All Exams >
Class 12 >
Chemistry Class 12 >
All Questions
All questions of CBSE New Pattern: Term lI Practice Questions for Class 12 Exam
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactant to decrease by half, i.e.,[A]t = [A]/2For first order reaction,t1/2 = 0.693/kThis means t1/2 is independent of initial concentration. Figure shows that typical variation of concentration of reactant exhibiting first order kinetics. It may be noted that though the major portion of the first order kinetics may be over in a finite time, but the reaction will never cease as the concentration of reactant will be zero only at infinite time.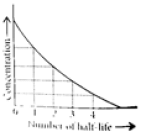 The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. A first order reaction has a rate constant k = 3.01 x 10-3 /s. How long it will take to decompose half of the reactant?
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. A first order reaction has a rate constant k = 3.01 x 10-3 /s. How long it will take to decompose half of the reactant?- a)2.303 s
- b)23.03 s
- c)230.3 s
- d)2303 s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactant to decrease by half, i.e.,
[A]t = [A]/2
For first order reaction,
t1/2 = 0.693/k
This means t1/2 is independent of initial concentration. Figure shows that typical variation of concentration of reactant exhibiting first order kinetics. It may be noted that though the major portion of the first order kinetics may be over in a finite time, but the reaction will never cease as the concentration of reactant will be zero only at infinite time.

The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. A first order reaction has a rate constant k = 3.01 x 10-3 /s. How long it will take to decompose half of the reactant?
a)
2.303 s
b)
23.03 s
c)
230.3 s
d)
2303 s

|
Ambition Institute answered |
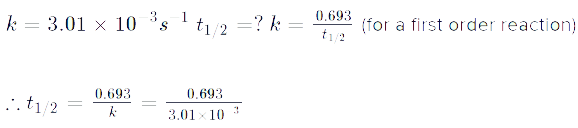
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :Assertion (A): In aniline, the substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions.Reason (R): The electron density is more at ortho and para positions.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :
Assertion (A): In aniline, the substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions.
Reason (R): The electron density is more at ortho and para positions.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
In aniline, the electron density is more at ortho and para positions than meta position, so, the substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions.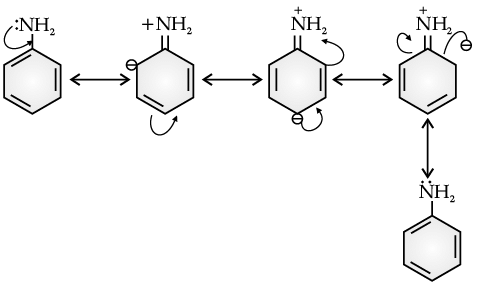

The above resonating structures of aniline show more electron density at the ortho and para positions.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. The total number of moles of chlorine gas evolved is- a)0.5
- b)1.0
- c)1.5
- d)1.9
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The total number of moles of chlorine gas evolved is
a)
0.5
b)
1.0
c)
1.5
d)
1.9
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
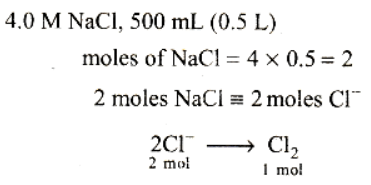
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.Q. Why is the activating effect of -NHCOCH3 group in the above reaction less than the activating effect of amino group?- a)Due to mesomeric effect of benzene ring.
- b)Due to inductive effect of alkyl group.
- c)Due to resonance effect of acetanilide.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Q. Why is the activating effect of -NHCOCH3 group in the above reaction less than the activating effect of amino group?
a)
Due to mesomeric effect of benzene ring.
b)
Due to inductive effect of alkyl group.
c)
Due to resonance effect of acetanilide.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen of acetanilide interacts with oxygen atom due to resonance as shown below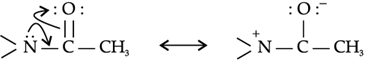

