All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Biology for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Biotechnology: Principle & Processes for EmSAT Achieve Exam
A bioreactor is:- a)Culture for synthesis of new chemicals
- b)Hybridoma
- c)Culture containing radioactive isotopes
- d)Fermentation tank
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A bioreactor is:
a)
Culture for synthesis of new chemicals
b)
Hybridoma
c)
Culture containing radioactive isotopes
d)
Fermentation tank
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Fermentation is defined more from the point of view of engineers. They see fermentation as the cultivation of high amount of microorganisms and biotransformation being carried out in special vessels called fermenter or bioreactors.
Two microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are- a)Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
- b)Vibrio cholerae and a tailed bacteriophage
- c)Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
- d)Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabditis elegans
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering are
a)
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens
b)
Vibrio cholerae and a tailed bacteriophage
c)
Diplococcus sp. and Pseudomonas sp.
d)
Crown gall bacterium and Caenorhabditis elegans
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens are the microbes found to be very useful in genetic engineering.
E. coli is a motile, gram negative, rod shaped bacterium which is a normal inhabitant of human colon. It is most extensively used in bacterial genetics and molecular biology.
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil bacterium. It has Ti plasmid (Tumour inducing plasmid) and it can be used for the transfer of a desired gene in dicot plants.
For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of :- a)Silver or Platinum
- b)Gold or Tungsten
- c)Silicon or Platinum
- d)Platinum or Zinc
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For transformation, micro-particles coated with DNA to be bombarded with gene gun are made up of :
a)
Silver or Platinum
b)
Gold or Tungsten
c)
Silicon or Platinum
d)
Platinum or Zinc
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
For gene transfer into the host cell without using vector microparticles made of tungsten and gold coated with foregin DNA are bombarded into target cells at a very high velocity. This method is called biolistics or gene gun which is suitable for plants.So the correct option is 'gold or tungsten'.
DNA fingerprinting can resolve:- a)Identification of a person
- b)Paternity dispute
- c)Maternity dispute
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA fingerprinting can resolve:
a)
Identification of a person
b)
Paternity dispute
c)
Maternity dispute
d)
All of above
|
|
Athul Chakraborty answered |
DNA fingerprinting can resolve:
Identification of a person:
- DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles.
- Every person's DNA is unique, except for identical twins, making DNA fingerprinting a highly accurate method for identification.
- By comparing DNA samples from a crime scene, for example, with the DNA profiles of suspects, forensic scientists can determine the identity of the perpetrator.
Paternity dispute:
- DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve paternity disputes.
- By analyzing the DNA profiles of a child and potential fathers, it is possible to determine the biological father.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential fathers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential father that are not present in the other potential fathers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological father.
Maternity dispute:
- Similarly, DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve maternity disputes.
- By analyzing DNA profiles of a child and potential mothers, it is possible to determine the biological mother.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential mothers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential mother that are not present in the other potential mothers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological mother.
All of the above:
- DNA fingerprinting can resolve all the mentioned scenarios: identification of a person, paternity disputes, and maternity disputes.
- This technique has revolutionized forensic science, allowing accurate identification of individuals involved in criminal activities.
- It has also played a crucial role in resolving legal disputes regarding parentage, ensuring the correct determination of biological relationships.
In conclusion, DNA fingerprinting is a powerful tool that can be used to resolve various scenarios, including the identification of individuals, determination of paternity, and resolution of maternity disputes. Its accuracy and reliability make it an indispensable technique in forensic science and legal proceedings.
Identification of a person:
- DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA profiles.
- Every person's DNA is unique, except for identical twins, making DNA fingerprinting a highly accurate method for identification.
- By comparing DNA samples from a crime scene, for example, with the DNA profiles of suspects, forensic scientists can determine the identity of the perpetrator.
Paternity dispute:
- DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve paternity disputes.
- By analyzing the DNA profiles of a child and potential fathers, it is possible to determine the biological father.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential fathers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential father that are not present in the other potential fathers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological father.
Maternity dispute:
- Similarly, DNA fingerprinting can also be used to resolve maternity disputes.
- By analyzing DNA profiles of a child and potential mothers, it is possible to determine the biological mother.
- This is done by comparing specific DNA markers between the child and the potential mothers.
- If the child shares common DNA markers with a potential mother that are not present in the other potential mothers, it indicates that the tested individual is the biological mother.
All of the above:
- DNA fingerprinting can resolve all the mentioned scenarios: identification of a person, paternity disputes, and maternity disputes.
- This technique has revolutionized forensic science, allowing accurate identification of individuals involved in criminal activities.
- It has also played a crucial role in resolving legal disputes regarding parentage, ensuring the correct determination of biological relationships.
In conclusion, DNA fingerprinting is a powerful tool that can be used to resolve various scenarios, including the identification of individuals, determination of paternity, and resolution of maternity disputes. Its accuracy and reliability make it an indispensable technique in forensic science and legal proceedings.
Restriction endonuclease- a)Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
- b)Synthesizes DNA
- c)Restricts the synthesis of DNA inside the nucleus
- d)Cuts the DNA molecule randomly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Restriction endonuclease
a)
Cuts the DNA molecule at specific sites
b)
Synthesizes DNA
c)
Restricts the synthesis of DNA inside the nucleus
d)
Cuts the DNA molecule randomly
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
Restriction endonuclease is a type of enzyme that can cleave molecules of DNA at a particular site called restriction site having polindromic sequence. These enzymes are produced by many bacteria and protect the cell by cleaving and destroying the DNA of invading viruses. Now a days, restriction enzymes are widely used in the techniques of genetic engineering.Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A'.
Selectable markers are the genes which code for resistance to _______- a)disease
- b)phages
- c)antibiotics
- d)foreign entity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Selectable markers are the genes which code for resistance to _______
a)
disease
b)
phages
c)
antibiotics
d)
foreign entity
|
|
Partho Roy answered |
Selectable markers are the genes that provide resistance to specific substances, allowing scientists to easily identify cells that have taken up foreign DNA. In this case, the correct answer is option 'C', antibiotics.
Explanation:
- Selectable markers are used in genetic engineering to identify cells that have successfully taken up foreign DNA. These markers can be genes that provide resistance to specific substances, such as antibiotics.
- The purpose of using selectable markers is to distinguish between cells that have incorporated the desired DNA and those that have not. By including a selectable marker in the DNA being introduced into cells, scientists can selectively grow only those cells that have successfully taken up the foreign DNA.
