. Dissolving in water disrupts the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the most stable gauche-conformer, leading to a decrease in its percentage.
Therefore, the correct statements concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol are B, C, and D.
Conformers are different arrangements of atoms that can be achieved by rotating around single bonds. For 2-fluoroethanol, there are three different conformers possible:
1) Anti-conformer
2) Gauche-conformer
3) Syn-conformer
Statement Analysis:
a) Anti-conformer is the most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable conformer of 2-fluoroethanol is the gauche-conformer.
b) There is intramolecular H-bonding in its most stable conformer - This statement is correct. In the most stable gauche-conformer, there is intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the hydroxyl (-OH) group and the fluorine atom.
c) The most stable conformer has greater steric strain than 2nd most stable conformer - This statement is incorrect. The most stable gauche-conformer has the least steric strain among all three conformers.
d) Dissolving in water lowers the percentage of the most stable conformer - This statement is correct. Dissolving in water disrupts the intramolecular hydrogen bonding in the most stable gauche-conformer, leading to a decrease in its percentage.
Therefore, the correct statements concerning various conformers of 2-fluoroethanol are B, C, and D.
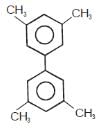
In which of the following molecels both phenyl rings are not coplanar ?- a)
- b)
- c)
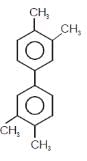
- d)
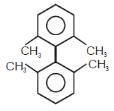
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following molecels both phenyl rings are not coplanar ?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Mahanda answered |
Option D is non planar due to steric hindrance at the ortho position.All the other three are co planar.
In which of the following pairs, first species is more stable than second ?- a)
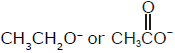
- b)
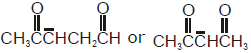
- c)
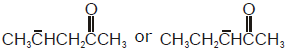
- d)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following pairs, first species is more stable than second ?
a)
b)
c)
d)


|
Sakshi Jain answered |
Due to delocalisation of charge at 3 consecutive places and hence more no.of resonating structures.So 'd' is correct option.
A hydrocarbon (R) has six membered ring in which there is no unsaturation. Two alkyl groups are atttached to the ring adjacent to each other. One group has 3 carbon atoms with branching at 1st carbon atom of chain and another has 4 carbon atoms. The larger alkyl group has main chain of three carbon atoms of which second carbon is substituted. Correct IUPAC name of compound (R) is- a)1-(1-Methylethyl)-2-(1-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
- b)1-(2-Methylethyl)-2-(1-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
- c)1-(1-Methylethyl)-2-(2-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
- d)1-(1-Methylethyl)-2-butylcyclohexane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrocarbon (R) has six membered ring in which there is no unsaturation. Two alkyl groups are atttached to the ring adjacent to each other. One group has 3 carbon atoms with branching at 1st carbon atom of chain and another has 4 carbon atoms. The larger alkyl group has main chain of three carbon atoms of which second carbon is substituted. Correct IUPAC name of compound (R) is
a)
1-(1-Methylethyl)-2-(1-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
b)
1-(2-Methylethyl)-2-(1-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
c)
1-(1-Methylethyl)-2-(2-methylpropyl)cyclohexane
d)
1-(1-Methylethyl)-2-butylcyclohexane

|
Nabanita Basu answered |
 In this molecules, π-electron-density is more on
In this molecules, π-electron-density is more on- a)C1 and C3
- b)C2 and C4
- c)C2 and C3
- d)C1 and C4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In this molecules, π-electron-density is more on
a)
C1 and C3
b)
C2 and C4
c)
C2 and C3
d)
C1 and C4

|
Sarthak Rajendra Bande answered |
In its resonating structures, C2 and C4 always show π-electron density
Which among these is not associated with aliphatic compounds- a)They contain (4n+2)pi electrons
- b)Contain straight chain compounds
- c)Contain branched chain compounds
- d)Has appropriate number of H-atoms and functional groups
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among these is not associated with aliphatic compounds
a)
They contain (4n+2)pi electrons
b)
Contain straight chain compounds
c)
Contain branched chain compounds
d)
Has appropriate number of H-atoms and functional groups

