SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The volume of air delivered by the compresso...
Start Learning for Free
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:
- a)Compressor capacity
- b)Compression ratio
- c)Free air delivery
- d)Swept volume
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor ...
Concept:
Compressor capacity: It is the quantity of air delivered by a compressor in m3/minute or m3/sec
Compression ratio: It is defined as the ratio of the volume of air before compression to the volume of air after compression. It is the ratio of total volume (V1) to the clearance volume (VC)
In other words, the compression ratio is the volume of air before compression to the volume of air after compression.
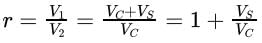
Free air delivery (FAD): The delivery volume reduced in the compressor to a pressure of 1 bar and temperature of 15∘C. The relative volume at that condition is known as Free Air Delivery.
Swept volume (Vs): The volume displaced or swept by the piston when it moves between the top dead center and bottom dead center.
Clearance volume: The difference between the total volume and the swept volume is the gap that remains between the piston head and the cylinder head when at the top dead center.
Most Upvoted Answer
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor ...
Compressor Capacity
Compressor capacity refers to the volume of air that a compressor can deliver within a specific time period. It is an important factor to consider when choosing a compressor for various applications, including industrial processes, pneumatic tools, and HVAC systems. The compressor capacity is typically measured in terms of cubic feet per minute (CFM) or liters per minute (LPM).
Factors Affecting Compressor Capacity
Several factors can affect the compressor capacity, including:
1. Compressor Type and Size: Different types of compressors, such as reciprocating, rotary screw, and centrifugal, have varying capacities. Additionally, the size of the compressor, including the motor power and cylinder size, can also impact its capacity.
2. Compression Ratio: The compression ratio is the ratio of the discharge pressure to the suction pressure. Higher compression ratios can reduce the compressor capacity as it requires more energy to compress the air to a higher pressure.
3. Temperature and Humidity: The ambient temperature and humidity can affect the density of the air. Warmer and more humid air is less dense, which can result in a decrease in compressor capacity.
4. Efficiency: The efficiency of the compressor also plays a role in its capacity. More efficient compressors can deliver a higher volume of air for a given power input.
Importance of Compressor Capacity
Understanding the compressor capacity is essential for selecting the right compressor for a specific application. If the compressor capacity is too low, it may not meet the air demand, leading to inefficiency and delays in operations. On the other hand, if the compressor capacity is too high, it can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased costs.
Moreover, the compressor capacity also determines the performance of pneumatic tools and equipment. Insufficient air supply can result in reduced tool efficiency and potential damage to the equipment.
Conclusion
Compressor capacity is the volume of air that a compressor can deliver within a specific time period. It is influenced by factors such as compressor type and size, compression ratio, temperature and humidity, and efficiency. Understanding the compressor capacity is crucial for selecting the appropriate compressor for various applications and ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Compressor capacity refers to the volume of air that a compressor can deliver within a specific time period. It is an important factor to consider when choosing a compressor for various applications, including industrial processes, pneumatic tools, and HVAC systems. The compressor capacity is typically measured in terms of cubic feet per minute (CFM) or liters per minute (LPM).
Factors Affecting Compressor Capacity
Several factors can affect the compressor capacity, including:
1. Compressor Type and Size: Different types of compressors, such as reciprocating, rotary screw, and centrifugal, have varying capacities. Additionally, the size of the compressor, including the motor power and cylinder size, can also impact its capacity.
2. Compression Ratio: The compression ratio is the ratio of the discharge pressure to the suction pressure. Higher compression ratios can reduce the compressor capacity as it requires more energy to compress the air to a higher pressure.
3. Temperature and Humidity: The ambient temperature and humidity can affect the density of the air. Warmer and more humid air is less dense, which can result in a decrease in compressor capacity.
4. Efficiency: The efficiency of the compressor also plays a role in its capacity. More efficient compressors can deliver a higher volume of air for a given power input.
Importance of Compressor Capacity
Understanding the compressor capacity is essential for selecting the right compressor for a specific application. If the compressor capacity is too low, it may not meet the air demand, leading to inefficiency and delays in operations. On the other hand, if the compressor capacity is too high, it can lead to unnecessary energy consumption and increased costs.
Moreover, the compressor capacity also determines the performance of pneumatic tools and equipment. Insufficient air supply can result in reduced tool efficiency and potential damage to the equipment.
Conclusion
Compressor capacity is the volume of air that a compressor can deliver within a specific time period. It is influenced by factors such as compressor type and size, compression ratio, temperature and humidity, and efficiency. Understanding the compressor capacity is crucial for selecting the appropriate compressor for various applications and ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The volume of air delivered by the compressor is called:a)Compressor capacityb)Compression ratioc)Free air deliveryd)Swept volumeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