Hence, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is less available for donation to benzene ring by resonance. Therefore, activating effect of – NHCOCH3 group is less than that of amino group.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.Assertion : Nitrating mixture used for carrying out nitration of benzene consists of conc. HNO3+ conc. H2SO4Reason : In presence of H2SO4, HNO3 acts as a base and produces NO2+ ions.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- c)If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
- d)If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Nitrating mixture used for carrying out nitration of benzene consists of conc. HNO3+ conc. H2SO4
Reason : In presence of H2SO4, HNO3 acts as a base and produces NO2+ ions.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
c)
If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
d)
If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
The assertion in this question states that the nitrating mixture used for the nitration of benzene consists of concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This is correct. In the nitration of benzene, a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is typically used as the nitrating agent.
The reason given for this assertion is that in the presence of sulfuric acid, nitric acid acts as a base and produces nitronium ions (NO2+). This is also correct. Nitronium ions are intermediates that are formed in the nitration of aromatic compounds, such as benzene. When nitric acid is mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid, the resulting mixture is highly acidic and can effectively transfer the nitronium ions to the aromatic compound, leading to the substitution of a nitro group onto the aromatic ring.
Therefore, both the assertion and the reason are correct, and the reason given is a correct explanation of the assertion. In this case, the correct answer is option 'A'.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. If cathode is a Hg electrode, then the maximum weight of amalgam formed from this solution is- a)300g
- b)446 g
- c)396 g
- d)256 g
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. If cathode is a Hg electrode, then the maximum weight of amalgam formed from this solution is
a)
300g
b)
446 g
c)
396 g
d)
256 g
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
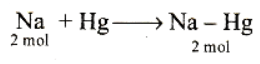
2 moles of amalgam = 23 x 2 + 2 x 200
= 446g
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. The rate constant of the reaction after 5 minutes is:- a)0.4290 min–1
- b)0.1297 min–1
- c)0.2197 min–1
- d)0.6591 min–1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The rate constant of the reaction after 5 minutes is:
a)
0.4290 min–1
b)
0.1297 min–1
c)
0.2197 min–1
d)
0.6591 min–1
|
|
Om Desai answered |
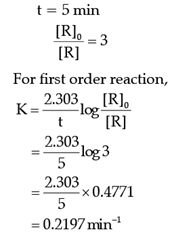
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. For a reaction,A + H2O → BRate ∝ [A]The order of the reaction is:- a)Zero order
- b)Fractional order
- c)Pseudo first order
- d)Second order
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. For a reaction,
A + H2O → B
Rate ∝ [A]
The order of the reaction is:
a)
Zero order
b)
Fractional order
c)
Pseudo first order
d)
Second order
|
|
Rhea Iyer answered |
Explanation:
The given reaction is represented as A → B, which means that A is getting converted into B. The rate of this reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of A, as mentioned in the question.
To determine the order of the reaction, we need to analyze how the rate of the reaction changes with the concentration of A.
Differential Rate Equation:
The rate of a reaction can be expressed using a differential rate equation, which shows the dependence of the reaction rate on the concentration of reactants. In this case, the rate equation is given as Rate ∝ [A].
Order of Reaction:
The order of the reaction is determined by the power to which the concentration term is raised in the rate equation.
In this case, since the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of A, it can be concluded that the reaction is a first-order reaction. This means that the concentration term is raised to the power of 1 in the rate equation.
The rate constant mentioned in the passage, 1.15 × 10–3s–1, is specific to a first-order reaction.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C) Pseudo first order, as it indicates that the reaction is first-order with respect to A.
The given reaction is represented as A → B, which means that A is getting converted into B. The rate of this reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of A, as mentioned in the question.
To determine the order of the reaction, we need to analyze how the rate of the reaction changes with the concentration of A.
Differential Rate Equation:
The rate of a reaction can be expressed using a differential rate equation, which shows the dependence of the reaction rate on the concentration of reactants. In this case, the rate equation is given as Rate ∝ [A].
Order of Reaction:
The order of the reaction is determined by the power to which the concentration term is raised in the rate equation.
In this case, since the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of A, it can be concluded that the reaction is a first-order reaction. This means that the concentration term is raised to the power of 1 in the rate equation.
The rate constant mentioned in the passage, 1.15 × 10–3s–1, is specific to a first-order reaction.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C) Pseudo first order, as it indicates that the reaction is first-order with respect to A.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:A galvanic cell consists of a metallic zinc plate immersed in 0.1 M Zn(NO3)2 solution and metallic plate of lead in 0.02 M Pb(NO3)2 solution.The following questions are multiple choice questions.Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. What product is obtained at cathode?- a)Zn
- b)Pb
- c)Zn2+
- d)Pb2+
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A galvanic cell consists of a metallic zinc plate immersed in 0.1 M Zn(NO3)2 solution and metallic plate of lead in 0.02 M Pb(NO3)2 solution.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. What product is obtained at cathode?
a)
Zn
b)
Pb
c)
Zn2+
d)
Pb2+
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Anode reaction: Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e–
Cathode reaction: Pb2+(aq) + 2e– → Pb(s)
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.Q. Aniline is a resonance hybrid of- a)3 structures
- b)6 structures
- c)2 structures
- d)5 structures
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Q. Aniline is a resonance hybrid of
a)
3 structures
b)
6 structures
c)
2 structures
d)
5 structures
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the IUPAC system.Few rules for naming coordination compounds are:(I) In an ionic complex, the cation is named first and then the anion.(II) In the coordination entity, the ligands are named first and then the central metal ion.(III) When more than one type of ligands are present, they are named in alphabetical order of preference with any consideration of chargeThe following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. As per IUPAC nomenclature, the name of the complex [Co(H2O)4(NH3)2]Cl3 is- a)tetra aqua diamine cobalt(II) chloride
- b)tetra aqua diamine cobalt(III) chloride
- c)diammine tetraaqua cobalt(II) chloride
- d)diammine tetraaqua cobalt(III) chloride
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the IUPAC system.
Few rules for naming coordination compounds are:
(I) In an ionic complex, the cation is named first and then the anion.
(II) In the coordination entity, the ligands are named first and then the central metal ion.
(III) When more than one type of ligands are present, they are named in alphabetical order of preference with any consideration of charge
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. As per IUPAC nomenclature, the name of the complex [Co(H2O)4(NH3)2]Cl3 is
a)
tetra aqua diamine cobalt(II) chloride
b)
tetra aqua diamine cobalt(III) chloride
c)
diammine tetraaqua cobalt(II) chloride
d)
diammine tetraaqua cobalt(III) chloride
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The IUPAC name of the complex given is Diamminetetraaquacobalt (III) chloride. The charge on the central Co atom is +3.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.Assertion : NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3.Reason : NF3 ionizes to give F– ions in aqueous solution.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- c)If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
- d)If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3.
Reason : NF3 ionizes to give F– ions in aqueous solution.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
c)
If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
d)
If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
It is a correct statement that NF3 is a weaker ligand than N(CH3)3, the reason is that fluorine is highly electronegative therefore, it withdraws electrons from the nitrogen atom. Hence, the lone pair of nitrogen atoms cannot be ligated. While N(CH3)3 is a strong ligand because CH3 has an electron releasing group.
Root pressure is maximum when- a)Tranpiration is high and abosrption is low
- b) Transpiration is very low and absorption is high
- c) Both are very high
- d)Both are very low
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Tranpiration is high and abosrption is low
b)
Transpiration is very low and absorption is high
c)
Both are very high
d)
Both are very low
|
|
Vartika Shukla (NEET Aspirant) answered |
Root pressure is the positive pressure that develops in the roots of the plants by active absorption of nutrients from the soil. The active absorption depends on the active accumulation of solute in xylem sap. Root pressure in maximum when transpiration is very low and absorption is high because transpiration is the output of water from a plant, and absorption is the input of water into a plant. If the output is low and input is high, the pressure will be at its greatest.
So, the correct answer is 'Transpiration is very low and absorption is high'.
So, the correct answer is 'Transpiration is very low and absorption is high'.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.Assertion : On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing.Reason : On increasing dilution, degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and molality of ions also increases.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- c)If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
- d)If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing.
Reason : On increasing dilution, degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and molality of ions also increases.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
c)
If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
d)
If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
|
|
Mansi Nair answered |
Assertion and Reason:
Assertion: On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing.
Reason: On increasing dilution, the degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and the molality of ions also increases.
Explanation:
The specific conductance of a solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. It is directly related to the concentration of ions in the solution. When a weak electrolyte, such as acetic acid, is dissolved in water, it partially ionizes into ions. The degree of ionization is the extent to which the weak electrolyte dissociates into ions.
Effect of Dilution on Specific Conductance:
When a solution is diluted, the concentration of the ions decreases. However, the volume of the solution increases. As a result, the total number of ions remains constant. Therefore, the specific conductance of the solution increases with increasing dilution.
Reasoning behind the Assertion and Reason:
The Assertion states that on increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing. This is true because the dilution of a solution leads to a decrease in the concentration of ions, resulting in an increase in the specific conductance.
The Reason states that on increasing dilution, the degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and the molality of ions also increases. This is incorrect because the degree of ionization of a weak electrolyte does not increase with dilution. In fact, the degree of ionization decreases with dilution due to the decrease in concentration. The molality of ions also does not increase with dilution, as the total number of ions remains constant.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect. The specific conductance of a solution increases with increasing dilution, but the reason provided for this is not correct. The degree of ionization of a weak electrolyte decreases with dilution, and the molality of ions does not increase with dilution. Therefore, option 'D' is the correct answer.
Assertion: On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing.
Reason: On increasing dilution, the degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and the molality of ions also increases.
Explanation:
The specific conductance of a solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. It is directly related to the concentration of ions in the solution. When a weak electrolyte, such as acetic acid, is dissolved in water, it partially ionizes into ions. The degree of ionization is the extent to which the weak electrolyte dissociates into ions.
Effect of Dilution on Specific Conductance:
When a solution is diluted, the concentration of the ions decreases. However, the volume of the solution increases. As a result, the total number of ions remains constant. Therefore, the specific conductance of the solution increases with increasing dilution.
Reasoning behind the Assertion and Reason:
The Assertion states that on increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing. This is true because the dilution of a solution leads to a decrease in the concentration of ions, resulting in an increase in the specific conductance.
The Reason states that on increasing dilution, the degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and the molality of ions also increases. This is incorrect because the degree of ionization of a weak electrolyte does not increase with dilution. In fact, the degree of ionization decreases with dilution due to the decrease in concentration. The molality of ions also does not increase with dilution, as the total number of ions remains constant.
Conclusion:
Based on the explanation above, it can be concluded that both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect. The specific conductance of a solution increases with increasing dilution, but the reason provided for this is not correct. The degree of ionization of a weak electrolyte decreases with dilution, and the molality of ions does not increase with dilution. Therefore, option 'D' is the correct answer.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Ecell should have a positive value for the cell to function.Reason (R): Ecathode < />anode.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is True
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Ecell should have a positive value for the cell to function.
Reason (R): Ecathode < />anode.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is True
|
|
Tanuja Kapoor answered |
Ecell = Ecathode – Eanode.
To have a positive value of Ecell, Ecathode should be greater than Eanode.
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells.In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.Assertion (A): At equilibrium condition Ecell = 0 or ΔrG = 0.Reason (R): Ecell is zero when both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is a correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells.
In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): At equilibrium condition Ecell = 0 or ΔrG = 0.
Reason (R): Ecell is zero when both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is a correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Keerthana Iyer answered |
Explanation:
Equilibrium Condition and Ecell:
- At equilibrium condition, the cell potential (Ecell) is zero.
- This means that the overall cell reaction has reached equilibrium, and no further net reaction occurs.
- The cell potential is zero when the forward and reverse reactions proceed at equal rates, resulting in no net voltage.
Same Metal Electrodes and Ecell:
- When both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal, the standard electrode potentials for the two half-cells are equal.
- This leads to a cell potential of zero since there is no potential difference between the two electrodes.
- As a result, at equilibrium, Ecell = 0 or ΔrG = 0 when same metal electrodes are used in the cell.
Therefore, in the given assertion and reason, both statements are correct. However, the reason provided is a correct explanation for the assertion. The equilibrium condition in a cell leads to Ecell being zero, and this is true when both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal.
Equilibrium Condition and Ecell:
- At equilibrium condition, the cell potential (Ecell) is zero.
- This means that the overall cell reaction has reached equilibrium, and no further net reaction occurs.
- The cell potential is zero when the forward and reverse reactions proceed at equal rates, resulting in no net voltage.
Same Metal Electrodes and Ecell:
- When both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal, the standard electrode potentials for the two half-cells are equal.
- This leads to a cell potential of zero since there is no potential difference between the two electrodes.
- As a result, at equilibrium, Ecell = 0 or ΔrG = 0 when same metal electrodes are used in the cell.
Therefore, in the given assertion and reason, both statements are correct. However, the reason provided is a correct explanation for the assertion. The equilibrium condition in a cell leads to Ecell being zero, and this is true when both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. The rate law equation is:- a)Rate = k [C2H6]
- b)Rate = k [C2H4]2
- c)Rate = k [C2H4]
- d)Rate = k [C2H4]2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the reactant. Hydrogenation of ethene results in the formation of ethane. The rate constant, k for the reaction was found to be 2.5 × 10–15s–1. The concentration of the reactant reduces to one-third of the initial concentration in 5 minutes. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The rate law equation is:
a)
Rate = k [C2H6]
b)
Rate = k [C2H4]2
c)
Rate = k [C2H4]
d)
Rate = k [C2H4]2
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |

Rate law equation, Rate = K [C2H4]
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to be ionic arising purely from electrostatic interactions between the metal ion and the ligand. Ligands are treated as point charges in case of anions or dipoles in case of neutral molecules. The five d orbitals in an isolated gaseous metal atom/ion have same energy, i.e., they are degenerate. This degeneracy is maintained if a spherically symmetrical field of negative charges surrounds the metal atom/ ion. However, when this negative field is due to ligands (either anions or the negative ends of dipolar molecules like NH3 and H2O) in a complex, it becomes asymmetrical and the degeneracy of the d orbitals is lifted. It results in splitting of the d orbitals.The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?- a)thiosulphato
- b)oxalato
- c)glycinato
- d)ethane-1,2-diamine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to be ionic arising purely from electrostatic interactions between the metal ion and the ligand. Ligands are treated as point charges in case of anions or dipoles in case of neutral molecules. The five d orbitals in an isolated gaseous metal atom/ion have same energy, i.e., they are degenerate. This degeneracy is maintained if a spherically symmetrical field of negative charges surrounds the metal atom/ ion. However, when this negative field is due to ligands (either anions or the negative ends of dipolar molecules like NH3 and H2O) in a complex, it becomes asymmetrical and the degeneracy of the d orbitals is lifted. It results in splitting of the d orbitals.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Which of the following is not a chelating agent?
a)
thiosulphato
b)
oxalato
c)
glycinato
d)
ethane-1,2-diamine

|
Pranav Pillai answered |
Explanation:
Chelating Agent:
- A chelating agent is a compound that forms multiple bonds with a metal ion to form a ring structure known as a chelate.
- Chelating agents have two or more donor atoms that can bind to a single metal ion.
Options:
- Thiosulphato: Thiosulphate ion (S2O3^2-) is a chelating agent as it has two oxygen atoms that can act as donor atoms to bind to a metal ion.
- Oxalato: Oxalate ion (C2O4^2-) is a chelating agent as it has two oxygen atoms that can bind to a metal ion.
- Glycinato: Glycinate ion (C2H4NO2^-) is a chelating agent as it has two oxygen atoms that can bind to a metal ion.
- Ethane-1,2-diamine: Ethane-1,2-diamine is not a chelating agent as it has only one nitrogen atom that can act as a donor atom to bind to a metal ion.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', thiosulphato, as it is a chelating agent with two donor atoms.
Chelating Agent:
- A chelating agent is a compound that forms multiple bonds with a metal ion to form a ring structure known as a chelate.
- Chelating agents have two or more donor atoms that can bind to a single metal ion.
Options:
- Thiosulphato: Thiosulphate ion (S2O3^2-) is a chelating agent as it has two oxygen atoms that can act as donor atoms to bind to a metal ion.
- Oxalato: Oxalate ion (C2O4^2-) is a chelating agent as it has two oxygen atoms that can bind to a metal ion.
- Glycinato: Glycinate ion (C2H4NO2^-) is a chelating agent as it has two oxygen atoms that can bind to a metal ion.
- Ethane-1,2-diamine: Ethane-1,2-diamine is not a chelating agent as it has only one nitrogen atom that can act as a donor atom to bind to a metal ion.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A', thiosulphato, as it is a chelating agent with two donor atoms.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. When the rate constant has same units as the rate of reaction, the order of the reaction is:- a)Zero order
- b)First order
- c)Second order
- d)Fractional order
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Concentration dependence of rate is called differential rate equation. Integrated differential equations give relation between directly measured experimental data i.e. concentration at different times and rate constant. The integrated rate equations are different for the reactions of different reaction orders. The first-order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10–3s–1.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. When the rate constant has same units as the rate of reaction, the order of the reaction is:
a)
Zero order
b)
First order
c)
Second order
d)
Fractional order

|
Jaideep Sengupta answered |
Answer:
Explanation:
In order to understand why the answer is option 'A' (Zero order), we need to understand the concept of reaction order and the units of the rate constant.
Reaction Order:
The reaction order of a chemical reaction is determined by the dependence of the reaction rate on the concentration of reactants. It is represented by the exponent to which the concentration term is raised in the rate equation.
Rate Constant:
The rate constant (k) is a proportionality constant that relates the rate of a reaction to the concentrations of reactants. It is specific for a particular reaction at a particular temperature.
Relationship between Rate Constant and Reaction Order:
The rate constant has units that depend on the overall order of the reaction. In a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants. Therefore, the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction.
Explanation of the Answer:
In this question, it is given that the rate constant is 1.15 × 10–3s–1. Since the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction, it implies that the reaction is zero order.
Reasoning:
In a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants. This means that even if the concentration of reactants changes, the rate of reaction remains constant. Therefore, the units of the rate constant and the rate of reaction are the same in a zero-order reaction.
Conclusion:
Based on the given information, we can conclude that when the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction, the order of the reaction is zero order.
Explanation:
In order to understand why the answer is option 'A' (Zero order), we need to understand the concept of reaction order and the units of the rate constant.
Reaction Order:
The reaction order of a chemical reaction is determined by the dependence of the reaction rate on the concentration of reactants. It is represented by the exponent to which the concentration term is raised in the rate equation.
Rate Constant:
The rate constant (k) is a proportionality constant that relates the rate of a reaction to the concentrations of reactants. It is specific for a particular reaction at a particular temperature.
Relationship between Rate Constant and Reaction Order:
The rate constant has units that depend on the overall order of the reaction. In a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants. Therefore, the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction.
Explanation of the Answer:
In this question, it is given that the rate constant is 1.15 × 10–3s–1. Since the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction, it implies that the reaction is zero order.
Reasoning:
In a zero-order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants. This means that even if the concentration of reactants changes, the rate of reaction remains constant. Therefore, the units of the rate constant and the rate of reaction are the same in a zero-order reaction.
Conclusion:
Based on the given information, we can conclude that when the rate constant has the same units as the rate of reaction, the order of the reaction is zero order.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Within the 3d series, manganese exhibits oxidation states in aqueous solution from +2 to +7, ranging from Mn2+(aq) to MnO−4 (aq). Likewise, iron forms both Fe2+(aq) and Fe3+(aq) as well as the FeO2−4 ion. Cr and Mn form oxyions CrO2−4, MnO−4, owing to their willingness to form multiple bonds. The pattern with the early transition metals—in the 3d series up to Mn, and for the 4d, 5d metals up to Ru and Os—is that the maximum oxidation state corresponds to the number of ‘‘outer shell’’ electrons. The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation (e.g., the stabilization of Co3+ by ammonia) or upon the pH (thus MnO42− (aq) is prone to disproportionation in acidic solution). Within the 3d series, there is considerable variation in relative stability of oxidation states, sometimes on moving from one metal to a neighbour; thus, for iron, Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+, especially in alkaline conditions, while the reverse is true for cobalt. The ability of transition metals to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states is marked with metals such as vanadium, where the standard potentials can be rather small, making a switch between states relatively easy.In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.Assertion (A): Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+.Reason (R): Fe3+ has 3d5 configuration while Fe2+ has 3d6 configuration.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Within the 3d series, manganese exhibits oxidation states in aqueous solution from +2 to +7, ranging from Mn2+(aq) to MnO−4 (aq). Likewise, iron forms both Fe2+(aq) and Fe3+(aq) as well as the FeO2−4 ion. Cr and Mn form oxyions CrO2−4, MnO−4, owing to their willingness to form multiple bonds. The pattern with the early transition metals—in the 3d series up to Mn, and for the 4d, 5d metals up to Ru and Os—is that the maximum oxidation state corresponds to the number of ‘‘outer shell’’ electrons. The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation (e.g., the stabilization of Co3+ by ammonia) or upon the pH (thus MnO42− (aq) is prone to disproportionation in acidic solution). Within the 3d series, there is considerable variation in relative stability of oxidation states, sometimes on moving from one metal to a neighbour; thus, for iron, Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+, especially in alkaline conditions, while the reverse is true for cobalt. The ability of transition metals to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states is marked with metals such as vanadium, where the standard potentials can be rather small, making a switch between states relatively easy.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion (A): Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+.
Reason (R): Fe3+ has 3d5 configuration while Fe2+ has 3d6 configuration.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
This can be understood as follows
Fe3+ has 3d5 , half filled configuration , whereas Fe2+ has 3d6 configuration.
Due to half filled , 3d5 stable configuration , the Fe3+ is more stable than the Fe2+.
Due to the same reason, the
B: Core of Fe3+ is more stable,
and C: IInd and IIIrd IP difference is less than 11.0 ev.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :Assertion (A): In aniline –NH2 group facilitates the electrophilic attack.Reason (R): It is due to decrease in electron density on the ring.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Benzene ring in aniline is highly activated. This is due to the sharing of lone pair of nitrogen with the ring which results in increase in the electron density on the ring and hence facilitates the electrophilic attack. The substitution mainly takes place at ortho and para positions because electron density is more at ortho and para positions. On reaction with aqueous bromine all the ortho and para positions get substituted resulting in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline. To get a monobromo compound, the amino group is acetylated before bromination. After bromination, the bromoacetanilide is acid hydrolysed to give the desired halogenated amine.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices :
Assertion (A): In aniline –NH2 group facilitates the electrophilic attack.
Reason (R): It is due to decrease in electron density on the ring.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.