- Antibiotic resistance genes are commonly used as selectable markers because they provide a clear and easy way to identify cells that have incorporated the desired DNA.
- In the presence of the antibiotic, only the cells that have acquired the antibiotic resistance gene will survive and grow. This allows scientists to easily select and isolate the transformed cells for further study or manipulation.
- For example, if a plasmid containing a desired gene of interest and an antibiotic resistance gene is introduced into bacterial cells, only the cells that have successfully taken up the plasmid will be able to grow in the presence of the antibiotic. This allows scientists to selectively isolate the transformed cells and study the function of the introduced gene.
- It is important to note that selectable markers can also be genes that provide resistance to other substances, such as phages (viruses that infect bacteria) or other toxic compounds. However, in this specific question, the correct answer is antibiotics.
Explanation:
- Selectable markers are used in genetic engineering to identify cells that have successfully taken up foreign DNA. These markers can be genes that provide resistance to specific substances, such as antibiotics.
- The purpose of using selectable markers is to distinguish between cells that have incorporated the desired DNA and those that have not. By including a selectable marker in the DNA being introduced into cells, scientists can selectively grow only those cells that have successfully taken up the foreign DNA.
- Antibiotic resistance genes are commonly used as selectable markers because they provide a clear and easy way to identify cells that have incorporated the desired DNA.
- In the presence of the antibiotic, only the cells that have acquired the antibiotic resistance gene will survive and grow. This allows scientists to easily select and isolate the transformed cells for further study or manipulation.
- For example, if a plasmid containing a desired gene of interest and an antibiotic resistance gene is introduced into bacterial cells, only the cells that have successfully taken up the plasmid will be able to grow in the presence of the antibiotic. This allows scientists to selectively isolate the transformed cells and study the function of the introduced gene.
- It is important to note that selectable markers can also be genes that provide resistance to other substances, such as phages (viruses that infect bacteria) or other toxic compounds. However, in this specific question, the correct answer is antibiotics.
Which metal microparticles are used in gene gun?- a)Aurum
- b)Nitrogen
- c)Magnesium
- d)Cuprum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which metal microparticles are used in gene gun?
a)
Aurum
b)
Nitrogen
c)
Magnesium
d)
Cuprum
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The microparticles of gold-coated with DNA are used in gene gun technique. Aurum is a Latin word for gold. Other metal used for this technique is tungsten.
Biolistics is also known as ______- a)micro-injection
- b)micro-pipetting
- c)insertional inactivation
- d)gene gun
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Biolistics is also known as ______
a)
micro-injection
b)
micro-pipetting
c)
insertional inactivation
d)
gene gun
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Biolistics is also known as a gene gun. It is a method in which cells are bombarded with high-velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA. It is mostly used for plant cells.
What temperature is suitable for heat-shock treatment?- a)100°C
- b)0°C
- c)42°C
- d)95°C
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What temperature is suitable for heat-shock treatment?
a)
100°C
b)
0°C
c)
42°C
d)
95°C
|
|
Partho Roy answered |
The suitable temperature for heat-shock treatment can vary depending on the specific experiment or protocol being used. However, a common temperature range for heat-shock treatment is typically between 37°C (98.6°F) and 42°C (107.6°F).
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct regarding restriction endonucleases?i. Hind II was the first restriction endonuclease discovered and cuts DNA at a specific sequence of six base pairs.ii. The convention for naming these enzymes is the first 2 letters of the name comes from the genus and the second one letter come from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated.iii. Exonucleases and endonucleases are both types of restriction enzymes that function by cutting DNA at specific sites.iv. Each restriction endonuclease can only recognize and cut palindromic sequences in the DNA.- a)i and ii
- b)ii and iii
- c)i and iv
- d)i, iii, and iv
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements given above is/are correct regarding restriction endonucleases?
i. Hind II was the first restriction endonuclease discovered and cuts DNA at a specific sequence of six base pairs.
ii. The convention for naming these enzymes is the first 2 letters of the name comes from the genus and the second one letter come from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated.
iii. Exonucleases and endonucleases are both types of restriction enzymes that function by cutting DNA at specific sites.
iv. Each restriction endonuclease can only recognize and cut palindromic sequences in the DNA.
a)
i and ii
b)
ii and iii
c)
i and iv
d)
i, iii, and iv
|
|
Raghavendra Roy answered |
Overview of Restriction Endonucleases
Restriction endonucleases, also known as restriction enzymes, are crucial in molecular biology for manipulating DNA. Let's evaluate the statements provided regarding these enzymes.
Statement Analysis
- i. Hind II was the first restriction endonuclease discovered and cuts DNA at a specific sequence of six base pairs.
- This statement is incorrect. Hind II was not the first restriction enzyme discovered; that title goes to Hind II's predecessor, Hind I. Additionally, while Hind II does cut DNA at a specific site, it does not necessarily cut at a sequence of six base pairs.
- ii. The convention for naming these enzymes is the first 2 letters of the name comes from the genus and the second one letter comes from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated.
- This statement is correct. For example, EcoRI is derived from Escherichia coli (genus: Eco, species: R).
- iii. Exonucleases and endonucleases are both types of restriction enzymes that function by cutting DNA at specific sites.
- This statement is incorrect. Exonucleases remove nucleotides from the ends of DNA, while endonucleases cut within the DNA strand. Only endonucleases are classified as restriction enzymes.
- iv. Each restriction endonuclease can only recognize and cut palindromic sequences in the DNA.
- This statement is correct. Most restriction enzymes recognize specific palindromic sequences in the DNA, which are sequences that read the same forwards and backwards.
Correct Statements
Based on the analysis, the correct statements are ii and iv. Thus, the correct answer is option 'c' (i and iv).
Restriction endonucleases, also known as restriction enzymes, are crucial in molecular biology for manipulating DNA. Let's evaluate the statements provided regarding these enzymes.
Statement Analysis
- i. Hind II was the first restriction endonuclease discovered and cuts DNA at a specific sequence of six base pairs.
- This statement is incorrect. Hind II was not the first restriction enzyme discovered; that title goes to Hind II's predecessor, Hind I. Additionally, while Hind II does cut DNA at a specific site, it does not necessarily cut at a sequence of six base pairs.
- ii. The convention for naming these enzymes is the first 2 letters of the name comes from the genus and the second one letter comes from the species of the prokaryotic cell from which they were isolated.
- This statement is correct. For example, EcoRI is derived from Escherichia coli (genus: Eco, species: R).
- iii. Exonucleases and endonucleases are both types of restriction enzymes that function by cutting DNA at specific sites.
- This statement is incorrect. Exonucleases remove nucleotides from the ends of DNA, while endonucleases cut within the DNA strand. Only endonucleases are classified as restriction enzymes.
- iv. Each restriction endonuclease can only recognize and cut palindromic sequences in the DNA.
- This statement is correct. Most restriction enzymes recognize specific palindromic sequences in the DNA, which are sequences that read the same forwards and backwards.
Correct Statements
Based on the analysis, the correct statements are ii and iv. Thus, the correct answer is option 'c' (i and iv).
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is _______- a)ligase
- b)lipase
- c)DNase
- d)RNase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is _______
a)
ligase
b)
lipase
c)
DNase
d)
RNase
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The enzyme which cleaves DNA is DNase. It catalyzes the breakdown of phosphodiester linkages of DNA. It is a type of endonuclease. Ligases are the enzymes used in the joining of two strands.
What is the purpose of treating bacterial cells or plant/animal tissue with enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, or chitinase in the process of recombinant DNA technology?- a)To release DNA from cells
- b)To remove proteins
- c)To isolate RNA
- d)To precipitate DNA with ethanol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the purpose of treating bacterial cells or plant/animal tissue with enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, or chitinase in the process of recombinant DNA technology?
a)
To release DNA from cells
b)
To remove proteins
c)
To isolate RNA
d)
To precipitate DNA with ethanol

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Enzymes like lysozyme, cellulase, and chitinase are used to break down cell walls and release DNA from cells.
Which plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens leads to tumor formation in dicots?- a)F plasmid
- b)Ti
- c)pUC
- d)pBR
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plasmid of Agrobacterium tumifaciens leads to tumor formation in dicots?
a)
F plasmid
b)
Ti
c)
pUC
d)
pBR
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumifaciens leads to tumor formation in dicots. ‘Ti’ stands for tumor-inducing. It may contain more than one T-DNA region. This plasmid is modified and used as a cloning vector.
The sequence of DNA from where replication starts is called _______- a)selectable marker
- b)origin of replication
- c)ter sequence
- d)genetic sequence
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The sequence of DNA from where replication starts is called _______
a)
selectable marker
b)
origin of replication
c)
ter sequence
d)
genetic sequence
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The sequence of DNA from where the replication starts is called the origin of replication. It is also written as ‘ori’. It is also responsible for controlling the copy number of target DNA. Bacteria usually have only one origin of replication.
What helps in identifying the successful transformants?- a)Ori
- b)Viruses
- c)Selectable markers
- d)Enzymes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What helps in identifying the successful transformants?
a)
Ori
b)
Viruses
c)
Selectable markers
d)
Enzymes
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
A selectable marker is a gene that helps in identifying successful transformants. They eliminate the growth of non-transformants and favor the growth of the desired organism. It is one of the features which facilitate cloning in a vector.
What may complicate the process of gene cloning within the cell?- a)One recognition site
- b)Foreign DNA
- c)More than one recognition site
- d)Antibody
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What may complicate the process of gene cloning within the cell?
a)
One recognition site
b)
Foreign DNA
c)
More than one recognition site
d)
Antibody
|
|
Partho Roy answered |
Cloning a gene involves the process of isolating a specific DNA fragment and replicating it in large quantities within a host cell. This process can be complicated by various factors, including the presence of multiple recognition sites.
Multiple Recognition Sites:
- Recognition sites are specific DNA sequences where restriction enzymes can bind and cut the DNA. These enzymes are essential for gene cloning as they allow the isolation of the gene of interest from the rest of the DNA.
- However, if there are multiple recognition sites within the DNA, it can lead to multiple fragments being produced upon digestion with the restriction enzyme. This can make it difficult to isolate the desired gene fragment and clone it effectively.
- For example, if there are two recognition sites for the same restriction enzyme within the gene of interest, it can result in three fragments: the desired gene fragment and two additional fragments.
- The presence of multiple fragments can complicate the cloning process as it becomes challenging to separate and purify the desired gene fragment from the others. It can also reduce the efficiency of the cloning process and result in lower yields of the desired gene.
Impact on Cloning Efficiency:
- Multiple recognition sites can also affect the efficiency of the cloning process. The presence of additional fragments increases the chances of unwanted recombination events during the cloning process.
- Recombination can occur between the multiple fragments, resulting in the loss or rearrangement of the desired gene fragment. This can lead to the failure of the cloning process or the production of incorrect gene copies.
- Furthermore, the presence of multiple recognition sites can also increase the likelihood of self-ligation, where the DNA fragments rejoin without the desired gene fragment. This can further reduce the efficiency of cloning.
To overcome the complications associated with multiple recognition sites, various strategies can be employed. These include using different restriction enzymes that recognize unique sites within the DNA, modifying the DNA sequence to eliminate or reduce the number of recognition sites, or using specialized cloning techniques such as site-directed mutagenesis.
In conclusion, the presence of multiple recognition sites within the DNA can complicate the gene cloning process by producing multiple fragments and reducing cloning efficiency. Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Multiple Recognition Sites:
- Recognition sites are specific DNA sequences where restriction enzymes can bind and cut the DNA. These enzymes are essential for gene cloning as they allow the isolation of the gene of interest from the rest of the DNA.
- However, if there are multiple recognition sites within the DNA, it can lead to multiple fragments being produced upon digestion with the restriction enzyme. This can make it difficult to isolate the desired gene fragment and clone it effectively.
- For example, if there are two recognition sites for the same restriction enzyme within the gene of interest, it can result in three fragments: the desired gene fragment and two additional fragments.
- The presence of multiple fragments can complicate the cloning process as it becomes challenging to separate and purify the desired gene fragment from the others. It can also reduce the efficiency of the cloning process and result in lower yields of the desired gene.
Impact on Cloning Efficiency:
- Multiple recognition sites can also affect the efficiency of the cloning process. The presence of additional fragments increases the chances of unwanted recombination events during the cloning process.
- Recombination can occur between the multiple fragments, resulting in the loss or rearrangement of the desired gene fragment. This can lead to the failure of the cloning process or the production of incorrect gene copies.
- Furthermore, the presence of multiple recognition sites can also increase the likelihood of self-ligation, where the DNA fragments rejoin without the desired gene fragment. This can further reduce the efficiency of cloning.
To overcome the complications associated with multiple recognition sites, various strategies can be employed. These include using different restriction enzymes that recognize unique sites within the DNA, modifying the DNA sequence to eliminate or reduce the number of recognition sites, or using specialized cloning techniques such as site-directed mutagenesis.
In conclusion, the presence of multiple recognition sites within the DNA can complicate the gene cloning process by producing multiple fragments and reducing cloning efficiency. Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Which technique is employed to check the progression of a restriction enzyme digestion in recombinant DNA technology?- a)PCR
- b)DNA ligation
- c)Agarose gel electrophoresis
- d)Reverse transcription
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which technique is employed to check the progression of a restriction enzyme digestion in recombinant DNA technology?
a)
PCR
b)
DNA ligation
c)
Agarose gel electrophoresis
d)
Reverse transcription

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Agarose gel electrophoresis is used to check the progress of a restriction enzyme digestion by separating DNA fragments based on size.
The plant cells can be lysed by using ______ enzyme.- a)lipase
- b)chitinase
- c)ligase
- d)cellulase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant cells can be lysed by using ______ enzyme.
a)
lipase
b)
chitinase
c)
ligase
d)
cellulase
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Cellulase is the enzyme used for the lysis of plant cells. It catalyzes cellulolysis, which is the breakdown of cellulose. Cellulase acts on the glycosidic linkages of cellulose. Cellulose is mostly found in plant cell walls along with other components.
Plasmids and ________ have the ability to replicate within bacterial cells independent of the control of chromosomal DNA.- a)bacteriophages
- b)fragments
- c)bacteria
- d)clones
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmids and ________ have the ability to replicate within bacterial cells independent of the control of chromosomal DNA.
a)
bacteriophages
b)
fragments
c)
bacteria
d)
clones
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Plasmids and bacteriophages can replicate within bacterial cells without the help of chromosomal DNA. Thus they are self-replicating and autonomous in nature. They have their own replication machinery.
Assertion (A): The use of alternative selectable markers in recombinant DNA technology simplifies the identification of recombinant colonies.Reason (R): These markers allow for the differentiation of recombinants from non-recombinants based solely on color change in the presence of a chromogenic substrate.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): The use of alternative selectable markers in recombinant DNA technology simplifies the identification of recombinant colonies.
Reason (R): These markers allow for the differentiation of recombinants from non-recombinants based solely on color change in the presence of a chromogenic substrate.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Bs Academy answered |
- Assertion (A) Analysis: The assertion is true because alternative selectable markers indeed facilitate a more efficient identification process for recombinant colonies, reducing the complexity associated with traditional antibiotic selection methods.
- Reason (R) Analysis: The reason is also true, as it accurately describes how these markers function by enabling visual differentiation through color change.
- Explanation: The reason directly explains the assertion, as the simplification of the identification process is a direct result of the color change method provided by alternative selectable markers.
- Ncert line: Selection of recombinants due to inactivation of antibiotics is a cumbersome procedure because it requires simultaneous plating on two plates having different antibiotics. Therefore, alternative selectable markers have been developed which differentiate recombinants from non-recombinants on the basis of their ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate.
The enzyme which cleaves RNA is _______- a)DNase
- b)ribonuclease
- c)ligase
- d)protease
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which cleaves RNA is _______
a)
DNase
b)
ribonuclease
c)
ligase
d)
protease
|
|
Shilpa Iyer answered |
Introduction:
RNA cleavage is a crucial process in various cellular activities such as gene expression, RNA degradation, and RNA processing. The enzyme responsible for cleaving RNA is called ribonuclease (RNase).
Explanation:
Ribonuclease (RNase):
- Ribonuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of RNA molecules.
- It plays a vital role in various biological processes, including RNA degradation and turnover, RNA processing, and regulation of gene expression.
- There are different types of ribonucleases that have evolved to perform specific functions in different cellular contexts.
DNase:
- DNase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA molecules, not RNA.
- It is responsible for degrading DNA and plays a role in DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and other DNA-related processes.
Ligase:
- Ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules by forming a covalent bond between them.
- It is involved in DNA repair, DNA replication, and other processes that require the joining of DNA or RNA fragments.
Protease:
- Protease is an enzyme that cleaves peptide bonds in proteins, not RNA.
- It is responsible for protein degradation, protein processing, and regulation of protein function.
Conclusion:
The enzyme that cleaves RNA is ribonuclease (RNase). It is specifically designed to recognize and cleave RNA molecules, playing essential roles in RNA degradation, processing, and gene expression regulation. DNase cleaves DNA, ligase joins molecules, and protease cleaves peptide bonds in proteins.
RNA cleavage is a crucial process in various cellular activities such as gene expression, RNA degradation, and RNA processing. The enzyme responsible for cleaving RNA is called ribonuclease (RNase).
Explanation:
Ribonuclease (RNase):
- Ribonuclease is an enzyme that catalyzes the cleavage of RNA molecules.
- It plays a vital role in various biological processes, including RNA degradation and turnover, RNA processing, and regulation of gene expression.
- There are different types of ribonucleases that have evolved to perform specific functions in different cellular contexts.
DNase:
- DNase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA molecules, not RNA.
- It is responsible for degrading DNA and plays a role in DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and other DNA-related processes.
Ligase:
- Ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the joining of two molecules by forming a covalent bond between them.
- It is involved in DNA repair, DNA replication, and other processes that require the joining of DNA or RNA fragments.
Protease:
- Protease is an enzyme that cleaves peptide bonds in proteins, not RNA.
- It is responsible for protein degradation, protein processing, and regulation of protein function.
Conclusion:
The enzyme that cleaves RNA is ribonuclease (RNase). It is specifically designed to recognize and cleave RNA molecules, playing essential roles in RNA degradation, processing, and gene expression regulation. DNase cleaves DNA, ligase joins molecules, and protease cleaves peptide bonds in proteins.
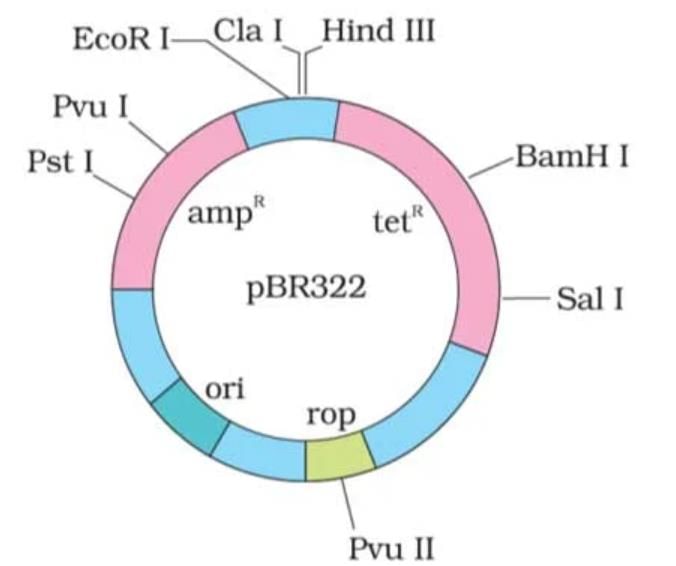
A cloning vector has two antibiotic resistance genes- for tetracycline and ampicillin. A foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline gene. Non-recombinants would survive on the medium containing :- a)ampicillin but not tetracycline
- b)tetracycline but not ampicillin
- c)both tetracycline and ampicillin
- d)neither tetracycline nor ampicillin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A cloning vector has two antibiotic resistance genes- for tetracycline and ampicillin. A foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline gene. Non-recombinants would survive on the medium containing :
a)
ampicillin but not tetracycline
b)
tetracycline but not ampicillin
c)
both tetracycline and ampicillin
d)
neither tetracycline nor ampicillin
|
|
Aditya Yadav answered |
Explanation:
Cloning Vector with Antibiotic Resistance Genes:
- The cloning vector contains two antibiotic resistance genes - one for tetracycline and one for ampicillin.
- These genes allow for the selection of bacteria that have taken up the cloning vector during the cloning process.
Insertion of Foreign DNA:
- In this case, a foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline resistance gene of the cloning vector.
- This insertion disrupts the functionality of the tetracycline resistance gene.
Survival on Selective Medium:
- Non-recombinants are bacteria that have not taken up the foreign DNA and still have functional tetracycline resistance.
- These non-recombinant bacteria will survive on the medium containing both tetracycline and ampicillin.
- The presence of ampicillin resistance gene allows these non-recombinants to survive on the medium.
Correct Answer:
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - non-recombinants would survive on the medium containing both tetracycline and ampicillin.
Cloning Vector with Antibiotic Resistance Genes:
- The cloning vector contains two antibiotic resistance genes - one for tetracycline and one for ampicillin.
- These genes allow for the selection of bacteria that have taken up the cloning vector during the cloning process.
Insertion of Foreign DNA:
- In this case, a foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline resistance gene of the cloning vector.
- This insertion disrupts the functionality of the tetracycline resistance gene.
Survival on Selective Medium:
- Non-recombinants are bacteria that have not taken up the foreign DNA and still have functional tetracycline resistance.
- These non-recombinant bacteria will survive on the medium containing both tetracycline and ampicillin.
- The presence of ampicillin resistance gene allows these non-recombinants to survive on the medium.
Correct Answer:
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - non-recombinants would survive on the medium containing both tetracycline and ampicillin.
Elution is:- a)Separating the restricted DNA fragments on agarose gel.
- b)Staining the separate DNA fragments with ethidium bromide
- c)cutting out of the separated band of DNA from the agarose gel and extracting them from the gel piece.
- d)constructing rDNA by joining the purified DNA fragments to the cloning vector.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Elution is:
a)
Separating the restricted DNA fragments on agarose gel.
b)
Staining the separate DNA fragments with ethidium bromide
c)
cutting out of the separated band of DNA from the agarose gel and extracting them from the gel piece.
d)
constructing rDNA by joining the purified DNA fragments to the cloning vector.

|
Infinity Academy answered |
- The separated bands of DNA are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece.
- This step is known as elution.
Line in NCERT: "The separated bands of DNA are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece. This step is known as elution."
Gel electrophoresis is used for- a)Construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
- b)Isolation of DNA molecules
- c)Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
- d)Cutting of DNA into fragments
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gel electrophoresis is used for
a)
Construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
b)
Isolation of DNA molecules
c)
Separation of DNA fragments according to their size
d)
Cutting of DNA into fragments
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Gel electrophoresis is used to separate macromolecules like DNA, RNA and proteins. DNA fragments are separated according to their size. Proteins can be separated according to their size and their charge (different proteins have different charges).
What is the primary function of the origin of replication (ori) in a DNA vector?- a)To provide a selectable marker.
- b)To initiate DNA replication.
- c)To enhance the stability of the DN
- d)To facilitate transformation into host cells.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of the origin of replication (ori) in a DNA vector?
a)
To provide a selectable marker.
b)
To initiate DNA replication.
c)
To enhance the stability of the DN
d)
To facilitate transformation into host cells.

|
Top Rankers answered |
The origin of replication (ori) is crucial for initiating the replication of the DNA within the host cells, ensuring that the DNA is copied during cell division.
Ncert Topic: Cloning Vectors
Ncert line: Origin of replication (ori) : This is a sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells. This sequence is also responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA
Which of the following is NOT considered a useful selectable marker for E. coli?- a)Ampicillin resistance gene
- b)Chloramphenicol resistance gene
- c)Tetracycline resistance gene
- d)Drug resistance E.coli gene against penicillin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT considered a useful selectable marker for E. coli?
a)
Ampicillin resistance gene
b)
Chloramphenicol resistance gene
c)
Tetracycline resistance gene
d)
Drug resistance E.coli gene against penicillin
|
|
Mohit Choudhury answered |
Understanding Selectable Markers in E. coli
Selectable markers are essential tools in molecular biology, particularly for the transformation and selection of genetically modified organisms. In the case of E. coli, certain markers are commonly used, while others may not be effective.
Common Selectable Markers
- Ampicillin Resistance Gene: This gene allows E. coli to survive in the presence of ampicillin, making it a widely used selectable marker for plasmids.
- Chloramphenicol Resistance Gene: Similar to the ampicillin resistance gene, this marker enables E. coli to grow in the presence of chloramphenicol, facilitating the selection of transformed cells.
- Tetracycline Resistance Gene: This gene provides E. coli with resistance to tetracycline, allowing for the selection of successfully transformed bacteria.