|
Ruchi Basak answered |
The aromatic compounds (4n+2)pi electrons, which comes under the classification of cyclic compounds and hence they are not associated with aliphatic compounds.
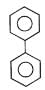
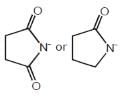
In which of the following molecules, all atoms are not coplanar ?- a)
- b)
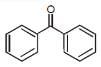
- c)
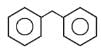
- d)
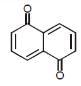
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following molecules, all atoms are not coplanar ?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Naina Menon answered |
Out of all of the molecules mentioned above, the molecule given in option (3) i.e. Biphenyl contains all the atoms which are coplanar. This is because, all the Carbon atoms present in Biphenyl are sp2 hybridised and their geometry is Trigonal planar.
Therefore, option (3) is correct.
Bond formation is:- a)always exothermic
- b)always endothermic
- c)neither exothermic nor endothermic
- d)sometimes exothermic and sometimes endothermic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond formation is:
a)
always exothermic
b)
always endothermic
c)
neither exothermic nor endothermic
d)
sometimes exothermic and sometimes endothermic

|
Ankit Mode answered |
Bond is formed if atoms are getting more stable after bond formation and being stable means less energy state so they release energy while bond formation so it is exothermic process
CH2 = CH – CH = CH – CH3 is more stable than CH3 – CH = C = CH – CH3 because- a)there is resonance in I but not in II
- b)there is tautomerism in I but not in II
- c)there is hyperconjugation in I but not in II
- d)II has more cononical structures than I.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
CH2 = CH – CH = CH – CH3 is more stable than CH3 – CH = C = CH – CH3 because
a)
there is resonance in I but not in II
b)
there is tautomerism in I but not in II
c)
there is hyperconjugation in I but not in II
d)
II has more cononical structures than I.

|
Nikitha Novalene Paul answered |
Whenever alternate double bonds are present that means the molecule is in Resonance! Resonance gives stability to a molecule
How are essential oils purified?- a)By steam distillation
- b)By condensation
- c)By chromatography
- d)By evaporation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How are essential oils purified?
a)
By steam distillation
b)
By condensation
c)
By chromatography
d)
By evaporation

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
Separation by distillation at the normal (1 atmosphere) boiling points is not an option, so water or steam is introduced into the distillation apparatus. The water vapor carries small amounts of the vaporized compounds to the condensation flask, where the condensed liquid phase separates, allowing easy collection.
In Friedel crafts alkylation and acylation the attacking reagent is an:- a)Electrophile
- b)Nucleophile
- c)Radical
- d)Ionic species
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Friedel crafts alkylation and acylation the attacking reagent is an:
a)
Electrophile
b)
Nucleophile
c)
Radical
d)
Ionic species

|
Aaditya Ghoshal answered |
A Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction in which a carbocation attacks an aromatic ring with the net result that one of the aromatic protons is replaced by an alkyl group. vinyl and aryl halides cannot be used to form carbocations.
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Ethane
- c)Cyclopropane
- d)Isobutane
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Ethane
c)
Cyclopropane
d)
Isobutane

|
Rithika Mukherjee answered |
Cyclopropane is a ring (cyclic) compound and hence it does not come with the examples of open chain compounds.
Separation of mixture into a column of adsorbent is known as:- a)Column Chromatography
- b)Adsorption chromatography
- c)Partition chromatography
- d)Thin layer chromaography
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Separation of mixture into a column of adsorbent is known as:
a)
Column Chromatography
b)
Adsorption chromatography
c)
Partition chromatography
d)
Thin layer chromaography

|
Aravind Kapoor answered |
Chromatography has been developed into a new method of separation of mixture of substances mainly when they are available in small amounts. This method is very useful when the components of a mixture have almost the same physical and chemical properties and hence can’t be separated by other usual methods of separations. The term chromatography means writing in colour (in Greek: Khromatos-colour, and graphos- written). It was discovered by Mikhail Tswett in 1906.
The process of separation of solid organic compounds is known as:- a)Differential extraction
- b)Sublimation
- c)Crystallisation
- d)Distillation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The process of separation of solid organic compounds is known as:
a)
Differential extraction
b)
Sublimation
c)
Crystallisation
d)
Distillation

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
The process by which an impure compound is converted into its crystals is known as crystallisation. It is based on the difference in the solubilities of the compound and the impurities in a suitable solvent.
Chapter doubts & questions for Properties of Organic Compounds - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Properties of Organic Compounds - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily