SSC Exam > SSC Questions > Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Dire...
Start Learning for Free
Insulation resistance of the cable is-
- a)Directly proportional to the length
- b)Indirectly proportional to the length
- c)Does not depends upon the length
- d)Constant
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the ...
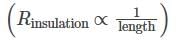
The rule may be stated: Insulation resistance should be approximately one megohm for each 1,000 volts of operating voltage, with a minimum value of one megohm.
Hence, the correct option is (B)
Most Upvoted Answer
Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the ...
Insulation resistance is the measure of how effectively the insulation material of a cable can resist the flow of electrical current through it. It is an important parameter in determining the quality and reliability of a cable.
Insulation resistance is indirectly proportional to the length of the cable. This means that as the length of the cable increases, the insulation resistance decreases. Conversely, as the length of the cable decreases, the insulation resistance increases.
Explanation:
- Insulation resistance is influenced by the length of the cable due to the nature of the insulation material. The insulation material used in cables has a certain resistance per unit length. As the length of the cable increases, the total resistance of the insulation material also increases.
- The resistance of the insulation material is inversely proportional to the insulation resistance. This means that as the resistance of the insulation material increases, the insulation resistance decreases. As the length of the cable increases, the resistance of the insulation material also increases, leading to a decrease in insulation resistance.
- The reason behind this inverse relationship is that longer cables have more insulation material, which results in a higher total resistance. This higher resistance allows more current to leak through the insulation, reducing the insulation resistance.
- On the other hand, shorter cables have less insulation material, resulting in a lower total resistance. This lower resistance restricts the flow of current through the insulation, thereby increasing the insulation resistance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the insulation resistance of a cable is inversely proportional to its length. This means that as the length of the cable increases, the insulation resistance decreases. It is important to consider the length of a cable when assessing its insulation resistance, as longer cables may have lower insulation resistance and may require additional measures to ensure proper insulation.
Insulation resistance is indirectly proportional to the length of the cable. This means that as the length of the cable increases, the insulation resistance decreases. Conversely, as the length of the cable decreases, the insulation resistance increases.
Explanation:
- Insulation resistance is influenced by the length of the cable due to the nature of the insulation material. The insulation material used in cables has a certain resistance per unit length. As the length of the cable increases, the total resistance of the insulation material also increases.
- The resistance of the insulation material is inversely proportional to the insulation resistance. This means that as the resistance of the insulation material increases, the insulation resistance decreases. As the length of the cable increases, the resistance of the insulation material also increases, leading to a decrease in insulation resistance.
- The reason behind this inverse relationship is that longer cables have more insulation material, which results in a higher total resistance. This higher resistance allows more current to leak through the insulation, reducing the insulation resistance.
- On the other hand, shorter cables have less insulation material, resulting in a lower total resistance. This lower resistance restricts the flow of current through the insulation, thereby increasing the insulation resistance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the insulation resistance of a cable is inversely proportional to its length. This means that as the length of the cable increases, the insulation resistance decreases. It is important to consider the length of a cable when assessing its insulation resistance, as longer cables may have lower insulation resistance and may require additional measures to ensure proper insulation.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Insulation resistance of the cable is-a)Directly proportional to the lengthb)Indirectly proportional to the lengthc)Does not depends upon the lengthd)ConstantCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