Why Penicillin Resistance is NOT a Useful Marker
- Drug Resistance E.coli Gene Against Penicillin: While penicillin resistance may seem like a viable option, it is not considered a useful selectable marker in E. coli for several reasons:
- Ineffectiveness in E. coli: E. coli is inherently resistant to penicillin due to its cell wall structure. Therefore, using a penicillin resistance gene does not provide a selection advantage, as E. coli can grow in penicillin-containing media without any genetic modification.
- Lack of Selection Pressure: Since E. coli can already survive in penicillin, it fails to distinguish transformed from non-transformed cells, rendering it ineffective as a selectable marker.
In conclusion, when selecting markers for E. coli, it is crucial to choose those that provide a clear selection advantage, such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, or tetracycline resistance genes, while avoiding options like penicillin resistance that do not serve this purpose.
Selectable markers are essential tools in molecular biology, particularly for the transformation and selection of genetically modified organisms. In the case of E. coli, certain markers are commonly used, while others may not be effective.
Common Selectable Markers
- Ampicillin Resistance Gene: This gene allows E. coli to survive in the presence of ampicillin, making it a widely used selectable marker for plasmids.
- Chloramphenicol Resistance Gene: Similar to the ampicillin resistance gene, this marker enables E. coli to grow in the presence of chloramphenicol, facilitating the selection of transformed cells.
- Tetracycline Resistance Gene: This gene provides E. coli with resistance to tetracycline, allowing for the selection of successfully transformed bacteria.
Why Penicillin Resistance is NOT a Useful Marker
- Drug Resistance E.coli Gene Against Penicillin: While penicillin resistance may seem like a viable option, it is not considered a useful selectable marker in E. coli for several reasons:
- Ineffectiveness in E. coli: E. coli is inherently resistant to penicillin due to its cell wall structure. Therefore, using a penicillin resistance gene does not provide a selection advantage, as E. coli can grow in penicillin-containing media without any genetic modification.
- Lack of Selection Pressure: Since E. coli can already survive in penicillin, it fails to distinguish transformed from non-transformed cells, rendering it ineffective as a selectable marker.
In conclusion, when selecting markers for E. coli, it is crucial to choose those that provide a clear selection advantage, such as ampicillin, chloramphenicol, or tetracycline resistance genes, while avoiding options like penicillin resistance that do not serve this purpose.
What is the purpose of using a selectable marker gene like ampicillin resistance in recombinant DNA technology?- a)To enhance DNA ligation
- b)To amplify the gene of interest
- c)To select transformed cells
- d)To extract the desired product
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the purpose of using a selectable marker gene like ampicillin resistance in recombinant DNA technology?
a)
To enhance DNA ligation
b)
To amplify the gene of interest
c)
To select transformed cells
d)
To extract the desired product

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Selectable marker genes like ampicillin resistance help in identifying and selecting cells that have taken up the recombinant DNA.
In recombinant DNA technology, what is the purpose of a bioreactor in the large-scale production of desired proteins?- a)To amplify genes of interest
- b)To isolate recombinant DNA
- c)To maintain cells in the log/exponential phase
- d)To perform agarose gel electrophoresis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In recombinant DNA technology, what is the purpose of a bioreactor in the large-scale production of desired proteins?
a)
To amplify genes of interest
b)
To isolate recombinant DNA
c)
To maintain cells in the log/exponential phase
d)
To perform agarose gel electrophoresis

|
Top Rankers answered |
A bioreactor is used to provide optimal conditions for cell growth, ensuring cells are in their physiologically most active phase.
What term is used to collectively refer to the separation and purification processes of a product in recombinant DNA technology?- a)Upstream processing
- b)Downstream processing
- c)Gene amplification
- d)PCR
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What term is used to collectively refer to the separation and purification processes of a product in recombinant DNA technology?
a)
Upstream processing
b)
Downstream processing
c)
Gene amplification
d)
PCR
|
|
Mahi Mehta answered |
Overview of Downstream Processing
Downstream processing is a crucial part of recombinant DNA technology, focusing on the recovery and purification of the desired product after it has been produced.
Key Aspects of Downstream Processing:
- Definition: Downstream processing refers to the series of steps involved in the extraction, purification, and formulation of biological products, such as proteins, enzymes, or nucleic acids, after they have been synthesized through upstream processing.
- Importance: It is essential for ensuring that the final product is pure, active, and suitable for use in research, therapeutic applications, or industrial purposes.
- Steps Involved:
- Separation: This initial step involves separating the product from the cellular components and culture medium. Techniques like centrifugation, filtration, and precipitation are commonly used.
- Purification: Once separated, the product undergoes purification processes, including chromatography (such as affinity or ion exchange chromatography), to achieve the desired level of purity.
- Concentration: Concentration techniques may be employed to reduce the volume and increase the concentration of the product, making it more suitable for storage or use.
- Formulation: Finally, the purified product is formulated for stability and efficacy, which may include the addition of stabilizers or excipients.
Conclusion
In summary, downstream processing is vital in recombinant DNA technology as it ensures that the produced biomolecules are effectively separated and purified, making them ready for application in various fields. Understanding this process is crucial for professionals working in biotechnology and related areas.
Downstream processing is a crucial part of recombinant DNA technology, focusing on the recovery and purification of the desired product after it has been produced.
Key Aspects of Downstream Processing:
- Definition: Downstream processing refers to the series of steps involved in the extraction, purification, and formulation of biological products, such as proteins, enzymes, or nucleic acids, after they have been synthesized through upstream processing.
- Importance: It is essential for ensuring that the final product is pure, active, and suitable for use in research, therapeutic applications, or industrial purposes.
- Steps Involved:
- Separation: This initial step involves separating the product from the cellular components and culture medium. Techniques like centrifugation, filtration, and precipitation are commonly used.
- Purification: Once separated, the product undergoes purification processes, including chromatography (such as affinity or ion exchange chromatography), to achieve the desired level of purity.
- Concentration: Concentration techniques may be employed to reduce the volume and increase the concentration of the product, making it more suitable for storage or use.
- Formulation: Finally, the purified product is formulated for stability and efficacy, which may include the addition of stabilizers or excipients.
Conclusion
In summary, downstream processing is vital in recombinant DNA technology as it ensures that the produced biomolecules are effectively separated and purified, making them ready for application in various fields. Understanding this process is crucial for professionals working in biotechnology and related areas.