|
Pragati Nair answered |
Explanation:
Assertion (A):
- The assertion that the –NH2 group in aniline facilitates the electrophilic attack is correct.
- This is because the lone pair of nitrogen in the –NH2 group is shared with the benzene ring, leading to an increase in electron density on the ring.
- The increased electron density makes the benzene ring highly activated and more susceptible to electrophilic attack.
Reason (R):
- The reason given, that there is a decrease in electron density on the ring, is incorrect.
- In fact, due to the sharing of the lone pair of nitrogen with the ring, the electron density on the ring increases.
- This increase in electron density at the ortho and para positions of the benzene ring makes these positions more reactive towards electrophilic substitution.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - Assertion is a correct statement but the reason is wrong.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product whereas alkylation of amines gives poly substituted product.Reason (R): Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is True
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product whereas alkylation of amines gives poly substituted product.
Reason (R): Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is True
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
In alkylation, an amine can react with alkyl halide to form next higher class of amine caused by the presence of electron pair on nitrogen which makes amine to behave as nucleophile and alkyl halide thus undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. When primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters to give monosubstituted amides as products. Acylation is carried out in the presence of a base stronger than the amine like pyridine which causes the shift of the equilibrium to the right side.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature.Reason (R): Unpaired electrons are present in their d-orbitals.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): [Cr(H2O)6]Cl2 and [Fe(H2O)6]Cl2 are reducing in nature.
Reason (R): Unpaired electrons are present in their d-orbitals.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is true
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
In the complexes, Co exists as Co2+ and Fe as Fe2+. Both of the complexes become Stable by oxidation of metal ion to Co3+ and Fe3+.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:According to Valence Bond Theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n−1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridisation to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding. In these questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.Assertion (A): In the square planar complexes, the hybridisation involved is dsp2.Reason (R): In [Ni(CN)4]2−. Here nickel is in +2 oxidation state and has the electronic configuration 3d8.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
According to Valence Bond Theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n−1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridisation to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding. In these questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): In the square planar complexes, the hybridisation involved is dsp2.
Reason (R): In [Ni(CN)4]2−. Here nickel is in +2 oxidation state and has the electronic configuration 3d8.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
The dsp2 hybrid orbitals are inner orbital complexes in which the electrons get paired up due to the presence of a strong field ligand. So, the electron pairs of the ligands occupy one d orbital, one s orbital and then 2p orbitals in a square planar geometry.
The 2s orbital is mixed with all three of the 2p orbitals, creating four hybridized sp3 orbitals. Each of these has 25% s and 75% p character; electron repulsion favours a tetrahedral shape, so the orbitals are 109.5° apart from each other.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion: Hoffmann's bromamide reaction is given by primary amines.
Reason: Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.- a)If both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)If both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)If A is true but R is false
- d)If Both A and R is False
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion: Hoffmann's bromamide reaction is given by primary amines.
Reason: Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.
Reason: Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.
a)
If both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
If both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
If A is true but R is false
d)
If Both A and R is False

|
Top Rankers answered |
The Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction prepares primary amines by treating an amide with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic sodium hydroxide solution. The resulting amine has one carbon atom less than the original amide.
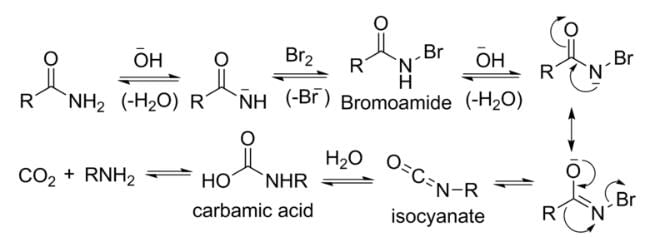
Therefore, the assertion is incorrect because Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction involves amides rather than primary amines, even though the product is a primary amine.
Reason:
Primary amines are less basic than secondary amines because secondary amines have more electron-donating alkyl groups, which enhance their basicity. Thus, the reason statement is also incorrect.
Primary amines are less basic than secondary amines because secondary amines have more electron-donating alkyl groups, which enhance their basicity. Thus, the reason statement is also incorrect.
Consequently, both the assertion and reason are wrong.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is - dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm. Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1 The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the both power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via., rate = k CAα CAβ the over-all order of the reaction is simply n = α + β + ----- (2) Such a reaction is said to be of the αth order with respect to the substance A, the βth order with respect to B.In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.Assertion: For a reaction: P + 2Q → Products, Rate = k [P]1/2[Q]1 so the order of reaction is 1.5Reason: Order of reaction is the sum of stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The rate of a reaction, which may also be called its velocity or speed, can be defined with relation to the concentration of any of the reacting substances, or to that of any product of the reaction. If the species chosen is a reactant which has a concentration c at time t the rate is - dc/dt, while the rate with reference to a product having a concentration x at time t is dx/dt. Any concentration units may be used for expressing the rate; thus, if moles per liter are employed for concentration and seconds for the time, the units for the rate are moles litre–1sec–1. For gas reactions pressure units are sometimes used in place of concentrations, so that legitimate units for the rate would be (mm. Hg) sec–1 and atm. sec–1 The order of a reaction concerns the dependence of the rate upon the concentrations of reacting substances; thus, if the rate is found experimentally to be proportional to the ath power of the concentration of one of the reactants A, to the both power of the concentration of a second reactant B, and so forth, via., rate = k CAα CAβ the over-all order of the reaction is simply n = α + β + ----- (2) Such a reaction is said to be of the αth order with respect to the substance A, the βth order with respect to B.
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion followed by a statement of Reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion: For a reaction: P + 2Q → Products, Rate = k [P]1/2[Q]1 so the order of reaction is 1.5
Reason: Order of reaction is the sum of stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The sum of powers of the concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression is called the order of that chemical reaction.
Order of reaction may or may not be equal to the sum of stoichiometric coefficients.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): EAg+/Ag increases with increase in concentration of Ag+ ions.Reason (R): EAg+/Ag has a positive value.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is True
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): EAg+/Ag increases with increase in concentration of Ag+ ions.
Reason (R): EAg+/Ag has a positive value.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is True
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
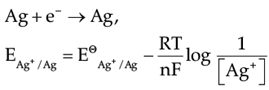
On increasing [Ag+], EAg+/ Ag will increase and it has a positive value.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A mixture of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) was separated by dissolving in chloroform followed by extraction with aqueous KOH solution. The organic layer containing compound (A), when heated with alcoholic solution of KOH produce C7H5N (C) associated with unpleasant odour.
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The alkaline aqueous layer (B) when heated with chloroform and then acidified give a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2. (B) is
- a)C6H5CHO
- b)C6H5COOH
- c)C6H5CH3
- d)C6H5OH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A mixture of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) was separated by dissolving in chloroform followed by extraction with aqueous KOH solution. The organic layer containing compound (A), when heated with alcoholic solution of KOH produce C7H5N (C) associated with unpleasant odour.
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The alkaline aqueous layer (B) when heated with chloroform and then acidified give a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2. (B) is
a)
C6H5CHO
b)
C6H5COOH
c)
C6H5CH3
d)
C6H5OH

