NEET Exam > NEET Questions > explain development of dicot embryo Related: ...
Start Learning for Free
explain development of dicot embryo
?Most Upvoted Answer
explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual...
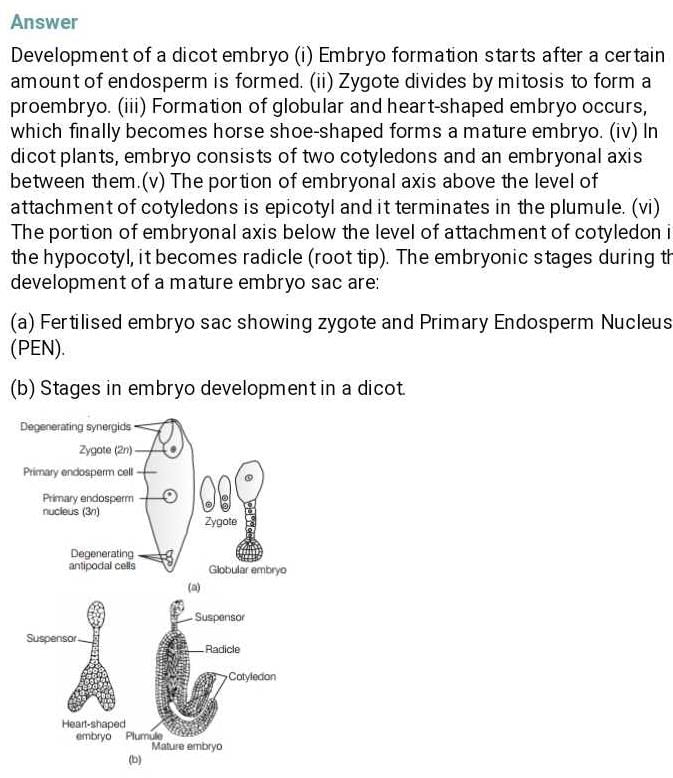
Community Answer
explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual...
**Development of Dicot Embryo**
The development of a dicot embryo occurs within the ovule of a flowering plant and involves several stages. Let's discuss each stage in detail:
1. **Fertilization**: After the process of pollination, the pollen grain lands on the stigma of the flower. The pollen tube then grows down through the style and reaches the ovule. The male gametes are released from the pollen tube and one of them fuses with the egg cell present within the ovule. This process is known as fertilization.
2. **Zygote Formation**: The fusion of the male gamete with the egg cell results in the formation of a zygote. The zygote is the first cell of the new plant and is diploid, containing two sets of chromosomes.
3. **Embryo Development**: The zygote undergoes several divisions to form an embryo. The first division of the zygote is transverse, leading to the formation of a terminal cell and a basal cell. The terminal cell gives rise to the embryo, while the basal cell forms the suspensor, which anchors the embryo to the parent plant. The suspensor also helps in the transfer of nutrients to the developing embryo.
4. **Embryonic Tissues**: The embryo further develops and differentiates into three primary embryonic tissues: the protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium. The protoderm gives rise to the epidermis, the outermost layer of cells. The ground meristem develops into the ground tissue system, including the cortex and pith. The procambium differentiates into the vascular tissue system, comprising the xylem and phloem.
5. **Cotyledon Formation**: Dicot embryos typically have two cotyledons, which are the first leaves of the new plant. The cotyledons develop from the embryo's terminal cell and play a crucial role in storing and providing nutrients to the developing seedling after germination.
6. **Maturation**: As the embryo continues to develop, it undergoes maturation, during which various structures, such as the shoot apical meristem, root apical meristem, and plumule, form. The shoot apical meristem gives rise to the shoot system, including stems, leaves, and flowers, while the root apical meristem develops into the root system. The plumule develops into the first true leaves of the plant.
Thus, the development of a dicot embryo involves fertilization, zygote formation, embryo development, formation of embryonic tissues, cotyledon formation, and maturation. These processes ultimately give rise to a fully developed dicot plant.
The development of a dicot embryo occurs within the ovule of a flowering plant and involves several stages. Let's discuss each stage in detail:
1. **Fertilization**: After the process of pollination, the pollen grain lands on the stigma of the flower. The pollen tube then grows down through the style and reaches the ovule. The male gametes are released from the pollen tube and one of them fuses with the egg cell present within the ovule. This process is known as fertilization.
2. **Zygote Formation**: The fusion of the male gamete with the egg cell results in the formation of a zygote. The zygote is the first cell of the new plant and is diploid, containing two sets of chromosomes.
3. **Embryo Development**: The zygote undergoes several divisions to form an embryo. The first division of the zygote is transverse, leading to the formation of a terminal cell and a basal cell. The terminal cell gives rise to the embryo, while the basal cell forms the suspensor, which anchors the embryo to the parent plant. The suspensor also helps in the transfer of nutrients to the developing embryo.
4. **Embryonic Tissues**: The embryo further develops and differentiates into three primary embryonic tissues: the protoderm, ground meristem, and procambium. The protoderm gives rise to the epidermis, the outermost layer of cells. The ground meristem develops into the ground tissue system, including the cortex and pith. The procambium differentiates into the vascular tissue system, comprising the xylem and phloem.
5. **Cotyledon Formation**: Dicot embryos typically have two cotyledons, which are the first leaves of the new plant. The cotyledons develop from the embryo's terminal cell and play a crucial role in storing and providing nutrients to the developing seedling after germination.
6. **Maturation**: As the embryo continues to develop, it undergoes maturation, during which various structures, such as the shoot apical meristem, root apical meristem, and plumule, form. The shoot apical meristem gives rise to the shoot system, including stems, leaves, and flowers, while the root apical meristem develops into the root system. The plumule develops into the first true leaves of the plant.
Thus, the development of a dicot embryo involves fertilization, zygote formation, embryo development, formation of embryonic tissues, cotyledon formation, and maturation. These processes ultimately give rise to a fully developed dicot plant.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants?
Question Description
explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants?.
explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants?.
Solutions for explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants?, a detailed solution for explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? has been provided alongside types of explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice explain development of dicot embryo Related: NCERT Solutions - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