The restriction enzyme needs to be in _____ form to cut the DNA.- a)impure
- b)pure
- c)mixed
- d)hybrid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The restriction enzyme needs to be in _____ form to cut the DNA.
a)
impure
b)
pure
c)
mixed
d)
hybrid
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The restriction enzyme needs to be in pure form to cut the DNA. The restriction enzymes are molecular scissors that cleave the DNA at specific recognition sites. Restriction enzymes are also known as restriction endonucleases or restrictase.
______ is a hydrophilic molecule.- a)Lipid
- b)DNA
- c)Palmitic acid
- d)Lipohilic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
______ is a hydrophilic molecule.
a)
Lipid
b)
DNA
c)
Palmitic acid
d)
Lipohilic
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
DNA is an example of a hydrophilic molecule. Hydrophilic molecules are water-loving and tend to dissolve in water easily. They carry a positive or negative charge.
Which divalent cations are usually used to make competent cells?- a)Carbon
- b)Nitrogen
- c)Copper
- d)Calcium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which divalent cations are usually used to make competent cells?
a)
Carbon
b)
Nitrogen
c)
Copper
d)
Calcium
|
|
Partho Roy answered |
Divalent cations, such as calcium (Ca2+), are commonly used in the preparation of competent cells. Competent cells are cells that have been treated to make them capable of taking up foreign DNA molecules, such as plasmids, through a process called transformation. This is an essential technique in molecular biology and genetic engineering.
Calcium ions play a crucial role in the preparation of competent cells due to their ability to neutralize the negative charges on the cell surface. This neutralization allows for the efficient binding of negatively charged DNA molecules to the cell membrane.
Here is a detailed explanation of why calcium is the most commonly used divalent cation for making competent cells:
1. Calcium-mediated transformation:
- Calcium ions facilitate the binding of DNA to the cell surface during transformation.
- The presence of calcium ions increases the efficiency of DNA uptake by the cells.
2. Membrane permeabilization:
- Calcium ions help to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, allowing DNA molecules to enter the cells more easily.
- This increased permeability is crucial for the successful uptake of DNA during transformation.
3. DNA binding:
- Calcium ions neutralize the negative charges on the cell surface and DNA molecules.
- This neutralization allows for the electrostatic interaction between DNA and the cell membrane, leading to the binding of DNA to the cell surface.
4. Enhanced DNA stability:
- Calcium ions also help to stabilize the DNA molecules, preventing their degradation by nucleases present in the cell.
- This stabilization is essential for the successful uptake and maintenance of foreign DNA within the transformed cells.
5. Compatibility with cells:
- Calcium ions are generally well-tolerated by cells and do not have toxic effects at the concentrations used for making competent cells.
- This makes calcium a suitable choice for cell transformation experiments.
In conclusion, calcium ions are commonly used as divalent cations to make competent cells due to their ability to facilitate DNA binding, increase membrane permeability, enhance DNA stability, and compatibility with cells. These properties make calcium an ideal choice for efficient and successful transformation experiments in molecular biology and genetic engineering.
Calcium ions play a crucial role in the preparation of competent cells due to their ability to neutralize the negative charges on the cell surface. This neutralization allows for the efficient binding of negatively charged DNA molecules to the cell membrane.
Here is a detailed explanation of why calcium is the most commonly used divalent cation for making competent cells:
1. Calcium-mediated transformation:
- Calcium ions facilitate the binding of DNA to the cell surface during transformation.
- The presence of calcium ions increases the efficiency of DNA uptake by the cells.
2. Membrane permeabilization:
- Calcium ions help to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, allowing DNA molecules to enter the cells more easily.
- This increased permeability is crucial for the successful uptake of DNA during transformation.
3. DNA binding:
- Calcium ions neutralize the negative charges on the cell surface and DNA molecules.
- This neutralization allows for the electrostatic interaction between DNA and the cell membrane, leading to the binding of DNA to the cell surface.
4. Enhanced DNA stability:
- Calcium ions also help to stabilize the DNA molecules, preventing their degradation by nucleases present in the cell.
- This stabilization is essential for the successful uptake and maintenance of foreign DNA within the transformed cells.
5. Compatibility with cells:
- Calcium ions are generally well-tolerated by cells and do not have toxic effects at the concentrations used for making competent cells.
- This makes calcium a suitable choice for cell transformation experiments.
In conclusion, calcium ions are commonly used as divalent cations to make competent cells due to their ability to facilitate DNA binding, increase membrane permeability, enhance DNA stability, and compatibility with cells. These properties make calcium an ideal choice for efficient and successful transformation experiments in molecular biology and genetic engineering.
The method by which recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell is called ________- a)heat-shock
- b)micro-injection
- c)transferring
- d)insertional inactivation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The method by which recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell is called ________
a)
heat-shock
b)
micro-injection
c)
transferring
d)
insertional inactivation
|
|
Siddharth Desai answered |
Micro-injection
Micro-injection is the method by which recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell. It involves the use of a fine glass micropipette to inject the DNA into the cell. This technique allows for precise delivery of the DNA into the nucleus, ensuring that it integrates into the host cell's genome.
Process of Micro-injection
1. Preparation of the DNA: The recombinant DNA is prepared by isolating the desired gene or DNA fragment and inserting it into a vector, such as a plasmid. The DNA is then purified and prepared for injection.
2. Isolation of the recipient cell: The animal cell that will receive the recombinant DNA is isolated and prepared for injection. This may involve culturing the cells in a suitable medium and ensuring they are in the appropriate stage of the cell cycle.
3. Micro-injection: A glass micropipette, with a diameter smaller than the cell, is used to physically inject the recombinant DNA directly into the nucleus of the recipient cell. The micropipette is carefully inserted into the cell using micromanipulators, which provide precise control over the injection process.
4. Integration of the DNA: Once inside the nucleus, the recombinant DNA may integrate into the host cell's genome. This integration allows the cell to produce the desired protein encoded by the inserted gene.
5. Cell culture and selection: After micro-injection, the cells are typically cultured in a suitable medium to allow them to grow and divide. Selection markers, such as antibiotic resistance genes, may be included in the recombinant DNA to identify and isolate cells that have successfully integrated the DNA.
6. Analysis and characterization: The cells that have successfully integrated the recombinant DNA can be further analyzed and characterized to confirm the presence and expression of the desired gene. This may involve techniques such as PCR, gel electrophoresis, and protein analysis.
Advantages of Micro-injection
- Provides precise control over the delivery of recombinant DNA into the nucleus.
- Allows for integration of the DNA into the host cell's genome.