|
Yash Kumar answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
The passage discusses the separation and identification of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) using different chemical reactions. Compound (A) is separated from compound (B) by dissolving the mixture in chloroform and extracting it with aqueous KOH solution. Compound (A) is then heated with an alcoholic solution of KOH to produce compound (C) with an unpleasant odor. Compound (B), on the other hand, forms a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2 when heated with chloroform and then acidified.
Identification of Compound (B):
To identify compound (B), it is heated with chloroform and then acidified. The resulting mixture of isomeric compounds has the molecular formula C7H6O2. From the given options, the correct answer is option 'D' - C6H5OH.
Explanation:
- The molecular formula C7H6O2 indicates the presence of 7 carbon atoms, 6 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms.
- Among the given options, only C6H5OH (phenol) matches the molecular formula.
- Phenol (C6H5OH) is an isomeric compound of molecular formula C7H6O2, making it the appropriate answer for compound (B).
Conclusion:
Compound (B) in the given passage is identified as C6H5OH (phenol) based on the reaction where it forms a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2 when heated with chloroform and then acidified.
Introduction:
The passage discusses the separation and identification of two aromatic compounds (A) and (B) using different chemical reactions. Compound (A) is separated from compound (B) by dissolving the mixture in chloroform and extracting it with aqueous KOH solution. Compound (A) is then heated with an alcoholic solution of KOH to produce compound (C) with an unpleasant odor. Compound (B), on the other hand, forms a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2 when heated with chloroform and then acidified.
Identification of Compound (B):
To identify compound (B), it is heated with chloroform and then acidified. The resulting mixture of isomeric compounds has the molecular formula C7H6O2. From the given options, the correct answer is option 'D' - C6H5OH.
Explanation:
- The molecular formula C7H6O2 indicates the presence of 7 carbon atoms, 6 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms.
- Among the given options, only C6H5OH (phenol) matches the molecular formula.
- Phenol (C6H5OH) is an isomeric compound of molecular formula C7H6O2, making it the appropriate answer for compound (B).
Conclusion:
Compound (B) in the given passage is identified as C6H5OH (phenol) based on the reaction where it forms a mixture of isomeric compounds of molecular formula C7H6O2 when heated with chloroform and then acidified.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): For complex reactions molecularity and order are not the same.Reason (R): Order of reaction may be zero.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): For complex reactions molecularity and order are not the same.
Reason (R): Order of reaction may be zero.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is true
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
For a complex reaction, Order of overall reaction = molecularity of slowest step As rate of overall reaction depends upon total number of molecules involved in slowest step of the reaction. Hence, for complex reactions, molecularity and order are not the same.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Colloids are stable.Reason (R): Brownian movement has a stirring effect, which does not allow the particles to settle.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is True
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Colloids are stable.
Reason (R): Brownian movement has a stirring effect, which does not allow the particles to settle.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is True
|
|
Gowri Menon answered |
Assertion (A): Colloids are stable.
Reason (R): Brownian movement has a stirring effect, which does not allow the particles to settle.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Colloids are a type of mixture where the particles are dispersed throughout a medium, but they do not dissolve or settle down. They have intermediate particle size between a solution and a suspension. The stability of colloids is a result of various factors, and one of the key factors is the Brownian movement.
Brownian movement:
Brownian movement is the random motion of particles suspended in a fluid. It is caused by the continuous collision between the particles and the molecules of the surrounding medium. This movement results in the dispersion and suspension of the particles, preventing them from settling down.
Stability of colloids:
The stability of colloids is primarily due to the Brownian movement. The continuous collisions between the particles and the molecules of the medium keep the particles in a state of constant motion. This motion prevents the particles from settling down, ensuring the stability of the colloidal system.
Explanation of the reason (R):
The reason mentioned in statement R is correct. Brownian movement indeed has a stirring effect on the particles, which does not allow them to settle. The random motion of the particles caused by the collisions with the surrounding molecules keeps them dispersed and suspended in the medium.
Explanation of the assertion (A):
The assertion mentioned in statement A is also true. Colloids are indeed stable due to the continuous Brownian movement. The stirring effect of the Brownian movement counteracts the gravitational force acting on the particles, preventing them from settling.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why colloids are stable. The continuous Brownian movement caused by the collisions between particles and the molecules of the medium keeps the colloidal particles dispersed and prevents them from settling down.
Reason (R): Brownian movement has a stirring effect, which does not allow the particles to settle.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Colloids are a type of mixture where the particles are dispersed throughout a medium, but they do not dissolve or settle down. They have intermediate particle size between a solution and a suspension. The stability of colloids is a result of various factors, and one of the key factors is the Brownian movement.
Brownian movement:
Brownian movement is the random motion of particles suspended in a fluid. It is caused by the continuous collision between the particles and the molecules of the surrounding medium. This movement results in the dispersion and suspension of the particles, preventing them from settling down.
Stability of colloids:
The stability of colloids is primarily due to the Brownian movement. The continuous collisions between the particles and the molecules of the medium keep the particles in a state of constant motion. This motion prevents the particles from settling down, ensuring the stability of the colloidal system.
Explanation of the reason (R):
The reason mentioned in statement R is correct. Brownian movement indeed has a stirring effect on the particles, which does not allow them to settle. The random motion of the particles caused by the collisions with the surrounding molecules keeps them dispersed and suspended in the medium.
Explanation of the assertion (A):
The assertion mentioned in statement A is also true. Colloids are indeed stable due to the continuous Brownian movement. The stirring effect of the Brownian movement counteracts the gravitational force acting on the particles, preventing them from settling.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why colloids are stable. The continuous Brownian movement caused by the collisions between particles and the molecules of the medium keeps the colloidal particles dispersed and prevents them from settling down.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Copper sulphate can be stored in a zinc vessel.Reason (R): Zinc is more reactive than copper.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is True
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Copper sulphate can be stored in a zinc vessel.
Reason (R): Zinc is more reactive than copper.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is True
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Zinc will get dissolved in CuSO4 solution, since zinc is more reactive than copper.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.Q. Give the major product of the following reaction:
- a)
- b)
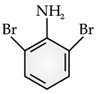
- c)
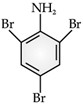
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The main problem encountered during electrophilic substitution reactions of aromatic amines is that of their very high reactivity. Substitution tends to occur at ortho and para positions. If we have to prepare monosubstituted aniline derivative, how can the activating effect of –NH2 group be controlled? This can be done by protecting the –NH2 group by acetylation with acetic anhydride, then carrying out the desired substitution followed by hydrolysis of the substituted amide to the substituted amine.
Q. Give the major product of the following reaction:


a)

b)

c)

d)
None of the above
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
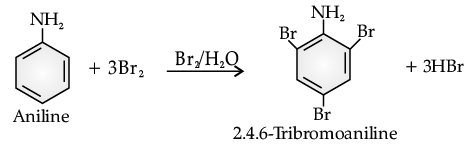
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.Assertion (A): Amines behave as a Lewis base.Reason (R): Amines have an unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Greater is the stability of the substituted ammonium cation, stronger should be the corresponding amine as a base. Thus, the order of basicity of aliphatic amines should be: primary > secondary > tertiary, which is opposite to the inductive effect based order. Secondly, when the alkyl group is small, like –CH3 group, there is no steric hindrance to H-bonding. In case the alkyl group is bigger than CH3 group, there will be steric hinderance to H-bonding. Therefore, the change of nature of the alkyl group, e.g., from –CH3 to –C2H5 results in change of the order of basic strength.
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): Amines behave as a Lewis base.
Reason (R): Amines have an unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
Amines behave as a Lewis base as they have an unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Conductivity of an electrolyte increases with decrease in concentration.Reason (R): Number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is True
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Conductivity of an electrolyte increases with decrease in concentration.
Reason (R): Number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is True

|
Akshay Shah answered |
Assertion: Conductivity of an electrolyte increases with decrease in concentration.
Reason: Number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution.
The correct answer is option D, which means that Assertion A is false and Reason R is true.
Explanation:
- Conductivity of an electrolyte is a measure of its ability to conduct electric current. It depends on the presence of ions in the solution.
- When an electrolyte dissolves in a solvent, it dissociates into positive and negative ions. These ions are responsible for carrying electric charge through the solution.
- The concentration of an electrolyte refers to the amount of solute (electrolyte) dissolved in a given amount of solvent (usually expressed in moles per liter).
- Assertion A states that the conductivity of an electrolyte increases with a decrease in concentration. This is not true. In fact, the conductivity of an electrolyte generally decreases with a decrease in concentration.
- Reason R states that the number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution. This is true. When an electrolyte solution is diluted, the overall volume of the solution increases while the amount of solute remains the same. As a result, the concentration of the electrolyte decreases. Since conductivity depends on the presence of ions, a decrease in concentration leads to a decrease in the number of ions per unit volume, resulting in a decrease in conductivity.
Conclusion:
- The assertion that conductivity of an electrolyte increases with a decrease in concentration is false.
- The reason that the number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution is true.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Reason: Number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution.
The correct answer is option D, which means that Assertion A is false and Reason R is true.
Explanation:
- Conductivity of an electrolyte is a measure of its ability to conduct electric current. It depends on the presence of ions in the solution.
- When an electrolyte dissolves in a solvent, it dissociates into positive and negative ions. These ions are responsible for carrying electric charge through the solution.
- The concentration of an electrolyte refers to the amount of solute (electrolyte) dissolved in a given amount of solvent (usually expressed in moles per liter).
- Assertion A states that the conductivity of an electrolyte increases with a decrease in concentration. This is not true. In fact, the conductivity of an electrolyte generally decreases with a decrease in concentration.
- Reason R states that the number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution. This is true. When an electrolyte solution is diluted, the overall volume of the solution increases while the amount of solute remains the same. As a result, the concentration of the electrolyte decreases. Since conductivity depends on the presence of ions, a decrease in concentration leads to a decrease in the number of ions per unit volume, resulting in a decrease in conductivity.
Conclusion:
- The assertion that conductivity of an electrolyte increases with a decrease in concentration is false.
- The reason that the number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution is true.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 Ohm. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. The cell constant of a conductivity cell ________.- a)Changes with change of electrolyte.
- b)Changes with change of concentration of electrolyte
- c)Changes with temperature of electrolyte.
- d)Remains constant for a cell.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 Ohm. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)
The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The cell constant of a conductivity cell ________.
a)
Changes with change of electrolyte.
b)
Changes with change of concentration of electrolyte
c)
Changes with temperature of electrolyte.
d)
Remains constant for a cell.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
The cell constant of a conductivity cell remains constant for a cell.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism.Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.- a)A is false and R is true
- b)A is true but R is false
- c)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- d)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type (X and L are unidentate) do not show geometrical isomerism.
Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
a)
A is false and R is true
b)
A is true but R is false
c)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
d)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
|
|
Priya Sen answered |
Assertion (A): Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type do not show geometrical isomerism.
- Understanding Complexes: Complexes of the form MX6 (where M is a metal and X is a ligand) and MX5L (where L is a unidentate ligand) typically have a coordination number of 6 or 5.
- Geometrical Isomerism: Geometrical isomerism arises when ligands can be arranged in different spatial orientations around the central metal atom. Common in coordination number 4 (e.g., tetrahedral or square planar complexes) and 6 (octahedral), the presence of different ligand types (e.g., bidentate) can lead to isomerism. However, in MX6 complexes with six identical ligands, geometrical isomers cannot form.
Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
- Coordination Number 6: While it is true that many complexes with a coordination number of 6 do not show geometrical isomerism, this is not universally applicable. For instance, octahedral complexes with different types of ligands (like in fac-mer isomerism) can show geometrical isomerism.
- Specificity of A: The assertion specifically addresses the MX6 and MX5L types, where MX6 has identical ligands and therefore cannot exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Conclusion
- Correct Evaluation: The assertion is true in the context of MX6 and MX5L complexes. However, the reason is misleading as it suggests that all coordination number 6 complexes lack geometrical isomerism, which is incorrect. Therefore, the correct choice is:
Option B: A is true but R is false.
- Understanding Complexes: Complexes of the form MX6 (where M is a metal and X is a ligand) and MX5L (where L is a unidentate ligand) typically have a coordination number of 6 or 5.
- Geometrical Isomerism: Geometrical isomerism arises when ligands can be arranged in different spatial orientations around the central metal atom. Common in coordination number 4 (e.g., tetrahedral or square planar complexes) and 6 (octahedral), the presence of different ligand types (e.g., bidentate) can lead to isomerism. However, in MX6 complexes with six identical ligands, geometrical isomers cannot form.
Reason (R): Geometrical isomerism is not shown by complexes of coordination number 6.
- Coordination Number 6: While it is true that many complexes with a coordination number of 6 do not show geometrical isomerism, this is not universally applicable. For instance, octahedral complexes with different types of ligands (like in fac-mer isomerism) can show geometrical isomerism.
- Specificity of A: The assertion specifically addresses the MX6 and MX5L types, where MX6 has identical ligands and therefore cannot exhibit geometrical isomerism.
Conclusion
- Correct Evaluation: The assertion is true in the context of MX6 and MX5L complexes. However, the reason is misleading as it suggests that all coordination number 6 complexes lack geometrical isomerism, which is incorrect. Therefore, the correct choice is:
Option B: A is true but R is false.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids are few of the major classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl groups. Aldehydes are prepared by dehydrogenation or controlled oxidation of primary alcohols and controlled or selective reduction of acyl halides. Ketones are prepared by oxidation of secondary alcohols and hydration of alkynes. Carboxylic acids are prepared by the oxidation of primary alcohols, aldehydes and alkenes by hydrolysis of nitriles and by treatment of Grignard reagents with carbon dioxide.Q. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.- a)Sodium hydrogensulphite
- b)Phenyl hydrazine
- c)Fehlings’ solution
- d)Grignard reagent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids are few of the major classes of organic compounds containing carbonyl groups. Aldehydes are prepared by dehydrogenation or controlled oxidation of primary alcohols and controlled or selective reduction of acyl halides. Ketones are prepared by oxidation of secondary alcohols and hydration of alkynes. Carboxylic acids are prepared by the oxidation of primary alcohols, aldehydes and alkenes by hydrolysis of nitriles and by treatment of Grignard reagents with carbon dioxide.
Q. The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
a)
Sodium hydrogensulphite
b)
Phenyl hydrazine
c)
Fehlings’ solution
d)
Grignard reagent
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Fehling’s solution does not react with acetone and benzaldehyde as aromatic aldehydes and ketones do not react with Fehling’s solution.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Within the 3d series, manganese exhibits oxidation states in aqueous solution from +2 to +7, ranging from Mn2+(aq) to MnO−4 (aq). Likewise, iron forms both Fe2+(aq) and Fe3+(aq) as well as the FeO2−4 ion. Cr and Mn form oxyions CrO2−4, MnO−4, owing to their willingness to form multiple bonds. The pattern with the early transition metals—in the 3d series up to Mn, and for the 4d, 5d metals up to Ru and Os—is that the maximum oxidation state corresponds to the number of ‘‘outer shell’’ electrons. The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation (e.g., the stabilization of Co3+ by ammonia) or upon the pH (thus MnO42− (aq) is prone to disproportionation in acidic solution). Within the 3d series, there is considerable variation in relative stability of oxidation states, sometimes on moving from one metal to a neighbour; thus, for iron, Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+, especially in alkaline conditions, while the reverse is true for cobalt. The ability of transition metals to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states is marked with metals such as vanadium, where the standard potentials can be rather small, making a switch between states relatively easy.In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.Assertion (A): Highest oxidation state is exhibited by transition metal lying in the middle of the series.Reason (R): The highest oxidation state exhibited corresponds to number of (n−1)d electrons.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Within the 3d series, manganese exhibits oxidation states in aqueous solution from +2 to +7, ranging from Mn2+(aq) to MnO−4 (aq). Likewise, iron forms both Fe2+(aq) and Fe3+(aq) as well as the FeO2−4 ion. Cr and Mn form oxyions CrO2−4, MnO−4, owing to their willingness to form multiple bonds. The pattern with the early transition metals—in the 3d series up to Mn, and for the 4d, 5d metals up to Ru and Os—is that the maximum oxidation state corresponds to the number of ‘‘outer shell’’ electrons. The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation (e.g., the stabilization of Co3+ by ammonia) or upon the pH (thus MnO42− (aq) is prone to disproportionation in acidic solution). Within the 3d series, there is considerable variation in relative stability of oxidation states, sometimes on moving from one metal to a neighbour; thus, for iron, Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+, especially in alkaline conditions, while the reverse is true for cobalt. The ability of transition metals to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states is marked with metals such as vanadium, where the standard potentials can be rather small, making a switch between states relatively easy.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion (A): Highest oxidation state is exhibited by transition metal lying in the middle of the series.
Reason (R): The highest oxidation state exhibited corresponds to number of (n−1)d electrons.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Higher oxidation states are usually exhibited by the members in the middle of a series of transition elements due to greater number of unpaired electrons in (n−1)d and ns orbitals at the middle of the series.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the IUPAC system.Few rules for naming coordination compounds are:(I) In an ionic complex, the cation is named first and then the anion.(II) In the coordination entity, the ligands are named first and then the central metal ion.(III) When more than one type of ligands are present, they are named in alphabetical order of preference with any consideration of chargeThe following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. The IUPAC name of [Ni(CO)4] is- a)tetracarbonylnickel(II)
- b)tetracarbonylnickel(0)
- c)tetracarbonylnickelate(II)
- d)tetracarbonylnickelate(0)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Coordination compounds are formulated and named according to the IUPAC system.
Few rules for naming coordination compounds are:
(I) In an ionic complex, the cation is named first and then the anion.
(II) In the coordination entity, the ligands are named first and then the central metal ion.
(III) When more than one type of ligands are present, they are named in alphabetical order of preference with any consideration of charge
The following questions are multiple choice question. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The IUPAC name of [Ni(CO)4] is
a)
tetracarbonylnickel(II)
b)
tetracarbonylnickel(0)
c)
tetracarbonylnickelate(II)
d)
tetracarbonylnickelate(0)
|
|
Priyanka Sharma answered |
When we write the IUPAC name for a coordination complex, if the coordination entity is neutral, then the name of Ligands comes first followed by the name of the metal and the oxidation state in ().
Thus, the IUPAC name for [Ni(CO)4] is Tetracarbonylnickel (0).
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.Assertion : Nitration of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.Reason : Acetylation increases the electron-density in the benzene ring.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
- c)If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
- d)If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Nitration of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason : Acetylation increases the electron-density in the benzene ring.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
c)
If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
d)
If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
|
|
Shalini Patel answered |
Acetylation decreases the electron-density in the benzene ring thereby preventing oxidation.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as..Assertion (A): Monobromination of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason (R): Acetylation of aniline results in the increase of electron density at the benzene ring.- a)If both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation o Assertion (A).
- b)If both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct
- c)If Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false
- d)If Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as..
Assertion (A): Monobromination of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason (R): Acetylation of aniline results in the increase of electron density at the benzene ring.
Reason (R): Acetylation of aniline results in the increase of electron density at the benzene ring.
a)
If both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation o Assertion (A).
b)
If both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct
c)
If Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false
d)
If Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.

|
Top Rankers answered |
In the reaction, the NH₂ group is protected by an acetyl group because it is highly reactive due to the lone pair on the nitrogen in aniline. The incoming NO₂ group tends to accept this lone pair effectively. Therefore, acetylation of the NH₂ group is performed to reduce its reactivity towards the incoming NO₂ group.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Cerium (Ce) exhibits +4 oxidation state.Reason (R): Ce4+ has 4f4 electronic configuration which is less stable.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true but R is false.
- d)A is false and R is True.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Cerium (Ce) exhibits +4 oxidation state.
Reason (R): Ce4+ has 4f4 electronic configuration which is less stable.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true but R is false.
d)
A is false and R is True.
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
Cerium exhibits +4 oxidation state because Ce4+ has 4f0 electronic configuration which is most stable.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:According to Valence Bond Theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n−1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridisation to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding. In these questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.Assertion (A): The paramagnetic octahedral complex, [CoF6]3− uses outer orbital (4d) in hybridisation (sp3d2).Reason (R): It is a high spin complex.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
According to Valence Bond Theory, the metal atom or ion under the influence of ligands can use its (n−1)d, ns, np or ns, np, nd orbitals for hybridisation to yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry such as octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybridised orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals that can donate electron pairs for bonding. In these questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): The paramagnetic octahedral complex, [CoF6]3− uses outer orbital (4d) in hybridisation (sp3d2).
Reason (R): It is a high spin complex.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The paramagnetic octahedral complex, [CoF6]3− uses outer orbital (4d) in hybridisation (sp3d2). It is a low spin complex.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Hydrolysis of an ester follows first order kinetics.Reason (R): Concentration of water remains nearly constant during the course of the reaction.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false and R is true
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Hydrolysis of an ester follows first order kinetics.
Reason (R): Concentration of water remains nearly constant during the course of the reaction.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false and R is true
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |

Hydrolysis of an ester follows first order kinetics as [H2O] remains nearly constant during the course of the reaction. It is a pseudo first order reaction.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The existence of coordination compounds with the same formula but different arrangements of the ligands was crucial in the development of coordination chemistry. Two or more compounds with the same formula but different arrangements of the atoms are called isomers. Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas and do not necessarily share similar properties. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, and geometrical isomers. There are two main forms of isomerism: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. The different chemical formulas in structural isomers are caused either by a difference in what ligands are bonded to the central atoms or how the individual ligands are bonded to the central atoms.The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:Q. Which of the following complexes show linkage isomerism?- a)[Co(H2O)5CO]3+
- b)[Cr(NH3)5SCN]2+
- c)[Fe(en)2Cl2]+
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The existence of coordination compounds with the same formula but different arrangements of the ligands was crucial in the development of coordination chemistry. Two or more compounds with the same formula but different arrangements of the atoms are called isomers. Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas and do not necessarily share similar properties. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, and geometrical isomers. There are two main forms of isomerism: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. The different chemical formulas in structural isomers are caused either by a difference in what ligands are bonded to the central atoms or how the individual ligands are bonded to the central atoms.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. Which of the following complexes show linkage isomerism?
a)
[Co(H2O)5CO]3+
b)
[Cr(NH3)5SCN]2+
c)
[Fe(en)2Cl2]+
d)
All of the above
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Linkage isomerism is the existence of coordination compounds that have the same composition differing with the connectivity of the metal to a ligand. Typical ligands that give rise to linkage isomers are: thiocyanate, SCN −, isothiocyanate, NCS −
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.Assertion (A): Aromatic 1° amines can be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.Reason (R): Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)Both A and R are False
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Aromatic 1° amines can be prepared by Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
Reason (R): Aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
Both A and R are False
|
|
Advait Das answered |
Assertion (A) Analysis
- Aromatic 1° amines can indeed be prepared through the Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
- This method involves the reaction of phthalimide with an alkyl halide to form a phthalimide derivative, which can then be hydrolyzed to yield a 1° amine.
- However, the assertion is misleading as it implies a more direct method than is effective for aromatic systems.
Reason (R) Analysis
- The reason states that aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
- This statement is true because aryl halides are quite stable and resistant to nucleophilic attack due to their aromatic nature, which stabilizes the halide bond.
- However, the reason does not directly explain the assertion, as the Gabriel synthesis can be applied to aliphatic amines rather than aromatic amines.
Conclusion
- Since both the assertion and the reason present valid points but do not correlate correctly, the correct answer is option 'D': Both A and R are False.
- The Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis does not yield aromatic amines effectively, and the explanation regarding aryl halides is valid but irrelevant to the process of synthesizing aromatic amines.
In summary, while both statements contain elements of truth, they do not support one another, leading to the conclusion that both are false in the context of the assertion and its reasoning.
- Aromatic 1° amines can indeed be prepared through the Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis.
- This method involves the reaction of phthalimide with an alkyl halide to form a phthalimide derivative, which can then be hydrolyzed to yield a 1° amine.
- However, the assertion is misleading as it implies a more direct method than is effective for aromatic systems.
Reason (R) Analysis
- The reason states that aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the anion formed by phthalimide.
- This statement is true because aryl halides are quite stable and resistant to nucleophilic attack due to their aromatic nature, which stabilizes the halide bond.
- However, the reason does not directly explain the assertion, as the Gabriel synthesis can be applied to aliphatic amines rather than aromatic amines.
Conclusion
- Since both the assertion and the reason present valid points but do not correlate correctly, the correct answer is option 'D': Both A and R are False.
- The Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis does not yield aromatic amines effectively, and the explanation regarding aryl halides is valid but irrelevant to the process of synthesizing aromatic amines.
In summary, while both statements contain elements of truth, they do not support one another, leading to the conclusion that both are false in the context of the assertion and its reasoning.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since d-electron bonding levels are involved, the cations-exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.Assertion (A): Cations of transition elements occur in various valence statesReason (R): Large number of oxides of transition elements are possible.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since d-electron bonding levels are involved, the cations-exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion (A): Cations of transition elements occur in various valence states
Reason (R): Large number of oxides of transition elements are possible.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Vivek Rana answered |
The lowest oxide of transition metal is basic because of some valence electron are not involved in bonding thus act as a base due to the availability of free electrons. The highest oxide of transition metal electrons of metal is involved in the bonding. Therefore, these electrons are not available for donation. Hence, they are acidic in nature.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Within the 3d series, manganese exhibits oxidation states in aqueous solution from +2 to +7, ranging from Mn2+(aq) to MnO−4 (aq). Likewise, iron forms both Fe2+(aq) and Fe3+(aq) as well as the FeO2−4 ion. Cr and Mn form oxyions CrO2−4, MnO−4, owing to their willingness to form multiple bonds. The pattern with the early transition metals—in the 3d series up to Mn, and for the 4d, 5d metals up to Ru and Os—is that the maximum oxidation state corresponds to the number of ‘‘outer shell’’ electrons. The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation (e.g., the stabilization of Co3+ by ammonia) or upon the pH (thus MnO42− (aq) is prone to disproportionation in acidic solution). Within the 3d series, there is considerable variation in relative stability of oxidation states, sometimes on moving from one metal to a neighbour; thus, for iron, Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+, especially in alkaline conditions, while the reverse is true for cobalt. The ability of transition metals to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states is marked with metals such as vanadium, where the standard potentials can be rather small, making a switch between states relatively easy.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion (A): The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals depends only on electronic configuration of the metal.
Reason (R): The number of electrons in the (n-1) d and ns subshells determine the oxidation states exhibited by the metal.
- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Within the 3d series, manganese exhibits oxidation states in aqueous solution from +2 to +7, ranging from Mn2+(aq) to MnO−4 (aq). Likewise, iron forms both Fe2+(aq) and Fe3+(aq) as well as the FeO2−4 ion. Cr and Mn form oxyions CrO2−4, MnO−4, owing to their willingness to form multiple bonds. The pattern with the early transition metals—in the 3d series up to Mn, and for the 4d, 5d metals up to Ru and Os—is that the maximum oxidation state corresponds to the number of ‘‘outer shell’’ electrons. The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation (e.g., the stabilization of Co3+ by ammonia) or upon the pH (thus MnO42− (aq) is prone to disproportionation in acidic solution). Within the 3d series, there is considerable variation in relative stability of oxidation states, sometimes on moving from one metal to a neighbour; thus, for iron, Fe3+ is more stable than Fe2+, especially in alkaline conditions, while the reverse is true for cobalt. The ability of transition metals to exhibit a wide range of oxidation states is marked with metals such as vanadium, where the standard potentials can be rather small, making a switch between states relatively easy.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
Assertion (A): The highest oxidation states of the 3d metals depends only on electronic configuration of the metal.
Reason (R): The number of electrons in the (n-1) d and ns subshells determine the oxidation states exhibited by the metal.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.

|
Arshiya Mehta answered |
Explanation:
- Assertion (A): The statement that the highest oxidation states of the 3d metals depend only on the electronic configuration of the metal is incorrect. The passage mentions that the highest oxidation states of the 3d metals may depend upon complex formation or pH conditions.
- Reason (R): The statement that the number of electrons in the (n-1) d and ns subshells determine the oxidation states exhibited by the metal is correct. The passage discusses how the highest oxidation state corresponds to the number of 'outer shell' electrons.
- Therefore, the assertion is incorrect while the reason is correct.
- Hence, the correct answer is option D: Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:In transition elements, generally, ions of the same charge in a given series show progressive decrease in radius with increasing atomic number. This is because the new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. But the radii of the third (5d) series are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second series. This phenomenon is associated with the intervention of the 4f orbitals which must be filled before the 5d series of elements begin. The filling of 4f before 5d orbital results in a regular decrease in atomic radii called Lanthanoid contraction. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series: Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+ (Atomic number: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)Assertion (A): Among the given ions, Cr3+ is the most stable in an aqueous environment.Reason (R): Cr3+ has half filled t32g.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
In transition elements, generally, ions of the same charge in a given series show progressive decrease in radius with increasing atomic number. This is because the new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. But the radii of the third (5d) series are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second series. This phenomenon is associated with the intervention of the 4f orbitals which must be filled before the 5d series of elements begin. The filling of 4f before 5d orbital results in a regular decrease in atomic radii called Lanthanoid contraction. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series: Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+ (Atomic number: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)
Assertion (A): Among the given ions, Cr3+ is the most stable in an aqueous environment.
Reason (R): Cr3+ has half filled t32g.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Cr3+, half filled t32g.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: In transition elements, generally, ions of the same charge in a given series show progressive decrease in radius with increasing atomic number. This is because the new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. But the radii of the third (5d) series are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second series. This phenomenon is associated with the intervention of the 4f orbitals which must be filled before the 5d series of elements begin. The filling of 4f before 5d orbital results in a regular decrease in atomic radii called Lanthanoid contraction. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series: Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+ (Atomic number: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)Assertion (A): Ti4+ ion is colourless.Reason (R): All valence electrons are unpaired in Ti4+ ion.- a)Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
- b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
- c)Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
- d)Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: In transition elements, generally, ions of the same charge in a given series show progressive decrease in radius with increasing atomic number. This is because the new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. But the radii of the third (5d) series are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second series. This phenomenon is associated with the intervention of the 4f orbitals which must be filled before the 5d series of elements begin. The filling of 4f before 5d orbital results in a regular decrease in atomic radii called Lanthanoid contraction. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series: Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+ (Atomic number: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)
Assertion (A): Ti4+ ion is colourless.
Reason (R): All valence electrons are unpaired in Ti4+ ion.
a)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c)
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.

|
Sanjana Bajaj answered |
Understanding the Assertion and Reason
The assertion and reason statements provided are related to the Ti4+ ion and its electronic configuration, which influences its color.
Assertion (A): Ti4+ ion is colourless.
- The Ti4+ ion has lost all four of its valence electrons (from the 3d and 4s orbitals).
- As a result, it has no unpaired electrons, which is a key factor in determining the color of transition metal ions.
Reason (R): All valence electrons are unpaired in Ti4+ ion.
- This statement is incorrect. In the Ti4+ ion, all electrons have been removed, leading to a completely empty d orbital.
- An unpaired electron is necessary for the absorption of light, which contributes to color; thus, if there are no unpaired electrons, the ion remains colorless.
Evaluation of the Statements
- Since the assertion is correct (Ti4+ is indeed colorless) and the reason is incorrect (not all valence electrons are unpaired in Ti4+), the correct answer is option "c": Assertion is correct, but the reason is wrong.
Conclusion
- The color of transition metal ions is significantly influenced by their electronic configurations.
- The presence of unpaired electrons typically indicates color, while a complete lack of unpaired electrons results in a colorless ion, as seen in the case of Ti4+.
The assertion and reason statements provided are related to the Ti4+ ion and its electronic configuration, which influences its color.
Assertion (A): Ti4+ ion is colourless.
- The Ti4+ ion has lost all four of its valence electrons (from the 3d and 4s orbitals).
- As a result, it has no unpaired electrons, which is a key factor in determining the color of transition metal ions.
Reason (R): All valence electrons are unpaired in Ti4+ ion.
- This statement is incorrect. In the Ti4+ ion, all electrons have been removed, leading to a completely empty d orbital.
- An unpaired electron is necessary for the absorption of light, which contributes to color; thus, if there are no unpaired electrons, the ion remains colorless.
Evaluation of the Statements
- Since the assertion is correct (Ti4+ is indeed colorless) and the reason is incorrect (not all valence electrons are unpaired in Ti4+), the correct answer is option "c": Assertion is correct, but the reason is wrong.
Conclusion
- The color of transition metal ions is significantly influenced by their electronic configurations.
- The presence of unpaired electrons typically indicates color, while a complete lack of unpaired electrons results in a colorless ion, as seen in the case of Ti4+.
Chapter doubts & questions for CBSE New Pattern: Term lI Practice Questions - Chemistry Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of CBSE New Pattern: Term lI Practice Questions - Chemistry Class 12 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 12 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry Class 12
133 videos|320 docs|161 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