- Can be used for a wide range of cell types and organisms.
- Enables the study of gene function and protein production in living cells.
Limitations of Micro-injection
- Labor-intensive and technically demanding technique.
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Low efficiency, as not all injected cells will successfully integrate the DNA.
- Risk of cell damage or death during the injection process.
Micro-injection is the method by which recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell. It involves the use of a fine glass micropipette to inject the DNA into the cell. This technique allows for precise delivery of the DNA into the nucleus, ensuring that it integrates into the host cell's genome.
Process of Micro-injection
1. Preparation of the DNA: The recombinant DNA is prepared by isolating the desired gene or DNA fragment and inserting it into a vector, such as a plasmid. The DNA is then purified and prepared for injection.
2. Isolation of the recipient cell: The animal cell that will receive the recombinant DNA is isolated and prepared for injection. This may involve culturing the cells in a suitable medium and ensuring they are in the appropriate stage of the cell cycle.
3. Micro-injection: A glass micropipette, with a diameter smaller than the cell, is used to physically inject the recombinant DNA directly into the nucleus of the recipient cell. The micropipette is carefully inserted into the cell using micromanipulators, which provide precise control over the injection process.
4. Integration of the DNA: Once inside the nucleus, the recombinant DNA may integrate into the host cell's genome. This integration allows the cell to produce the desired protein encoded by the inserted gene.
5. Cell culture and selection: After micro-injection, the cells are typically cultured in a suitable medium to allow them to grow and divide. Selection markers, such as antibiotic resistance genes, may be included in the recombinant DNA to identify and isolate cells that have successfully integrated the DNA.
6. Analysis and characterization: The cells that have successfully integrated the recombinant DNA can be further analyzed and characterized to confirm the presence and expression of the desired gene. This may involve techniques such as PCR, gel electrophoresis, and protein analysis.
Advantages of Micro-injection
- Provides precise control over the delivery of recombinant DNA into the nucleus.
- Allows for integration of the DNA into the host cell's genome.
- Can be used for a wide range of cell types and organisms.
- Enables the study of gene function and protein production in living cells.
Limitations of Micro-injection
- Labor-intensive and technically demanding technique.
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise.
- Low efficiency, as not all injected cells will successfully integrate the DNA.
- Risk of cell damage or death during the injection process.
The molecule which dissolves in water is called _______
- a)hydrophilic molecule
- b)hydrophobic molecule
- c)insoluble molecule
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The molecule which dissolves in water is called _______
a)
hydrophilic molecule
b)
hydrophobic molecule
c)
insoluble molecule
d)
None of these
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The molecule which dissolves in water is called hydrophilic molecules. They are polar in nature which helps them in dissolution in water. Being hydrophilic in nature DNA cannot pass through the cell membrane.
The cells which have the ability to incorporate foreign DNA within them are called ______- a)water-loving
- b)plasma cells
- c)competent cells
- d)hydrophobic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cells which have the ability to incorporate foreign DNA within them are called ______
a)
water-loving
b)
plasma cells
c)
competent cells
d)
hydrophobic
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
Some bacterial cells have the ability to incorporate foreign DNA within them. These cells are called competent cells. This leads to the alteration of the genetic material of the cell.
Which macromolecules are present along with DNA within the cell?- a)Lipids, polysaccharides
- b)Bacteria
- c)Vectors, organelles
- d)Viruses
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which macromolecules are present along with DNA within the cell?
a)
Lipids, polysaccharides
b)
Bacteria
c)
Vectors, organelles
d)
Viruses
|
|
Shivani Mishra answered |
Macromolecules present along with DNA within the cell:
Explanation:
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms. It is located within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the nucleoid region of prokaryotic cells. However, DNA does not exist alone within the cell. There are several other macromolecules that coexist with DNA and play important roles in cellular processes. These macromolecules include lipids and polysaccharides.
Lipids:
Lipids are essential components of cells and have various functions. They are hydrophobic in nature and can be found in the cell membrane as phospholipids, which form the lipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer provides a barrier that separates the cell's internal environment from the external environment. Lipids also serve as a source of energy storage in the form of triglycerides. Additionally, lipids play a role in cell signaling and act as precursors for the synthesis of hormones and other signaling molecules.
Polysaccharides:
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates that are composed of long chains of monosaccharides. They serve as an energy storage molecule in cells. For example, plants store glucose as starch, while animals store glucose as glycogen. Polysaccharides also play a structural role in cells. For instance, cellulose is a polysaccharide that forms the cell wall in plant cells, providing rigidity and support.
In conclusion, along with DNA, lipids and polysaccharides are present within the cell. Lipids are involved in various cellular processes such as membrane structure and energy storage, while polysaccharides function in energy storage and structural support.
- Lipids: Lipids are organic molecules that are insoluble in water. They include fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids. Lipids play various roles in the cell, including serving as a structural component of cell membranes, providing energy storage, and participating in cell signaling pathways.
- Polysaccharides: Polysaccharides are large carbohydrate molecules composed of long chains of monosaccharides. They are involved in energy storage and structural support in cells. Examples of polysaccharides include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Explanation:
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a macromolecule that carries genetic information in all living organisms. It is located within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the nucleoid region of prokaryotic cells. However, DNA does not exist alone within the cell. There are several other macromolecules that coexist with DNA and play important roles in cellular processes. These macromolecules include lipids and polysaccharides.
Lipids:
Lipids are essential components of cells and have various functions. They are hydrophobic in nature and can be found in the cell membrane as phospholipids, which form the lipid bilayer. The lipid bilayer provides a barrier that separates the cell's internal environment from the external environment. Lipids also serve as a source of energy storage in the form of triglycerides. Additionally, lipids play a role in cell signaling and act as precursors for the synthesis of hormones and other signaling molecules.
Polysaccharides:
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates that are composed of long chains of monosaccharides. They serve as an energy storage molecule in cells. For example, plants store glucose as starch, while animals store glucose as glycogen. Polysaccharides also play a structural role in cells. For instance, cellulose is a polysaccharide that forms the cell wall in plant cells, providing rigidity and support.
In conclusion, along with DNA, lipids and polysaccharides are present within the cell. Lipids are involved in various cellular processes such as membrane structure and energy storage, while polysaccharides function in energy storage and structural support.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biotechnology: Principle & Processes - Biology for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biotechnology: Principle & Processes - Biology for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for EmSAT Achieve
157 videos|173 docs|136 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup